What is cardia
The human body consists not only of organs, but also of many sphincters.
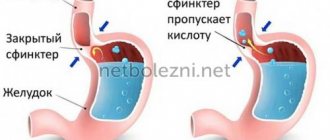
They ensure the transfer of contents from organ to organ. The role of the sphincter is played by the orbicularis muscle, the contraction of which causes narrowing and closure. In combination with vascular formations and folds of the mucous membrane, this muscle forms the sphincter apparatus. The cardia of the stomach is one of the sphincters. It functions as an inlet valve into the gastric section from the esophagus. If everything is functioning correctly, the cardiac sphincter remains closed when the person is not consuming food. During eating, the cardia opens, so food can pass into the stomach. In addition, the cardia blocks the return of food masses. This process is normal.
What is gastric cardia insufficiency? When the sphincter stops closing, the cardia is unable to prevent the internal contents, which provokes reflux. In simple words, there is a reflux of food, hydrochloric acid and gastric juice into the esophagus from the stomach.
This condition of the cardia is called chalazia. If symptoms of this disease are detected, it is recommended not to delay treatment. Useful articles on the topic - what is gastric metaplasia Treatment of cardia insufficiency
Prokinetics to increase the activity of the lower esophageal sphincter. These are Metoclopramide and Domperidone. They are prescribed 3-4 times a day before meals, sometimes the doctor may double the dose.
- Special medications to suppress reflux. Among them is “Propulsid” (“Cisapride”). Such products come in the form of tablets, suspensions and suppositories.
- Medicines to suppress heartburn. These are “Smecta”, “Gaviscon”, “Almagel”, etc.
Folk remedies for the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have long been successfully used along with officially recognized pharmaceutical drugs. But when choosing, you should definitely consult with your doctor, who will recommend the safest and most effective recipe depending on the characteristics of the body and the stage of the disease.
To get rid of pathologies of cardiac sphincter, medicinal herbs are recognized as the most effective recipes. This is plantain juice, a decoction of calamus roots, an infusion of dandelions, etc.
Features of treatment
An important component of the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux is recommendations for lifestyle modification.
Non-drug therapy for pathology includes:
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Correction of the diet (if necessary, reducing the volume of food, the nature and time of its consumption). It is extremely important to have your last snack 3-4 hours before bedtime and not eat at night.
- Refusal to wear tight and tight clothing, which increases intra-abdominal pressure.
- Raising the head end of the bed by 30⁰ (or 15 cm), using pillows or special stands.
- For obesity – getting rid of excess body weight.
- If possible, limit the intake of medications that contribute to the occurrence of reflux.
An important factor influencing the success of treatment is adherence to a diet for GERD.
Medicines used in the treatment of GERD:
- Type 2 histamine receptor blockers (roxatidine, famotidine, nizatidine).
- Antacids - used to neutralize hydrochloric acid and relieve heartburn attacks.
- Proton pump inhibitors (rabeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole) - effectively reduce the concentration of hydrochloric acid, are easily tolerated and have a minimal number of adverse reactions.
- Prokinetics (domperidone, metoclopramide) - increase the tone of the cardiac and lower esophageal sphincters, improve the evacuation of food masses from the stomach.
Folk remedies can be used as additional methods of treating gastroesophageal reflux disease, but the possibility of their use must be discussed with the attending physician.
Dear Yuri! A large set of measures is required. You should know that GERD recurs in most patients, which is why treatment (even preventative) should be carried out regularly.
Re: Doctor! Please tell me whether reflux esophagitis can be cured.
Thank you, I will have to do regular treatment.
Content
Treatment of cardia insufficiency requires complex treatment. It is necessary to follow four basic rules: cure the underlying disease (the cause of non-closure of the cardia), relieve intra-abdominal pressure and reduce excess weight, and follow a strict diet. Before starting treatment, you must undergo a full examination of the body, after which the doctor will prescribe an individual course, according to the symptoms and results.
Drug treatment consists of taking parkinetics: perinorm, metamol, raglan, metoclopramide. These medications increase the tone of the muscle ring and nothing gets from the stomach into the esophagus.
It is also necessary to restore digestive function and eliminate inflammation of the esophageal mucosa. Painkillers are often prescribed.
For gastritis, you need to take coating medications and antibiotics. For sphincter motility, your doctor may prescribe domperidone taken before meals.
There are many over-the-counter medications available for heartburn. To prevent it, you should only eat while sitting and not lie down after eating. When sleeping, the head should be 15 cm higher than the body (high pillows, raised head of the bed).
I don’t understand what makes doctors treat the effect and not the cause.
Author, look for Helicobacter pylori and treat yourself for it. Along with the cure for this extremely common infection, heartburn will disappear, and then reflux. It’s hard to believe in fairy tales about some special stomach disorder when you know how common this infection is.
At the same time, you need to control the quality of the foods you eat. It is dangerous to eat something that cannot be heat treated. And buy something that is not sold packaged.
Many people suffering from gastric cardia insufficiency do not even know what it is.
This disease refers to pathologies of the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Drug treatment of cardia pathology involves the use of regulators of motor activity of the lower esophageal sphincter. This group of drugs includes: metoclopramide, domperidone.
Metoclopramide (Raglan, Cerucal, Dimetpramide, Bimaral) is prescribed in a dose of 10 mg. three times a day.
Sometimes you can increase the intake to 4 times a day. For intramuscular use - 2 ml.
single dose. Intravenously twice a day, 2 ml.
Domperidone is used in a dose of 0.01 g three times a day. Take before meals.
Sometimes you can double the daily dose. Pathological gastroesophageal reflux can be suppressed using the drug propulsid (cisapride).
The dosage will be from 5 to 10 mg. two or three times a day.
You can use another form of the drug - in suppositories. The dose will be 30 mg.
per day. The drug is used both in combination with other medications and as monotherapy.
The consequences of the disease can be quite serious: peptic ulcers, esophageal strictures, gastroesophageal bleeding. Therefore, timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery and prevents the development of complications.
Vladivostok
Registered user
Good afternoon, I’m 23 years old, and for the last year I’ve been a lot nervous about VSD. Pain in the stomach, liver and pancreas often occurs.
I was diagnosed with dyskinisia since childhood, but it only showed itself seriously now. I take holosas, but I see virtually no changes - the bile does not go away.
There are no stones, the doctors say that I have a twisted gallbladder. I did an FGDS, as a result I write what is bad: In the stomach on an empty stomach there is a large amount of light bile with flakes.
In the antrum of the stomach there is mucous membrane with areas of hyperemia. In the duodenum, the mucosa is pink, with areas of hyperemia, and there is bile in the intestinal lumen.
NO Helecobacteria. Conclusion: Cardia failure; Erythematous gastropathy; Duodenal-gastric reflux.
Do you suffer from heartburn, and does eating food cause you to belch? Can't get rid of the bitter taste and bad breath? These may be the first signals indicating that there may be insufficiency of the gastric cardia (cardiac sphincter) - a disease that has become widespread recently. What is it and how to get rid of it, let's figure it out together.
The development of cardiac gastric sphincter can directly depend on a person’s lifestyle.
The essence of the disease
Bulbit - inflammation of the proximal duodenum - is one of the most common consequences of advanced chronic gastritis.
It can also be caused by a number of other pathological processes (see the article giving a general concept of this type of duodenal lesion and its causes).
How is bulbitis treated?
For bulbitis, therapy is based on the foundation of the fight against the primary disease, be it Helicobacter gastritis, Crohn's disease or giardiasis. A specific treatment regimen is developed in accordance with individual diagnostic results.
In addition to taking a standard set of medications, the patient can try certain traditional methods of treatment (but it is permissible to resort to them only after consultation with a doctor).
Non-drug treatment of the disease
If a person is diagnosed with gastric cardia insufficiency, treatment should begin as early as possible. And first of all, it will begin with the following measures:
The diet consists not only in the fact that the patient begins to eat properly at certain hours, but also in the fact that he will not overeat and eat at night. You should not lie down after eating for at least 2 hours. You need to include more pureed soups and cereals in your diet.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that are irritating:
- chips;
- all products during the preparation of which chemical preservatives and flavor enhancers were added;
- tea (strong);
- coffee;
- fatty and fried foods;
- tangerines, grapefruits;
- food containing a large amount of spices, salt, spices, as well as all smoked foods;
- homemade pickles and marinades.
You should have dinner approximately 3 hours before bedtime. It is not allowed to eat immediately before going to bed.
Other restrictions in the patient’s life are also shown:
- you need to give up clothes that squeeze your stomach;
- for the same reason, it is necessary to limit the wearing of tight belts;
- you need to sleep on a bed with a raised headboard;
- you don’t need to bend down often and you shouldn’t work very long and hard;
- if a person’s activity involves the need to work hard and often bend over, then it is advisable for him to change jobs.
Treatment methods
Treatment of gastric cardia insufficiency should be comprehensive and include medication and diet therapy. It is possible to use folk remedies, but they must be selected by a doctor, since not all recipes from “grandmother’s chest” are harmless.
Diet therapy
If the patient is overweight, if the gastric cardia is insufficient, he is prescribed a special diet aimed at reducing body weight. In addition, a dietary diet must be followed to reduce the load on the stomach and eliminate the impact of irritating foods on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
The diet should comply with the following recommendations:
- During the day you need to take 4-5 meals;
- portions should be small (after eating there should be a feeling of slight hunger);
- breakfast, lunch and dinner should be at approximately the same time every day;
- During the day you need to drink about 2 liters of water;
- The last meal should not be taken later than 3 hours before bedtime;
- For cooking, food processing methods such as boiling, stewing, baking, steaming are used;
- the temperature of food and drinks should be neutral (neither hot nor cold);
- It is recommended to drink a glass of warm water 15-20 minutes before meals.
Approximate daily diet:
- first breakfast: oatmeal on water with a piece of butter;
- second breakfast: cottage cheese casserole (low-fat cottage cheese, eggs are used for preparation, a small amount of sugar and butter, semolina can be added);
- lunch: soup with buckwheat in vegetable broth;
- dinner: steamed fish, stewed vegetables;
- second dinner: apple baked in the oven.
Drug therapy
The prescription of medications depends on what disease contributed to the development of gastric cardia insufficiency. If gastritis, ulcers and other gastrointestinal diseases are present, they are treated.
To relieve inflammation and normalize the contractility of the sphincter, bismuth preparations and prokinetic drugs can be prescribed. To eliminate unpleasant symptoms such as nausea and heartburn, antacids and proton pump blockers are prescribed.
In some cases, for example, if cardia failure is caused by a hernia, surgical intervention is necessary. Surgery is also necessary if the disease is in an advanced stage. In this case, the valve is sutured.
Causes and risk factors
Insufficiency of the gastric cardia can occur for a variety of reasons against the background of:
- poor nutrition, overeating;
- excess weight;
- gastritis or ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines;
- insufficient physical activity;
- pyloric spasms;
- increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, which is associated with pregnancy or ascites;
- increased intragastric pressure;
- surgical intervention on the sphincter area;
- heavy physical labor;
- grasping hernia (hiatal hernia);
- sedentary lifestyle.
Feelings of the disease and its diagnosis
An important step in diagnosing the disease is collecting complaints. A thorough and competent interview with the patient will allow the doctor at this stage to weed out many pathologies with similar symptoms, as well as prescribe the necessary examinations.
Necessary studies to make a diagnosis of GERD:
- Biochemical blood test.
- FEGDS is an invasive method for examining the upper parts of the digestive system, which allows you to reliably detect the presence of reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, identify inflamed mucous membranes and erosions, stenosis, and measure pH.
- X-ray examination of the esophagus with contrast. With its help, it is possible to record the return passage of the contrast agent into the lumen of the esophagus, to detect a hernial protrusion in the area of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm; assess the degree of stricture, if present, and exclude a tumor process.
- Daily changes in pH inside the esophagus are the most reliable method for diagnosing reflux disease.
An electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the heart, spirometry, and plain chest radiography are prescribed, rather, with the aim of excluding other organic pathologies (angina pectoris, bronchial asthma, etc.).
If there is a suspicion of GERD during pregnancy, an internal examination is carried out only in severe cases of the pathology. In other cases, only symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Symptoms of insufficiency are similar to those of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so in no case should you self-diagnose and begin treatment.
You should definitely contact a gastroenterologist for a detailed examination and proper prevention.
The main symptoms of the disease are constant attacks of heartburn, including even without eating, frequent belching of air, attacks of nausea, regurgitation of stomach contents.
If this happens quite often, then the sick person needs to see a doctor to check for insufficiency of the gastric cardia.
- X-ray of the upper part of the digestive system;
- endoscopy (examination of the inside of the esophagus);
- daily ambulatory pH-metry of the esophagus (test to determine the amount of acid in the esophagus);
- gastrofibroscopy (determines pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract);
- biopsy followed by histological examination;
- fibrogastroduadenoscopy (FGDS) - examination of the gastric mucosa.
- eradication of the diagnosis itself;
- reducing internal abdominal pressure in the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduction and eradication of symptoms;
- regulation of the gastric cardia.
- antacids that reduce the acidity of gastric juice and relieve heartburn (“Ranitidine”, “Almagel”);
- drugs for healing the gastric mucosa (“Omeprazole”);
- antiemetic drugs (“Regidron”);
- analgesics (“Solpadeine”);
Medicines and diet for insufficiency of the gastric cardia help cure the disease. Weight is restored to normal. In some cases, surgery is necessary.
Drugs
Causes of the disease: organic factors
There are many reasons for the occurrence of cardiac insufficiency. It is customary to divide them into two large groups:
- organic causes;
- functional reasons.
Organic factors in the occurrence of the disease are those phenomena that are not directly related to disruption of the muscle ring. Organic factors cause negative operating conditions for the gastric valve, which is the impetus for their disruption. They are:
- compression deficiency resulting from improper diet, as a result of overeating or infrequent consumption of food, but in large portions;
- complete lack of physical activity;
- formation of a diaphragmatic hernia;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the digestive system such as gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.;
- consumption of food before going to bed in large quantities;
- excess weight.
In addition, an inflammatory disease of the walls of the esophagus - esophagitis - can provoke the appearance of cardiac sphincter. Cardia failure will develop as the underlying disease progresses.
But there is an important nuance. It is worth understanding that any disease of the digestive system can provoke cardia insufficiency: atrophic gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis, etc.
The group of functional causes includes those factors that are directly related to disruption of the sphincter. These include:
- a significant increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- significant increase in pressure in the stomach;
- spasms of the valve connecting the stomach and duodenum.
In addition, the appearance and development of gastric cardia insufficiency may be associated with surgical interventions. For example, the operation intentionally or unintentionally affected this area.
What it is?
The cardia of the stomach is a ring-shaped sphincter, localized between the esophagus and stomach. In turn, the sphincter is a valve that prevents gastric contents from entering the esophagus. In the absence of pathological conditions, the sphincter opens, allowing food to pass into the stomach, after which the valve closes again. With cardia insufficiency, the work of the sphincter is disrupted and it stops closing. Thus, the cardia of the stomach loses its ability to retain gastric juice, as a result of which it does not enter the esophagus.
Since the stomach contains an acidic environment, and the esophagus is predominantly neutral, the entry of gastric juice into the esophagus can damage the walls of the organ, causing ulcers and burns. In the absence of a treatment process, there is a high probability of the formation of malignant tumors.
Causes
The exact causes of cardiac failure remain unknown. There are many theoretical assumptions regarding this disease, but none of them has practical confirmation. At the same time, there are two practically opposite theories:
- The first asserts that cardia insufficiency is a multi-etiological disease, the development of which may be associated with the action of many factors.
- The second theory is based on the impossibility of the occurrence of similar diseases under the influence of various factors, for which reason cardia failure should be considered as a whole complex of diseases with similar common symptoms.
However, among the most likely causes of the pathological condition in question, the following should be answered:
- infectious pathogens of viral origin that can cause inflammatory changes in the nerve trunks with subsequent disruption of the stomach and esophagus;
- deficiency in the body of various mineral components and vitamins;
- psychogenic disorders;
- various diseases of the digestive tract, which are characterized by increased gas formation and overdistension of the stomach.
Degrees
Symptoms of cardia insufficiency tend to increase. In accordance with the dynamics of changes in the esophagus, there are 3 degrees of cardia insufficiency:
- 1st degree. This stage is characterized by the absence of closure of the valves. It is functional in nature with periodic occurrences. In this case, there are no changes in the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube and other morphological dynamics;
- 2nd degree. Here there is a lack of complete closure of the sphincter of the upper stomach. The diameter is closed only halfway. It is also possible for the folds of the esophageal mucosa to fall out in the gastric lumen;
- 3rd degree. At this stage, there is complete absence of closure of the sphincter walls. In this case, gastric perilstatics persists, but pronounced inflammatory and erosive lesions of the organ mucosa are noted.
According to the nature of motor activity disorders, there is the following classification of cardia insufficiency:
- Hypermotile. It is caused by excessive perilstatics, aimed at pushing the food bolus.
- Hypomotile. Characterized by a significant decrease in the intensity of perilstatic movements. Food masses can remain in the esophagus for a long time and spill out through the gag reflex.
- Amotylic. There is a lack of perilstatics of the esophageal tube.
To enlarge the picture, click on it.
Symptoms
The intensity of the symptoms of the disease directly depends on the degree of the disease. The symptoms manifest themselves most clearly at stage 3 of cardia failure. However, there are symptoms and signs, the manifestation of which makes it possible to diagnose the disease at the very beginning, in the early stages:
- weakness and frequent dizziness that appear after a period of vigorous activity or physical exertion;
- heartburn that appears regardless of food intake (considered by experts to be one of the main symptoms);
- burping is also one of the main signs;
- frequent attacks of nausea and vomiting (with the release of large amounts of bile);
- chest pain;
- rumbling;
- pain predominantly in the epigastric region.
As the disease progresses, the intensity of symptoms increases. Belching may include stomach contents. Often it is constant belching and heartburn that is a reason to suspect the presence of insufficiency of the gastric cardia.
Symptoms
If the work of the cardiac sphincter is rarely disrupted, it is almost not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The severity of the patient’s condition depends on the causes of the pathology and the characteristics of its course. Typically, obvious signs appear only at stage 2, gradually worsening.
Attention: prolonged cardia failure always leads to damage to the esophageal mucosa. The condition of the stomach and the entire digestive system also worsens.
The development of this pathology is often indicated by the following symptoms:
- frequent belching of air or even undigested food;
- heartburn not associated with food intake;
- pain and discomfort in the stomach;
- burning sensation and pain in the esophagus or behind the sternum;
- nausea, vomiting, often mixed with bile;
- bloating, flatulence;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- headaches, dizziness;
- chronic cough, often developing into asthmatic bronchitis.
The main symptom of the pathology is frequent belching or heartburn
Each person has individual manifestations of the disease; they may not occur all at once, but only some. But the malaise usually worsens due to overeating, when taking a horizontal position or after physical activity. Moreover, the consumption of certain foods leads to a deterioration of the condition only in cases where the pathology is associated with stomach diseases.
Symptoms of pathology
Gastric cardia insufficiency is 95% an acquired disease and only 5% is a congenital defect. Valve non-closing has 3 degrees of violation:
Cardiac insufficiency of the 2nd degree can be cured comprehensively, but non-closure of the valve of the 3rd degree must be treated with surgery. Echosigns are poorly defined and resemble reflux esophagitis in nature. Valve deficiency is determined by the main symptoms:
PAY ATTENTION! Do not prolong gastritis or an ulcer until stomach cancer, it is better to be on the safe side, but this will be necessary. read the story of Galina Savina >>
- belching of air or acid;
- heartburn in the esophagus, throat and stomach;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- multiple stomatitis;
- vomiting bile;
- pain, bloating, distension behind the sternum;
- lump in throat;
- heavy salivation;
- weakness.
Diagnosis of pathology
Not wanting to see a doctor, many are interested in whether it is possible to cure gastric cardia insufficiency on their own by taking medications and using traditional medicine methods. As already mentioned, the symptoms observed when gastric contents reflux into the esophagus may also be present in other gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, without the help of a competent gastroenterologist, it will not be possible to effectively treat gastric cardia insufficiency.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient for an X-ray of the stomach and esophagus, an endoscopic examination (during this, material can be collected for histological examination). To determine the level of acidity, pH measurements of the stomach and esophagus are performed.
Compliance with diet and nutrition
Already at the first stage of the development of the problem, there is an urgent need to correct the nutrition system. Initially, the correct regimen is established - food is taken several times a day (4-5), in small portions. At the same time, meal times every day should coincide as much as possible. After the next meal, lying down is prohibited for 2 hours.
It is also important to remove the factor of mucosal irritation, that is, all foods that can provoke it are excluded from the diet. This is too hot or cold food, fried, spicy, smoked, highly salted, coarse, seasonings, alcoholic drinks, coffee, chocolate, etc.
The basis of the diet should be soups and delicate foods, steamed, boiled or baked. Before eating anything, the patient needs to drink a glass of clean water. The emphasis is on plant foods (vegetables and fruits). The last meal should be at least a couple of hours before bedtime.
Degrees
There are 3 degrees of sphincter non-closure:
- 1st degree – the amount of incomplete closure of the cardia is about 1/3 of the diameter of the esophagus;
- 2nd degree – non-closure increases to half the diameter of the esophagus;
- Stage 3 – the valve stops closing completely.
As valve insufficiency develops and intensifies, the symptoms of GERD increase, esophagitis appears, and a serious complication may follow - degeneration of the esophageal mucosa: Barrett's esophagus.
The intensity of the symptoms of the disease increases as the functioning of the sphincter worsens. There are 3 degrees of cardia insufficiency, each of which has its own clinical signs and manifestations.
There are three degrees of the disease:
- I – has a functional character. Disturbances in the functioning of the valve are observed periodically, but changes in the mucous tube of the esophagus, as well as other morphological changes, are absent.
- II - the valve of the upper gastric section stops closing, closing its diameter only by half, as a result of which folds of the mucous membrane of the esophagus may fall out into the stomach.
- III – characterized by a complete cessation of the process of closing the walls of the sphincter. At this stage of the disease, gastric peristalsis is preserved, and the presence of pronounced inflammatory and erosive changes is noted in its mucous membrane.
Anatomy of the stomach
At the junction of the esophagus and the stomach there is the lower esophageal sphincter (another name is the cardiac sphincter), which separates the esophagus and stomach. It is a kind of “valve” that allows food to pass in only one direction - from the esophagus to the stomach. It also prevents the acidic contents of the stomach from entering the esophagus.
The esophagus enters the stomach at an acute angle, which promotes one-way movement of food. As the stomach fills with contents, the angle of the connection becomes even more acute. The esophagus ends with a labial fold of the mucous membrane, which protrudes into the lumen of the stomach. It prevents food from flowing back into the esophagus during the opening of the cardiac sphincter. The pressure inside the stomach is much higher than in the esophagus. When it is filled with food, the tone of the cardia increases, and the oblique muscle fibers of the stomach and the diaphragmatic ligament also contract.
The cardia is considered a functional formation and is formed from the muscular layer of the stomach and the oblique fibers of its membrane. During normal functioning of the sphincter, an alkaline or neutral reaction of the internal environment is maintained in the esophagus.
Insufficiency of the gastric cardia (chalazia) is a violation of the obturator function of the sphincter, which is chronic and recurrent. The main function of the cardiac sphincter is lost - protecting the esophagus from the reflux of gastric juice and digestive enzymes into it. Contact of aggressive gastric contents with the mucous membrane of the esophagus can cause burns, ulcers and complications of malignant degeneration of mucosal cells.
The reflux of stomach contents with gastric juice and digestive enzymes into the esophagus is called reflux. It is not considered a pathology if it occurs during or immediately after eating. Reflux is a physiological process, provided that it is not repeated many times and lasts only a few seconds. If, as a result of the ingress of acidic contents, persistent changes appear on the esophageal mucosa or reflux repeats frequently and at night, this is a pathological process and requires treatment.
Disease severity
The stage of cardiac failure is established through instrumental diagnostics. According to the gastroentnrological classification, there are three stages of failure of the cardiac sphincter, and three forms of abnormal peristalsis (gastrointestinal motility).
Stages of valve dysfunction:
- Stage I – partial closure of the valve. The pulp closes partially (2/3 of the healthy state of the organ). Symptoms appear after eating or smoking.
- Stage II - The cardiac opening of the stomach closes only halfway. The gastric mucosa forms folds and moves towards the esophagus (prolapse is formed).
- Stage III - the cardiac sphincter ceases to function. Due to the constant aggression of acid, inflammation of the esophageal mucosa (esophagitis) develops.
Forms of peristalsis:
- hypermotility - intense functioning, not justified by the digestive load;
- hypomotility – decreased motor skills by half;
- amotility – lack of contractions to move food.
Determining the staging is necessary to select the correct treatment tactics and medications.
Photo gallery of prohibited products
Dishes with lots of spices
Smoked meats
Alcohol
Spicy dishes
Chocolate
Foods high in preservatives
Fried foods
Coffee
Photo gallery of drugs
Metoclopramide
Raglan
Cerucal
Diet price
Meals include regular foods, but increased protein content in the form of dairy dishes and cottage cheese, meat and fish should also be present daily. The estimated cost of weekly meals can range from 1400-1500 rubles.
The disease does not appear on its own. Gastric cardia insufficiency is a consequence of other disorders of the human digestive system. It is against the background of these diseases that this disease appears. Treatment of cardial insufficiency is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, which served as a kind of impetus for the occurrence of cardiac sphincter.
Treatment is based on the principles of healthy nutrition. It is worth considering that if you are overweight, your doctor recommends trying to lose it.
The diet prescribed by a specialist includes fractional meals in small portions. It is not recommended to take a horizontal position for two to three hours. The best option would be a walk or minimal physical activity.
The diet must include:
- soups;
- semi-liquid cereals;
- vegetables;
- fruits.
It is strictly prohibited to consume foods that can cause irritation to the esophagus. It is necessary to exclude from the diet sweets, flour, smoked and semi-finished products, fried and fatty foods, marinades, and too hot seasonings (it is better to exclude them completely). Food should only be consumed warm. And immediately before eating you need to drink 200 ml (a glass) of water at room temperature. It is not recommended to drink tap water.
In addition, it is strictly prohibited:
- wear tight clothing that restricts movement and puts pressure on the abdominal cavity;
- bend over frequently and engage in heavy physical activity;
- lift weights.
In addition, experts recommend sleeping with the head of the bed slightly elevated.
Treatment
The attending physician will suggest therapy depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease. Treatment of gastric cardia insufficiency begins with eliminating or correcting the cause of the disease. Obese people are advised to lose excess weight. If there are disturbances in your eating regimen, you should adjust it, and do not overeat at night. Do not take a horizontal position immediately after eating. A gentle diet is prescribed, fried, spicy, fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and heavy foods are excluded.
If a concomitant pathology of the stomach is detected, for example, gastritis or an ulcer, it needs to be eliminated. They take enveloping drugs to reduce the acidity of gastric juice. Antibiotics and medications that restore the mucous membrane are prescribed to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection.
Gastric cardia insufficiency continues to be treated with medications. They use drugs to increase the tone of the sphincter between the esophagus and stomach and improve peristalsis: metoclopramide, raglan. For increased secretion of hydrochloric acid and heartburn, medications such as Almagel and Smecta are prescribed.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is resorted to. If the cause of insufficiency is a hiatal hernia, it is repaired. The surgeon decides what surgical method to treat cardia insufficiency depending on the severity of the process. Operations are used to narrow the ring of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, suturing the wall of the esophagus to the stomach, and forming additional transverse folds in the esophagus. Other methods are also being developed.
Treatment with folk remedies can be used as an addition to the main therapy after consultation with a doctor. This method cannot be used on its own. Traditional healers suggest using decoctions of St. John's wort and yarrow, dandelion syrup, and plantain juice.