- Lack of orgasm
- Fever
- Lower abdominal pain
- Increased fatigue
- Irritability
- Painful urination
- Menstrual irregularities
- Depression
- Discomfort during intercourse
- White vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor
- Bleeding during absence of menstruation
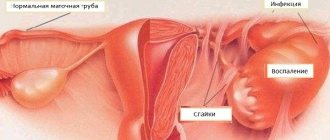
Oophoritis is an inflammatory process that forms in the fallopian tubes. As a result of the development of this disease, the fallopian tubes become fused with the ovaries. As a result, infertility may occur. It is impossible to say exactly what causes the onset of an inflammatory disease. The pathology affects girls aged 25–35 years and women during menopause.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Subtypes
- Bilateral
- Left-handed
- Right-handed
Causes of the disease
Salpingitis and oophoritis are somewhat interrelated. As a rule, this pathological disease cannot appear on its own. The inflammatory process begins due to salpingitis, that is, inflammation of the fallopian tubes. The following factors may contribute to the development of salpingitis:
- infectious diseases;
- diseases that are sexually transmitted.
The main reasons that contribute to the progression of the inflammatory process include the following:
- smoking;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- pathologies that lead to a significant weakening of the human immune system;
- diseases that cause metabolic disorders;
- hypothermia;
- non-regular sexual partners.
Salpingitis and oophoritis are two interrelated processes. The first very often entails the second.
Reasons for appearance
Most often, the chronic form of oophoritis develops after incorrect or incomplete treatment of the acute form. But chronic oophoritis can also occur if treatment is not started in a timely manner, if the symptoms of the disease were mild and the woman did not consider it necessary to visit a doctor. The development of the disease can also be influenced by such reasons as complicated childbirth, hypothermia suffered by the patient, and the influence of infections, including genital infections.
Chronic oophoritis occurs as a result of the spread of an infection that has already entered the body. Therefore, it occurs together with another disease that needs to be treated simultaneously with this pathology.
Most often, the ovaries become inflamed due to salpingitis and adnexitis. Their development can be provoked by bacteria such as chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas and other sexually transmitted infections. In rare cases, chronic oophoritis is caused by an infection from the abdominal cavity. This could be, for example, ordinary appendicitis or another disease. Streptococci, staphylococci or general infectious infection of the body are another reason for the development of chronic oophoritis.
Among other probable causes of chronic oophoritis, it is necessary to indicate endocrine diseases, the presence of other chronic infections, and pathologies of the genitourinary system. Smoking, constant stress, overwork are other reasons for the possible occurrence of ovarian inflammation.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease can occur in two forms - acute and chronic.
In acute oophoritis, the following symptoms can be observed:
- elevated, unstable temperature;
- discharge of leucorrhoea with a pungent odor;
- bleeding during the absence of menstruation;
- lower abdominal pain;
- systematic sharp pain when urinating.
Chronic oophoritis has the following symptoms:
- acute pain, mainly in the lower abdomen (characteristic symptom);
- unpleasant feeling during sex;
- instability of the menstrual cycle;
Symptoms of oophoritis
Depending on the patient’s condition, the following additional symptoms are possible with chronic oophoritis:
- increased fatigue;
- depression, irritation;
- lack of orgasm.
The presence of additional symptoms depends on the cause that triggered the progression of the pathology. It is worth noting that the additional symptoms described above can also be observed in acute oophoritis. It is possible to distinguish between chronic oophoritis and acute oophoritis only with the help of instrumental tests.
Signs of oophoritis, as a rule, are always pronounced. The patient notes a deterioration in her condition, she begins to experience pain in the lower abdomen. If these signs of oophoritis are present, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Symptoms and manifestations
During a gynecological examination, symptoms such as enlarged ovaries and their pain during the examination are noted. Common symptoms of inflammation of one ovary are fatigue, fever, and pale skin. Conventional antipyretic methods are ineffective. In addition, there is pain in the lower abdomen - on the right or left, depending on which ovary is affected.
The appearance of bleeding between menstruation is also one of the symptoms. Other signs of chronic oophoritis include the presence of vaginal discharge, decreased libido, and irritability. If the patient has developed chronic bilateral oophoritis, the symptoms manifest themselves as intense pain in the lower abdomen, in the groin, radiating to the lower back.
The appearance of uterine bleeding between menstruation, painful urination, nervousness and tension, disturbed sleep - all these signs indicate chronic bilateral oophoritis.
The chronic form of the pathology is characterized by other symptoms that are not the main ones for inflammation of the ovaries. This may be irritability, insomnia, decreased activity, and rapid onset of fatigue. The main difference between the chronic course is the lesser severity of symptoms and pain, otherwise it is completely similar to the acute form. At the same time, it is chronic oophoritis that most often becomes the cause of infertility and violations of the basic functions of the ovaries.
Subtypes
In modern medicine, the following subtypes of the disease are distinguished:
- bilateral oophoritis;
- right-sided oophoritis;
- left-sided oophoritis.
Bilateral oophoritis
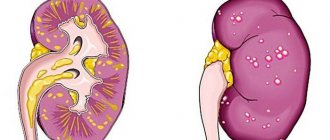
Bilateral oophoritis is inflammation in both ovaries. The signs of oophoritis with this subtype of the disease correspond to the points described above.
On palpation, pain in the lower abdomen and significant compaction in the ovarian area may be felt. To make an accurate diagnosis, several instrumental and laboratory studies should be performed. Symptoms of bilateral oophoritis are similar to appendicitis and salpingitis.
Left-sided oophoritis
Left-sided oophoritis is the formation of an inflammatory pathological process in the left fallopian tube and ovary. The symptoms are the same as described above. The only difference is that with left-sided oophoritis the pain is localized on the left, in the lower abdomen.
Right-sided oophoritis
Almost the same symptoms are diagnosed with right-sided oophoritis. The pain is localized on the right side, also in the lower abdomen. Diagnosis is exactly the same as for other forms of the disease.
Bilateral oophoritis
As we have already said, inflammatory processes can occur in both ovaries at once. We will not talk about the symptoms, or rather, we will not list those mentioned above. We will focus our attention on how bilateral oophoritis differs from unilateral oophoritis. In this case, upon palpation in the lower abdomen, painful sensations appear, enlargement of the ovaries and compaction at the site of the abscess are felt. Further diagnostics include tests where inflammation is indicated by an increase in the number of leukocytes, a decrease in the albumin-globulin ratio, C-reactive protein, and ESR. Laparoscopy makes it possible to determine the stage of development of the disease, its location and, if necessary, administer medications. Also, in the process of making a final diagnosis, an ultrasound scan is required. All this is necessary so that the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and can prescribe the correct treatment. After all, bilateral oophoritis can be confused with adnexitis, salpingitis or appendicitis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing the disease is quite difficult. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to conduct a series of instrumental and laboratory tests. It is also very important to know the possible causes of the onset of the disease.
The diagnostic program includes the following:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- diagnosis of the condition of the pelvic organs;
- tests to detect infection.
If during the examination infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted are discovered, additional tests are prescribed.
In addition to the diagnostic methods described above, laparoscopy is used. It is this method of instrumental diagnostics that makes it possible to diagnose ovarian inflammation at an early stage and fully examine the uterus.
Laparoscopy
This research technique is used if the patient complains of systematic pain in the lower abdomen, and the prescribed treatment does not produce results.
Diagnosis of the disease
The onset of chronic oophoritis sometimes occurs without characteristic symptoms. The only manifestation that will help identify it is a slight pain syndrome in the ovarian area. When determining the disease, it should be remembered that chronic salpingitis and oophoritis can occur simultaneously. They have similar symptoms, and due to the close proximity of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, inflammation easily passes from one organ to another. This complicates diagnosis and complicates subsequent treatment. Basically, the inflammatory process begins to develop in the fallopian tubes, and after that it moves to the ovaries.
Ultrasound for determining oophoritis is not effective, because it only shows changes that have occurred as a result of the development of the inflammatory process. Effective diagnostic methods include laparoscopy. Using an endoscope, you can completely examine the ovaries and accurately determine the signs of inflammation. This modern equipment is very effective and is used to identify and treat inflammation, as well as for surgical intervention. The advantage of this method is the high accuracy of diagnosis, low traumatic procedure, and rapid recovery after the examination.
Chronic oophoritis can be identified during examination of a woman who complains of infertility and menstrual irregularities. To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to study the medical history. Serious attention should also be paid to laboratory tests, general blood and urine tests. By the increased number of leukocytes, the development of the inflammatory process can be determined. A smear taken from the vagina and urethra will make it possible to more accurately determine the type of inflammation. Other types of tests using PCR and ELISA methods will help identify the infection that caused the inflammatory process, which is very important when prescribing treatment.
Pregnancy
Unfortunately, this disease practically eliminates the possibility of getting pregnant. However, if you have the above symptoms, this does not mean that you have oophoritis. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor.
During the development of this pathology, the fallopian tubes and ovaries irreversibly change, which makes the process of bearing a fetus very problematic. If, of course, you manage to get pregnant at all.
It is still possible to become pregnant in the chronic form or with right-sided oophoritis if you undergo a special course of treatment from a specialist before conception.
It is worth remembering that with this disease complications during pregnancy are possible:
- fetal infection;
- risk of miscarriage.
Therefore, before becoming pregnant, you should get advice from your doctor. Treatment of oophoritis should only be carried out by a highly qualified specialist.
Chronic bilateral oophoritis
In some cases, the pathological process spreads to the peritoneum: periadnexitis develops. If there is an accumulation of purulent secretion, a diagnosis of “pyosalpinx” is made, and if there is an accumulation of transparent secretion, a diagnosis of “hydrosalpinx” is made. Pyovar is a purulent inflammation of the ovary; as the infection spreads, pelvioperitonitis develops.
- pain in the lower abdomen, groin area or lower back;
Chronic oophoritis and its complications pose a threat to women:
The adhesive process can cause ectopic pregnancy, ovarian fibrosis, and as a result - changes in hormonal levels and infertility. To prevent adhesions, absorbable drugs and balneological treatment are used.
Inflammation can move from the right tube to the left and vice versa. Right-sided oophoritis can be confused with appendicitis, so careful diagnosis is required.
- diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.);
- uterine bleeding.
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin or lower back;
- deterioration of the central nervous system;
- elevated temperature, which is not affected by antipyretics;
- cycle disruptions (delays, pain);
Acute oophoritis can develop on one side only or on both. If right-sided oophoritis is suspected, as a rule, the patient must be examined by a surgeon to rule out appendicitis.
Treatment of chronic oophoritis is long-term. Sometimes it includes not only therapeutic procedures, but also spa treatment.
Due to swelling and tenderness of the ovary, palpation does not give a clear picture.
If one ovary is affected, left-sided oophoritis or right-sided oophoritis is diagnosed. The causes of the disease are the same: gynecological manipulations, infections of the genital and other organs, weak immunity (autoimmune oophoritis occurs), stress, hypothermia. Symptoms:
Complications of the chronic form:
An accurate diagnosis can be made based on gynecological history (finding out the causes of inflammation, provoking factors and the specifics of the reproductive system), laboratory tests (high level of leukocytes) and gynecological examination (enlarged ovaries, impaired mobility). An ultrasound examination is also carried out (echo signs allow one to determine the degree of inflammation), bacteriological examination, and PCR diagnostics.
The most informative diagnostic method is laparoscopy. Indications for the procedure are prolonged pain of unknown origin, unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant, and ineffectiveness of drug therapy. During laparoscopy, impaired patency of the fallopian tubes, the presence of infection and adhesions, and formations in the ovaries and tubes are observed.
Treatment is prescribed after the gynecologist makes an accurate diagnosis. How the doctor will treat the disease depends on the degree and stage of its development, causes and symptoms.
Treatment of the disease
The course of treatment directly depends on the reasons that provoked the progression of the disease in the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Treatment of oophoritis is carried out only in a hospital setting.
The course of treatment is prescribed after determining the exact cause of the disease and carrying out diagnostics. Painkillers and antibiotics must be prescribed. At the initial stage, if there are no contraindications, ice can be applied to the lower abdomen to reduce pain.
If an acute stage of the disease is diagnosed, then, in addition to medications, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed. If the adhesive process has not yet begun, absorbable drugs and the following procedures are prescribed:
- gynecological massage;
- mud therapy.
Gynecological massage
If taking antibiotics and other medications does not produce results, then surgical intervention is possible - complete removal of the ovaries (such treatment is radical).
Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, since the disease can not only go into a chronic stage, but also cause the development of a serious complication - infertility. Folk remedies can only be used in tandem with synthetic medications and only with the permission of the attending physician.
Treatment
— acute oophoritis and the presence of other genital diseases;
The chronic form is characterized by periodic pain and cycle disorders.
Oophoritis treatment: advanced and chronic form is more difficult to treat and may lead to the need for surgery. Treatment of the chronic form has the main goal: achieving an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, strengthening the immune system and the ability to become pregnant in the future.
Treatment of oophoritis in the acute stage begins with antibiotic therapy, with at least two drugs prescribed to exclude the possibility of the disease progressing to the chronic stage. In the first period, it is recommended to prescribe an injection form of administration, including intravenous; in the future, you can switch to tablet forms of drugs. Therapy is carried out in a hospital setting. Sanitation is mandatory, and, if necessary, drainage of the abdominal cavity. In the presence of purulent foci, a puncture is performed with the obligatory introduction of medications into the cavity.
Prevention
Oophoritis can only be partially prevented. Since the disease can develop due to sexually transmitted infections, you should be careful about the intimate side of your life and choose the right contraceptives.
In addition, you should adhere to the following rules:
- avoid hypothermia;
- monitor genital hygiene;
- Healthy food;
- Be examined by a gynecologist at least twice a year.
If you have one or two symptoms, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. At the initial stage, oophoritis can be cured.
What to do?
If you think you have oophoritis
and symptoms characteristic of this disease, then a gynecologist can help you.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Classification and symptoms
However, not all forms of oophoritis are caused by certain pathogens. Recently, autoimmune oophoritis has been diagnosed extremely often.
Firstly, this is the exclusion of sexual activity without the use of barrier methods of contraception. This will avoid sexually transmitted diseases and reduce the risk of oophoritis.
The disease can lead to a variety of complications. The most common among them:
- stress;
General intoxication of the body develops. The pain is pronounced, radiating to the rectum, buttock, and lumbar region.
To date, the causes and mechanism of the disease have not been fully studied. It is reliably known that this disease is usually accompanied by other autoimmune diseases, such as hypothyroidism of the thyroid gland, lupus erythematosus and others.
If the inflammatory process of the ovary occurs in an acute form, the woman experiences severe pain and weakness, complains of difficulty urinating, and notes abnormal discharge.
Acute oophoritis or serous, develops rapidly and usually accompanies acute salpingitis. The disease begins with:
Ovarian oophoritis in the acute stage lasts from 5 to 15 days and without proper treatment, becomes chronic.
It should be understood that parallel treatment of the genital area is often carried out to prevent re-infection.
- overwork, hypothermia;
The causes of bilateral chronic oophoritis are different:
In addition to the main cause of the disease, provoking factors can be identified:
Oophoritis is often a secondary disease resulting from infection from the affected fallopian tubes. Inflammation can be provoked by both conditionally pathogenic bacteria, which in some quantities inhabit the microflora of a healthy person, and pathogenic bacteria, sexually transmitted ones, if the use of barrier contraceptive methods is ignored.
In the medical environment, inflammation of the ovaries is called oophoritis. It can be present in acute, subacute and chronic form, spread to 1 or 2 ovaries at once. It is the bilateral form of the chronic type that is most difficult to cure. And this must be done if you want to maintain women’s health and conceive a child. So, today we will talk in detail about the symptoms, causes and methods of treatment of this disease, so that we know how to deal with it effectively.
Description of the disease
Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers are prescribed.
Bilateral oophoritis involves damage to both ovaries. The reasons are the same as for unilateral inflammation. Symptoms:
Chronic oophoritis, its symptoms:
In this article we will talk about such a common disease as oophoritis.
Hypergonadotropic insufficiency and normogonadotropic ovarian insufficiency are the result of an autoimmune process in the ovaries.
Women's health is very fragile. And, as you know, you need to take care of it from a very young age. Hypothermia, incompletely cured concomitant diseases, fungal and bacterial sexually transmitted infections - all this can cause significant harm to a woman’s body and affect her reproductive functions.
In the treatment of a chronic process, special attention is paid to complications that occur in 90% of cases, namely, the adhesive process in the pelvis. Bilateral oophoritis leads to the formation of fallopian adhesions on both sides, left-sided oophoritis - on the left side, respectively, right-sided - on the right.
Antibiotic treatment includes drugs from the cephalosporin and penicillin group (Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Timentin, etc.). Antimicrobial agents (Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin) have been proven effective in the treatment of acute and chronic forms. Oophoritis can be treated with Metronidazole (analogous to Tinidazole), which is almost always included in treatment.