Infection
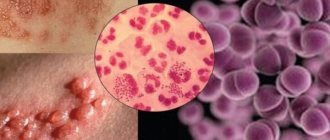
The causative agent of gonorrhea is gonococcus, a small gram-negative bacterium with a round shape and a bumpy surface. Very often, microorganisms form in pairs and are located inside immune cells - leukocytes.
Experts identify the following routes of possible infection:
- During unprotected sexual intercourse. The highest risk of the disease occurs during anal and vaginal intercourse.
- Oral sex is rare, but leads to the development of clap. This is due to the destructive effect of salivary enzymes on bacteria.
- Contact or household transmission of gonorrhea from a sick person or carrier to a healthy person is considered unlikely, since the microorganisms that cause the sexually transmitted disease are unstable in the environment.
- Vertical transmission, in which gonorrhea is transmitted during childbirth from an infected mother to the newborn.
Outside the human body, bacteria quickly die when exposed to sunlight, when boiled or treated with disinfectants. This feature of these pathogens refutes myths about the disease that relate to methods of infection. Gonorrhea is not transmitted by shaking hands, sharing glasses, shared towels or washcloths. You also cannot become infected in public toilets (through the toilet), when visiting a swimming pool or sauna.
Most often, gonorrhea is recorded during unprotected homosexual contacts; this fact is due to the fact that pathogens more actively penetrate through damage to the mucous membranes, which often occur during anal sex.
Development mechanism and reasons
The causative agent of gonorrhea (gonorrhea) is gonococcus (Neisseriagonorrhoeae), a gram-negative spherical bacterium. Its cells are shaped like beans. The bacteria are classified as diplococci, as they are most often grouped in pairs. Diplococci quickly die in the external environment, unable to tolerate dry air and sunlight. These bacteria die quickly even when boiled; they also cannot tolerate all antiseptics: chloramine, hydrogen peroxide, bleach. Therefore, you can become infected with gonorrhea after unprotected sex with a sick person.
Once in the human body, gonococci penetrate the urethra and, with the help of microvilli, attach to the mucous membrane, forming colonies on it. The immune system triggers a protective reaction by producing macrophages in the area where microorganisms are located. Macrophages, in turn, produce phagocytes, but gonococci are protected by a special capsule that prevents these substances from penetrating inside. The process of phagocytosis is not completed, and diplococci are located inside immune cells, and their death does not occur. For this reason, an accumulation of pus occurs in the man’s body, which consists of dead phagocyte cells and viable gonorrhea bacteria.
Course of the disease
During sexual contact with a carrier of the infection, gonococci appear on the mucous membranes of a healthy person and linger on the surface of epithelial cells for several hours. At this time, you can apply emergency measures to prevent STDs, aimed at destroying the pathogen and avoiding the onset of the disease.
After 2 hours, bacteria begin to actively multiply, penetrate into the intercellular space, connective tissue, anterior urethra, gonads, which leads to acute gonorrhea. With further development of the inflammatory process, some gonococci penetrate into the posterior urethra. This increases the risk of prostatitis, infection of the epididymis and seminal vesicles. In case of a significant decrease in the body's defenses (with immunodeficiency, taking chemotherapy and cytostatics), severe gonococcal arthritis and sepsis may develop.
One of the features of gonorrhea is “incomplete phagocytosis,” in which bacteria absorbed by immune cells are not destroyed, but, on the contrary, are spread throughout the body.
Urologists consider urination immediately after sexual intercourse and the use of local antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin) to be the most effective way to prevent STDs during casual or questionable sexual intercourse. A stream of urine washes away most of the pathogenic microorganisms from the urethral mucosa, thereby reducing the risk of developing the disease.
Gonococci - what is it?
If men experience discomfort when urinating, it is recommended to be diagnosed by a doctor. Possible malaise is evidence of a sexually transmitted disease. Gonorrhea is caused by extracellular parasites called gonococci.
Pathological microorganisms are capable of causing a pathogenic process on the mucous membrane in the genitourinary system.
Bacteria enter the male body through unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner. The disease can develop for a long period in the patient’s genitals.
At the same time, the patient has no idea that a rather dangerous problem is forming in his body.
After visiting your doctor, do not be afraid of the diagnosis. You should familiarize yourself with the proper information and learn about gonococci - what kind of bacteria they are and how to treat them.
Signs of gonococcal urethritis
The incubation period for infection with gonorrhea is on average 2-14 days, after which the clinical symptoms of the disease begin to rapidly manifest. Occasionally, the latent period can extend to several months, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult. In a man’s body, gonorrhea can occur in acute, chronic (after improper treatment) and latent (latent) forms.
Signs of acute urethritis caused by gonococcal infection are:
- The appearance from the urethra of copious, purulent-mucous discharge, which in consistency resembles thick cream.
- Increased urination.
- Discomfort, burning when urinating.
- Redness of the glans penis, opening around the urethra and foreskin.
- Itching, local increase in temperature in the area of the glans penis.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor accompanying the discharge.
- Pain and bloody discharge from the urethra during intimate contact.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, painful on palpation.
- Cloudy urine.
- Fever, headaches and muscle pain.
If treatment is carried out incorrectly or in its absence, inflammation can spread to the testicles, leading to orchiepididymitis or the development of serious complications such as infertility.
A feature of gonorrhea is terminal pain when urinating, accompanied by the release of 1-2 drops of blood.
Gonorrhea symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is purulent discharge from the urethra in men and from the genitals in women. Symptoms of gonorrhea in men appear 3-7 days after infection. The disease manifests itself as follows:
- Initially, mucus is secreted from the urethra; it is yellow or greenish-yellow in color, viscous in consistency.
- After 3 or more days, the mucus is replaced by pus.
- There is discomfort in the urethra, itching and burning.
- At the moment of urination, pain occurs, this is due to the fact that when passing through the urethra, urine irritates the damaged mucosa even more.
- Pallakiuria is a condition where the urge to urinate becomes more frequent, but urine output is minimal.
With female gonorrhea, the symptoms are erased and practically do not manifest themselves. The chronic stage of the disease has its own characteristics. Almost all the signs of gonorrhea in men described above appear weaker and intermittently.
The chronic stage of gonorrhea is divided into two main types:
- Primary chronic course - sometimes gonococcus entering the human body does not cause symptoms of the disease. This may be due to the characteristics of the immune system or the properties of the pathogen itself.
- Transition from the acute stage to the chronic form. Most often this happens when the acute stage of gonorrhea is not treated correctly.
In case of chronic gonorrhea with erased symptoms or their absence, it is very important to carry out all laboratory tests in a timely manner so as not to further develop the disease.
The most common complications of gonococcal infection include inflammation of the epididymis (epidermitis).
As a result of neglect of the disease, dissemination of gonococcal infection may develop, affecting the skin, joints, brain, liver and heart. When gonococci get into the eyes, gonococcal conjunctivitis develops.
Symptoms of gonorrheal epididymitis are:
- fever;
- the appearance of pain and swelling in the appendage;
- the place of the vas deferens turns red.
If a man discovers such manifestations of the disease, he should undergo additional diagnostics in order to make an accurate diagnosis.
In the acute stage of the disease, it will be enough to take a smear for laboratory testing. But in the chronic stage, culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is performed.
Acute gonorrheal proctitis
Since gonococci have a tropism for epithelial cells of the mucous membranes, in addition to urethritis, they often cause proctitis. Most often, inflammation of the rectal mucosa is recorded among gay men.
Clinical signs of gonococcal prostatitis appear 5-10 days after infection. Venereologists and proctologists include:
- Intense itching in the anus and anus.
- Frequent constipation alternating with diarrhea, pain during bowel movements, false urges.
- Discharge from the rectum with purulent contents.
- The appearance of blood and mucus in the stool.
- Bloating.
- Increased body temperature, general weakness.
The symptoms of the disease are often erased and disguised as the manifestation of other diseases (intestinal infections, hemorrhoids, anal fissure, ulcerative colitis). That is why, if the slightest complaints appear that may indicate the development of this disease, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and research.
The favorite location of gonococci is the mucous membrane at a distance of 5 cm from the external anal sphincter, which must be remembered when diagnosing and taking scrapings for analysis.
Complications of gonorrhea
A long-term gonorrheal infection, without appropriate effective treatment, invariably provokes complications that are dangerous to the life and health of a man. Within a few days, untreated gonococcal urethritis can ascend through the genitourinary tract and cause cystitis and prostatitis. These diseases are accompanied by frequent and painful urination, pain in the perineum, which increases with sexual arousal, heaviness, and discomfort in the testicles. Acute gonorrheal prostatitis further leads to decreased sperm quality and infertility.
If the inflammatory process involves the epididymis, acute gonorrheal epididymitis is registered. Its manifestations include: redness and swelling of the scrotum, soreness in the groin. This condition threatens the formation of scars that narrow the lumen of the vas deferens, which can lead to infertility.
A pathological process in the urethra that lasts for a long time often leads to urethral stricture, which causes stagnation of urine, its reflux into the ureters, and the occurrence of kidney diseases.
Urologists identify certain factors that can increase the risk of complications:
- Concomitant infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genital tract, which are in the acute and chronic phase (cystitis, prostatitis, BPH).
- The presence of other sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, chlamydia).
- Weakening of local immunity after treated STDs, reinfection of gonorrhea.
- Prolonged sexual arousal, dissatisfaction with sexual life.
- Frequently interrupted sexual intercourse, which is used for contraception.
- Increased physical activity, frequent stress, anxiety.
- Bad habits - alcohol abuse, smoking.
- Preference in the diet for spicy, fried, spicy and pickled foods.
Very often, especially with a latent infection, the patient consults a doctor not at the initial stage of the disease, but after complications arise, which can lead to difficulties in treatment.
The most serious complication of gonorrhea is the development of a generalized infection - sepsis, which occurs with multiple organ failure and frequent damage to the heart valves.
Diagnosis of the disease
In the classic course of acute gonococcal urethritis, an experienced urologist or venereologist may suspect the disease based on the patient’s complaints alone. However, the correct diagnosis is made based on the results of smear examinations and urine tests. It is extremely rare for gonorrhea to be diagnosed serologically, usually only when the disease is latent.
A venereologist tells more about diagnostic methods for suspected gonorrhea in the video.
The “gold standard” for diagnosing gonorrhea is microscopy of a smear from the urethra and inoculation of the resulting biological fluid on a nutrient medium.
To increase the reliability of the results, it is necessary to carefully follow the rules for taking samples:
- Before taking a smear from the urethra, a man must not urinate for 4 hours.
- 2 days before the procedure, it is necessary to stop taking antibiotics and using local antiseptics.
- For clinical symptoms of prostatitis, a prostate massage is performed before taking a smear.
- If chronic gonorrhea is suspected, it is necessary to carry out a provocation - use drugs that stimulate the release of gonococci from the lumen of the urethra. For this purpose, the administration of gonovaccine, the intake of heavily peppered, salty foods, and the lubrication of the urethra with protargol or silver nitrate are used.
The diagnosis of gonococcal proctitis is made on the basis of a visual examination of the rectum, scraping, examination of mucopurulent discharge and rinsing water. Sowing the obtained biological materials on nutrient media is often accompanied by determining the sensitivity of bacteria to drugs. Determining the most effective antibiotic is an important step in prescribing treatment, it helps speed up the patient’s recovery and minimizes the likelihood of developing chronic forms and complications.
Laboratory tests for gonorrhea include the use of PCR methods, in which the DNA of the infectious agent is detected in biological secretions taken for examination. The ICD-10 code for gonococcal infection is A54.9, which is what is most often indicated in medical records and sick leave certificates, maintaining medical confidentiality.
A modern effective way to diagnose gonorrhea is the ligase chain reaction, the sensitivity and specificity of which is 99%. It allows you to identify gonococci and chlamydia in one test sample.
Treatment of gonorrhea in men
Complex therapy used for patients with gonorrhea is based on the use of antibacterial drugs.
The most commonly used:
- Penicillin drugs - Benzylpenicillin, Bicillin, Ampiox.
- Levomycetin. When prescribing it, B vitamins and ascorbic acid must be used, due to the pronounced toxicity of the antibiotic.
- Antibiotics of the tetracycline group.
- Claforan is a modern cephalosporin antibiotic that is effective for advanced gonorrheal urethritis.
If a mixed infection is detected, the specialist may prescribe several antibiotics at the same time or recommend taking a broad-spectrum drug.
Drugs that can boost immunity are effective against gonorrhea. These include potassium orotate, Methiuracil, Glyceram. In order to resolve infiltrates formed during long-term urethritis, aloe extract and Trypsin are used subcutaneously.
The gonococcal vaccine is used for the purpose of provocation when taking tests; it is also used as an auxiliary treatment in case of unsatisfactory results after antibiotic therapy.
During therapy, you should follow a diet (avoid alcohol, salty, spicy foods), refrain from intense physical activity and sexual intercourse, and avoid nervous shock.
When gonorrhea is detected, it is necessary to examine the patient’s sexual partner, since she may be a carrier of the infection or suffer from chronic, asymptomatic gonorrhea.
When taking antibiotics, it is imperative to use drugs that restore normal microflora. This prevents the occurrence of dysbiosis and the development of bacterial and fungal complications.
Prevention of gonorrhea and complications
Complications of gonorrhea in men include infertility caused by epididymitis or prostatitis, severe damage to the kidneys and urinary tract, arthritis and sepsis.
Gonorrheal arthritis is a severe inflammation of the joints, accompanied by fever, pain and swelling of the affected areas. A peculiarity of its course is damage to the knee and ankle joints. It is possible to prevent these pathological conditions by correctly selecting an antibiotic and timely initiation of treatment.
Measures to prevent infection include careful selection of sexual partners, use of a barrier method of contraception for any type of sexual contact, careful adherence to personal hygiene rules and regular medical examinations.
Gonorrhea, like any other disease, is easier to treat in the initial stages, which is why, if unpleasant symptoms appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Disease prevention
Prevention of the disease includes the following measures:
- Regular medical examination. When a person is infected, all of their sexual partners must be tested. If parents in a family suffer from this disease, then their daughter should also undergo examination, since the female body is more susceptible to infection, and the consequences can be sad.
- Use a condom if you are unsure of your partner.
- Infection with gonorrhea does not depend on immunity; remember that re-infection is possible. If there is a risk of infection, for example after unprotected sex, immediately urinate and wash the external genitalia with soap and water. After some time, treat the external genitalia with any antiseptic (cidipol, gibitan, miramistin). Such means cannot completely protect against infection, but there is a chance of not getting sick. The main thing is that the time interval between sexual intercourse and treatment is not long.
Remember that if you have any suspicious symptoms, you should consult a doctor.