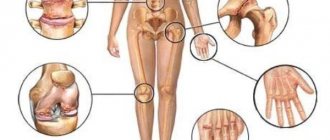
Rheumatic diseases are pathological conditions caused by systemic or local damage to connective tissue, most often manifested by articular syndrome. The severity of the diseases varies from mild local pain to severe life-threatening diseases (for example, systemic lupus erythematosus). Due to the fact that rheumatic diseases are chronic and progressive, patients need not only to adapt to the physical difficulties associated with limited movement, but also to overcome psychological problems. Rheumatic diseases are divided into groups:
- Polyarthritis of unknown origin. This group includes chronic polyarthritis, Reiter's disease, etc.
- Acquired diffuse connective tissue diseases. This group includes systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, scleroderma, Sjögren's syndrome and several inflammatory arterial diseases.
- Active rheumatism caused by streptococci.
- Systemic arthritis. This group includes hemorrhagic vasculitis, Whipple's disease, ulcerative colitis, ovine and caprine brucellosis, serum sickness, and drug-induced allergic reactions.
- Degenerative joint diseases. This group includes all arthrosis and spondylosis.
- Soft tissue diseases. This group includes inflammation of the subcutaneous fat, diseases of the muscles, tendons, joint capsules and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Joint infections caused by bacteria, fungi and various viruses.
- Traumatic joint damage.
- The functions of the joints may also be impaired due to other diseases of the internal organs. This group includes gout, hemophilia and rickets.
- Joint damage due to neoplasms, for example, the occurrence of tumors in bones, muscles or joints as a result of leukemia.
- Congenital connective tissue diseases, such as congenital hip dysplasia.
- Other diseases, for example, Tietze syndrome, aseptic bone necrosis.
What is rheumatism of the joints?
Rheumatism is a reactive disease following infection with group A streptococci (Lancefield classification). One to three weeks after infection, bacterial inflammation of various organ systems occurs. Components of the streptococcal membrane, some types of M protein, act as an antigen and stimulate the production of antibodies.
However, streptococcal antigens are similar in structure to the body's own proteins. The resulting antibodies react to endogenous structures and cause inflammation.
Reasons for the development of rheumatism
The main causes of the disease in adults and children are the same:
- malnutrition;
- decreased immunity;
- the presence of streptococcal infection (scarlet fever, pharyngitis, tonsillitis and a number of others);
- hypothermia of the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- lack of exercise;
- overwork.
The disease affects adolescents aged 7 to 15 years; girls who have had diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, tonsillitis) or streptococcal infection are three times more likely to get sick.
Rheumatism of the joints - symptoms and causes
If a person has a family history of rheumatic diseases, they may have an increased risk of developing one of them, in particular rheumatic joint disease.
In addition, women tend to be more vulnerable to this disease and other autoimmune diseases. The reasons for this are still not fully understood. Estrogen may play a role and promote inflammation.
Rheumatic joint disorders can occur at any age. Some conditions tend to develop at certain points in a person's life. For example, articular rheumatism tends to manifest itself between the ages of 40 and 60, and read about thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities here.
A distinctive feature of the symptoms of the disease is that wear and tear on the joints and ligaments leads to severe and sometimes unbearable pain. The following general signs indicate the presence of the disease.
- Swelling in one or more joints of the body.
- The appearance of stiffness around the joints.
- The presence of constant and recurring pain experienced without any possible cause.
- Sudden difficulty in movement.
Other characteristic symptoms vary depending on the individual. These may include:
- Feverish condition.
- Pain and tenderness of the joints.
- Swelling or redness in the joint area.
- Small nodules inside the skin.
- Chest pain.
- Lethargy and weakness.
- Uncontrolled body movements.
Stages of development and types of rheumatism
The disease often worsens in spring and autumn.
There are three stages of the active phase of rheumatism:
- Minimal (grade I), symptoms can only be seen when diagnosed using ECG and FCT. In studies, the indicators are only slightly deviated from the norm.
- Moderate (II degree). An elevated temperature is observed, all the symptoms of carditis are revealed, joint pain, weakness, and fatigue appear.
- Maximum (III degree). There is an acute and subacute phase of the disease, all the symptoms of the disease and possible complications are encountered. A well-designed treatment program prevents the acute form of the disease and complications of cardiosclerosis - and heart disease.
Mostly children from 7 to 15 years old are affected. It is exclusive before 3 years of age and rarely occurs after 30 years of age. The onset of rheumatic fever 2-3 weeks after a sore throat, nasopharyngitis or sinusitis that has not been treated.
Symptoms:
- Great pallor when anemia.
- High temperature, accompanied by severe sweating, body pain, and chills.
- Hot and painful joints.
- Increased joint volume.
- Regression of pain without complications.
- Sometimes Maynet's nodules appear under the skin and in the area of the affected joints.
- The appearance of spots on the skin (maculopapules - slightly noticeable spots).
- Frequent abdominal pain with hepatomegaly (increased liver volume) or rheumatic peritonitis.
Rheumatism mainly affects the knees, wrists, ankles and is characterized by severe and short-term pain in the joints. Migrating pain moves, after a few days, from one joint to another.
Volatile rheumatism is provoked by the following factors:
- Young age.
- Genetic factors.
- Socio-economic factors.
- The emergence of a streptococcal epidemic in crowded places: schools, army.
Treated with antibiotics and corticosteroids as prescribed by a doctor.
Rheumatism that persists over time, passes through attacks and periodic exacerbations - is called chronic. Chronic inflammation develops over a long period of time and can be caused by an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the cartilage.
Most often they get sick:
- overweight older people;
- women after menopause;
- athletes who use their joints intensively.
Inflammation of the tissues around the joint due to injury or excessive stress can cause inflammation of the muscles, tendons, and ligaments around the joint.
The acute phase develops 1-3 weeks after an infectious disease.
Symptoms:
- joint pain;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- hyperhidrosis;
- weakness;
- fast fatiguability.
Signs
The first symptoms of the disease appear 3 weeks after a person recovers from an infectious inflammation, for example, streptococcus, pharyngitis or tonsillitis. Since there may be no clear signs of streptococcal infection, doctors diagnose acute respiratory infections and prescribe appropriate therapy. And if joint rheumatism is not treated, the disease may occur a second time, especially if the immune system is weak. As a result, joint rheumatism develops, and after just a few days of a cold, inflammation occurs. These may be the knee or wrist areas, the elbow or shoulder area, small joints of the fingers or toes are rarely affected.
The inflammatory process does not affect all joints at once; first one begins to bother, then the second, and so on, and thus rheumatism begins. Outbreaks occur over a short period of time, but each process affects the heart, and if measures are not taken in time, you can get a disease such as rheumatic heart disease or chorea.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is made through a routine medical examination, in which the doctor asks the patient questions:
- about the duration of pain;
- about the nature of the pain, which joints are affected;
- How pain manifests itself when examining joints.
Depending on the location of the pain and symptoms, additional tests are performed:
- Blood analysis.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound scanning.
- CT scan.
- Analysis of fluid in the joint for the presence of bacteria or hardened crystals.
During the active phase of rheumatism, the following is observed:
- increased ESR;
- moderate leukocytosis with a shift to the left;
- anemia.
Diagnosis is made based on medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and X-rays of the hands and feet.
Diagnosis of rheumatism
Rheumatism of the joints can be diagnosed based on a visual examination, during which the doctor will check for the presence of symptomatic manifestations such as inflammation, rash or nodules under the skin, abnormal heart rhythm, which is done by performing certain simple movement tests.
If rheumatism of the joints was identified earlier, the doctor will refer the patient for an additional blood test (more about this procedure -), which will search for antibodies associated with a possible infection in the blood.
Signs and symptoms of rheumatism
Rheumatism is a general term for diseases that can affect joints, bones, tendons, muscles, connective tissue, and sometimes internal organs.
There are many different forms that differ:
- duration of pain;
- location of pain;
- number of affected joints;
- duration of symptoms;
- other associated symptoms (digestive tract, skin, eyes, etc.).
Main reasons:
Treatment of rheumatism in adults
The patient is prescribed bed rest and proper nutrition. Etiological or etiotropic treatment is the elimination of foci of streptococcal infection. Penicillin therapy is carried out for two weeks. Pathogenetic treatment - steroid and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and medications.
The success of treatment depends on the correct treatment plan. For treatment, the use of painkillers is indicated.
Analgesics are used to relieve pain:
- Aspirin.
- Paracetamol.
- Ibuprofen.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain and inflammation of connective tissue in the form of ointments and tablets:
Centrally acting muscle relaxants:
- Tolperisone.
- Baclofen.
- Ditilin.
The main purpose of antibiotics is to suppress streptococcal infections. For this purpose, drugs of the penicillin group and broad-spectrum antibiotics (Erythromycin, Ampicillin) are used. Therapy is carried out for at least one week according to a specific scheme in a hospital setting.
In the future, for 5 years, prevention of relapse, as well as complications, is carried out as prescribed by a doctor using the latest generation drugs:
- Bicillin - 3 is indicated for exacerbations of the disease.
- Bicillin - 5 is indicated for the prevention of relapse of the disease.
- Penicillin.
It is necessary to be very careful when treating infections. It is better not to ignore the need to take antibiotics according to the regimen and protocol prescribed by the doctor. They can save you from harmful consequences.
They are used for autoimmune diseases associated with the formation of antibodies that attack one's own body rather than protect it from germs:
- Mercaptopurine.
- Azothioprine.
- Lakeran.
Chondoprotectors help treat joints:
- Glucosamine.
- Artron.
- Alflutop.
Corticosteroid hormones are prescribed for severe pain and active inflammatory process:
- Prednisolone.
- Diprospan.
- Hydrocortisone.
- Celeston.
Surgery: knee replacement – replaces a joint that is too damaged by osteoarthritis. This happens when a person cannot straighten the joint and there are no other methods other than surgery.
Physiotherapy is an important support for patients with rheumatism. In the case of inflammatory rheumatism, physiotherapy sessions can reduce pain and alleviate the suffering of patients. More and more practitioners are using new methods to treat inflammatory pain.
Physiotherapy is actively used together with other treatment methods. In order to rehabilitate patients, rheumatological services offer studios with special simulators, where they teach how to cope with life's difficulties. Exercise machines are part of the patient's therapeutic education and an important step in the treatment of rheumatism.
There are several sanatoriums that offer standards of treatment to patients suffering from rheumatism. Rheumatism is treated in sanatoriums in Kislovodsk and Crimea.
In sanatoriums, patients can receive health treatments:
- oxygen and sodium chloride baths;
- radon, dry carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide baths - prescribed to patients with rheumatic carditis;
- cryosauna - chambers using medical liquid nitrogen;
- mud balneotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- diadynamic therapy - treatment with electric current;
- bioptron - light therapy.
If a child has suffered a streptococcal infection and the first symptoms of joint pain appear, rush to the doctor. And if there is a genetic predisposition, then a diagnosis needs to be carried out, even if there are no signs of problems with the joints yet.
Treatment of childhood rheumatism is carried out in a hospital using medications, with a strict two-week bed rest. The next two to three weeks are not strictly bed rest. Board games and breathing exercises are recommended.
Medicines used to treat children:
- Corticosteroid hormones (Prednidazolone, Triamsolone);
- NSAIDs (Voltaren, Indomethacin);
- Immunosuppressants (Delagil, Chlorbutin).
Bicillin - 5 is indicated for the prevention of rheumatism in children during remission, as well as as anti-relapse therapy.
Just a village
Not much is known about the history of the village of Osoviny. It was first mentioned in 1842 - as a “small village” of 3 farms. However, by the end of the century the settlement had grown - its population exceeded 650 people.
Residents were engaged in peasant farming - both in the last years of tsarism and under Soviet rule. There was no Tatar population here, and as a result, the Osovins were not deported. But the opposite process took place - during the campaign to resettle villagers from other regions to Crimea, already in 1944, 204 families from Tambov appeared in the village, and in the early 1950s, more migrants from Ukraine.
However, the village was not lucky - currently there are just over 230 permanent residents. Such a small settlement simply cannot have developed infrastructure. There is no special bus service to Osoviny, and internal roads leave much to be desired.
The weather in the village is determined by a combination of an almost Mediterranean climate, determined by the influence of the Azov Sea and the steppe. Summers here are dry and quite hot.
The heat is easily tolerated thanks to the almost constant gentle wind. However, reviews from many tourists indicate that this apparent coolness is insidious - you can get very “burnt” in the sun and not notice it. The swimming season begins early - in mid-May.
How to treat rheumatism with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine offers a wide range of options for treatment at home:
- For the treatment of gout and rheumatism, compresses made from fresh hemlock leaves are very helpful. Pour boiling water over fresh leaves, apply to the sore spot, and cover with cling film and a bandage to relieve pain.
- Rheumatism is treated with bee stings: the method is to apply a bee to sting the sore spot. On the first day you need 1 bee. A day later there are already 2 bees. The bite is made 4-5 centimeters away from the first place. Every other day they take 3 bees. And so on until five. Then you need to take a two-day break and repeat in the reverse order: 5, 4, 3, 2.1.
- Take 30 grams of yellow acacia leaves, 200 ml of vodka. Leave for 7 days. Take 1 tsp. 3 times a day.
- Take 20 grams of elm, pour a glass of boiling water. Simmer over low heat for 10 minutes. Then leave for 3 hours. The tincture is taken 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.
- Take 2 tbsp. l. fresh dandelion flowers, add 2 tbsp. l. Sahara. Leave in a cool, dark place for 8-9 days, then squeeze out the juice. Take 3 times a day, 1 tsp.
Nikolai Maznev in his clinic collected many recipes for getting rid of rheumatism:
- The main therapy for inflammatory rheumatism during remission is a course of thalassotherapy.
- Active exercises in hot water will reduce joint pain.
- Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the sacroiliac joint and spine. Gradually, the spine loses flexibility, mainly men suffer. Sea mud is shown.
- Periarthritis most often affects the hip and shoulder joints. Causes stiffness and pain. Restores functions: physical exercise and underwater hydromassage shower.
Treatment of rheumatism in China and Israel
In China, rheumatism is treated with an integrated approach to healing the whole body. The most common methods are: herbal treatment, acupuncture, massage.
Treatment of rheumatism in Israeli clinics is based on the use of gifts from the Dead Sea and homeopathic medicines. However, it is impossible to do without traditional treatment regimens, so Israeli doctors use different combinations of drugs in combination with plasmapheresis and immunomodulators.
Prevention
| This section is missing references to information sources. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark was set on May 9, 2020 . |
Includes hardening the body, improving living conditions, working hours at work, and fighting streptococcal infections. To prevent relapses in the spring and autumn, drug prophylaxis is carried out with bicillin in combination with salicylates or ortofen (Voltaren), indomethacin, hingamine, or year-round prophylaxis is carried out with monthly administration of bicillin-5.
How does articular rheumatism occur and progress?
Joint damage occurs 10–14 days after an upper respiratory tract infection. These may be diseases that are caused by hemolytic streptococcus: tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, rhinitis, scarlet fever. Less commonly, other bacteria, viruses or allergens.
Infectious agents provoke the production of protective antibodies, which combine with antigens of pathogenic bacteria and form special immune complexes.
Through the bloodstream, these complexes spread throughout the body, settle on connective tissue cells, and cause aseptic inflammation (non-purulent) in the tissues of the joints.
Streptococcal antigens eventually turn into autoantigens and contribute to the development of an autoimmune response. The immune system synthesizes antibodies against its own tissues (immunological error), which worsens the course of the pathological process.
Click on photo to enlarge
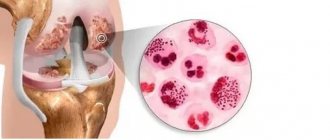
Changes in connective tissue occur in several stages:
- In connective tissue, the amount of glycosaminoglycans (part of the complex proteins proteoglycans) increases, which absorb moisture and swell.
- The inflammatory process leads to the destruction and death of connective tissue collagen (fibrinoid change, necrosis).
- Granulomas – nodular formations (granulomatosis) – form around the foci of dead cells.
- The process ends with sclerosis (replacement of working tissue with dense scars).
At the stage of fibrinoid changes, the pathology becomes irreversible.
In 60 or 70% of cases, the acute form of the disease occurs with the involvement of joints in the inflammatory process.
The most characteristic signs of the disease are fever and sharp pains that occur in some joints, and after some time suddenly appear in others.
With timely administration of medications, articular rheumatism can be eliminated within the first 2 days. If left untreated, all acute manifestations subside on their own, but in this case it can become constantly recurrent and will often worsen.
After the articular manifestations of rheumatism disappear, signs of damage to internal organs come to the fore. In 80% of cases - the heart and blood vessels, less often - periarticular tissues, kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract organs and nerves.
Rheumatism of the joints: what is it, symptoms and treatment, differences from rheumatic
- Ankle
- Carpal
- Knee
- Elbow
- Brachial
- Hip
- Spine
Rheumatism is an inflammatory infectious-allergic systemic pathology that affects connective tissue structures.
The leading clinical manifestations of the disease are elevated body temperature and multiple symmetrical arthralgias of a volatile nature. Rheumatism is characterized by both simultaneous and sequential involvement of several joints in the pathological process.
The main reason for the development of the disease is an inadequate response of the immune system to the introduction of certain pathogenic microorganisms.
In the diagnosis of rheumatism, the most informative are serological and bacteriological studies: determination of the level of C-reactive protein, detection of elevated antibody titers. To determine the extent of joint damage, radiography, MRI, and CT are performed. Treatment is conservative using immunosuppressants, glucocorticosteroids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Pathogenesis, causes, provoking factors
It is important to know! Doctors are shocked: “An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists...” Read more…
Rheumatism of the joints is most often diagnosed in children and adolescents aged 7-15 years. Representatives of the weaker sex are most susceptible to developing pathology. The pathology affects not only the musculoskeletal system, but the serous membranes, skin, cardiovascular and central nervous systems.
When studying the etiological aspects, a relationship was discovered between the occurrence of rheumatism and the previous penetration into the body of pathogens of scarlet fever, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, erysipelas, and otitis media. These group A beta-hemolytic streptococci provoke the development of an inflammatory process.
They release toxic products of their vital activity into the surrounding space, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of general intoxication.
More than 95% of people with streptococcal infections fully recover after a course of antibiotic therapy and acquire lasting immunity to pathogens.
The remaining infected people do not develop a full-fledged immune response.
Therefore, with the repeated penetration of beta-hemolytic streptococci, the development of a complex autoimmune inflammatory reaction is observed. The role of provoking factors are:
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- being in large groups during an unfavorable epidemiological situation;
- unbalanced diet, lack of foods high in microelements, fat- and water-soluble vitamins;
- frequent hypothermia;
- aggravated medical history, including family history.
After the introduction of infectious agents into the body, the immune system produces a large amount of antistreptococcal antibodies - antistreptolysin-O, antistreptohyaluronidase, antistreptokinase, antideoxyribonuclease B.
Immune complexes begin to rapidly form from immunoglobulins, streptococcal antigens, and components of the complement system. They circulate in the bloodstream, spreading throughout the body and settling in connective tissue structures.
Where immune complexes are localized, aseptic autoimmune inflammatory processes are launched. Streptococcal antigens are characterized by pronounced cardiotoxic properties, so most autoantibodies are formed to the heart muscle.
The recurrent, progressive course of joint disease is caused by repeated infection, stress and depression, and hypothermia.
| Forms of rheumatism | Characteristic features of the development of pathology |
| Acute | A rheumatic attack occurs suddenly, all symptoms are pronounced. Characterized by polysyndromic (involvement of all organs) lesions, high activity of the inflammatory process. The therapy performed is highly effective |
| Subacute | The relapse can last up to six months. Clinical manifestations are of moderate severity, attack activity is moderate. The result of treatment depends on the state of the patient’s immunity |
| Protracted | A rheumatic attack lasts more than 6 months. Its dynamics are sluggish, inflammation activity is low. Signs of damage can appear only from the musculoskeletal system. When carrying out diagnostic measures, only a previously formed heart defect is usually detected, and new signs of joint damage are still absent |
| Recurrent | Clinical manifestations are polysyndromic; damage not only to joints, but also to internal organs progresses rapidly. Characterized by an undulating course with frequent painful relapses |
Clinical symptoms and differences between rheumatoid and rheumatoid arthritis
With rheumatism, signs of joint damage occur in 20% of examined patients. Many pathologies of the cardiovascular system manifest themselves as pain in the heart, and arthralgia is quite specific and directly indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the joints.
The clinical picture of rheumatism is similar to the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. They occur 7-14 days after an infection has already been suffered - pharyngitis, scarlet fever, tonsillitis. That is, a person considers himself completely healthy when his condition sharply worsens again.
Body temperature rises to 39°C, he complains of weakness, fatigue, headaches, suffers from excessive sweating, chills.
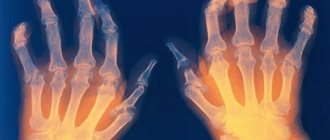
Unlike rheumatoid arthritis (which greatly facilitates diagnosis), it initially affects not the small metatarsophalangeal joints of the hands and feet, but the large joints - ankles, knees, shoulders, elbows.
The nature of arthralgia is multiple, symmetrical and volatile. This means that several paired joints are affected at once, and pain is felt throughout the day in different joints.
The main symptoms of rheumatism include:
- swelling and swelling of the joints, especially in the morning;
- redness of the skin over the joint, hyperemia;
- a sharp decrease in range of motion, stiffness;
- the formation of dense, round, painless, inactive nodules localized to the joint area;
- The severity of pain increases with increased physical activity or lifting heavy objects.
The pathology in most cases is benign. Even an acute inflammatory process does not provoke damage to cartilage, bone, and connective tissue joint structures. There is no deformation of the joints, but moderate pain persists for quite a long time.
“Doctors are hiding the truth!”
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day...
>
Symptoms are most intense at the beginning of a rheumatic attack due to increased body temperature and fever. A specific aches in the joints arise, aching, dull, pressing, “gnawing” pain appears that does not subside at night. The similarity between rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis lies in the obligatory presence of extra-articular symptoms.
The general state of health worsens, the functional activity of some vital systems decreases. With rheumatism, the membranes of the heart become inflamed, interruptions in the functioning of the heart occur, and in especially severe cases, patients are diagnosed with circulatory failure. One of the complications is chorea, which manifests itself in involuntary muscle twitching.
Diagnosis of rheumatism
The primary diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, external examination, and medical history. A recent streptococcal infection is a definite clue.
When conducting bacteriological studies, an increased titer of antibodies produced by the immune system to destroy pathogenic bacteria is established. These are antistreptolysin, antistreptokinase, antihyaluronidase. A biological sample taken from the throat is inoculated into nutrient media.
The stage of the inflammatory process is determined by the number of formed colonies. The final diagnosis is made after detecting the following diagnostic criteria for rheumatic fever:
- polyarthritis - damage to several joints;
- presence of subcutaneous nodules;
- ring-shaped erythema is a polyetiological disease of the skin;
- clinical manifestations of carditis, chorea;
- joint pain due to fever;
- increased blood sedimentation rate, leukocytosis, the presence of C-reactive protein in a general blood test;
- prolonged P–Q interval on the electrocardiogram.
X-rays, CT, and MRI are performed to assess the condition of articular structures and exclude other inflammatory and degenerative pathologies. Differential diagnosis with tuberculosis, neuroses, and nonspecific endocarditis is also necessary.
What happens if there is no treatment
Each stage of pathology lasts no more than 2 months. During each relapse, repeated tissue lesions occur in the area of the formed fibrous foci.
In addition to the joints, the tissue of the heart valves is involved in the inflammatory process; numerous sclerotic changes occur in their valves.
They begin to grow together, which significantly increases the likelihood of subsequent acquired heart disease. The following symptoms are characteristic of rheumatic carditis:
- strong heartbeat;
- pulmonary edema, shortness of breath;
- heart pain of varying intensity;
- increased fatigue, weakness;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
Rheumatic carditis is diagnosed most often in patients 14-25 years old. Its clinical manifestations may be minor, but severe damage to the heart valve can also be detected. Rheumatism causes disruption of the central nervous system, especially in children.
This is expressed in moodiness, irritability, absent-mindedness, and apathy. In the future, problems arise with memorization, speech, and concentration. In adults and children, damage to the abdominal organs is possible.
Abdominal syndrome develops - abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting occur.
Causes of the disease
The development of articular rheumatism is based on a combination of factors. Here are the main ones:
- past infectious diseases (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, erysipelas, viral infections);
- weakened immune system;
- hereditary predisposition (the presence of genes that increase the risk of developing rheumatism).
People who have had a streptococcal infection
Women (get sick 3–4 times more often than men)
Insolation (sun exposure), hypothermia
Children – from 7 to 14 years old
Workers and students in large groups
Mental and physical stress
People living in poor social conditions (damp, cold housing, poor diet)
Characteristic symptoms
Symptoms of articular rheumatism are usually acute.
The disease begins with simultaneous damage to several joints at once - both shoulders, elbows, ankles or knees. The pain is sharp, the joints are swollen, red, painful and hot to the touch.
Click on photo to enlarge
Due to severe pain, it is difficult for a person with rheumatic arthritis (inflammation of several joints) to make any movements.
He has a high temperature (up to 40 degrees), sweating, weakness and other signs of general intoxication (poisoning by inflammatory products) appear.
A characteristic sign of articular rheumatism is an increase and decrease in pain and inflammation, first in some joints and then in others.
In 1 or 2% of patients, the disease occurs with skin manifestations - red spots or rings that do not itch and are located on the inner surface of the arms and legs, on the stomach or neck.
Subcutaneous rheumatic nodules in the joint area are very rare.
A very unpleasant, but infrequent manifestation of articular rheumatism is a constantly recurring form. In this case, regular exacerbations are replaced by short and incomplete periods of recovery, and damage to internal organs (heart, lungs) progresses very quickly.
It is the articular form of rheumatism that is rarely complicated. Other complications of the disease are more dangerous:
- heart damage (heart disease, rheumatic carditis, myocarditis, cardiosclerosis, endocarditis, pericarditis);
- damage to the central nervous system and sensory organs (chorea - increased muscle tension, impaired coordination of movements);
- vascular damage (vasculitis);
- damage to periarticular tissues (ligaments, tendons, their membranes, inflammation of periarticular bursae).
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease depend on its type.
Articular rheumatism
Signs of articular rheumatism in adults are observed in the joints of the knees, shoulders, elbows, fingers and toes. This happens:
- limiting fever to a temperature of 38-40°C. Daily temperature fluctuates by 1-2°C, there is no chills;
- profuse sweating;
- joint pain that increases with passive or any active movement, accompanied by soft tissue swelling and effusion into the joint cavity.
The local temperature of the skin in the problem area increases, and pain occurs when pressed with fingers. Inflamed joints do not allow you to perform movements in full and with maximum amplitude, since rheumatic arthritis disorganizes the connective tissue.
Large joints become inflamed symmetrically. Inflammation becomes “volatile”: it subsides in some joints, but immediately increases in others. Without treatment, the pain disappears after 2 - 4 weeks. New medications can cure inflammation in 1 to 3 days.
Rheumatic carditis
If there is no heart defect, then the course of rheumatic myocarditis will be of moderate severity. The process involves the myocardium and lining of the heart. It is accompanied by intoxication, stabbing pain, tachycardia, and low blood pressure. Symptoms of heart failure often include:
- dizziness, fatigue;
- shortness of breath, arrhythmia;
- swelling and pain of the legs;
- darkening of the eyes or fainting;
- sometimes the veins of the neck swell, the liver enlarges;
- ascites appears.
On fluoroscopy, you can notice a slight increase in the size of the heart, often to the left, less often in the form of diffuse expansion. There are cases of insufficient blood circulation due to primary rheumatic myocarditis.
In children with diffuse myocarditis:
- the myocardium becomes acutely inflamed, swells, and its functional activity is impaired;
- the child’s condition is worsened by shortness of breath, aching constant heart pain, rapid heartbeat;
- the skin turns pale;
- The veins of the neck swell.
The x-ray shows that the heart is significantly enlarged. The apical impulse becomes weak and the tones are muffled. The pulse is frequent and weakly filled. Myocarditis can lead to rheumatic cardiosclerosis, then the contractile function of the myocardium decreases: the apical impulse weakens, the tones are muffled, and systolic murmur appears . In this case, rheumatic heart defects develop.
Manifestations of other types of disease
With rheumatic chorea, damage to small cerebral vessels occurs. The psyche and swallowing function are impaired, weakness appears, and movements become uncoordinated.
With cutaneous rheumatism, rheumatic nodules and ring erythema form on the skin.
Rheumatic pleurisy is accompanied by chest pain, nonproductive cough, shortness of breath, and general weakness.
Pericarditis can be dry or exudative. Dry pericarditis is characterized by constant pain in the heart muscle, friction noises of the pericardium in the area of the edge of the sternum on the left. Exudative pericarditis continues the pathology - effusion appears, pain subsides when the inflamed layers of the pericardium are separated due to the accumulation of exudate.
Diagnostics
How to treat rheumatism of the joints? To prescribe treatment, you need to establish the correct diagnosis. This is quite difficult, because the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are very similar to other types of arthritis (rheumatoid, reactive, infectious).
The diagnosis is helped by making major and minor diagnostic criteria (signs) and tests confirming a previous streptococcal infection.
Polyarthritis – inflammation of several joints
Clinical signs – high fever, acute joint pain
Carditis – inflammation of the lining of the heart
Instrumental signs - ECG of the heart, ultrasound, radiography of joints and lungs, etc.
Chorea is a disease caused by nerve damage
Laboratory signs – increase in antistreptolysin, antistreptokinase, presence of hemolytic streptococcus in throat swabs
Erythema (ring-shaped red spots on the skin), subcutaneous rheumatic nodules
The diagnosis is made with a certain combination of these signs (for example, 1 major and 2 minor). A prerequisite is laboratory confirmed presence of hemolytic streptococcus.
Clinic
Symptoms appear 1-3 weeks after an acute streptococcal infection. Rheumatism manifests itself in 5 syndromes:
Rheumatic carditis
Rheumatic carditis (cardiac form) is an inflammatory lesion of the heart involving all the linings of the heart (rheumopancarditis), but primarily the myocardium (rheumomyocarditis).
Manifestations:
- Symptoms of intoxication (weakness, fatigue, sweating, loss of appetite);
- Pain in the heart area of a pulling, stabbing nature;
- Increased body temperature to febrile levels (more than 38 degrees);
- Moderate hypotension;
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- Changing the boundaries of the heart;
- Addition of symptoms of left ventricular and right ventricular heart failure;
- Weakening of tones, most often muting of the first tone;
- With severe myocardial damage, a gallop rhythm may be auscultated;
- A diastolic murmur may be auscultated, characterized by blood turbulence during the transition from the atria of the heart to the ventricles due to the operation of a valve affected by rheumatic endocarditis with thrombotic masses superimposed on it;
- In the early stages of the disease, rheumatic endocarditis is indicated by a rough systolic murmur, the sonority of which increases after physical activity; sometimes it becomes musical.[1]
Rheumopolyarthritis
Rheumatic polyarthritis (articular form) is an inflammatory lesion of the joints, with changes characteristic of rheumatism.
Manifestations:
- Predominant damage to large joints (knees, elbows, ankles);
- A remitting fever appears (38-39 °C), accompanied by sweating, weakness, and nosebleeds;
- Pain in the joints: feet, ankles, knees, shoulders, elbows and hands;
- Symmetry of the lesion;
- Rapid positive effect after using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Benign course of arthritis, joint deformation does not remain.
Rheumochorea
Rheumochorea (St. Vitus's Dance) is a pathological process characterized by the manifestation of vasculitis of small cerebral vessels. Mostly occurs in children, more often in girls.
Manifestations:
- Motor restlessness, activity;
- Grimacing, impaired handwriting, inability to hold small objects (cutlery), uncoordinated movements. Symptoms disappear during sleep;
- Muscle weakness, as a result of which the patient cannot sit, walk, swallowing and physiological functions are impaired;
- Changes in the patient’s mental state - aggressiveness, selfishness, emotional instability appear, or, on the contrary, passivity, absent-mindedness, increased fatigue.
Cutaneous form of rheumatism
Manifestations
:
- Ring erythema - rashes in the form of pale pink ring-shaped rims, painless and not raised above the skin;
- Erythema nodosum is a limited thickening of dark red skin areas ranging in size from a pea to a plum, which are usually located on the lower extremities.
- Sometimes, with significant capillary permeability, small skin hemorrhages appear;
- Rheumatic nodules are dense, inactive, painless formations located in the subcutaneous tissue, joint capsules, fascia, aponeuroses;
- Pale skin, sweating
Rheumopleurisy
Manifestations:
- Pain in the chest when breathing, worsening with inspiration;
- Temperature increase;
- Nonproductive cough;
- Dyspnea;
- On auscultation, a pleural friction noise is heard;
- Lack of breathing on the affected side.
The digestive organs are relatively rarely affected by rheumatism. Sometimes there are acute abdominal pains (abdominal syndrome) associated with rheumatic peritonitis, which are more common in children. In some cases, the liver is affected (rheumatic hepatitis). Quite often, changes in the kidneys are detected: protein, red blood cells, etc. are found in the urine, which is explained by damage to the vessels of the kidneys, and less often - the development of nephritis.
Treatment methods
The disease can be cured completely. With timely and correct prescription of medications, articular manifestations of rheumatism (rheumatic arthritis) completely disappear within 2–4 weeks.
Treatment of rheumatism of the joints begins with strict bed rest (from 12 to 20 days) and the prescription of different groups of medications:
- Anti-inflammatory, painkillers (Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Ibuprofen) in ointments, injections or tablets.
- Anti-inflammatory hormonal drugs (Prednisolone).
- Penicillin or other antibiotics to fight streptococcal infections (Bicillin).
If necessary, the attending physician may prescribe:
- immunosuppressants that suppress the activity of the immune system (Chlorbutin);
- plasmapheresis procedure (purification of blood plasma from autoimmune antibodies and toxic substances).
Starting from the first days of therapy, the patient must follow a fairly strict diet (table No. 10 R). This diet helps reduce swelling and inflammation of connective tissue.
Basic principles of the diet:
- limit carbohydrate intake to 250 g per day, sugar to 30 g, liquid to 1 liter, salt to 3 g;
- exclude coffee, strong meat broths, alcohol, seasonings, fried, fatty, salty foods, baked goods, mature cheeses, chocolate, cocoa;
- reduce the amount of animal protein in the diet - to 80 g per day, animal fat - to 30 g, vegetable fat - to 40 g;
- Include foods rich in vitamins PP, C, B into your diet - liver, nuts, cottage cheese, milk, dried fruits, legumes, eggs, cabbage;
- Steam meat and fish, boil vegetables well;
- eat in fractional portions (up to 5 times a day), do fasting days (curd and milk, potato, kefir, apple) once a week.
During the recovery period, the patient gradually moves to a less strict diet. He is allowed coffee, black tea, unlimited amounts of liquid, and butter.
After the acute inflammation subsides, the patient is prescribed physical therapy:
- Ultraviolet irradiation of joints.
- UHF (treatment with high-frequency electromagnetic pulses).
- Warming up with a Sollux lamp (incandescent lamp placed in a reflector).
- Dry heat for joints (heating pads).
To eliminate the residual effects of rheumatoid arthritis, the attending physician may prescribe therapeutic massage.
Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis may take 12 to 30 days.
Folk remedies are used mainly to treat chronic forms of the disease. Home Remedies Recipes:
- Lilac tincture. Pour 1/4 cup of buds and lilac flowers (equal parts) with 1 cup of vodka, let it brew under a tight lid for 10 days. When ready, drink 50 drops 3 times a day. Rheumatism is treated in this way for 3 to 6 months.
Garlic tincture. Chop 80 g of garlic (crush, cut, grate), pour in 1 glass of vodka, let stand for 10-12 days, when ready, take 15 drops 3 times a day. Course duration: 3–6 months.
- Decoction of bean leaves. Take 20 g of dry bean leaves, pour 1 liter of hot water, heat over low heat for 3-4 hours, strain after cooling, drink 0.5 cups once a day.
- Fresh juices. Mix fresh carrot juice (7 parts) and celery juice (3 parts), drink the mixture 0.5 cups 3 times a day.
Treatment
Treatment of joint rheumatism is aimed at reducing swelling (see), pain and maintaining the basic functions of the joints. Although there is no effective therapy for this condition, there are medications available that can significantly slow the progression of the disease.
Therapy typically involves a systems approach among patients, doctors, and therapists. A rheumatologist is the doctor who monitors and determines the best course of treatment for the patient.
Treatment for rheumatoid disease may include the use of steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Both regimens of different medications help reduce inflammation. Steroids also reduce an overactive immune system, which can help minimize symptoms and prevent damage to joint tissue.
Prevention of joint rheumatism
What preventative measures will help avoid the appearance of rheumatoid arthritis?
Relapses (recurrences) of the disease are prevented within 3 or 5 years after treatment. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics in the fall and spring.
Prognosis for recovery
The prognosis for articular rheumatism is good. In 40% of cases, with timely treatment, the disease can be completely eliminated. After treatment, joint functions are completely restored.
Articular rheumatism rarely causes severe complications. Impaired mobility, tissue fusion and pain in the joint area in most cases are the consequences of rheumatoid damage to the periarticular tissues (ligaments, tendons, tendon and muscle membranes).
The most severe form of articular rheumatism is continuously recurrent. It quickly leads to damage to internal organs and systems and can cause the development of severe heart disease.
Psycho-emotional dependence of a person on magnetic storms
According to psychoendocrinologist Natalya Gridasova, when magnetic storms intensify in August 2020, unfavorable days will come for the healthy population of the planet.
Due to solar activity, there is a significant reduction in the amount of oxygen in the air. This leads to partial hypoxia, when all tissues of the body lack the substance.
✅ At the same time, the adrenal glands begin to intensively release stress hormones into the blood - adrenaline and cortisol. As a result, particularly sensitive people experience a number of emotional shocks:
- sudden anxiety;
- causeless anxiety;
- oppression.
Are you a weather-sensitive person?
Yes, I feel any change in the weather. Only pills save me.
78.72%
Only during strong magnetic storms.
18.94%
No.
2.34%
Voted: 940
All this affects performance, as it causes a sharp jump in blood sugar and impairs memory.
According to the expert, during this period anxiety increases significantly in people with unstable mental health:
- their aggressiveness increases;
- the number of inadequate decisions increases;
- Depression intensifies.
❌ According to Gridasova, the statistics of road accidents increases sharply during the period of solar unrest.