How to suspect an inguinal hernia?
An experienced doctor only needs to look at the problem to determine the correct diagnosis. Here's how:
- a round protrusion from the abdomen down into the perineal area,
- appears in an upright position, sometimes after coughing, straining, heavy lifting, or crying in an infant
- disappears or is easily adjusted manually, as soon as the patient lies on his back,
- usually painless upon medical examination and gentle palpation (feeling).
Sometimes adults can accurately name the event after which the hernia appeared.
What special symptoms will the doctor see?
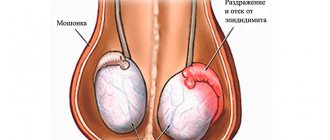
- Asymmetrical enlargement of the scrotum in the case when the hernia is unilateral.
- Deviation of the penis to the healthy side.
- If the penis is large, it can be almost completely “hidden” in the scrotum and folds of skin.
- In girls, there is a painless enlargement of one labia.
- The surgeon will try to insert the tip of a finger into the inguinal canal and ask you to cough. At the same time, he will feel shocks from the internal organs in the direction from the abdominal cavity to the outside. This is called a "positive cough impulse."
Sometimes patients are bothered by aching pain on the side of the protrusion, problems with digestion or urination, depending on which organ descends into the hernial sac.
What organs end up in the sac formed by the hernia?
When the abdominal muscles dissect, a small gap will inevitably form, but some organs can still get into it.
At the same time, the man notices a protrusion of skin in a small area in his lower abdomen. The main danger of organs getting into this sac is that the hernia may be strangulated. This, in turn, is dangerous because parts of the organs will simply be pinched in the pouch. If surgery to remove a hernia is not performed in a timely manner, necrosis of the following abdominal organs may begin to develop:
- Big seal.
- Parts of the cecum, small or sigmoid colon.
- Appendix.
- Bladder.
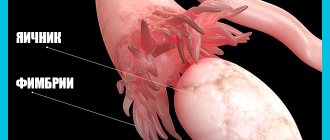
- Fallopian tubes, if a woman has a hernia.
Pinching these organs can be very dangerous. If the process of necrosis of their parts begins, the surgeon will simply have to remove them so that an inflammatory process does not begin in the abdominal cavity.
We recommend reading:
A lump appears in a man’s groin - what to do;A man’s left testicle hurts – reasons;
Pain in the groin on the left or right - article.
Differential diagnosis
The doctor must determine whether it is an inguinal hernia or other similar conditions:
- Newborns experience hydrocele (hydrocele), a condition in which fluid from the abdominal cavity leaks into the scrotum through a small opening in the inguinal canal. They can be distinguished by diaphanoscopy: the doctor will examine the scrotum with a special flashlight to see translucent fluid or intestinal loops that do not allow rays to pass through.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes in the area of the inguinal fold. It is caused by an infection, often there is an accompanying wound on the affected leg, and the swelling is red, painful and hot to the touch. Patients may have a fever and general malaise.
- Oncological diseases of the testicle, its membranes and spermatic cord.
- Varicocele is an enlargement of the veins of the pampiniform plexus around the testicle, which also appears in an upright position and with tension. As a rule, boys from adolescence and older suffer from it.
First of all, an ultrasound of the inguinal canals and scrotum is prescribed. The study will help determine some features:
- position and size of the hernial sac,
- contents of hernial protrusion,
- condition of the openings and walls of the inguinal canal.
This study is complemented by an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, and in women, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Through these procedures, it is possible to clarify which part of the intestine is trapped in the hernial protrusion, and whether there is an ovary or fallopian tube there. Ultrasound is the safest and most painless diagnostic method with no contraindications.
In doubtful cases, herniography is prescribed - an X-ray examination in which a contrast agent is injected into the abdominal cavity under local anesthesia, then the patient lies on his stomach and strains. In this case, the contrast flows into the hernial sac, and it becomes visible on the x-ray.
In rare cases, an x-ray contrast examination of organs that may fall into the inguinal hernial protrusion - loops of the large intestine and bladder - is performed. They are called irrigography and cystography, respectively.
To make a final diagnosis in complex cases of abdominal pathology, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. Under general anesthesia, one or more punctures are made in the abdominal wall, and a video camera and lighting device are inserted into the abdomen. With their help, the endoscopist surgeon carefully examines each organ until the problem can be determined - the source of pain or inflammation.
Laparoscopy is performed in a specially equipped operating room. The patient lies on his back, but during the procedure he can tilt either the head end of the operating table or the foot end. This allows for a more thorough inspection. During the diagnostic procedure, it is possible to collect material for histological examination. If possible, treatment is carried out during the same surgical procedure.
Unlike ultrasound and radiography, diagnostic laparoscopy requires hospitalization and observation for a couple of days in the hospital, even with a favorable outcome. If the results of laparoscopy reveal a gynecological, gastroenterological or oncological disease, the patient is transferred to a specialized hospital, where further examination and treatment are carried out.
- Causes of the disease
- A visit to the doctor is mandatory
- Ultrasonography
- Alternative diagnostic methods
- Is a relapse possible?
To quickly and reliably diagnose a protruding formation in the groin, an ultrasound of the inguinal hernia should be performed.
Inguinal hernia is one of the diseases that affects mainly men. It is very common in children, but adults can also suffer from a similar disease. The causes and methods of dealing with the disease are different, but the symptoms and diagnosis of an inguinal hernia are similar in all cases.
This phenomenon is most often observed in boys in the first years of life. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the inguinal canal. It all starts during the intrauterine development of the fetus. The testicles, which should be in the scrotum while the fetus is inside the womb, are located in the abdominal cavity. During development, the testicles descend into the scrotum, and at this moment an anomaly can occur when the testicle, descending, takes a piece of peritoneum with it. This creates a kind of pocket where internal organs can fall out, and over time fatty deposits can accumulate, which press and bulge.
Causes of the disease
Localization of the hernial sac in the groin area is the most common among all types of abdominal hernias. The wide prevalence of this pathology among males is determined by the specific structure of the inguinal canal, which is wider and shorter than in women, and is also not so strongly reinforced by muscle tissue and tendon layers.
An inguinal hernia can be congenital or acquired, so the etiological factors in each situation will be different. For example, in the first case, the main causes of the pathology are a disruption in the process of descent of the testicle from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum, against the background of which other internal organs may extend beyond the abdominal cavity.
As for the acquired form, the most common provocateurs of a hernia are:
- excessive body weight;
- specific working conditions associated with constant lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- chronic constipation;
- conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure;
- weakness of the abdominal muscles;
- a wide range of injuries to the anterior abdominal wall;
- congenital weakness of the inguinal ring;
- diseases in the clinical picture of which there is a strong, lingering cough;
- the occurrence of chronic infectious processes in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- inflammatory lesion of the prostate gland;
- various dysfunctions of the genitourinary system;
- addiction to bad habits, in particular smoking, which causes chronic cough;
- sudden weight loss;
Previous surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity can provoke the formation of a hernial sac in the groin:
- excision of the gallbladder;
- resection of the stomach or duodenum;
- appendix removal;
- adnexectomy;
- hysterectomy.
Direct inguinal hernia in the elderly is a consequence of age-related changes in muscle tissue in general and the abdominal muscles in particular.
Causes of the disease
Causes or factors that provoke the occurrence of an inguinal hernia:
- Weak inguinal ring and the connective tissue itself. As a rule, this factor is congenital.
- Excessive physical activity. When lifting weights, we “rest” against the peritoneum, which is where the pressure comes during straining.
Any load that is characterized by an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity can become a catalyst for the formation. Even a severe cough, vomiting or chronic constipation can cause this.
To diagnose and confirm the presence of an inguinal hernia in a patient, it is necessary to undergo a number of different consultations.
Return to contents
Recovery after inguinal hernia surgery
The patient is discharged after the operation in one or two days, but a week later a return visit to the doctor is necessary to remove the suture material. For a month after surgery, physical activity should be avoided, especially those associated with sudden sudden tension. Two weeks after the operation, the patient can have sex and lead a normal lifestyle.
At first after the operation, the hernia site may hurt, after 8-12 hours the doctor changes the bandage, and discharge may be found on it. Suppuration of postoperative sutures is a fairly common phenomenon; to avoid this, the dressing should be changed more often. A special bandage helps to reduce pain, speed up the healing of the postoperative wound and the engraftment of the mesh graft; it should only be applied by a specialist.
For the mesh implant to fully engraft and become overgrown with connective tissue, it takes at least two months; after six months, the hernia is completely healed and the risk of relapse is significantly reduced. After the rehabilitation period (1 month), you can perform therapeutic exercises that strengthen the abdominal wall. To do this, pump the press (from a position with bent legs to reduce the load) or do push-ups from the floor. Push-ups strengthen the muscle corset and put stress on almost all muscle groups, so it is advisable to use them to prevent relapse of the disease. However, it is best to practice swimming - the load on the muscles is quite intense, but does not cause excessive stress and is distributed evenly.
Diet after surgical treatment of inguinal hernia
The diet after removal of a hernia excludes foods that can cause indigestion. To exclude an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and reduce the load on the operated area, the patient should have normal bowel movements, without constipation or diarrhea.
To do this, food is taken in small portions, the frequency of meals increases to six times a day. Food should be liquid and rich in protein (fish, cottage cheese, eggs, boiled beef).
Products that cause intestinal irritation are excluded from the diet. These include smoked foods, sweet, spicy and sour foods, fatty meats, coffee and carbonated drinks.
Scrotal swelling after surgery for inguinal hernia - what to do?
Swelling of the groin area after surgery is normal and is caused by impaired lymphatic drainage. Doctor intervention is required only if swelling and redness does not subside 10-14 days after surgery. To reduce pain, the doctor may prescribe analgesics; calcium supplements, antihistamines and vitamin supplements, in particular vitamin D, help relieve swelling.
Also, to prevent postoperative complications, it is recommended to wear swimming trunks made of thick cotton material, without taking them off even at night. Special bandages that can be used for a month after surgery help reduce the load on the operated area.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors
A visit to the doctor is mandatory
If you suspect the presence or beginning of the development of an inguinal hernia, you should first consult a doctor. This type of examination is carried out by a surgeon. Diagnosis of adults is also carried out by a urologist. The surgeon must examine the groin area, palpate the inguinal ring, this is done through the scrotum. The doctor may ask you to sit and stand and tense your abdominal muscles. To examine the child, you must contact a pediatric surgeon.
In case of acute pain or suspected injury, hospitalization or an ambulance will most likely be required.
Return to contents
In what cases is it prescribed for men and women?
Statistics say that 70% of all abdominal hernia diseases are inguinal hernias.
This applies to both adults and children. The pathology is more typical for men: out of 5 cases of the disease, only one will be in a female patient. Although the factors that influence the development of the disease are characteristic of both sexes and occur approximately equally in both men and women. Among the factors for the development of inguinal hernias:
- anatomical features of the body structure;
- hereditary predisposition;
- tendency to prolonged constipation;
- disruption of nerve connections in the abdominal muscles, resulting in their atrophy;
- persistent cough;
- significant sports activities or heavy physical labor;
- difficult or frequent labor.
Manifestations of the disease will depend on the size and location of the formation, the location especially affects the symptoms. There are a number of signs that suggest the development of an inguinal protrusion:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, the intensity of which increases with physical activity, especially when lifting weights;
- the formation located in the groin changes under the influence of load;
- problems with urination;
- disruption of the digestive tract.
Ultrasonography
Often, diagnosing an inguinal hernia does not cause any difficulties, and to make a diagnosis, an examination by a doctor is enough, who will immediately prescribe the necessary treatment and regimen. However, some cases require additional diagnostic tools, especially if there is doubt about the diagnosis. An inguinal hernia is similar to the following types of diseases:
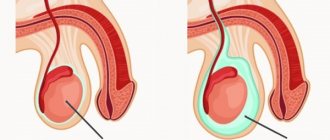
- Hydrocele, or hydrocele of the testicle. It differs from a hernia in that the extra “pocket” is filled not with an internal organ from the peritoneum, but with fluid. It happens that this fact is discovered directly during the operation. However, both diseases have the same treatment, so even if they are confused, no harm will happen.
- Inflamed inguinal lymph node. Often, inflammation of the lymph node is characterized by an increase in body temperature and pain at the site of inflammation. But there are times when these symptoms are absent. Then you can determine the cause at the moment of palpation. The lymph node is denser, the hernial pocket is soft.
In order to finally establish the diagnosis, the surest way is to undergo an ultrasound of the groin area. The ultrasound examination process itself is not difficult or painful. The doctor conducting the examination carefully examines the object of doubt itself, the inguinal canal, the scrotum. He will record all observations and transmit them to the patient.
During an ultrasound of the groin area, you can see exactly what the “pocket” is filled with: intestine or fluid, and thus understand whether it is a hernia or dropsy.
Based on these data, the surgeon will be able to accurately determine the location, size, filling of the “pocket,” associated problems and, of course, establish an accurate diagnosis. Based on the ultrasound, a course of treatment will be prescribed, which usually includes surgery.
Along with ultrasound, it is often necessary to carry out an X-ray examination of the pelvic area. This is especially true in cases. A hernia can cause complications on the pelvic joints. A strangulated hernia aggravates the patient's condition with nausea, sometimes vomiting, difficulties in passing gases, and leads to problems with stool. In order to carry out the operation efficiently, these examination methods are first used. In addition, blood and urine samples are taken before surgery.
After the operation, the ultrasound examination will most likely need to be repeated. This is done in order to look at the result of the operation and treatment and prevent complications in time.
The word “hernia” has long been known to medical science. In our body, all organs have their places - everything is in its own shell and is located exactly where it should be functionally. With a hernia, this order of arrangement is disrupted - some of the internal organs go beyond their place and begin to bulge. Inguinal hernia in men, the symptoms and treatment of which we will consider in detail below, is the most common pathology, accompanied by severe pain and entailing serious complications.
Recovery period↑
After the operation, the patient is in the hospital for two days, the sutures are removed after a week. For a month, it is necessary to limit physical activity and not overexert yourself. After this, it is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles. Push-ups and abdominal swings are suitable for this. Regular swimming exercises have the best effect, since the load is evenly distributed across all muscle groups.
A man needs to adhere to a gentle diet. Your daily diet should include foods that help normalize digestion and prevent intestinal disorders. The daily food intake should be divided into six meals; the menu must include low-fat fermented milk products, boiled or stewed beef, eggs, and fish. Spicy and smoked foods, fatty fish and meat, confectionery and sweets, and carbonated drinks are prohibited.
Main symptoms of inguinal hernia in men
At the beginning of the development of the disease, a man may not feel any discomfort. The hernia first appears as a small swelling in the groin area. Over time, this swelling begins to increase slightly in size, causing some discomfort, and pain may appear. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- A swollen area in the groin area, which, depending on the location of the man, can change its size - become smaller or larger.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- At the slightest physical exertion, painful sensations occur in the area of the inguinal swelling.
- There may be a burning sensation below.
- With a hernia, large men experience discomfort when walking.
Forecast
The prognosis for an uncomplicated hernia, provided it is diagnosed in a timely manner and treated correctly, is favorable. As complications develop, it worsens, some of the complications pose an immediate threat to life.
Recurrences of inguinal hernia are observed in 5-10% of patients due to an incorrectly selected surgical method, the patient’s failure to comply with doctor’s instructions in the postoperative period, excessive physical exertion, etc.
With timely detection of an inguinal hernia and its removal, the prognosis is favorable. The woman’s ability to work is fully restored in a short time.
If the hernial contents are strangulated and complications arise, the prognosis worsens significantly. It is most serious with the development of diffuse peritonitis; the mortality rate in this case, according to various authors, ranges from 5 to 20%.
Removal of an inguinal hernia in men, provided the operation is performed as planned, leads to a complete recovery of the patient and restoration of his ability to work in a short time. The development of incarcerated inguinal hernia and complications worsen the prognosis.
Types of disease
Treatment of inguinal hernia in men depends on its nature and type. There are several types of this disease.
- Congenital hernia - most often occurs due to immaturity of the inguinal canal and connective tissue. Occurs in premature boys.
- Acquired - due to the anatomical structure, as well as the amount of physical activity a man does.
- Oblique - the hernial sac passes through the internal inguinal ring in an oblique direction.
- Direct – caused by muscle weakness, comes out depending on the spermatic cord. It has a spherical shape.
What is strangulation of the hernial sac?
An inguinal hernia in men, the symptoms of which may not appear for quite a long time, can be large. Typically, the resulting hernial sac contains intestinal loops, in which the contents of the gastrointestinal tract are constantly moving. In most cases, protruding intestinal loops are not compressed by the hernial orifice and continue to normally perform their contractile function, as a result of which feces or food masses move freely into their cavities. Therefore, most patients can independently adjust the hernial sac back into the peritoneal cavity, and in some cases, intestinal loops can return to their original place on their own without additional manipulation.
An inguinal hernia in men, the consequences of the development of which can manifest itself in the form of any complications, can cause its owner a lot of unpleasant sensations. One of these complications is strangulation of an inguinal hernia neoplasm. The main reasons for the development of this phenomenon may be as follows:
- a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure, as a result of which various parts of the intestinal loops enter the hernial sac. Moreover, the size of the hernial orifice is too small to accommodate all the protruding organs. As a result, compression of the intestines occurs, which leads to the occurrence of stagnant processes, such as compression of blood vessels;
- in more rare cases, the development of such a complication as strangulation of a hernia occurs as a result of the accumulation of feces in it, which leads to a gradual increase in pressure on the intestinal walls and ultimately provokes strangulation.
This phenomenon can cause various complications, which are expressed in the form of disturbances in the digestive function of the body, bloating and constipation, as well as disturbances in the processes of spermatogenesis, which, in turn, leads to infertility in men.
Diagnostic measures for inguinal hernia in men
A reliable method of diagnosing the disease is examination by a specialist. The doctor diagnoses a hernia in a man in two positions: standing and lying down. Then, during some physical activity, he watches the bloating behavior - he tells you to cough or strain. Performs palpation of the protrusion to determine how far it can be reduced.
If the symptom complex is unclear, the specialist may prescribe an additional examination using devices. This is irrigoscopy
(examination of the rectum and lower intestines for the presence of internal tumors and damage to the walls).
Herniography
is also often used - the injection of contrast liquid into the abdominal cavity to determine the nature, size and development of the hernia.
The doctor may also prescribe an ultrasound of the scrotum
for reliable diagnostic results.
All these research methods show the degree of development of the disease and help predict the behavior of an inguinal hernia in men and the treatment of this disease.
Treatment
The traditional method of treatment is removal of the hernia. Conservative methods are used extremely rarely - when there are contraindications for surgery. If the disease is at the initial stage of development and does not show symptoms, doctors may resort to a wait-and-see approach with constant monitoring of the patient. If the disease is characterized by large protrusion and pain, then surgery cannot be avoided.
There are many methods of performing the operation, in particular:
- Lichtenstein method - the wall of the inguinal canal is strengthened with a mesh. This method is one of the most effective, practically does not cause relapses and has a short rehabilitation period.
- The Trabucco method is similar to the Lichtenstein method and involves the use of a flat prosthesis that does not require fixation of sutures.
- Laparoscopic hernioplasty - during the operation, a polypropylene mesh is installed with preliminary separation of the hernial sac from the transverse fascia and spermatic cord.
After surgery, a person is prescribed to wear a special bandage, which will maintain muscle tone and prevent relapse. Upon discharge from the hospital, the patient must follow a number of doctor’s recommendations:
- avoid carrying heavy objects and excessive physical activity for at least six months;
- follow a diet that includes the consumption of dairy products, fish, and lean meat;
- do not overeat to prevent overstrain of the abdominal wall;
- eliminate smoking and alcohol;
- refuse food that can lead to fermentation in the intestines (pickles, smoked meats).
For an inguinal hernia in men, treatment can only be carried out in a medical facility. No folk remedies can cure the disease, although they can delay its development for some time. In any case, self-medication entails dangerous complications, so at the first signs of pathology it is recommended to visit a doctor.
Inguinal hernia treatment in men
Modern medical science emphasizes that inguinal hernia of the stronger sex can only be treated through surgery. Various gymnastics, traditional medicine and conservative methods are powerless here, since the condition can only worsen.
Surgical intervention for this disease is carried out using two methods:
- classic (Lichtenstein operation);
- laparoscopic (gentle method).
The first method is cutting the sore spot. This operation takes place in several stages:
Stage 1:
the hernial sac is dissected. This manipulation must be carried out by a highly qualified specialist, as there is a danger of damaging the intestinal walls. The incision itself is 10-12 cm in size, made slightly above the inguinal ligament, parallel to it.
Stage 2:
the surgeon's assessment of the condition of nearby internal organs. If they are not damaged or inflamed, they return to the abdominal cavity.
Stage 3:
This is the final manipulation. At this stage, the hernial sac is removed to strengthen the inguinal canal, and the surgeon sutures the mesh allograft. Then the skin incision is sutured. With such strengthening, the probability of recurrence of the disease is no more than 1%.
This operation is now performed using local anesthesia, although general anesthesia is sometimes used.
An inguinal hernia is a tumor-like protrusion of the intestine, omentum, ovary, fallopian tube through an open hernial orifice into a weakened inguinal canal. In adults, the disease occurs with increased intra-abdominal pressure and softening of connective tissue. Men are susceptible to hernia up to ten times more often due to the fact that the short and wide canal is less strengthened by muscles. An inguinal hernia in newborns occurs when the pouch is not closed. Ultrasound of an inguinal hernia in a child is a necessary diagnostic procedure for a congenital disease caused by connective tissue pathology. Acquired hernia occurs in adolescents against the background of increased physical activity. An appointment for an ultrasound examination of an inguinal hernia must be made if the following symptoms are present:
- heaviness in the lower abdomen, rare pain during exercise;
- a protrusion that, when pressed, returns to the pocket;
- discomfort when moving and exercising;
- painful menstruation due to prolapse of the fallopian tube or ovary;
- pain when urinating with a sliding form of the disease;
- flatulence and constipation when part of the intestine gets into the bag;
- asymmetrical enlargement of the scrotum (scrotal hernia);
- penis deviated in the opposite direction;
- enlarged labia on the side of the hernia in women.
If these symptoms occur, for differential diagnosis of the disease and informed choice of treatment methods, it is recommended to do an ultrasound of the inguinal hernia; in Moscow and Moscow region the average cost of the study is 1,500 rubles.
Treatment without surgery
To date, there are no non-surgical methods for treating hernias that doctors would consider effective. Any of the conservative methods is not able to give a sustainable result and prevent the problem from worsening. However, men continue to use them as self-medication, and some even claim improvement in their condition. It is important to consult with your surgeon before attempting any of the methods listed below. In case of an increased risk of complications, such therapy will be a banal delay.
Visceral therapy
This refers to the manual reduction of the contents of the hernial sac back into the abdominal cavity. The technique gives short-term results. Already at the first strong tension, the tubercle will return to its place. Reduction procedures should be carried out by an experienced specialist. Inept handling can lead to aggravation of the problem and even strangulation of the hernia.
Folk recipes
People recommend making compresses on the hernia from a decoction of oak bark, sauerkraut juice, and rubbing ointments based on propolis and goose fat. Such methods of treatment are the most questionable. None of them can eliminate or even weaken the effect of the main provocateurs of a hernia: muscle weakness and pressure inside the abdominal cavity. Cold compresses and ice rubs actually accelerate pinching and provoke the reactive development of complications.
Exercises
Some traditional medicine practitioners recommend training the abdominal and groin muscles to get rid of a hernia. Doctors say that such actions should have been taken before the problem appeared. Physical activity (including focusing on the abs) will only accelerate the growth of the hernia. If a man is radically opposed to surgery, exercise therapy can be used (under the supervision of a physical rehabilitation specialist). To prevent increased intra-abdominal pressure, experts recommend yoga or water exercises for men.
Bandage
Doctors recognize wearing a bandage (a special inguinal corset) as the only effective method of correcting the symptoms of an inguinal hernia without surgery. This approach only eliminates unpleasant sensations. A bandage or corset simply supports the organs that come out of the abdomen, instead of the muscles. As soon as the man takes it off, a hernia appears.
The use of a bandage is appropriate in case of small reducible hernias. Then the doctor himself may recommend doing physical exercises in a bandage to strengthen the muscles and prevent further growth of the hernia.
The use of such devices has some nuances:
- excessively prolonged use of the bandage can aggravate muscle atrophy;
- the device must be chosen together with a doctor (there are left-, right-, and bilateral corsets, so it is important not to confuse them);
- measurements to purchase a bandage must be taken by a specialist;
- It is also better to do the first fitting together with a doctor to make sure that the groin corset is used correctly;
- There are no bandages suitable for scrotal hernia.
When purchasing, it is important to pay attention to the rigidity of the device, the elasticity of the material, its ability to allow air to pass through, the ability to adjust the size individually, and the quality of the seams and Velcro. The crotch corset is worn only over underwear.
Features of the procedure
An experienced surgeon can easily identify a hernia during examination, but to exclude a number of other pathologies with similar symptoms (varicocele, hydrocele, inguinal lymphadenitis, femoral hernia, oncology), additional studies must be performed:
- Perform an ultrasound of the scrotum and an ultrasound of the inguinal canals - the procedure is prescribed for men if it is quite difficult to determine the nature of the detected formation by palpation. Women are advised to make an appointment for a pelvic ultrasound.
- Conduct herniography - a study using a contrast agent. While lying on your stomach, the contrast enters the bag and glows on the resulting x-ray.
- Do a laparoscopy - perform surgery under general anesthesia. This type of study allows you to take material for histology.
An ultrasound of the groin is not necessary to diagnose a hernia in the classic course of the disease. If the surgeon conducts a differential diagnosis with a hydrocele or in the presence of a small protrusion, groin ultrasound is the method of choice for primary hardware diagnosis.
An important feature of the ultrasound diagnostic procedure for an inguinal hernia is the ability to determine the contents of the pocket. So, with a hydrocele (dropsy of the testicle), the cavity is filled with fluid, and with a hernia, it is filled with intestinal loops. No preparation is required for an ultrasound of the groin area.
Treatment methods
The main method of eliminating an inguinal hernia is surgery, which alone guarantees the cure of the hernia. In cases where the operation is impossible for medical reasons, auxiliary means are used: physical therapy, wearing a bandage.
Unfortunately, these methods do not give a 100% result. To prescribe surgery and related treatment, you must consult a doctor. You can get a free consultation from a qualified specialist on our website.
Surgery
The operation can be performed in two ways: both open and using an endoscope. The operation is carried out as planned, first the following preparation is carried out:
- An ultrasound is performed.
- General urine and blood tests are taken.
- A survey is conducted to identify contraindications for surgery. They may be:
- Acute infections.
- Chronic diseases in the acute stage.
- Purulent infections.
- Heart failure, risk of thrombosis.
- General poor condition of the body, exhaustion or suppression of the immune system.
- Individual intolerance to drugs.
- Preparation of the surgical field: on the day of surgery, the groin and abdomen are shaved.
- A cleansing enema is given.
In an open operation, the tissue above the inguinal canal area is completely dissected; if an organ has been pinched, it is washed with warm saline and returned to the abdominal cavity. The hernial orifice is stitched with a special suture, and the hernial sac is cut off. At the second stage of the operation, plastic surgery of the anterior wall of the inguinal canal is performed to avoid relapse. Plastic surgery can be performed either using your own tissues, for example, the tendon plate of the oblique abdominal muscle, or using synthetic materials.
Endoscopic surgery is easier to tolerate by the body, since only four punctures are performed. The disadvantages of this method include an increased risk of relapse.
Non-surgical methods
If due to the condition of the body it is not possible to perform surgery, wearing a bandage is indicated. The exception is strangulated hernias, which are operated on in any case. When wearing a bandage, the following effects are achieved:
- Gentle pressure on the abdominal wall partially compensates for the function of the abdominal muscles.
- Prevents the prolapse of abdominal organs into the hernial sac.
- Masks a defect.
It is also possible to perform therapeutic exercises to gently strengthen the abdominal muscles and the walls of the inguinal canal. A specialist will help you choose therapeutic exercises.
How is an ultrasound of an inguinal hernia performed in men, women and children?
Ultrasound examination is painless and does not require preparation. An ultrasound of an inguinal hernia in a child, as a rule, does not cause fear or tears. The patient lies down on the couch, the sonologist applies a gel that prevents the formation of air bubbles between the sensor and the skin, and begins the study. The results of the ultrasound examination are displayed on the screen. An ultrasound of an inguinal hernia in men provides reliable information about the disease, but for a reliable diagnosis, men also need to register for an ultrasound of the inguinal canal and scrotum. Women are prescribed additional pelvic examinations.
A dangerous complication of the disease is a strangulated hernia, which negatively affects the joints located in the pelvic area. In women, strangulation can lead to removal of the ovary or part of the intestine; a complication of the disease in men leads to loss of the testicle. Inguinal hernia accounts for up to 95% of newborn hernias. Without performing a groin ultrasound procedure, accompanying timely diagnosis according to indications and treatment in young children, the disease can be fatal.
The price for an ultrasound of an inguinal hernia in Moscow and Moscow Region ranges from 900 to 4000 rubles. In order to sign up for an ultrasound examination of an inguinal hernia, select a medical center in the Clinics section, read reviews about doctors and leave your contact information in a special form.
An inguinal hernia (abbreviated as inguinal hernia) is diagnosed in a short time. Its definition does not cause any particular difficulties. When you consult a doctor while the disease is in a calm stage, the accuracy of diagnosis increases.
The examination is carried out by a surgeon. Based on his conclusion, subsequent decisions regarding the treatment of the operation are based.
An inguinal hernia can appear suddenly, or it can make itself felt gradually. An example is a hernia caused by a lifted weight. Such a hernia is easy to see. And if the PGR has a floating state, then a visual manifestation will occur if certain conditions are met.
There are several methods for diagnosing a hernia. All of them have proven themselves and can complement each other.
Symptoms of inguinal hernia manifestations are similar to signs of other diseases.
Hydrocele is a manifestation of hydrocele of the testicular membranes. Manifests itself in the form of an enlarged scrotum. Because of this, at the initial stage, hydrocele can be confused with PGR.
Varicocele is a manifestation of varicose veins in the spermatic canal. Accompanied by pain in the groin area. The scrotum increases in size.
Lymphadenitis - symptoms similar to varicocele. Is an inflammation of the lymph nodes.
A femoral hernia appears just below the spermatic canal.
The initial stages of all these diseases are similar to each other and resemble PGR. Therefore, to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, a complete examination is required.
Forms of the disease
Inguinal hernias can be congenital or acquired.
According to the location of the hernial sac:
- inguinal – the hernia protrudes into the cavity of the inguinal canal, but does not extend beyond the level of the external opening of the inguinal canal;
- cordial - the contents of the hernial sac descend into the scrotum to the spermatic cord;
- inguinal-scrotal – the hernial contents reach the testicle, stretching the scrotum;
- oblique - the contents pass through the entire inguinal canal. This form is the most common and can be either congenital or acquired. The acquired one has an oblique direction only in the initial stages of the pathology; with an increase in the hernia, the internal opening of the inguinal canal expands inward. In most cases, an indirect inguinal hernia is unilateral;
- direct – passage of the hernia contents into the inguinal canal through the peritoneal wall is observed, while the internal opening of the inguinal canal is not affected. As a rule, this form occurs as a result of overexertion and is bilateral;
- interstitial rectus (subcutaneous) – protrusion of the hernia occurs into the subcutaneous tissue of the aponeurosis of the external oblique abdominal muscle;
- sliding – there is an additional protrusion of the inner lining of the abdominal cavity. In this case, not only the small intestine can emerge from the abdominal cavity, but also the walls of the bladder, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovary, etc. This is the most dangerous form of inguinal hernia, since it is more capable of strangulation than others.
Oblique and direct inguinal hernias
With a combined form of inguinal hernia, two or more hernial sacs are identified on one side. In this case, the hernias do not communicate with each other; each of them has its own hernial orifice. The pathology is relatively rare.
We suggest you read: Pain in the heart with osteochondrosis
Based on the ability of the contents of the hernial sac to return to its original position (reduce), hernias are:
- not disadvantaged;
- disadvantaged.
Inguinal hernias in women are only direct, which is explained by the absence of the spermatic cord in the female inguinal canal.
A hernial protrusion can be reducible (in the supine position its size decreases or it completely disappears) and irreducible.
When the hernial sac is compressed in the area of the hernial orifice, a strangulated inguinal hernia develops in women.
Sliding inguinal hernias are especially dangerous. They are formed by the visceral and parietal sheets of the peritoneum and are prone to frequent strangulation.
Inguinal hernias in men, depending on the characteristics of the anatomical structure, are divided into several types:
- Oblique. They can be either congenital or acquired. The hernial contents are located inside the structures of the spermatic cord along the inguinal canal. Oblique inguinal hernias, in turn, are divided into inguinal-scrotal (the hernial protrusion descends into the scrotum), cordial (the hernial sac is located in the inguinal canal at the level of the spermatic cord) and canal (the hernial sac is located at the level of the outer ring of the inguinal canal).
- Direct. This type refers to acquired hernias. They are characterized by the passage of a protrusion outside the spermatic cord through the inguinal space.
- Combined. They are quite anatomically complex formations, which consist of two or more hernial sacs passing through different hernial openings.
- Direct interstitial (subcutaneous). The hernial sac is located in the subcutaneous tissue of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle, without descending into the scrotum.
The process of inguinal hernia formation
Inguinal hernias in men can be reducible or irreducible. With reducible hernias, the hernial protrusion may disappear, slipping back into the abdominal cavity. If the hernial sac becomes fused with the hernial contents, then the hernia becomes irreducible.
Sliding inguinal hernias are also isolated. In this case, not only the parietal, but also the visceral layer of the peritoneum takes part in the formation of the hernial sac. Most often, the hernial contents of such inguinal hernias in men include the wall of the bladder.
If, after removal of an inguinal hernia in a man, the protrusion appears again, then such hernias are called recurrent.
According to the characteristics of the clinical course, inguinal hernias can be uncomplicated or complicated.
Methods for diagnosing an inguinal hernia:
- examination by a doctor;
- undergoing irrigoscopy;
- herniography;
- examination by a surgeon.
There are several stages of examining a patient by a surgeon to clarify the diagnosis. Often, the surgeon additionally prescribes an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis.
First, the doctor examines the groin area. And he conducts a survey of the patient to clarify such points as: whether there is pain in the groin, the period of hernia manifestation, what stress the patient experiences in everyday life and in professional activities.
In some cases, manifestations of PGR are unnoticed by the patient. In other cases, a person feels aching pain in the lower abdomen. They may intensify during physical activity. It happens that slight overexertion already provokes a hernia to appear.
With the initial strangulation, sharp pain occurs with the effect of the hernia being unreducible. Such a diagnosis may precede referral for surgery.
The patient is in a standing position. The doctor must evaluate the protrusion by its location, size and determine the type of hernia - direct, oblique, combined.
When the PGR descends into the scrotum, an oblique type is likely. When located above the seminal canal and without specific boundaries, a direct PGR is likely, also located above the pubic bone or nearby. When located below the pubis, predominantly outward, these are signs of a femoral hernia.
After interviewing and examining the patient, the doctor proceeds to palpation of the formation. This happens while lying down. The doctor will try to reduce the hernia and then apply pressure to the inguinal ring. Next, when the patient coughs, based on the reaction of the formation, the doctor diagnoses the type of PH - oblique or straight.
If a sliding hernia is present, it will probably not show up during examination using classical diagnostic methods. Then other technologies are connected, for example, ultrasound.
Diet
A diet that must be followed not only while in the hospital, but also in the future will help you recover faster. The main goals of the diet: prevention of constipation and increased gas formation, weight loss, saturation of the body with useful vitamins and minerals that help to recover faster. During the period after surgery, you need to eat soft, ground food - puree, soufflé, ground porridge. Gradually the diet is expanded.
Treatment of an inguinal hernia will proceed faster if you saturate the body with useful vitamins and minerals
Meals should be small, at least four times a day. You need to consume more protein, so recovery will be faster. Protein is found in large quantities in the following foods:
- chicken meat;
- cottage cheese;
- buckwheat;
- chicken eggs;
- fish.
On the first day after surgery, you can consume meat and vegetable broths, soft-boiled eggs, fruit juices, and jelly. The next day, the diet can be expanded, but the food should still be ground and semi-liquid. You can add boiled or steamed fish, soups with cereals, and grated porridge to your diet. In the future, meals are gradually expanded, moving to a full menu.
For the entire recovery period after surgery, you need to avoid alcoholic beverages, foods that cause bloating and increased gas formation (cabbage, peas, fresh cucumbers), and foods that cause constipation. You should not eat flour or sweets, limit strong tea and coffee.
Ultrasound of the scrotum and inguinal canals
Ultrasound - ultrasound examination of the scrotum and inguinal canals is one of the ways to study a hernial protrusion. An experienced specialist can do without it.
Ultrasound is used if the formation is difficult to diagnose due to its small size or if the doctor has certain doubts.
The ultrasound examination method is effective only from the moment when the hernial sac is full, that is, it already contains the organ that has prolapsed there. Otherwise, the ultrasound will not show anything.
In the absence of protrusion of the hernia, it can be assumed that the hernial sac is empty.
To create a reliable picture, an additional ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed. For women, pelvic examination is important.
Diagnosis of pathology↑
First, the doctor visually determines the presence of a hernia, its shape, size and location, and checks whether the lesion is reducible and whether there is pinching. The contents of the hernial sac are determined using:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and groin area - provides information about the exact size of the hernia and the internal organs involved in the pathological process.
- X-ray methods - the abdominal organs are examined (herniography), large intestine (irrigoscopy).
- Diaphanoscopy - the hernial sac is illuminated with a lamp; the method is less informative than ultrasound and x-rays.
Irrigoscopy
The method for determining the inguinal growth is irrigoscopy. It is used when a sliding hernia with mild symptoms is suspected.
This hernia is difficult to diagnose. Therefore, X-ray examination comes to the rescue.
During irrigoscopy, the colon is examined and X-rays are taken.
Before the study, bowel cleansing is recommended, which will increase the quality of the diagnosis. To do this, a diet without fruits and vegetables is prescribed for several days. Meat becomes the main product. Before the procedure, the next dinner and breakfast are excluded. You are only allowed to drink still water.
During irrigoscopy, a special substance is injected into the colon, followed by an X-ray contrast apparatus. This method provides a way to study the intestines and diagnose its defects and diseases.
For a sliding hernia, it is permissible to use cystoscopy, cystography, and ultrasound of the bladder.