Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning
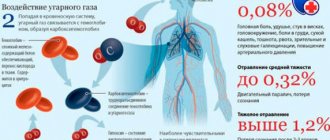
Signs of carbon monoxide poisoning develop quickly. The extent of their manifestation depends on the amount and concentration of CO (carbon monoxide) inhaled, and the time spent in a smoky environment.
The following are the main symptoms and signs of mild to moderate carbon monoxide poisoning:
- Severe headache, dizziness. The pain may be pulsating and localized in the temporal region. With severe intoxication, the pain is acute and spread over the entire surface of the head.
- Pain in the eyes and lacrimation develop due to irritation of the conjunctiva of the eyes by smoke.
- Nausea and vomiting. Vomiting is observed at the height of the headache; it does not bring relief, as it occurs due to irritation of the vomiting center, which is localized in the brain.
- Feeling of tinnitus, and seeing spots, spots, and flickering dots before the eyes.
- Tachycardia – rapid heartbeat (pulse). Heart rate may be above 100.
- Decreased arterial blood pressure (hypotension).
- Shortness of breath. Due to lack of oxygen, a person begins to breathe rapidly.
In case of severe poisoning, the above symptoms are accompanied by:
- Impaired consciousness. Due to impaired blood supply to the brain, a person begins to gradually “load” and fall into stupor, and then into a coma. He stops answering questions and responding to stimuli.
- General convulsions of the whole body that occur against a background of depressed consciousness. Against the background of convulsions, voluntary bowel movements and urination may occur.
- Impaired breathing and pulse. With severe poisoning from combustion products, a person begins to breathe shallowly and not rhythmically, not regularly. The pulse becomes very frequent (about 130 beats/min.) and weak.
What are the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning?
CO is similar in chemical structure to iron (the main component of hemoglobin, the protein that transports oxygen to tissues throughout the body). Due to carbon monoxide poisoning, hemoglobin is degenerated into carboxyhemoglobin, and the supply of oxygen to the entire body is disrupted. This leads to persistent hypoxia. The brain, kidneys, and cardiovascular system primarily respond to a lack of oxygen.
Timely provision of first aid for carbon monoxide poisoning can prevent the following complications:
- Brain death and internal organ failure.
- Acute renal failure.
- Anemia.
- Acute myocardial infarction.
- Brain swelling.
- Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding into brain tissue).
- Pneumonia (lung inflammation)
How does CO affect the body?
This gas enters the blood very quickly and actively binds to hemoglobin . As a consequence, carboxyhemoglobin , which is more closely related to hemoglobin than oxyhemoglobin (oxygen and hemoglobin). The resulting substance blocks the transfer of oxygen to tissue cells. hypoxia develops .
Carbon monoxide in the body binds to myoglobin (a protein in skeletal muscle and heart muscle). As a result, the pumping function of the heart decreases and severe muscle weakness develops.
Carbon monoxide also enters into oxidative reactions, which disrupts the normal biochemical balance in tissues.
First aid to the victim
Providing first aid for carbon monoxide poisoning can be carried out by people without medical education at home, or in any other place where poisoning has occurred. To help the victim, you need to know what to do in case of carbon monoxide poisoning and in what sequence to perform the actions.
If you witness a person being poisoned with CO, there is no need to be confused. His life depends on your actions. Pull yourself together and focus. The list below details what to do and how to provide first aid for carbon monoxide poisoning:
- Lead or carry the victim out of the smoke-filled room. While moving it, do not forget about your safety. Cover your mouth and nose with a damp cloth or gauze to prevent further exposure to CO2.
- Once the poisonous gas has stopped poisoning you and the injured person, immediately call emergency medical help. In this case, you should tell the dispatcher in detail about what happened, name, if possible, your location as accurately as possible, and describe the condition of the poisoned person. Perhaps the dispatcher will give you some recommendations, stick to them.
- If the poisoned person is unconscious, you should lay him on his side. In this position, the risk of tongue retraction is minimal.
- The victim should be provided with a free flow of fresh air and oxygen. Unbutton his shirt and tie. If you are indoors, open all windows and curtains wide open.
- If you have ammonia with you, give it to the poisoned person to smell. This alcohol may help bring him back to consciousness.
- If the person has not lost consciousness, give him sweet hot tea, coffee, or water. This way you can increase his blood pressure and overcome hypotension.
- If there is no breathing or pulse, you need to start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (this is described in detail in the next section of the article).
The above emergency care for carbon monoxide poisoning will help a person survive until the ambulance arrives.
Please note that such assistance should only be provided when there is no immediate danger to your life.
General information
If carbon monoxide , then we are talking about a serious pathological condition. of carbon monoxide enters the body .
This condition is dangerous to health and life, and if you do not seek help from specialists in a timely manner, death from carbon monoxide may occur.
Carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide, CO) is a product that is released during combustion and enters the atmosphere. Since poisonous gas has no smell or taste, and it is impossible to determine its presence in the air, it is very dangerous. In addition, it can penetrate through soil, walls, and filters. Many people are interested in the question of whether carbon monoxide is heavier or lighter than air; the answer is that it is lighter than air.
That is why it is possible to determine that the concentration of carbon monoxide in the air is exceeded using special devices. You can also suspect CO poisoning if a person rapidly develops certain symptoms.
In urban environments, the concentration of carbon monoxide in the air is increased by vehicle exhaust gases. But poisoning from car exhaust gases can only occur at high concentrations.
Basics of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation consists of chest compressions, artificial respiration and intravenous administration of drugs that stimulate myocardial contraction (adrenaline, atropine). In domestic conditions, when providing first aid, no medications are administered.
Please note that before performing resuscitation, you need to make sure that the person’s heart is not beating and there is no breathing. It is best to check the pulse at the aorta (a large blood vessel that runs on the anterolateral surface of the neck), and listen to breathing by placing your ear to the chest.
you should only perform chest compressions when performing CPR To do this, place one hand on top of the other and press them on the middle third of the person’s sternum.
The elbows should be straight. The chest should be pressed 3-4 cm. The frequency of chest compressions is 100/min. The rhythm of resuscitation is similar to the tempo of the song “Staying alive” by the Bee Gees. This musical composition is used to teach the basics of CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) at medical universities and colleges.
If there are two of you, you can add artificial respiration to the resuscitation measures. To do this, open the person’s mouth using your hand or gauze and clean it of excess contents (vomit, blood, tooth fragments). Then inhale mouth to mouth through gauze or cloth. Every 15 chest compressions, you need to take 2 breaths.
Every minute you should quickly monitor the presence of a pulse in the aorta and breathing. If they do not appear, continue resuscitation until the medical team arrives. Change places every 5 minutes, this way you will save energy.
What does first aid consist of?
First medical aid (FAM) is provided by the medical team that responded to the call. It is carried out in a safe and smoke-free room, or in an ambulance. Doctors measure pulse, blood pressure, blood saturation (oxygen saturation in the blood), assess the general condition of the patient, and collect anamnesis from him and those around him.
Before transporting the victim to the hospital, doctors stabilize his condition. PMP consists of:
- Oxygen therapy. The person wears a mask through which a moistened oxygen mixture is supplied.
- Intravenous administration of solutions. This is necessary to relieve intoxication from poisonous gas and raise blood pressure. Reopoliglucin, Reosorbilact, Glucose, Trisol, Disol, and saline solution may be administered.
- Injecting corticosteroids, which will raise blood pressure and help prevent swelling of the brain.
- In the presence of convulsive syndrome, anticonvulsant drugs (magnesia, sibazon) are administered intravenously.
- Resuscitation, which is carried out according to vital signs.
After the patient’s condition has been stabilized, the ambulance team takes him to the nearest intensive care unit, where treatment continues.
What does inpatient treatment consist of?
The main method of treatment for poisoning with fumes is to keep the victim in a hyperbaric pressure chamber. With the help of this equipment, carboxyhemoglobin is removed from the body, which interferes with the full supply of oxygen to all tissues of the body.
In the hospital, intravenous administration of solutions to detoxify the body continues. The volume of medical hospital care depends on the degree of injury to the person, associated injuries, and skin burns. The patient is given antibacterial drugs that prevent the development of pneumonia. The patient constantly receives oxygen mixtures. The duration of hospitalization depends on the condition of the victim.
Anyone can be poisoned by fumes. Knowing the basic rules of first aid can save the life of the person next to you. During its provision, you must be sure of your safety and not be in a smoky room. The victim should immediately call an ambulance, which will stabilize the patient’s condition and take him to the intensive care unit.
Preventive recommendations
How to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning? To avoid CO poisoning, the following poisoning prevention measures are necessary:
- at enterprises where CO is used, conduct regular training and provide work areas with CO detectors;
- use only serviceable and high-quality heating equipment;
- when heating with stoves, clean and check chimneys for functionality;
- ventilate rooms or use ventilation where open flame appliances are used (gas stove and water heater);
- take precautions when the car engine is running in the garage - sufficient ventilation and air exchange, make sure not to fall asleep while the engine is running in the car;
- Do not spend a lot of time near roads (motorways) with active traffic.
Thus, being alert and aware of the possible risks of carbon monoxide poisoning will help prevent an emergency situation. Otherwise, if you are poisoned by fumes, you must not panic and follow the recommendations given. Clarity and coherence of actions will preserve not only health, but also life.