First aid
If an adult or child is bitten by an animal, the following actions must be taken:
- Shallow bite . Wash the injured area well using antibacterial soap or laundry soap. The latter is more effective, since it contains more alkali. As is known, the rabies virus dies when exposed to alkali. Keep the injured area under running water for at least 5 minutes.
- Strong bite . If the dermis is damaged sufficiently, the bite is deep, the dermis is torn, and there is a strong flow of blood, then there is no point in trying to stop it. The animal's saliva is washed away along with the blood. Afterwards, wash the wound with soap and water for a quarter of an hour.
In any case, actions in case of animal bites should include:
- The wound itself and the skin around it must be treated with an antiseptic. This can be an alcohol solution of iodine, ethyl alcohol, Miramistin and other means.
- Apply a sterile bandage over it. This will help avoid secondary infection.
Then try to take the victim to the emergency room.
Emergency ambulance call
Immediately after providing first aid for an animal bite, call a doctor if:
- scratches and bites came from a street animal, and there is no information about whether it is vaccinated;
- the bite is extremely deep, and the dermis is torn so much that the bottom of the wound is not visible;
- the bite was caused by an animal that is drooling profusely.
In this case, the person is urgently hospitalized with suspected infection. If you are bitten by a cat or dog, be sure to observe the behavior of the animal. This will allow you to determine what caused the behavior - character or rabies.
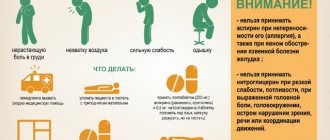
If bitten by an insect
The most unpleasant consequences of a conflict with insects are an allergic reaction to bites and infection of the wound. In the first case, antihistamines will be useful, in the second - antiseptics.
When mosquitoes, midges and horseflies bite, they leave particles containing microorganisms that can lead to infection of the wound.
Wash the affected area with warm water and soap, apply anti-itch ointment.
When a bee , a sac of poison and a sting remain in the skin. Remove them without squeezing, so as not to provoke the release of poison. Wash the bite area with soap and water, apply an antiseptic, then a soothing ointment.
If an insect bites your hand, first of all remove the rings from your fingers - there is a possibility of swelling.
If an insect bites you on the neck, lips, tongue, or area near the eyes , apply ice to the affected area, take an antihistamine, and consult a doctor immediately. The swelling caused by such bites is dangerous.
The tick must be removed very carefully, trying not to tear off the proboscis embedded in the skin. This is where tweezers come in handy: grab the parasite with it and, shaking it slightly, pull it out. Disinfect the wound immediately.
Diagnostic measures and therapy
During the initial visit to the clinic in case of a bite from domestic or wild animals, an anamnesis is taken. Sampling for bacteriological examination and initial treatment of the damaged area are also indicated. Treatment of the wound consists of washing the injured area with water or saline solution.
For shallow lesions, disinfectants such as:
- povidone-iodine;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin, etc.
Wound suturing is recommended for fresh, uninfected wounds. Fresh are considered those after which no more than 6 hours have passed. Indications for hospitalization of a bitten person are:
- sepsis;
- fever;
- severe swelling;
- loss of limb function;
- infection with dangerous infections, etc.
Prescription of preventive antibacterial treatment is indicated for bites by cats, foxes, rats, and dogs. Also, antibiotics for an animal bite are prescribed if the wound is localized in the area of the limbs, face, genitals, severe injury is observed, or bones and joints are affected.
The choice of antibiotic is made based on the test results obtained. Before this, therapy is carried out with amoxicillin/clavulanate. Take 625 mg 3 times a day for adults. In case of a complicated bite, the antibiotic is administered intravenously.
What to do with a bitten animal?
What to do after a bite with an animal directly depends on what kind of animal it is. The simplest case is if it is your animal or the animal of a friend. Then you will know for sure whether he has received all the necessary vaccinations and how healthy the animal is at the moment.
If the bitten animal is not familiar to you, but it looked well-groomed and domesticated, then you need to try to find out who its owner is. After establishing the identity of the owner, you need to ask him for all the information about the animal, its health status and vaccinations. It is advisable that the information be confirmed by a certificate from a veterinary hospital. But even the presence of such a certificate does not eliminate the need for further monitoring of the animal.
The most difficult thing is if you are bitten by a wild or stray animal. In a situation with wild animals, vaccination against tetanus and rabies must be immediate and complete, since the likelihood of infection is extremely high. Wild animals practically do not attack people, and therefore this situation clearly indicates that the animal has some kind of disease.
A cat bite usually causes a deeper puncture wound than a dog bite, and therefore is more dangerous in terms of infection.
If you are bitten by a stray animal that you can track, for example, it constantly lives next to a store, restaurant, or in the yard, then you will have to visit it every day for 10 days. If something happens to the animal, such as it getting sick, dying or disappearing, a full course of rabies vaccination must be started immediately. If the vaccination course began immediately after the bite, then after 10 days, if the animal is in good health, vaccination can be stopped.
Bites from dogs, cats and other animals
Consequences
In addition to injury and bleeding, there is a risk of infection, including the rabies virus, in the case of large and.
Algorithm of actions
- Stop the bleeding and apply a bandage to the wound
- Assess the risk of rabies and refer for vaccination (usually at the nearest emergency room) if indicated.
- Assess the risk of tetanus and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate prophylaxis → table. 10-2.
- Prescribe an antibiotic prophylactically (drug of first choice - 1.0 g 2 × per day) p / o for 3-5 days for wounds: puncture or deep (especially due to cat bites); from crushed tissues; in areas with impaired venous or lymphatic drainage; hands or close proximity of bones or joints; requiring surgical treatment; in patients with weakened immune systems; due to bites inflicted by humans.
Common viper bites
The most common venomous snake in the Russian Federation; usually brown or brown in color (sometimes gray or greenish), with a diamond pattern along the body and an H or X shaped mark on the head.
Mechanism and consequences
The venom contains, among other things, phosphatase (which causes the release of histamine) and hyaluronidase; also hemolytic effect, can lead to kidney damage and hemorrhagic syndrome. 1/4 of those bitten have no symptoms of poisoning, mortality
Symptoms: at the site of the bite - a small, leaking, painful wound with surrounding swelling of the subcutaneous tissue; in case of severe poisoning, over time the following may occur: abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, rash and petechiae on the skin, bleeding from the gums, hematuria, tachycardia, hypotension, disturbances of consciousness.
Algorithm of actions
1. Cover the wound with sterile gauze and immobilize the limb. Suction, cutting and any other manipulation of the wound area are harmful.
2. If swelling of a limb spreads to the torso or if severe general symptoms appear, especially disturbances of consciousness:
1) maintain the functions of vital organs;
2) slowly inject prothiotrium serum intravenously (into the non-affected limb!) it is a foreign protein that can cause anaphylaxis. If antithrombotic serum is not available → apply an algorithm for the treatment of anaphylaxis, especially the administration of adrenaline;
3) perform a blood draw for a general analysis and determination of the concentration of electrolytes and creatinine in plasma, as well as the Ministry of Emergency Situations, prescribe a general urine test.
Consequences
The consequences of animal bites depend directly on the individual. Dog and cat bites can cause such complex consequences as rabies. If help is not provided in a timely manner, the person dies. Therefore, immediately after a bite, preventive vaccination is carried out.
In addition, the following consequences may occur:
- infection of the body by various bacteria;
- poisoning of the body with toxins;
- psychological shock;
- tissue scarring;
- tetanus;
- contractures, etc.
Even snake bites should not be treated with indifference, since some are poisonous and the bite can provoke intoxication of the body.
Bite wounds - how are they different?
Bite wounds are different in nature from others. Firstly, because bacteria and infections can penetrate into the blood of an animal (all of them are contained in the saliva of animals). The risk of contracting tetanus and rabies from wild street animals should not be excluded.
Bacteria from the animal's saliva penetrate into the blood, as a result there is a risk of bacteremia - a disease leading to complications in the form of: brain abscess, meningitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis and even arthritis.
Types of Animal Bites
There are two types of bites, including:
- A bite in which the animal only pierces the skin with its teeth is superficial;
- A bite in which the damage to the skin is so severe that the bleeding cannot be stopped and the edges of the wound are not visible - a lacerated bite.
Damage to the neck and head, as well as damage to the integrity of the skull bones or mechanical damage to internal organs are considered extremely dangerous. Such injuries can be severe and even fatal.
Prevention
To prevent animal bites, you need to follow simple measures:
- do not feed or try to catch a wild animal such as a raccoon, squirrel, fox, etc.;
- avoid contact with wild animals, even those who seem friendly;
- do not stick your fingers into the cages of animals in the zoo or pet stores;
- be extremely careful when playing with pets;
- do not disturb the animal when it is eating or feeding its young.
By following simple rules, you can protect yourself. But if the attack could not be avoided, then you should not hesitate to contact a specialist.
Why are animal and insect bites dangerous?
Nature has endowed insects and animals with protective properties: stings, fangs, jaws, claws, poisonous substances. An encounter with wild, unorganized animals that bite a person can result in infection with rabies, tetanus, and whooping cough. Insect bites cause allergies, poisoning, and diseases of the nervous system.
Unknown dog bites
Bites from unknown dogs are dangerous. To prevent such a bite, you should never touch or stroke other people's dogs, look them in the eyes (this is a signal to attack first), run, give food, and, moreover, correct it (the dog will protect the food). If the dog approaches, you should stop. If bitten, first aid must be provided. If the bleeding is small, there is no need to stop it; this is a specific wound wash. Then wash the wound with any disinfectant (if none is available, dilute laundry soap in water); treat the skin around the wound with 5% iodine tincture, apply an aseptic bandage, and send to a medical facility where a special serum (anti-rabies) is injected. They give 7...25 rabies vaccinations in the form of subcutaneous injections into the abdomen. The dog should be isolated for 10 days, because the disease (rabies) may appear in it in 8...10 days. If the animal has died, an autopsy is performed to diagnose rabies.