Skin melanosis is an excessive deposition of the melanin pigment in the epidermis. This substance is produced by special cells (melanocytes) and is designed to protect skin cells from the sun's rays. Light-skinned people produce this pigment in smaller quantities than dark-skinned people. Normally, melanin is activated only under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. In this case, a tan appears on the skin. If this pigment is deposited in large quantities, a disease occurs - melanosis. It is accompanied by a change in skin color.
What it is
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor that rapidly develops from melanocytes. These cells produce melanin, the pigment that gives the growths their dark color. In most cases, melanomas are located on the skin. Very rarely they appear on the mucous membranes or on the retina of the eye.
The disease is quite difficult to diagnose in the early stages. The fact is that melanomas form against the background of moles or birthmarks. Often, at the beginning of tumor development, it is simply not noticeable. This is the main danger of the disease. In just a year, it affects the lymph nodes, and then, through the vessels, spreads to most internal organs.
The course of the disease is very difficult to predict, which makes it one of the most complex forms of cancer.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Endocrine disorders and hereditary predisposition play an important role in the formation of pathology.
At the same time, among the leading causes of melanosis are adrenocortical insufficiency of adrenal tissue, and, in addition, a decrease in the production of melanophore hormone by pituitary cells.
Among the forms of melanosis, pathological and physiological are distinguished. In the second case, pigmentation disorder is present in people with dark skin color and occurs under the influence of sunlight. In the case of a pathological condition, the melanin pigment is deposited in excess quantities in those areas where it is present normally (brain membranes, skin, eyes). Sometimes it appears in areas where it is not normally present (brain, kidneys, mucous membranes). Hyperpigmentation can be either focal or diffuse. In the tissues of the optical system, hyperpigmentation is often focal in nature.
Typically, such changes are diagnosed in patients of color.
Causes
Modern technologies are developing quite quickly, but, unfortunately, this is not enough to determine the main cause of the development of skin melanoma. Existing theories suggest that the process of tumor formation is associated with molecular genetic disorders. Let's consider the causes of malignant cancer formations:
- exposure to solar radiation and ionizing radiation;
- getting sunburn;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- injury to nevi and moles;
- hereditary predisposition;
- increased size of moles and birthmarks on the body;
- chronic irritations;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diseases provoked by the immune system;
- changes in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- the appearance of papillomavirus.
In connection with metastasis, difficulties sometimes arise in determining the underlying factor in the development of the disease.
The appearance of skin melanoma is also influenced by the color of a person’s skin. People with lighter skin tones are most susceptible to the disease.
Prevention
The use of protective creams against exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the main preventive measure against melasma. These cosmetics absorb, reflect and scatter UV rays.
Creams with filters must be used by people with hypersensitive skin and a predisposition to melasma, adolescents, pregnant women, women who have entered menopause, those who have undergone cosmetic procedures (peeling, laser therapy, skin lightening) and plastic surgery.
Doctors recommend adjusting the diet and creating a rational menu. Include in your diet foods enriched with C, A, E and PP (vegetables, fruits, herbs, vegetable oils, seafood, nuts, legumes).
Cosmetic procedures that eliminate pigmentation should be carried out during periods of reduced solar activity. The services of a cosmetologist are usually used in October-January.
If age spots occur, you should visit a dermatologist. The doctor will determine the nature of the disease, identify its cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
Mole and melanoma
The majority of moles on the human body are formed by the age of twenty-five. But, for some reasons, they may appear later. One such factor is, for example, pregnancy. Also, moles, or as doctors call them, nevi, may disappear.
Nevus, like melanoma, is a tumor. The difference is that a mole is a benign tumor. It does not pose any danger to the body and does not require removal, while melanoma is malignant, life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
The greatest danger is posed by newly formed moles that appear in adulthood. Often, they hide within themselves the germ of a future tumor. Under no circumstances should you try to get rid of a new mole on your own. This will expose you to additional risk.
If you notice a dark spot on your skin that is rapidly growing and has jagged edges, consult a doctor. As a rule, early neoplasms are well treated. On the contrary, a large formation, more than a couple of millimeters thick, is usually fatal.
Modern medicine does not guarantee cure for late-stage melanoma. Unfortunately, the death rate is about 80%, and the number of cases is increasing every year.
Various methods of treating tumor pathology
The sooner the doctor can detect melanoma and begin treatment, the more effective it will be. If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, doctors prescribe a course of radiation and chemotherapy that will prevent the growth and further progression of the tumor. If the formation can be removed without harm to the patient, doctors resort to surgery. In the event that the disease is discovered too late, the issue of palliative (supportive) treatment is considered. It is not capable of killing melanoma, but it can provide the patient with the necessary standard of living and relieve pain.
The main goals of tumor treatment:
- reduction of discomfort;
- increase in life expectancy;
- preventing the development of secondary complications and further progression of melanoma;
- prevention of penetration of metastases into various parts of the body;
- normalization of the body’s vital functions;
- stimulation of regeneration and repair processes of soft tissues.
Radiation and chemotherapy to fight the disease
Conservative therapy is the treatment of choice for melanoma. Since this tumor is often located on the surface of the skin, such treatment methods bring a noticeable effect due to the targeted effect.
Radiation therapy is a supportive technique, since melanoma has low sensitivity to various radiations. This method is based on a targeted effect on the pathological neoplasm. The patient is placed in a special chamber, after which the device is turned on. Radiation, passing through soft tissue, affects only tumor cells, destroying their DNA - the repository of genetic material. At the same time, further growth and development of the tumor is inhibited, while healthy tissue remains unharmed. The duration and intensity of the course of radiation therapy is determined by the patient's attending physician. The technique has many side effects, which include sudden weight loss, changes in appetite and sleep disturbances. The recovery period lasts from two to six months.
Radiation therapy helps prevent tumor growth by destroying its DNA
Chemotherapy is the use of anticancer pharmaceutical drugs in large doses, which also interfere with the growth and development of the pathological tumor. All such drugs are introduced into the body through intravenous injections or droppers: this ensures the most complete and rapid distribution of them in the soft tissues. Doctors often combine several medications at once to achieve the maximum possible effect.
Antineoplastic drugs used to treat melanoma:
- Methotrexate;
- Cisplatin;
- Carboplatin;
- Avastin;
- Remaxol;
- Vinblastine;
- Vincristine;
- Carmustine.
Other groups of remedies that help fight the symptoms of the disease:
- Painkillers reduce the severity of discomfort and allow the patient to normalize sleep and normal rhythm of life. Most often used for this purpose: Morphine, Codeine, Omnopon, Narcotine, Fentanyl, Pentazocine, Methylmorphine, Buprenorphine.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve swelling and itching of soft tissues. The most common medications are: Nise, Ketorol, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Tamoxifen, Analgin, Nimesulide, Ibuklin, Voltaren.
Photo gallery: drugs used to combat the disease
Methotrexate inhibits tumor growth
Morphine is a narcotic analgesic used for severe pain.
Nise is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that reduces swelling
Surgical elimination of pathology
In addition to conservative therapy, there are also surgical methods for treating malignant neoplasms. It is worth noting that operations for melanoma are performed in less than 40% of cases, since the tumor responds well to conservative therapy. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- damage to more than one organ or limb;
- lack of effect from conservative treatment for 3 months;
- large size of the tumor.
In some cases, tissue transplantation may be necessary to close a particularly massive skin defect.
Contraindications to surgical treatment of melanoma are:
- the patient’s age is too young or old (risk of cardiac arrest);
- metastasis to various organs and tissues at the last stage of development of the disease;
- allergic reaction to anesthetic drugs;
- personal refusal of the patient or his guardians to carry out such a procedure.
The scope of the intervention largely depends on the stage of the tumor and its growth into neighboring organs. The smaller the size of the tumor, the more gentle the operation will be. In this case, doctors usually try to leave almost invisible and thin scars that do not cause defects in appearance.
A scar forms at the site of the tumor
Stages of surgical intervention:
- Treatment of the surgical field. The area where the melanoma is located is wiped with alcohol and iodine solution. This procedure helps prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering the wound and developing a secondary infection.
- Using a scalpel, the surgeon carefully makes an incision, while grasping the skin a few centimeters beyond the wound. In the face, neck and chest area, doctors try to leave as much healthy tissue as possible to reduce the size of the scar. The changed skin is removed along with the melanoma.
- If the formation is in the second or later stages of development, it is necessary to remove the nearest lymph nodes and fatty tissue. They accumulate cellular elements, which can subsequently lead to relapse of the disease.
- The final stage of surgery is suturing the wound. If the skin has sufficient elasticity and the size of the removed area does not exceed 5 centimeters, doctors tighten the edges together using thin sutures. Larger defects are closed by transplanting soft tissue from other areas.
- The patient's rehabilitation takes place in the oncology department. If necessary, doctors bandage and clean the suture daily, and also teach the victim how to independently care for the wound after discharge.
What does melanoma look like?
At first glance, skin melanoma at the initial stage does not have any signs, since this disease is no different from an ordinary birthmark or mole. Due to the large number of species, difficulties arise in determining the diagnosis, so it is almost impossible to independently recognize the disease and requires the help of a doctor with a complete examination of the body.
The first sign of skin melanoma is considered to be an elevation of the birthmark above the skin, with characteristic signs: bleeding with minor injury, the appearance of irregularities and changes in size.
A dangerous formation, as a rule, is accompanied by excessive pigmentation at the site of the mole, as a result of which the color changes to brown or black. In rare cases, a characteristic feature is a rim around the neoplasm of dark shades. According to statistics, there are about a hundred birthmarks on the human body; if their number increases sharply, this is a reason for immediate contact with a specialized doctor.
Main risk factors
Most often, the disease occurs with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays. Therefore, people should not stay in such premises for a long time.
Important! The ultraviolet factor also includes sunburn, which in turn was suffered in childhood. Melanoma can also occur against the background of a burn.
The second risk factor is quite common - genetically white skin color. Many people will ask why do these people get melanoma? It's simple, white skin color indicates insufficient melanin synthesis. Therefore, the disease can occur with skin phototypes I-II, for example: light skin, eyes, the presence of freckles on the epidermis.
Additional reasons:
- Skin cancer and melanoma occur in Parkinson's disease. Men are prone to the disease; according to the theory, the relationship is primarily due to a general genetic predisposition.
- Age . At a young age, epidermal melanoma is rare; it occurs more often in old age, since the skin is influenced by external and internal factors throughout life. For example: exposure to ultraviolet rays, long-term use of medications, smoking.
- Sexual predisposition. Androgens stimulate the growth of malignant tumors, so melanoma occurs more often in males. But women can also develop the disease, the main reason being long-term use of hormonal drugs.
- Immunodeficiencies. If the function of the immune system is reduced, it cannot recognize and destroy altered DNA cells.
- Benign formations on the skin or precancerous formations.
In addition to these reasons, melanoma can occur when consuming large amounts of fat and animal proteins.
Melanoma symptoms
If we consider the symptoms of the disease, they may vary at different stages. Therefore, the following signs appear depending on the development of the disease:
- changes in the symmetry of formations are observed;
- the coloring of moles (nevi) changes from dark to light color, and vice versa;
- increase in diameter of formations (exceeds five millimeters);
- blurred edges of tumors;
- the density of birthmarks changes to softer;
- begins to secrete colorless or bloody fluid in the affected area;
- A burning sensation occurs and crusts form from the secreting fluid.
Having reached a later stage of development, it is observed:
- pigmentation around the affected area of the skin;
- violation of the integrity of birthmarks and nevi;
- bleeding from neoplasms;
- the occurrence of pain and itching in the affected area.
When metastases appear:
- disturbing pain in the temporal region;
- changes in skin color to gray;
- lymph nodes increase in size;
- convulsions occur;
- sudden weight loss, followed by weight loss and exhaustion of the body;
- a continuous (chronic) cough appears.
Existing forms of skin melanoma
There are three main forms of the disease:
- malignant lentigo. Mainly spreads to the face or neck. In more rare cases, it forms on closed areas of the skin, such as the arms, legs or back.
- nodular melanoma. It is often observed in people who have crossed the half-century mark. This is the most complex form of the disease. Forms on the neck, scalp, back or limbs.
- acral melanoma. Characterized by distribution within the epidermal layer, but often extends outward. Affects the palms, soles, fingertips, or oral mucosa.
Primary diagnosis requires care. There is a classic way to determine the disease:
- Examination of moles for asymmetry and unusual shape.
- Uneven edges of a mole may also indicate the development of the disease. Melanomas have a curved, wavy outline.
- Ordinary moles are uniform in color, but tumors combine several colors or shades.
- They also pay attention to the size of moles. At the initial stage, the “dangerous” mole increases in size.
- “complex” change in a mole. Changes in shape and color, the appearance of other pathological signs, such as itching or bleeding.
If one or more signs are detected, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Types of disease
There are three types of skin melanoma:
- superficially widespread. This is the most common form, accounting for up to 75% of all cases. It is usually characteristic of representatives of the Caucasian race; middle-aged people suffer from the disease more often. The formations in this case are small, complex in shape, with uneven edges. The color can be different: from reddish-brown to dark with bluish splashes. Such neoplasms may have bloody discharge. The tumor grows, spreading across the surface and/or deeper. Vertical growth may not occur for several months and sometimes years;
- nodal Up to 30% of cases occur in this form. This is a more dangerous, aggressive type of skin cancer. It grows quickly (4-24 months) and can also develop on the skin without much damage or change. Symptoms of progressive melanoma of this type suggest vertical growth of the tumor. Its color is uniform - black or dark blue. Sometimes such a tumor is not pigmented, similar to a papule or nodule (but this is rare);
- malignant lentigo. Symptoms of this type of melanoma usually occur in people over 60 years of age. They are detected least often (up to 10% of cases). Usually the disease affects open areas of the body - they are covered with dark or light-colored nodules up to 3 millimeters in diameter. The tumor grows for a relatively long time on the upper parts of the skin (twenty years or more), often including hair follicles.
With such a variety of tumors, it is extremely important to know what to look for so that melanoma is diagnosed on time and allows you to achieve maximum results from treatment.
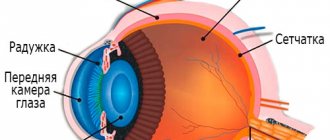
Symptoms of eye melanoma
At different stages of development, the symptoms of the disease may vary:
- At the first stage, there are no symptoms as such, but slight clouding in the retinal area may be observed, which does not affect the level of vision;
- The second stage of development is characterized by tissue inflammation and pain in the eyes. A flashing effect occurs, forming spots and blurry black or white dots;
- The spread of the tumor extends beyond the boundaries of the eyeball, and violations of the integrity of the sclera may be observed;
- The last stage of development of ocular melanoma is accompanied by metastasis of internal organs. The occurrence of severe pain, rapid weight loss, clouding of the lens and hemorrhages are symptoms of the last stage of the disease. In this case, it is extremely important not to confuse the disease with similar tumor formations.
If eye melanoma has reached its peak of development, retinal detachment is possible. Therefore, a timely visit to an ophthalmologist will help determine the correct diagnosis and prevent serious consequences.
Diagnostics
Contact a specialist, and he will prepare the appropriate examination method, which will allow you to determine the current stage of the disease, identify the cause and assist in selecting the optimal, most effective treatment. The following diagnostic methods exist:
- biopsy sampling. The top layer of skin is scraped and the biological material is examined to determine the stage of development and its quality. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, which does not cause harm to health and does not cause pain;
- dermoscopic examination - examination of the deepest layers of the skin under a dermatoscope, which makes it possible to more accurately determine the focus of the disease and the stage of its development;
- cytological research method;
- collection of analysis in laboratory conditions;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the affected area of the skin and internal organs;
- detection of the disease using x-ray examination;
- analysis to determine tumor markers;
- research at the cellular level.
After the examination, doctors make diagnoses based on the results obtained. These methods allow us to determine the current stage of the disease with 95 percent accuracy and assess the general condition of the body. With metastasis, it is possible to determine the localization of tumors.
The prognosis of treatment directly depends on the time of contacting a doctor and diagnosis. If you get tested quickly when symptoms first appear, your chances of recovery can increase dramatically.
Melanosis of the skin: causes, symptoms and prevention of manifestations
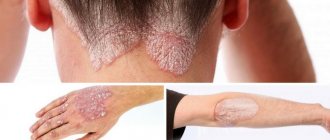
Melanosis is an excessive focal accumulation of melanin in organs and tissues. It appears as unaesthetic dark spots that foundation cannot cope with.
What is it and what are its features?
Melanin is a coloring pigment in the basal layer of the epidermis. It is produced by melanocyte cells to protect against UV radiation. The color of the skin and eyes is determined by the number of granules of a given pigment. They are a security system for DNA: they protect cell nuclei from genetic deformation by ultraviolet radiation.
Light-skinned people have little melanin, while dark-skinned people have the epidermis filled with it as much as possible. Melanocytes, regardless of the time of year, produce pigment. When the mechanism of melanin formation is balanced, the number of pigments is normal, and they are activated only under the influence of ultraviolet irradiation (sun, solarium), covering the body with a tan.
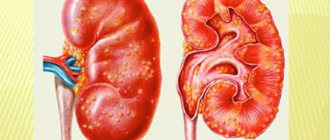
Sometimes the pigment begins to be deposited in excess in the skin and in those parts of the body where melanocytes do not exist (in the mucous membranes, in the brain, in the kidneys). This disorder is called melanosis.
Causes and symptoms
Cutaneous melanosis can be caused by:
- diseases of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries;
- severe infectious diseases: syphilis, malaria, dysentery and tuberculosis;
- intoxication with petroleum products, resins, arsenic;
- taking furocoumarins, sulfanimods, tetracycline;
- extreme stage of lice infestation;
- vitamin deficiency (scurvy, pellarga);
- heredity.
Symptoms of melanosis (other names - melanopathy, melasma):
- spotty, diffuse pigmentation of the skin (may occur in newborns);
- increased sensitivity of the epidermis to ultraviolet rays;
- consolidation of focal pigmentation into large zones;
- dermatic edema, hyperkeratosis (thickening of the stratum corneum), atrophy of the dermis;
- itching and irritation of the affected areas;
- disorders of the nervous system and endocrine glands.
Kinds
Dermatologists distinguish two types of congenital melanosis:
Progressive reticular melasma is a disease of hypersensitivity to sunlight.
Characteristic signs of pathology are:
- extensive patchy pigmentation;
- the formation of melanophores (mobile pigment cells), accompanied by edema and keratosis.
Excessive melanoblastosis (neurocutaneous) is a tumor melanosis transmitted to the fetus through the placenta by maternal melanoma metastases. Symptoms:
- accumulations of melanophores on the body of a newborn;
- histological analysis shows a high concentration of melanin in brain cells and neurons.
Melanosis can develop in two layers of skin:
| Type of cutaneous melanosis | External symptoms | Laboratory results | Treatment effectiveness |
| Epidermal | Black, dark and light brown spots | Melanin in the superficial layers of the dermis. Melanocyte size is increased, dendrites are activated | He is being treated. Easy and in a short time |
| Dermal | Gray-blue spots | Macrophages in the superficial and middle layers of the dermis | He is being treated. Long and difficult to influence |
Melanopathies are divided into primary (the causes are not clear) and secondary (the results of disorders associated with other diseases).
Primary:
- hereditary pigmentation: freckles, melanism, Peutz-Jeghers-Touraine syndrome, lentiginosis;
- pigmented nevi (moles), juvenile lentigo;
- linear pigmentation of the forehead, chloasma, melasma, senile lentigo;
- cachectic melasma, Addison's disease, toxic hyperpigmentation of the dermis;
- drug-induced Riehl melanosis, Hofmann-Habermann toxomelanoderma, pigmented reticular poikiloderma of the neck and face;
- actinic melasma, Buschke-Eichorn marble pigmentation, parasitic hyperpigmentation.
Secondary:
- melanosis due to syphilis, tuberculosis;
- hyperpigmentosis after lichen planus, acne, neurodarmatitis, eczema.
Types of hypermelanosis that affect the face are considered unpleasant from an aesthetic point of view:
- juvenile and senile lentigo - pigment spots: in young men - rounded in shape, affecting the mucous membranes, in older people - accumulations of pigmented areas, a clear sign of skin aging;
- Becker's nevus is a hyperpigmented area of skin with increased hair growth;
- melasma – brownish-yellow and brown spots due to hormonal changes (pregnancy);
- photodermatosis - hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation in the form of a weeping rash and itchy redness (sun allergy);
- post-acne symptom - spots after acne.
Diagnostics
Hypermelanosis of the skin is fraught with potential danger: sometimes they provoke the appearance of a malignant melanoma tumor. Therefore, when pigmented areas appear on the body, it is important to consult a dermatologist who will conduct a diagnosis to establish the type of melanosis and determine the course of treatment.
Methods for diagnosing melanosis of the skin:
- Visual inspection (with a Wood's lamp) and palpation of the area.
- Finding out the medical history of the patient and his relatives.
- Dermoscopy (examination with a dermatoscope, which provides a multiple magnification of the examination area).
- Computer diagnostics (hardware examination of the skin and automatic comparison with the standard).
- Histological study of a microslide (section of the epidermis and dermis).
- Biopsy (in cases where there is confidence that hyperpigmentation has not led to the development of melanoma).
Treatment
The initial stage of melanosis can be treated with folk remedies, rubbing the skin with hydrogen peroxide, parsley or lemon juice, apple cider vinegar or salicylic acid. To defeat hypermelanosis, drug therapy will be required in several stages:
| Direction of treatment | Therapy |
| Eliminating irritants | Application of photoprotective creams |
| Elimination of contacts with toxic substances (polycyclic hydrocarbons) | |
| Treatment of provoking diseases (pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, nervous and endocrine systems) | |
| Basic treatment | Use of endocrine gland drugs |
| Anti-intoxication drugs | |
| Taking vitamins C, PP, A, E | |
| Pharmacy antioxidants: enterosorbents and hepatoprotectors | |
| Antihistamines | |
| Corticosteroids (for severe forms) | |
| Locally - lotions | |
| Removal of hypermelanotic lesions | Enzyme, electrical, chemical or ultrasonic peeling |
| Biorevitalization, mesotherapy (injections) | |
| Photothermolysis (a new key in treatment!) | |
| Laser resurfacing |
Forecast and prevention of occurrence
Skin melanosis can be successfully cured with timely consultation with a doctor. Many forms of hardware cosmetology allow you to completely remove hyperpigmentation and restore the epidermal cover.
The main preventive measure against melanosis is the use of protective agents against UV radiation. The filters they contain absorb, reflect and scatter ultraviolet rays.
Creams recommended:
- people with sensitive skin;
- predisposed to melanosis;
- after cosmetic procedures: dermabrasion, peeling, whitening, laser resurfacing, plastic surgery;
- during periods of physiological changes (adolescence, pregnancy).
The second measure is to carry out cosmetic peeling and whitening procedures during the season when the sun is least active. The best time is from October to January.
Proper nutrition and the use of vitamin complexes with vitamins C, PP, A and E are recommended.
The article has been verified by portal experts
articles:
(2 3.50 out of 5) Loading...
Treatment
The treatment method for skin melanoma will depend on the severity of the disease.
- Surgical intervention (the melanoma is removed and 1 to 3 centimeters of skin are excised to eliminate the source of the disease);
- Radiation treatment (this method is typical for the second stage of the disease, as cancer cells begin to spread to the lymph nodes);
- Having reached the third stage of development, therapeutic therapy is prescribed (chemotherapeutic drugs that suppress the affected cells are taken);
- In advanced forms of the disease, combination therapy is prescribed, which includes radiation and chemotherapy (systemic or regional). As a rule, the drugs Vero Tamoxifen, Zitazonium, Dacarbazine Lachema, Deticen, and Belustin are used;
- Radiation therapy is the most effective method in the treatment of skin melanoma, since irradiation allows it to reach the deepest layers of the epidermis and act on the site of the disease;
- Taking immunotherapy drugs helps suppress or destroy cells affected by cancer. This method is prescribed after surgery for several months to reduce the risk of relapse.
After you undergo treatment, you must regularly visit a dermatologist and oncology specialist and submit biological material for analysis in order to monitor your health and exclude relapses of skin melanoma.
It is prohibited to treat a disease with folk remedies without consulting a doctor, since practice has established that the remedies created by the people have a detrimental effect on the body and the disease progresses at an accelerated pace.