Classification of nuclear fuel
Depending on the main component, all technical fluids are divided into seven large groups:
- Based on organophosphorus compounds . They are used as coolants used in special equipment.
- Based on organofluorine compounds . They are used as release and manometric liquids, in particular in measuring instruments.
- Based on chlorine compounds . Used in solvents. The main representatives: dichloroethane, tri- and perchloroethane.
- Based on glycols . Components of automobile antifreeze and brake fluids, including ethylene glycol, antifreeze.
- Alcohol based . Widely used in production as solvents. The most famous representative is methanol.
- YATZ with toxic additives . Technical synthetic oils with anti-wear, protective, anti-corrosion properties.
- Leaded gasolines . They are used for the operation of special automotive equipment.
How poisoning occurs and the main symptoms
Poisoning by technical liquids can occur both at home and at work if safety precautions are not followed. The most common categories of patients are young children, alcohol abusers, and industrial workers. Symptoms of damage depend on the type, route of entry into the body, concentration and duration of action of the toxic substance. The most severe intoxication is ethylene glycol, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and methylene.
Motor fuel
Gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, diesel fuel are petroleum products used as motor fuel. Poisoning by them occurs both when inhaling the vapors and when consumed by mouth. These YATH have a psychotropic effect and adversely affect the liver, kidneys, and respiratory system. Leaded gasoline, which contains tetraethyl lead, is especially dangerous.
Coolants
This is a general name for products that play the role of coolant in cooling systems of engines and other devices. Antifreezes are widely used in the operation of vehicles - liquids that do not freeze at low temperatures. As a rule, they consist of an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol.
In the second half of the twentieth century, coolants for automobile engines, produced in the USSR under the Tosol brand (“Tosol-A”, “Tosol-AM”), became very popular. Later this name became a household name.
Most often, antifreeze poisoning occurs through accidental or intentional ingestion. The sensitivity of organisms to poison can vary, and its lethal dose ranges from 50-500 ml.
Anti-freeze
Windshield washer fluid, or anti-freeze, is poured into the car's windshield washer reservoir to remove dirt from the glass. For a long time, it included technical ethanol, but after tightening state regulation of alcohol, it was replaced by the more expensive isopropanol. Poisoning is rare, mostly affecting young children who may mistake the bright liquid in the car for juice or soda. Serious toxic effects occur when more than 50 ml of antifreeze is ingested.
Illegal manufacturers make windshield washer fluid based on toxic ethylene glycol and methyl alcohol. This is very dangerous, since counterfeit anti-freeze causes poisoning not only when swallowed, but also when inhaling vapors entering the car interior through the ventilation holes .
- headache;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- lack of coordination;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- stomach ache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- labored breathing;
- in severe cases - depression of consciousness, coma.
Brake fluid
The purpose of the brake cylinder is to transmit force from the main brake cylinder to the wheels. As a rule, they contain polyglycols and their esters that are toxic to the body. Silicones are used less frequently.
Brake fluid poisoning occurs when ingested. Since the substance has a sweetish taste and looks like liquor, people often try to drink it for the purpose of intoxication. Even small amounts of liquid cause serious health effects, and in most cases such intoxication is fatal.
- nausea, vomiting;
- sharp abdominal pain;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- severe dizziness.
In the absence of treatment, after 36-48 hours:
- decreased amount of urine excreted;
- jaundice;
- hemoptysis;
- depression of consciousness, coma, death.
Turpentine
A liquid oil mixture obtained from the resins of coniferous trees. Widely used as a solvent for paint and varnish products, as well as in everyday life for cleaning parquet floors. In addition, turpentine is a well-known traditional medicine that is used to treat pain in the joints and back.
Signs and stages of gas toxicity
Poisonous and dangerous gases have different chemical compositions and have different effects on the body. Signs of intoxication differ depending on the substance. Some of them are slow-acting and the symptoms may not appear immediately.
General symptoms of poisoning with toxic fumes:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- tinnitus, lethargy;
- pain in the eyes, respiratory organs;
- with some gases, a characteristic odor may emanate from the victim;
- cough;
- hallucinations, loss of consciousness;
- diarrhea as a result of the influence of toxic substances;
- involuntary relaxation of the anus or sphincter on the bladder;
- change in breathing;
- arrhythmia, cardiac arrest;
- coma, death;
- a metallic taste in the mouth is a typical sign of hydrogen sulfide poisoning;
- convulsions.
Some poisonous chemical gases - phosgene, carbon dioxide - cause death from suffocation, nitrous gases - painful foamy vomiting with blood.
There are 4 stages of substance poisoning. Classification is based on the severity of symptoms:
- Mild form – breathing problems, feeling of drowsiness, weakness, pain in the eyes.
- Medium form - when interacting with toxic compounds, the first signs of disruption of higher nervous activity and brain function, heart rhythm appear.
- Severe – pulmonary edema develops, the victim loses consciousness, and coma is possible.
- Instant – manifests itself when poisoned by several chemicals at the same time. Without emergency help, respiratory and cardiac arrest occurs, and brain death occurs within 5 minutes.
First aid
Most often, nuclear fuels enter the body when they are ingested. First aid for poisoning with technical liquids is as follows:
- Immediately seek medical help: call an ambulance or independently deliver the victim to a medical facility.
- Tube gastric lavage (up to clean rinsing water).
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Taking saline laxatives and enterosorbents.
- Warming.
- Administration of specific antidotes (if available).
- If the victim is in critical condition, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Ethyl alcohol can be considered an antidote for poisoning with antifreeze, brake fluid and methanol-based antifreeze. It partially blocks the formation of nephrotoxic metabolites in the liver. Therefore, one of the methods of treating poisoning with nuclear fuel in a hospital is the intravenous administration of ethanol.
If an adult victim does not have the opportunity to seek medical help, to reduce the consequences of poisoning, you can take a dose of strong alcohol (at least 40 degrees), bringing the blood alcohol concentration to 100 mg/dl (which corresponds to a mild degree of intoxication). The measure is effective only at the early stage of helping the victim.
First aid for poisoning with nuclear fuel vapors should also be provided immediately. The standard algorithm includes:
- Removing the victim from the contaminated atmosphere.
- Call an ambulance.
- Rinsing the mucous membranes and rinsing the mouth with clean water.
- Oxygen therapy.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- According to indications - hemosorption, hemodialysis, blood transfusion.
- Vitamin therapy.
The use of antidotes for gas poisoning
Further treatment of poisoning with toxic fumes is carried out at a medical institution.
For some substances, the use of antidotes is indicated, for others - symptomatic treatment, normalization of the state of the respiratory system, and removal of metabolites of chemical substances.
Poisonous asphyxiating gases and antidotes.
| Toxic substance | Antidote |
| Sarin | Atropine, budaxim – no later than 10 minutes after the lesion |
| Nitrogen | No symptomatic therapy |
| Ammonia | Inhalation of acetic or citric acid fumes, subcutaneous morphine or atropine. Symptomatic therapy |
| Bromine | Alkaline inhalations, use of sodium thiosulfate. Table salt – up to 20 g per day, symptomatic treatment |
| Sulfur dioxide | None, symptomatic therapy |
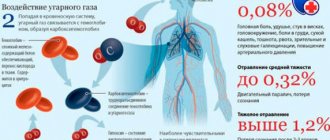
| Carbon monoxide | Oxygen therapy, neuroleptics, symptomatic treatment |
| Fluorinated substances | Atropine, symptomatic therapy for exposure to toxic compounds |
| Chlorine | Absent, symptomatic therapy |
| Vapors of gasoline and other hydrocarbons | It is forbidden to induce vomiting. No antidote has been developed; symptomatic treatment is indicated. |
| Hydrocyanic acid | Inhalation of isoamyl nitrite, polythionates |
| Mustard gas | There is no antidote, careful treatment of the skin, mucous membranes of the throat, nasal passages with a soda solution |
Antidotes are administered by medical workers, the dosage is determined based on the severity of the injury, the age of the victim, and the type of toxic chemical gas. Each case of poisoning is individual. You can buy an antidote at the pharmacy, but its administration requires the medical skills of an emergency physician or resuscitator.
Prevention measures
To avoid nuclear fuel poisoning, it is enough to follow standard preventive measures:
- When in contact with toxic liquids, wear protective clothing and shoes.
- Work with nuclear fuel in well-ventilated areas. If the permissible concentration of poison in the inhaled air is exceeded, use a gas mask or other protective equipment.
- Observe safety precautions at work and at home.
- Keep liquids used in everyday life out of the reach of children.
Despite their wide scope of application, technical fluids pose a particular danger to humans, and poisoning with them leads to serious consequences for health and life. Timely first aid significantly alleviates the condition of the victim and improves his prognosis for recovery.
Poisonous gases: carbon dioxide, household gas, methane, hydrogen sulfide.
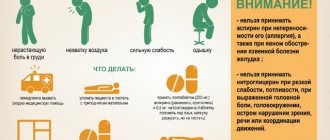
In case of poisoning with poisonous gases:
- Remove the victim from the danger zone and into fresh air.
- Lay the victim down and unfasten his clothes. Apply cold to your head
- Rub your chest and body. Cover warmly. Give ammonia a whiff
If the condition worsens, give plenty of sweet drinks (tea).
If you lose consciousness for more than 4 minutes, turn over on your stomach and apply cold to your head.
Strongly not recommended
In order to avoid incorrect actions in emergency situations, you need to know not only what will help in case of poisoning, but also become familiar with what you absolutely cannot do.
Almost all measures from the list below can lead to negative consequences for the poisoned person:
- if the cause of poisoning is accidental consumption of acid, artificial vomiting should not be induced,
- You should also not induce vomiting in an unconscious person and in children of a younger age category,
- It is not recommended to use a heating pad to warm the abdominal area,
- you should absolutely not give the patient drugs against diarrhea when it appears, since in this way the natural cleansing of the body occurs,
- It is not recommended to consume dairy and fermented milk products, sweet juices and carbonated drinks on the first day.
Advice! In case of poisoning with chemicals and narcotic substances, you should not take any measures, give the patient any medications or drink until qualified assistance is provided.
It should be noted that regardless of the form and degree of intoxication of the body, as well as the reason that provoked such a condition, it is necessary to immediately call a doctor to provide emergency assistance to children in case of poisoning.
The child’s body is the most vulnerable; in addition, children of a younger age category cannot adequately assess their own condition. Lack of timely assistance can lead to negative consequences and aggravation of the patient’s condition.
Classification
Depending on the place of occurrence, there are:
- accidental poisonings;
- production;
- household;
- medical errors;
- suicidal;
- criminal.
According to the way the poison enters the body:
- oral method (through the mouth);
- inhalation (by inhalation);
- percutaneous (through the skin);
- injection.
Based on the type of poison present, poisoning is classified into:
- carbon monoxide and lighting monoxide;
- pesticides;
- acids and alkalis;
- medicines;
- alcohol;
- food poisoning.
Depending on the severity, poisoning can be:
Poisons have irritating, hemolytic, cauterizing and other effects on the human body. In addition, they can selectively act on individual systems and organs (heart, kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, blood and nervous system).
Prevention
- do not eat foods that have expired, as well as those that look spoiled and have an unpleasant odor;
- wash your hands with soap before preparing food;
- do not eat unfamiliar foods;
- wash vegetables and fruits before eating;
- In production, follow safety rules and work in a well-ventilated area;
- strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations when taking prescribed medications;
- observe proportions when diluting pesticides in the country;
- in houses with stove heating, make sure that the dampers are open.
| Before using the information provided by medportal.org, please read the terms of the user agreement. |
Gastric lavage
The first stage of treatment is gastric lavage aimed at removing toxins. A weak solution of manganese is best suited for the procedure. The color of the liquid after all crystals have completely dissolved should be pale pink. The volume of the prepared solution is from 1.5 to 2 liters. This amount should be drunk completely to induce vomiting. If potassium permanganate is not available, you can use water in which sea or table salt is dissolved.
The naturally occurring urge to vomit is not enough to completely cleanse the body. Accordingly, it is necessary to artificially provoke the phenomenon with the help of two fingers inserted into the mouth to press the root of the tongue. To get the best effect, it is recommended to carry out the procedure several times until the water expelled from the stomach becomes completely clear. If there is no feeling of nausea and urge to vomit, we can conclude that the spoiled product has moved to the intestinal area, which indicates the futility of artificial evacuation.
Quite often, the body, trying to protect itself from intoxication, independently provokes the appearance of diarrhea, since harmful toxins are eliminated quickly and effectively along with diarrhea. If there is no diarrhea, an enema or laxatives will help provoke its appearance.