Biosynthesis of cholesterol
Cholesterol is produced in the human liver under the action of special enzymes.
Its biosynthesis is a “trigger” mechanism for the production of synthesis of hormones and fat-soluble vitamins. The enzyme HMG reductase triggers the production of cholesterol. Regulation of its synthesis is carried out according to the principle of negative feedback. If cholesterol exceeds normal values, the amount of HMG reductase decreases and lipid production stops. Fat-rich chylomicrons also suppress cholesterol production.
The degree of synthesis suppression varies depending on the individual characteristics of the organism. But there is a direct connection between dietary fat intake and blood lipid levels. About 1000 mg of cholesterol is synthesized per day. After fulfilling its biological role, the substance is eliminated from the body naturally.
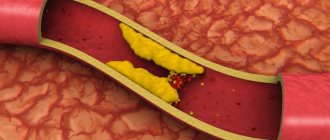
Problems arise when the amount of fat consumed exceeds the permissible value or the structure of the liver is disrupted. Excess lipids are deposited on the walls of blood vessels. With sufficient accumulation, cholesterol plaques form, which narrow the lumen of the vessel and cause severe changes.
Cholesterol reserves are “stored” in many tissues. Normally, up to 10% is deposited on the walls of the arteries.
This substance performs a number of functions that affect the functioning of the body. Here are just a few of them:
- maintain the structure of cell walls;
- influence the creation of bile acids;
- promote the production of vitamin D;
- support the production of certain hormones.
Atheroma spots resemble small fatty lumps that form inside the vessels. Atheroma is also known by other names - atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries.
Over the years (in some cases, several months are enough for this process), areas of atheroma may become larger and thicker. Subsequently, due to the accumulation of fats on the walls of blood vessels, the arteries narrow and blood flow weakens. Narrowing of the diameter of the coronary arteries is the cause of angina. Sometimes a blood clot (during thrombosis) can encounter atheromas.
This course of events ends in a heart attack, stroke or other serious cardiac problems. Thus, atherosclerotic plaques can cause angina, heart attack, stroke, ischemic attacks, and peripheral arterial diseases. By the way, diseases of the cardiovascular system caused by atheroma are the most common cause of mortality and poor health.
A proper diet is a sure helper in the fight against “bad” cholesterol. So, what foods are the most beneficial for health, what from our table will help reduce LDL levels and strengthen the cardiovascular system?
"Hercules"
Soluble fiber, which is contained in rolled oats, helps in the best way to reduce cholesterol levels. In addition, you should look for soluble fiber in beans, apples, pears, prunes and barley porridge.
Scientists have calculated that 5-10 grams of soluble fiber consumed daily significantly reduces blood lipid levels. And by the way, providing yourself with the recommended levels of this substance is not as difficult as it might seem. For example, one serving of rolled oats contains approximately 6 g of fiber. If you supplement the dish with fruits and vegetables, then the total amount will be approximately 10 g. And this is even more than the minimum norm.
A handful of nuts can affect your cholesterol levels. Walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts, peanuts, pine or pistachios - you can take any of those that you like. All of them contain mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids that strengthen blood vessels. But when choosing nuts as a cure for cholesterol, it is important to give preference to natural products, without sugar coating or salt.
Avocado
This powerful source of nutrients can also reduce LDL levels. Especially useful for overweight people.
Olive oil
Two tablespoons of olive oil per day is enough for the body to feel the benefits. A strong heart and normal cholesterol are the main benefits of this product. But you shouldn’t get too carried away with it, because, like avocado, it contains quite a lot of calories.
Milk serum
Scientists have proven that the protein contained in the whey of dairy products can also influence LDL and total cholesterol levels in a downward direction. Therefore, you should not exclude natural dairy foods from your diet.
In addition to these foods, salmon, flaxseeds, cholesterol from plants, citrus fruits and soy will help in the fight against LDL. So don’t immediately look for cholesterol-lowering pills. Especially when the concentration of the substance is not much higher than normal.
Features of synthesis
In order for cholesterol to form either atherosclerotic plaques (which simultaneously become “patches” on the damaged artery wall and internal “spacers” in the area where, without them, atrophy of the muscle layer would lead to its occlusion - collapse of the area), or hormones, or other products, it must first be synthesized in the body in one of three places:
- skin;
- intestines;
- liver.
Since liver cells (their cytosol and smooth endoplasmic reticulum) are the main suppliers of the compound (50% or more), the synthesis of the substance should be considered from the perspective of the reactions occurring in it.
Cholesterol synthesis occurs in 5 stages - with sequential formation:
- mevalonate;
- isopentenyl pyrophosphate;
- squalene;
- lanosterol;
- cholesterol itself.
The chain of transformations would be impossible without the participation of enzymes that catalyze each stage of the process.
Video about cholesterol synthesis:
Where does the body get cholesterol from?
About 70 - 80% of cholesterol is synthesized in our body (mainly by the liver), the remaining 20 - 30% we get from food.
However, there is another type of blood fat that is closely related to cholesterol: triglycerides. Triglycerides are absorbed from the intestines into the bloodstream during food digestion, but they and cholesterol are not allowed to circulate freely in the blood, so the liver packages them along with proteins into “packets” called lipoproteins.
In these “packets,” cholesterol and triglycerides are released into the blood and transported throughout the body. Reaching cells, they are used “here and now” in the form of energy/building material or stored for later.
Elevated triglyceride levels can also increase your overall risk of developing heart disease, but if they are very high they can also cause other serious problems such as pancreatitis.
Myth No. 3. Cholesterol has a secondary function in the body.
Actually : no, it's not. Cholesterol is an essential component of fat metabolism and a structural part of hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, vitamin D, bile acids necessary for the digestion of fats, and it is used to build cell membranes. In the blood, cholesterol is in a free state and bound to proteins. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) - complexes of cholesterol with less protein ("bad" cholesterol) - cause inflammation in blood vessels! Their level increases in the blood with metabolic disorders leading to atherosclerosis.
High-density lipoproteins (HDL) - high-protein complexes of cholesterol ("good" cholesterol) - have protective properties for blood vessels.
The norm for HDL cholesterol is 1.2 for men, 1.5 for women. A decrease in indicators by 20% several times (3-4) increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis. An increase in indicators is observed against the background of intense physical activity, under the influence of drugs that reduce the overall level of lipids.
The normal LDL level is less than 3.5 mmol/l for healthy people. In risk groups, those with existing heart and vascular diseases, or those who have already had a heart attack or stroke, the norms are much lower and are determined individually. An increase in LDL concentration (above 4.0 mmol/l) is possible while taking non-selective beta blockers, diuretics, and contraceptives. A decrease in LDL can be observed as a result of fasting, lung diseases, anemia, and malignant neoplasms.
Don't be afraid of fat. How to eat to get rid of atherosclerosis? More details
Where does the body get cholesterol from?
In the human body, these substances are combined from carbon and hydrogen atoms. They acquire a crystalline structure, which ensures the strength of these complexes. Together with phospholipids, their biosynthesis is carried out in peripheral tissues and liver hepatocytes. All these substances are derivatives of cholesterol.
If a person is static most of the time, then “harmful” lipids will certainly begin to deposit on the walls of the arteries.
- Sedentary lifestyle of the patient. If a person is bedridden due to illness, or simply prefers to spend his free time on the couch, he experiences stagnation of biological fluids in the bloodstream. This is how atherosclerotic plaques form.
- Poor nutrition. Errors in the diet provoke an imbalance of low and very low density lipoproteins, triglycerides and cholesterol molecules in the plasma.
- Preferences in food of animal fats. Particularly high levels of low- and very low-density lipoproteins, triglycerides and other bad fats are found in turkey, goose, pork, and offal.
- Ignoring the use of certain medications that reduce the concentration of components of the bloodstream.
In order to reduce the concentration of cholesterol in the bloodstream, it is important to return to an active lifestyle, engage in sufficient physical activity, and eat right. The removal of cholesterol molecules from the body occurs through integration into cell walls, transfer to the needs of the digestive system, and also integration into certain hormones. Therefore, it is very important to organize the activities of all these bodies.
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance called sterol, which is found in the membranes of all cells of a living organism.
Humans need it for the production of hormones, vitamin D, and some enzymes. The highest concentrations of cholesterol are found in liver and brain cells. By the way, gallstones are also cholesterol. This fact explains the strange name of the substance, which, translated from Greek, means two words: “bile” and “solid.”
The body is able to independently produce cholesterol for its needs (almost 75 percent of the total). In the body, this substance is produced by different cells. But most of all, almost a quarter of the total amount, is produced by the liver. In addition, sterol is synthesized in the intestines and in the layers of the skin.
In addition, sterol can enter the body with food. But, according to some researchers, cholesterol in this variation is poorly absorbed by the intestines, so obtained from foods, it has little effect on the total amount of the substance in the blood. Although, we immediately note that such a statement is only one of many theories.
In the human body they are presented in two types. The first type is low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Or, as they are also called, “bad” cholesterol with an altered molecular structure (it is this substance that is responsible for blocking arteries and cardiac diseases, since it contributes to the creation of atherosclerotic plaques).
The second type is high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good” cholesterol. This substance, on the contrary, prevents the development of atheroma (blockage of blood vessels), since it works to remove “bad” cholesterol. To put it in a rather primitive way, HDL elements capture “bad” sterol and transport it to the liver, where these particles are processed and excreted from the body.
Meanwhile, for the proper functioning of the body, it is important to maintain adequate levels of both types of lipoproteins.
The definition of “high cholesterol” refers to an increased amount of a substance in the blood. But this condition is not accompanied by any symptoms, which is why many are not even aware of their bad tests. Meanwhile, people with elevated sterol are many times more likely to encounter coronary artery disease.
To a certain extent, the level of sterol in the blood can vary depending on dietary principles. However, and doctors also agree, people eating the same diet may have different levels of cholesterol in their blood. Although, if you give up fatty foods, the indicators will undoubtedly decrease.
In some people, very high cholesterol may be genetic. This phenomenon is called familial hypercholesterolemia.
Generally, the higher your LDL (“bad” cholesterol), the higher your health risks. And by the way, a blood test that only measures total cholesterol can be misleading. An overall high indicator does not yet give an idea which lipoprotein is not normal. On the other hand, if total cholesterol is elevated, then it is possible that there is only HDL in excess, which does not cause health problems. But in order not to guess, but to be confident in your health, it is important to determine the levels of substances of both groups.
Cholesterol is both a friend and an enemy of humans. It is essential for normal functioning of the body, but if its levels in the blood rise too much, there is a risk of heart attack. Giving up poor nutrition and switching to a healthy diet gives a good chance of reducing “bad” sterols.
UK nutritionists have compiled a list of 6 groups of superfoods that help reduce sterol levels. This:
- soy products: milk, desserts, meat substitutes, beans, tofu (at least 15 g per day);
- nuts (a handful);
- oatmeal and barley;
- fruits and vegetables;
- foods rich in polyunsaturated fats.
In addition, the British have also compiled a list of six foods that are most dangerous for people with high cholesterol. It consists of:
- butter;
- ghee;
- margarine;
- lard;
- fatty and processed meats;
- milk fats.
It seems that everyone already knows that high cholesterol causes health problems. But how dangerous an excess of “fat” is and what causes such deviations from the norm, people without medical education can rarely clearly explain. Bypassing the heavy medical terminology, we will try to talk about this as clearly as possible.
So, two types of lipoproteins “live” in the vessels. “Good” HDL collects excess cholesterol and transports it to the liver. There the substance is processed and removed from the body. At the same time, there is a “harmful” sterol analogue. It travels through the body in a different direction - from the liver, and periodically sticks to the walls of blood vessels. Over time, this accumulation of “fatty wax” narrows the patency of the arteries. This is how atherosclerosis occurs.
For people who already have cardiac problems or have been diagnosed with liver disease, the consumption of cholesterol-rich foods is important, if not reduced to zero, then at least minimized as much as possible. The same applies to people after operations. They should not consume cholesterol for at least two and a half months.
Many people are interested in what symptoms high LDL causes. And that’s the rub. None! Often, only the occurrence of cardiovascular disease opens the patient's eyes to his cholesterol level. Therefore, doctors increasingly recommend that people over 20 years of age, as well as people in the risk category, have their blood tested every 4-6 years.
Laboratory test results show cholesterol levels in milligrams per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). But in order to understand how safe “bad” and total cholesterol levels are for a person, doctors also analyze other factors (age, family history, smoking, hypertension).
LDL HDL 20 percent of triglyceride levels.
It is good for the body when there is more HDL than other lipids. Triglycerides are the most common type of lipid (fat) in the body. Its level depends on age, gender and other factors. A high concentration of triglycerides in combination with increased LDL and decreased HDL is an alarming signal. It may indicate the presence of fatty accumulations on the walls of blood vessels (atherosclerosis).
But it’s not just medications that can lower cholesterol levels. If you follow certain tips, you can also protect yourself from harmful fats.
For this:
- Read food labels. It is important to give preference to foods that do not contain trans fats, as well as foods with low cholesterol levels.
- Limit your consumption of red meat and fatty dairy products. Instead of margarines, use natural vegetable oils. Avoid fried foods.
- Eat more fiber. Tests have shown that with its help it is possible to reduce the concentration of sterol by 10 percent.
- If high cholesterol runs in your family, exercise early and eat a healthy diet. Even if your laboratory lipid levels are normal.
- Are you overweight? Get rid of it as quickly as possible, and your risk of atherosclerosis will decrease by almost 10 percent.
Milk serum
Myth #1: High cholesterol is not hereditary.
In fact : It is transmitted. Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disorder caused by a series of mutations in the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene on chromosome 19. This genetic defect affects the liver's ability to effectively regulate the level of "bad" cholesterol, that is, low-density lipoprotein (LDL). This leads to increased overall cholesterol levels and can provoke a risk of cardiovascular disaster (heart attack, stroke).
Different forms of the disease are inherited. In the case of autosomal recessive inheritance, a child who has received two pathological genes from each parent will become ill, and then hypercholesterolemia will manifest itself in childhood. This condition of the child requires mandatory drug treatment. With an autosomal dominant type of inheritance of the disease, there may be two variants of the manifestation of the disease. When a child receives one pathological gene from a parent, the disease is milder and appears later. In another case, he inherits two pathological genes (the disease occurs in early childhood and is more severe). In addition to these forms, there are forms of primary hypercholesterolemia of other types of inheritance and acquired hypercholesterolemia. They are easier to treat.
To exclude genetic risks, you can conduct an analysis for the genetic risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease, predisposition to dyslipidemia.
Cholesterol winners. New medications have appeared that can save you from heart attacks. Read more
How to calculate health risk?
Calcium in the blood is present in three forms: physiologically active and two inactive. The first is free ionized calcium in the blood, which accounts for almost half of the total amount. The rest are inactive forms: bound to anions (Ca lactate, Ca phosphate, Ca bicarbonate and others) and bound to proteins, usually albumin.
Norm Ca
Normally, calcium in the blood of an adult ranges from 2.15 to 1.5 mmol/l. For a newborn baby, the norm for Ca is 1.75 mmol/l. The daily value for an adult is 800 to 1200 mg Ca. For women during pregnancy, the daily norm increases and ranges from 1000 to 1200 mg, otherwise the deficiency will lead to the leaching of the mineral from the teeth and bones, which can lead to osteoporosis and dental diseases.
The mineral takes part in many biological processes, namely:
- maintains normal heart rate and the condition of the cardiovascular system as a whole;
- participates in the transmission of nerve impulses, maintains the normal functioning of the nervous system;
- makes teeth and bones strong;
- takes part in muscle contraction;
- involved in the process of blood clotting and regulation of cell membrane permeability;
- participates in iron metabolism and regulation of enzyme activity;
- normalizes the functioning of the endocrine glands.
There are two types of tests to determine serum calcium levels. This is an analysis for ionized and an analysis for total calcium in the blood. More complex, but also more accurate, is the ionized calcium test. There are cases when the total calcium content in the blood is normal, but ionizing Ca is elevated.
Blood testing for calcium must be done in the following cases:
- for bone pain;
- for the diagnosis of osteoporosis;
- before surgery;
- for muscle diseases;
- for pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- for oncological diseases;
- for diseases of the digestive system.
The level of calcium in the blood is strictly regulated in the body by parathyroid hormone, which is produced by the parathyroid gland. High calcium in the blood is called hypercalcemia in medicine. This condition can lead to serious consequences, in some cases irreversible.
Among the reasons for increased calcium are the following:
- the most common cause is hyperparathyroidism, which is characterized by increased activity of the parathyroid glands, which leads to excessive production of parathyroid hormone;
- lung, kidney, ovarian cancer;
- metastases in the bones (when bone tissue is destroyed, calcium is released into the blood);
- myeloma, leukemia, lymphoma;
- excess vitamin D;
- sarcoidosis and other granulomatosis;
- spinal tuberculosis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- dehydration of the body;
- rapid bone growth (Paget's disease);
- hereditary hypercalcemia, asymptomatic;
- taking certain medications (thiazide diuretics);
- milk-alkali syndrome;
- acute renal failure.
How to treat?
In addition, you need to follow the following recommendations:
- drink more fluids so that Ca is excreted by the kidneys, sometimes intravenous fluid infusion is necessary;
- take medications that slow down the destruction of bone tissue;
- if other methods do not help, hemodialysis may be prescribed to remove waste products from the bloodstream;
- Sarcoidosis and other autoimmune diseases may require corticosteroids.
Causes of Low Ca
Ca may be low for the following reasons:
- osteoporosis;
- lack of vitamin D (rickets);
- decreased thyroid function;
- chronic renal failure;
- liver failure;
- mechanical jaundice;
- osteomalacia;
- pancreatitis;
- cachexia;
- taking certain anticonvulsants and antitumor drugs.
How to increase?
These are vitamins D and C. The first helps calcium to be absorbed in the intestines by interacting with proteins that are needed to transport Ca into the blood through the intestinal membrane. In addition, vitamin D maintains the balance of calcium and phosphorus during bone mineralization. Vitamin C increases the body's defense against fungi, such as Candida, which interfere with the body's ability to absorb calcium.
Ca is found in the following foods:
- dairy: cheeses, milk, yogurt;
- fish roe, salmon, sardines;
- vegetables: broccoli, turnips, kale;
- beans, peas.
Caffeine should be avoided, as well as products with phytic and oxalic acid, which block calcium. These include chocolate, poppy seeds, cocoa, nuts, seeds, cereals, beets and others.
Tablets that increase calcium levels should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, as they can have many side effects. They need to be taken along with vitamins C, D, magnesium.
Conclusion
The normal level of calcium in the blood serum must be maintained. This important element is involved in many physiological processes. Its deficiency, as well as its excess content, can cause significant harm to human health.
Causes of low uric acid in the blood
Increased cholesterol is caused by two types of factors: modified and unmodified.
The easiest way to influence cholesterol levels is to avoid excessive fat intake. In particular, nutritionists recommend limiting foods that contain:
- trans fats;
- saturated fats;
- cholesterol (found in foods of animal origin).
In addition, abnormal levels of sterol may appear against the background of certain diseases:
- diabetes;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- hormonal imbalances in women;
- thyroid dysfunction.
Anabolic steroids, corticosteroids, and progestins can increase LDL levels and lower HDL.
Perhaps all people are at varying degrees of risk of developing atherosclerotic plaques. But certain circumstances can accelerate the process of formation of fat accumulation in the vessels. These include:
- unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, poor diet with high salt intake);
- hypertension;
- high levels of triglycerides in the blood;
- diabetes;
- kidney dysfunction;
- elevated con cholesterol.
And if a person is still able to at least partially influence the factors mentioned above, then there are nuances that cannot be changed, and they can also cause atherosclerosis. This:
- genetic predisposition;
- early menopause in women;
- male gender (men are more susceptible to the disease);
- age (this risk increases with age).
And most importantly, these factors interact with each other. The presence of two or more of the above points is a reason to monitor your health more carefully.
Doctors often resort to using a so-called cardiac risk factor calculator. In this case, age, gender, bad habits, blood pressure and cholesterol levels are taken into account. This calculator was developed after many years of monitoring several thousand people.
- 20% and above – high risk of cardiac diseases for the next decade;
- 10-20% – moderate risk;
- less than 10% – low danger.
Where to start reducing cholesterol
After the list of references, you will find a more detailed story about the complex for deep cleansing and nutrition with NutriDetox + microflora reboot. If possible, start there and listen, of course, to the recommendations on nutrition and increasing physical activity. The course will take you a month.
In the second month - use Anti-Aging Complex.
Next, during the winter, when metabolic processes slow down, it is logical to return to Megapolynol for 3-4 months to “clean the blood vessels,” and also regularly use NutriDetox active fibers
Literature:
1. Rybakova G.V. “Cholesterol and its effect on the body,” Vestnik NGEI, 2011. 2. Tyuryumin Ya. L., Shanturov V.A., Tyuryumina E.E. “Physiology of cholesterol metabolism (review)”, Acta Biomedica Scientifica, 2-12. 3. Glickman RM, Sabesin SM Lipoprotein metabolism // The Lever Biology and Pathobiology; 3 ed./Eds IMArias, JLBoyer, N.Fausto (et.ol.) – NY: Raven Press, 1994. – P.391-414. 4. Ulmer H.F. “Human Physiology”: In 3 volumes – M.: Mir, 1996.-230 p. 5. L.E. Panin “Lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis.” Siberian Scientific Medical Journal, 2006. 6. N.A. Zabokritsky “Probiotics as a new class of modern medical immunological drugs.” Electronic scientific and educational bulletin “Health and education in the XXI century”, 2020. 7. Zimmerman Ya.S. "Eubiosis and dysbiosis of the gastrointestinal tract: myths and realities." J. "Clinical Medicine", 2013. 8. Ejtahed HS, Mohtadi-Nia J., Homayouni-Rad A, Niafar M, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Mofid V, Akbarian-Moghari A. Effect of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis on lipid profile in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Dairy Sci. 2011; 94(7): 3288-94. 9. Morel DW, Hessler JR, Chisholm GM // J. lipid res. – 1983. – Vol.24 – P. 1070-1076. 10. Ulmer H.F. “Human Physiology”: In 3 volumes. – M.: Mir, 1996. – 230 p. 11. Suslikov V.L. “Atherosclerosis and its consequences in the aspect of the teachings of V.I. Vernadsky.” J. "Health and education in the XXI century", 2007. 12. Avaliani V.M., Popov V.A., Martyushov S.I. “New views on the mechanism of development of atherosclerosis, review of the literature.” J. “Human Ecology”, 2005.
What is LDL and HDL cholesterol?
Let's look at how they differ.
Commonly called "bad cholesterol" because in excess it can lead to health problems. These lipoproteins contain a lot of cholesterol. The main purpose of LDL is to deliver cholesterol to cells where it is needed.
The LDL particle is a ligand for the LDL receptor and contains one molecule of the protein apolipoprotein B-100, which stabilizes the structure. LDL particle sizes range from 18 to 26 nm in diameter.
HDL's job is to carry cholesterol from cells back to the liver, where it can be broken down and removed from the body. We tend to call it "good cholesterol" because it helps your body stay healthy and prevent disease. HDL contains a lot of protein and very little cholesterol.
The high protein content relative to fat allows HDL to have the highest density among lipoproteins. HDL particles are much smaller than LDL - 8-11 nm in diameter.
Why is it needed?
Cholesterol crystals strengthen the membranes of all cells involved in vitamin, energy, and hormonal metabolism. Membranes surround all cells and are a selective barrier with the help of which a certain composition is maintained both inside cells and in the extracellular space.
Cholesterol is resistant to temperature changes and makes cell membranes permeable, regardless of climate and season, as well as changes in human body temperature. In other words, cholesterol metabolism affects the entire biochemistry of the body.
How to reduce high cholesterol?
Norm Ca
For example:
- Diet high in saturated fat;
- Insufficiently active lifestyle, when fats are not consumed as energy;
- Genetic factors in which fats are not processed in the usual way;
- Deficiency of sex hormones and thyroid hormones;
- Lack of vitamin D;
- High cholesterol is also affected by deficiency of iodine, iron, vitamin B12;
- Too much sugar in the diet.
Regarding sugar, it is worth noting that it is a common culprit of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels and arteries. When sugar attaches to hemoglobin, it turns it into a kind of “hedgehog” that scratches the walls of blood vessels. To repair these damages, cholesterol is used as a kind of rivet to hide the damage. Over time, atherosclerotic plaques can form in the places of these “rivets”.
| Cholesterol mmol/l | Interpretation |
| 5.2 or less | Desired level (low risk) |
| 5,2 — 6,2 | High risk border |
| 6.2 or more | High risk |
It is assumed that with the LDL/HDL ratio {amp}lt; 4 Cholesterol cannot be deposited on the walls of blood vessels.
| LDL | HDL | Interpretation |
| {amp}lt; 4 mmol/l | {amp}gt; 1 mmol/l | Desirable |
| 4 - 5 mmol/l | 1 - 0.9 mmol/l | Border |
| {amp}gt; 5 mmol/l | {amp}lt; 0.9 mmol/l | High risk |
During pregnancy, cholesterol and triglyceride levels can increase significantly. Therefore, a cholesterol test will not be accurate during this period. It is recommended to wait at least three months after your baby is born to take a cholesterol test.
Women may also find their cholesterol levels increase during menopause.
High blood cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis
It is absolutely forbidden to prescribe statins to yourself, and this is not a typical excuse in the spirit of “consult your doctor.” You should consult a doctor in any case, because statins seriously affect homeostasis and require lifelong use by sick people.
Let's look at more gentle ways to reduce blood cholesterol levels.
Reduce your trans fat intake. Trans fats increase bad cholesterol (LDL) and lower good cholesterol (HDL). It is difficult to avoid trans fats because they are found in fried foods, baked goods (cakes, pies, frozen pizza, cookies) and margarine. However, if you want to improve your lipoprotein profile, then you need to avoid consuming them.
Add fiber to your diet. Foods such as oatmeal, apples, prunes and beans contain a lot of fiber, which prevents the body from absorbing cholesterol. Research shows that people who consume 5 to 10 grams of fiber daily see a decrease in LDL levels.
Fiber makes you feel full. However, be careful. Eating too much fiber can cause cramps and bloating. Increase your intake slowly.
Eat nuts. Many types of nuts reduce bad cholesterol. This is because they contain sterols, which, like fiber, keep the body from absorbing cholesterol. Just don't overdo it, nuts are very high in calories.
Vitamins. Vitamins are essential for the normal functioning of the body, so it is not surprising that some of them reduce cholesterol and its negative properties. For example, one of these vitamins is niacin (Vitamin PP). Folic acid (Vitamin B9) has also proven to be a good heart protector. However, it is worth noting that you need to follow the recommended dosage because they can be toxic if consumed in excess of what is needed.
It would be appropriate to look at a table that presents studies of dietary supplements and their effects on “risk of mortality from all causes.” Data were taken from a recent systematic review that included 277 studies with 992,129 participants.
Impact of dietary supplements and diets on all-cause mortality Image: Annals of Internal Medicine
Read more about this in the publication: Fish oil is not effective for cardiovascular diseases
Stay away from cigarettes. Smoking can raise LDL and lower HDL. In one study, people who quit smoking saw their “good” cholesterol rise by 5% in one year.
Lose excess weight. You don't have to get in perfect shape to improve your lipoprotein profile. If you are overweight, just losing 10 pounds will reduce your LDL by 8%.
Spices are not only delicious but also healthy. Spices such as garlic, curcumin, ginger, coriander and cinnamon not only make food tastier but also improve your cholesterol profile. Research shows that eating half to one clove of garlic every day can reduce cholesterol levels by up to 9%. However, remember that not all spices are healthy.
Consume kefir and yogurt. Consumption of dairy products has been considered harmful to our cardiovascular health. However, recent research shows that consuming fermented milk products (like kefir and yogurt) may help reduce “bad” LDL cholesterol, blood pressure, the risk of stroke, heart disease and diabetes.
That's all, we hope our article was useful to you. And also, dear readers, if you find incorrect information or other errors, please write about it in the comments.
Myth No. 5. You don’t need to do cholesterol tests until you are 40 years old.
In fact : no, you can’t treat yourself like that. It is necessary to control the level of cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides from the age of 25. A sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy snacks, addiction to alcohol, which has a damaging effect on the liver, and smoking can lead to increased cholesterol levels. It is important to understand that hypercholesterolemia (level more than 5.2 mmol/l) quadruples the risk of developing atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and arterial hypertension.
To find out whether lipid levels are normal, it is enough to take a biochemical blood test - a detailed lipid spectrum:
- Cholesterol;
- Triglycerides;
- HDL cholesterol;
- LDL cholesterol.
Keeping your cholesterol under control and getting your blood tested regularly is an important point in maintaining your health.
Bad and good cholesterol. What you need to know about this important connection Read more
How to understand the numbers in analyzes
LDL cholesterol:
- optimal: less than 100 mg/dl;
- near optimal: from 100 to 129 mg/dl;
- borderline high: 130 to 159 mg/dL;
- high: 160 to 189 mg/dL;
- very high: 190 mg/dl.
Total cholesterol content:
- normal: less than 200 mg/dl;
- borderline high: 200-239 mg/dL;
- high: 240 mg/dL and above.
HDL cholesterol:
- low: below 40 mg/dl;
- high: 60 mg/dL and above.
Triglycerides:
- normal: 200 mg/dL or less;
- borderline normal: 200-399 mg/dL;
- high: 400-1000 mg/dl;
- very high: 100 mg/dL and above;
- high: 160 mg/dL and above.
VLDL
Very low density lipoproteins are the type of fractions that are responsible for the transfer of triglycerides and cholesterol from the liver to other organs and tissues. It is produced by the liver tissue in cases where a person consumes excessive amounts of fatty junk food.
Cholesterol metabolism in the human body
Triglycerides are cells that come from the intestines. They become LDL after processing by the liver. Their fractions contain regular cholesterol. During normal functioning of the body, the concentration of such cells in the blood does not exceed 1 mmol/liter. In most cases, determination of this parameter is necessary to determine the type of dyslipoproteinemia.
By itself, this parameter has no diagnostic value. For a comprehensive assessment of the body’s condition, the amount of VLDL is assessed in combination with other indicators. This type of cholesterol is most likely to provoke the formation of plaques on the surface of blood vessels. With an increased level of this indicator in the blood, the risk of developing pathologies increases.
If you start therapy in time to reduce the amount of this substance in the blood, the body will quickly cope with this problem. Also, the risk of complications will be minimal. If the amount of VLDL is high over a long period of time, the risk of developing pancreatitis increases.
Lipid therapy
Hyperlipidemia is a condition in which cholesterol and triglyceride levels are elevated.
Treatment in this case is determined individually, depending on the cholesterol level. When it is in the range of 100-160 mg/dL, in the so-called low level, but other risk factors are present, diet and exercise can lower lipid concentrations. At levels of 130-190 mg/dL, various medications are already used to correct the condition. Among the most popular:
- satins - interfere with the production of enzymes responsible for the production of cholesterol;
- folic acid - catalyzes lipid oxidation in the liver, which helps reduce the concentration of LDL and triglycerides;
- A medicine that binds to bile acid—slows the production of cholesterol in the liver.
In addition, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, nicotinic and folic acids, vitamins B12 and B6 help reduce lipoprotein levels. Also, substances that affect cholesterol levels are found in green tea, soy protein and garlic.
Myth No. 4. Hypercholesterolemia cannot be treated
In fact : no, it is actually curable. Hypercholesterolemia can be treated, including familial hypercholesterolemia. For this purpose, complex therapy methods are used. First of all, statins and fibrates are prescribed - special lipid-containing drugs that reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood, inhibit its formation in the liver, and reduce absorption in the intestines.
Modern drugs have appeared - monoclonal antibodies (PCSK9 inhibitors), they are administered several times a month and are used when standard therapy is ineffective.
Non-drug methods include diet and exercise to normalize weight and prevent obesity, giving up bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking).
Disturbances in cholesterol synthesis
As in all processes of the human body, certain problems can arise in the process of cholesterol synthesis. They often occur due to metabolic disorders. In the case of cholesterol, it can be high or low, based on this, its general indicators and symptoms occurring in the body differ.
When your cholesterol level is 6-8, what should you do?
Lack of good cholesterol
In certain diseases, there may be a lack of good cholesterol. This may occur due to disorders of the thyroid gland, heart problems and diabetes. Also, a certain genetic predisposition may contribute to the appearance of low cholesterol.
Some of the consequences that a person with low cholesterol may face include:
- Childhood rickets, which occurs due to failure to absorb the necessary calcium;
- Early aging, which occurs due to the destruction of cell membranes without Q10 transport;
- Weight loss, which is based on a low level of fat breakdown;
- Suppression of the body's defenses;
- The appearance of debilitating pain in the heart, as well as in the muscles. Infantile rickets Early aging Weight loss Appearance of debilitating pain in the heart Suppression of the body's defenses
Problems associated with a lack of healthy cholesterol can be solved by simply following a diet. It is necessary to eat dairy products, fish and vegetable oils.
Excess cholesterol
If a person, on the contrary, has a large amount of cholesterol, his health will also be at risk.
The body will experience problems such as:
- Development of hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver;
- Weight gain;
- A disorder of general lipid metabolism that is harmful to humans;
- Development of chronic inflammatory processes.
With excessive accumulation of cholesterol, numerous atherosclerotic accumulations are formed, which clog blood vessels in the form of plaques. A large amount of bile is also produced, which simply does not have time to leave the gallbladder. This automatically causes the formation of stones in the organ, and the heart and numerous blood vessels in the body suffer greatly.
If left untreated, there is a risk of developing myocardial infarction, stroke and other equally dangerous problems.
Determination of total cholesterol content using the enzymatic method using the “Novohol” kit
Principle
Based on the use of coupled enzymatic reactions catalyzed by: 1) cholesterol esterase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters to free cholesterol; 2) cholesterol oxidase, which catalyzes the conversion of cholesterol to cholestenone with the formation of hydrogen peroxide; 3) peroxidase, which catalyzes the oxidation of 4‑aminoantipyrine with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of phenol to form a pink-crimson colored product.
Normal values
| Serum (specified method) | 20‑29 years old | 3.70‑6.51 mmol/l |
| 30‑39 years old | 4.25‑7.04 mmol/l | |
| 40‑49 years | 4.37‑7.70 mmol/l | |
| over 50 years old | 4.55‑8.24 mmol/l | |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | 0‑0.013 mmol/l | |
| Saliva | 0.065‑0.233 mmol/l | |
| Bile | hepatic | 2.1‑5.4 mmol/l |
| cystic | on average 11.1 mmol/l | |
Influencing factors
Overestimation of results with colorimetric research methods occurs when there is a high content of bilirubin, hemoglobin, and vitamin A in the sample; with the enzymatic method - oxycorticosteroids and the use of anticoagulants (fluorides, oxalates).
Clinical and diagnostic value
Serum
A significant increase in cholesterol content is observed with hyperlipoproteinemia type IIa (familial hypercholesterolemia), type IIb and III (polygenic hypercholesterolemia, familial combined hyperlipidemia), a moderate increase is observed with hyperlipoproteinemia type I, IV, V, as well as liver diseases (intra- and extrahepatic cholestasis) , kidney diseases, malignant tumors of the pancreas, hypothyroidism, diseases of the cardiovascular system, pregnancy, diabetes.
A decrease is detected in hyperthyroidism, liver cirrhosis, malignant liver tumors, hypoproteinemia and ab-lipoproteinemia.
Cerebrospinal fluid
The accumulation of cholesterol is detected in meningitis, a brain tumor or abscess, cerebral hemorrhages, and multiple sclerosis.
A decrease in values is found in cerebral and cortical atrophy.
Determination of the concentration of free and esterified cholesterol in blood serum
Free cholesterol is capable of forming sparingly soluble compounds with digitonin, tomatine, and pyridine sulfate. Most often, an aqueous-alcoholic or isopropanol solution of digitonin is used.
Principle
Cholesterol is extracted from whey using isopropyl alcohol, the extract is divided into two parts, and the content of total cholesterol is determined in one. In another portion of the extract, free cholesterol is precipitated with digitonin, the supernatant is discarded, and the precipitate is dissolved and the content of free cholesterol is determined by any method. The content of esterified cholesterol is calculated as the difference between total and free.
Normal values
| Serum | the fraction of esterified cholesterol makes up 60‑80% of the total |
Clinical and diagnostic value
The cholesterol esterification coefficient is an important functional test of the liver. The decrease in the coefficient is proportional to the decrease in liver function: acute and exacerbation of chronic hepatitis, obstructive jaundice, cirrhosis of the liver. The degree of esterification also depends on the activity of the serum enzyme lecithin-cholesterol acyl-transferase, so storing the sample at room temperature may change the ratio between the free and esterified cholesterol fraction.