Symptoms
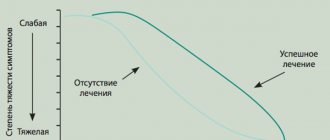
If a doctor has diagnosed a mild concussion, the symptoms of which disappear quickly enough (within a few hours or days), the patient does not need hospital treatment.
The patient may be at home, where he should remain in bed. In this case, medications are rarely required; the patient often only needs to take traditional medicine (sedative infusions and decoctions). If you suspect a moderate or severe concussion, loved ones should seek emergency help. The first signs of a concussion, indicating a serious condition:
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting.
- The occurrence of severe dizziness. The condition is controlled with medications.
- The appearance of black dots, spots, and splitting of objects in the eyes. Hearing impairment (constant noise or ringing) that does not go away for a long time.
- Problems with orientation (uncertain movements, unsteady gait).
- The appearance of severe weakness.
- The occurrence of severe headaches. In such cases, the patient is prescribed additional examinations (MRI or CT scan of the brain) to exclude the occurrence of an internal hematoma.
- The appearance of speech dysfunction (slurred speech, forgetfulness, difficulty answering simple questions).
With a moderate or severe concussion, single symptoms from the above may appear or several symptoms may occur simultaneously.
A tumor appears and a hematoma forms.
- pain;
- tumor;
- hematoma;
- limitation of motor function.
The wounded area swells, causing suffering. The painful condition periodically intensifies as a result of the effect on the nerve endings. Then it subsides. The injury lasts for a long time, up to several months, depending on the severity of the injury.
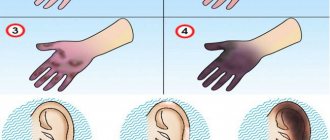
If the integrity of the vessels is damaged, a hematoma appears as a consequence of injury to small vessels. The bruise does not go away for up to two weeks, changing color from purple to yellow.
Breathing difficulties occur after a chest injury.
The blow affects the limitation of vital functions of the body: lameness, decreased vision, it is impossible to move the arm. Breathing difficulties occur after a chest injury. The rib area feels like it's burning with pain when trying to breathe in air. It is difficult to breathe deeply, and inside the organs are tightly compressed. I want to squeeze my chest tightly with my hands. Only after this is it possible to breathe.
Short-term disturbance of consciousness (up to 30 minutes), retrograde and anterograde amnesia, headache, nausea, vomiting, pallor of the skin, tachycardia, short-term arterial hypertension, spontaneous nystagmus, sluggish pupillary reactions, slight smoothness of the nasolabial fold, unstable asymmetry of deep and superficial reflexes.
Concussion, according to medical qualifications, is divided into three degrees, and first aid is provided based on visible clinical signs.
- The first degree of concussion is characterized by dizziness, there may be a slight fainting that lasts 1-2 minutes. The victim complains of nausea, one-time vomiting, stress causes increased breathing and pulse jumps. After about thirty minutes the condition returns to normal, but a headache may remain.
- In the second degree of concussion, a person’s disorientation in space lasts more than twenty minutes, the fainting is deep, the victim has a gait disturbance, weakness and trembling of the limbs. Visually noticeable pallor of the skin, sweat on the face, discrepancy of proteins when looking at a certain object. Speech is incoherent, reaction to what is happening is slow.
- Anyone can identify the symptoms of a third-degree concussion. This is a deep faint, after which the victim does not remember the moment of injury. There is pale skin, breathing problems, slow pulse, and profuse sweating. The person cannot stand on his feet, his movements are uncoordinated, and his speech is slurred. With a severe concussion, there is a risk of injury to the internal parts of the brain, rupture of small and large vessels, and coma.
Signs of a concussion
It is quite difficult for a person far from medicine to recognize a concussion in a victim, especially if the injury is not too serious and does not have obvious external signs. It is worth noting that not all symptoms appear immediately. Some may make themselves felt several hours after the incident.
In addition, each degree of concussion (there are only three) also manifests itself in its own way. It turns out that you just need to understand whether there is a concussion and decide on further actions. The following are typical signs of a concussion.
- noticeable external injuries, nosebleeds;
- Strong headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- inhibited reactions, loss of orientation in space;
- visual and hearing impairments;
- unsteadiness in the legs.
Help for severe cases
Lay the victim down. In case of vomiting - prevention of aspiration of vomit into the respiratory tract. Cold on the head.
First aid for a concussion depends on the severity of the injury. How serious the situation is can be seen from the obvious signs.
Mild degree
A mild degree can be determined in the first hour after hitting the head. In some situations, a short-term loss of consciousness occurs for up to 5 minutes, but it may not exist. After 20 minutes, the person’s condition returns to normal: he can speak clearly, walk independently and navigate in space. Subsequent symptoms usually appear within 24 hours.
Average degree
Moderate, like mild, is not always accompanied by fainting, which in rare cases can last more than 5 minutes. Immediately after an injury or return of consciousness, the patient experiences a severe headache, is unable to clearly explain what happened, has difficulty speaking and orienting himself in space.
Severe degree
The most dangerous situation both at the time of the incident and for the state of health in the future. As a rule, it is accompanied by fainting, but in rare cases a person can remain conscious all the time.
The victim does not remember what happened to him. When trying to stay on his feet, he falls, and in some cases he cannot even stand up. As a result of disruption of most brain functions, he is unable to speak clearly and describe his state of health. It is accompanied by noise in the head and ripples in the eyes, severe nausea and weakness.
The worst sign of severe severity may be bleeding from the ears during a concussion. This fact indicates a skull injury, which can be either open or closed.
It is important to understand that no action you take will change the severity of the injury already received, but can alleviate its consequences and significantly speed up the healing process. There are also cases in which it is more advisable to do nothing until the ambulance arrives.
Now we will talk about emergency measures, that is, about desirable actions on the part of people who are close to the victim and who do not have medical education. After calling an ambulance, everything must be done to alleviate the patient’s general condition.
General recommendations include the following:
- providing the patient with peace;
- ensuring proper ventilation if located indoors;
- abstaining from active actions (you should not try to get a person to talk, put him on his feet, give him something to drink, feed, etc.);
- eliminating noise and harsh light source.
These steps are recommended for all types of concussions, brain injuries, and contusions. Then it all depends on the specific case and additional symptoms.
Regardless of how exactly such specific bruises were received by a person, they end with the brain hitting the inner walls of the skull. The result is not long in coming, manifesting itself in swelling of varying degrees of severity. It is the swelling that causes the manifestation of the dominant symptoms of a standard concussion.
An external mechanical influence due to increased pressure on the head area can provoke such a phenomenon. This definition even includes everyday hits against lockers or during a game of football. Sometimes this pathology is a consequence of a sharp fall or sudden braking of a vehicle.
In ordinary life, most often the victims of the disease are children of approximately school age who do not control their strength during various outdoor games.
In order for pre-medical care to have an effect, experts recommend first thoroughly understanding the diagnosis. Even ordinary people will be able to identify it if they use a diagram of the main features as a guide. The sooner medical care is provided to the victim, the faster he will complete his rehabilitation course.
Due to the fact that human brain activity has not been thoroughly studied by scientists, no one can accurately answer how serious the consequences of ignoring an injury may be. It is believed that in the absence of timely support, patients will not be able to quickly cope with even the simplest tasks in the future. Such inhibition can be observed for months.
Also, in untreated patients, the risks of developing:
- alcohol addiction;
- Parkinson's disease;
- sudden death.
To prevent such a sad outcome, it is worth learning to recognize threatening symptoms and provide high-quality pre-medical care.
If the patient is in a supine position, he cannot be lifted - this will be done by ambulance workers. The best thing to do is to carefully place a flat pillow or a sheet or towel folded several times under his head. The use of a high pillow is unacceptable, since there is a possibility of additional injuries to the neck or spine.
If the patient has lost consciousness, reviving him using ammonia, splashing water and similar methods is strictly prohibited: a sudden movement of the head as a result of awakening can cause additional brain damage.
Vomiting can start at any moment, so carefully turn the victim's head to the side so that as a result of the possible release of vomit, he does not choke or choke.
Providing first aid for severe concussion must be competent and timely. The faster the patient gets into the hands of qualified specialists, the faster his health will be restored. Maximum non-interference will be required from you.
If you lose consciousness, do not, under any circumstances, try to revive the victim. Do not try to rotate it or change its position - this is dangerous. Open windows and doors to improve air circulation in the room or vehicle if the incident occurs in an enclosed space. If you are outdoors, try to protect the victim from direct sunlight in an accessible way.
In case of rain or cold, do not try to dress him, but cover him with a blanket or your own outerwear, if possible. Monitor your symptoms carefully: the more detailed information the ambulance team receives, the more timely and qualified their assistance will be.
Here you need to act extremely carefully, since we are talking about traumatic brain injury. It is likely that the upper spine was also damaged, so the patient’s head position must be stable.
Do not try to provide him with a more comfortable position, place a pillow on him or transfer him to a soft surface: the patient can only be carried on a hard stretcher and this should be done by ambulance workers.
In any case, you won’t be able to stop bleeding from your ears during a concussion on your own, but blood loss can lead to the most undesirable consequences. In this situation, every minute counts. When you call the ambulance, describe the situation in detail. A resuscitation team may need to be dispatched.
Medical care for head injuries is provided only in a hospital setting. The only action on the part of emergency personnel is to treat the wound or stop bleeding, if any. Other treatment methods are permissible only after a thorough diagnosis.
Taking medications, including painkillers, is possible only with the permission of the attending physician: there are patients who are allergic to certain categories of medications, and, in addition, there are cases when taking medications can blur the symptoms and complicate the diagnosis. It follows from this that self-medication is strictly prohibited.
The recovery period after injury lasts from one to three weeks. In elderly patients and people suffering from other diseases, the treatment process may be delayed. In order for the patient to return to a full life as quickly as possible, during sick leave he must follow the following recommendations:
- follow the schedule for taking medications prescribed by the doctor;
- refrain from listening to music, watching movies, working on the computer, reading and activities that require visual concentration, such as small crafts, crossword puzzles, online games, etc.;
- maintain bed rest, avoid sudden movements;
- do not be nervous, exclude the possibility of any, even the most minor stress;
- get as much rest as possible - sleep and rest in this case are the best medicines;
- follow a diet, eat foods rich in vitamins, refrain from “heavy” foods such as fatty meats, mushrooms, etc., since the body spends too much energy to digest them;
- regularly ventilate the room, since fresh air not only promotes a speedy recovery process, but also alleviates symptoms;
- eliminate sources of bright light - it irritates the eyesight;
- talk on the phone as little as possible (ideally, don’t talk at all);
- Do not play sports under any circumstances, avoid any activity.
As an aid, with the permission of the attending physician, you can use relaxing herbal decoctions and other folk remedies - this will certainly help the patient with a concussion and alleviate his condition.
Complications can arise in two cases: if the treatment rules were not followed, or as a result of an unfortunate combination of circumstances, the patient received an additional injury or health problem.
Complications are as follows:
- sleep disturbance;
- confusion;
- lack of appetite;
- hearing and speech impairment;
- frequent vomiting;
- severe tinnitus and unbearable headaches;
- hallucinations;
- problems with wound healing (if any) or new bleeding;
- blood from the nose;
- blood pressure disorders;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- new loss of consciousness.
In this situation, we are no longer talking about the rules of first aid for a concussion. Self-medication is strictly unacceptable, since both the health and life of the patient are at risk. It is necessary to contact a physician who has previously observed the patient and is familiar with his clinical picture. Most likely, urgent hospitalization will be required. Further recommendations from medical personnel may be individual.
Degrees of concussion
First aid for a concussion depends on the severity of the injury. How serious the situation is can be seen from the obvious signs.
Mild degree
A mild degree can be determined in the first hour after hitting the head. In some situations, a short-term loss of consciousness occurs for up to 5 minutes, but it may not exist. After 20 minutes, the person’s condition returns to normal: he can speak clearly, walk independently and navigate in space. Subsequent symptoms usually appear within 24 hours.
Average degree
Moderate, like mild, is not always accompanied by fainting, which in rare cases can last more than 5 minutes. Immediately after an injury or return of consciousness, the patient experiences a severe headache, is unable to clearly explain what happened, has difficulty speaking and orienting himself in space.
Severe degree
The most dangerous situation both at the time of the incident and for the state of health in the future. As a rule, it is accompanied by fainting, but in rare cases a person can remain conscious all the time.
The victim does not remember what happened to him. When trying to stay on his feet, he falls, and in some cases he cannot even stand up. As a result of disruption of most brain functions, he is unable to speak clearly and describe his state of health. It is accompanied by noise in the head and ripples in the eyes, severe nausea and weakness.
The worst sign of severe severity may be bleeding from the ears during a concussion. This fact indicates a skull injury, which can be either open or closed.
First aid for a concussion
With age, a person loses strength, becomes confused in coordination, and loses vision and hearing. Old people do not want to put up with age and continue to live an active life: they walk with their grandchildren, help with housework, work in the garden, and enjoy beekeeping and fishing. Age-related changes in blood vessels, bones and tissues form a severe hematoma even with light blows. Elderly people cannot be treated on their own. Even a minor injury can cause complications.
Rest and fixation of the source of pain will help to avoid serious consequences.
Rest and fixation of the source of pain will help to avoid serious consequences. The doctor should prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Local anesthetics in the form of ointments and creams reduce hematoma. An accident with an elderly person undermines health and aggravates chronic illness. It is necessary to act quickly and carefully to help in moments of tragedy.
The goal is to relieve physical suffering. The following procedure will help you avoid complications after injury:
- stop the risk factor;
- restore cardiac and respiratory functions;
- stop the bleeding;
- fix the fracture;
- prevent complications;
- support the vital functions of the victim’s body.
Regardless of the nature of the injury, injury requires responsible handling. A fall or blow can trigger a serious diagnosis. It is better to see a doctor for an objective assessment of any degree of bruise. Qualified treatment relieves pain and bruises in a few days. Ignoring a medical examination on the principle that “it will heal on its own” can lead to a serious outcome. Timely assistance for a bruise will save a person from health problems.
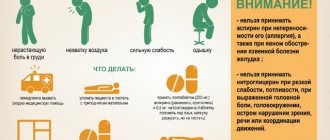
- Ensuring peace. The conscious victim must be placed on a flat horizontal surface with his head raised.
— The unconscious victim is placed on his right side, his face is turned to the ground, his left arm and leg are bent at the joints. First you need to make sure that the patient does not have bone fractures. This position is necessary to prevent the tongue from sinking, suffocation from vomit and the free passage of air into the lungs.
If possible, tight clothing should be removed. During the cold season, the patient is covered with a blanket. If the victim shows signs of spinal cord damage - lack of sensitivity in the limbs, numbness and immobility, then it is not recommended to touch the patient and move him from the place.
— In case of breathing problems or weak cardiac activity, first aid consists of performing a heart massage; before doing this, you need to make sure that the ribs are not damaged. It is advisable not to let the victim sleep until the doctor arrives, distracting him with conversations and questions. You can apply ice to the impact area, or frozen foods can replace it.
If there are wounds on the head, they are covered with an aseptic bandage; the patient is not recommended to give any liquids to drink, as this may cause vomiting. In case of prolonged absence of medical care, analgesics and sedatives can be given. Children of any age should be immediately taken to the hospital after being injured; if their condition is serious, they can use a passing vehicle for transportation.
The events are the same. Intramuscularly 2 ml of 50% analgin solution.
How not to help with a concussion: the main “taboo” of helping
Head injuries can have serious consequences, so a doctor's examination is the first thing the victim needs to ensure. Even when the symptoms are ambiguous and it is difficult to make a diagnosis, the patient can expect hospitalization and examination in a hospital.
If you must provide first aid for a head injury and possible concussion, your main goal should be not to harm the victim. Let’s remember the main “don’ts” for a concussion:
- It is not recommended to move a patient after an injury. This can only be done by a medical team after a preliminary examination.
- Do not give food or drink to the victim if a concussion is suspected. This may cause vomiting.
- Absolutely refrain from administering any medications to a person with signs of a concussion. The body's reaction to drugs can lead to worsening of the condition and irreparable consequences.
- Never slap the face or shake a victim who has lost consciousness; this will only worsen the injury.
So the warnings are clear, but what about the recommendations? Let's look at the rules for providing emergency care for a concussion.
Medical emergency care
Medical Center
Peace. Clearing the airways from vomit. If the tongue sinks - fixation by stitching.
Immediate evacuation to a hospital (medical hospital) by ambulance, in a lying position on a stretcher, accompanied by a doctor or paramedic. For nosebleeds, lie on your side.
Omedb, hospital
Hospitalization in a surgical or neurosurgical department. Echoencephaloscopy, radiography of the skull. Lumbar puncture. If intracranial pressure increases, dehydrating agents are used; for intracerebral hypotension - drink plenty of fluids, intravenous administration of 5% glucose solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Nechaev E.A.
Instructions for emergency care for acute diseases, injuries and poisonings. Part I
Published by Konstantin Mokanov
Medical Center
Omedb, hospital
Medical Center
Omedb, hospital
Diagnosis of injury
In case of a concussion of any complexity, you must contact the medical center for medical assistance. A child or adult must be examined by the following specialists:
- traumatologist;
- neurosurgeon;
- neurologist.
Interesting Help if you cut your leg with glass
To clarify the diagnosis, doctors conduct a general examination of the victim and collect anamnesis. The following research methods are used for diagnosis:
- neurosonography;
- X-ray of the skull;
- echo-encephalography;
- computed tomography;
- MRI;
- lumbar puncture;
- electroencephalography.
Signs of bruise
It is quite difficult for a person far from medicine to recognize a concussion in a victim, especially if the injury is not too serious and does not have obvious external signs. It is worth noting that not all symptoms appear immediately. Some may make themselves felt several hours after the incident.
In addition, each degree of concussion (there are only three) also manifests itself in its own way. It turns out that you just need to understand whether there is a concussion and decide on further actions. The following are typical signs of a concussion.
Primary symptoms:
- noticeable external injuries, nosebleeds;
- Strong headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- inhibited reactions, loss of orientation in space;
- visual and hearing impairments;
- unsteadiness in the legs.
Primary symptoms appear immediately or within a few minutes after the injury. In a mild form, they may not appear immediately or not be expressed. One of the listed symptoms is enough to understand that the injury is more serious than a bruise that does not pose a significant threat to health.
If your fears are confirmed, you need to take the necessary measures and, before the ambulance arrives, provide first aid for a concussion to the victim.
Secondary symptoms:
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- feeling of weakness;
- pale complexion;
- loss of appetite;
- sleep disorders.
Depending on the severity of the concussion, the time for secondary symptoms to appear varies from 20 minutes to several hours after the incident. It turns out that first aid for a concussion is no longer relevant - treatment is needed. In this situation, you will be required to provide the victim with conditions under which his condition, if not improved, then at least will not worsen.
Less common symptoms:
- trembling of the eyeballs, inability to focus;
- confusion, inappropriate answers;
- amnesia, which can be either short-term or long-term.
The signs listed above occur in rare cases and are not always symptoms of a concussion, therefore they are considered in conjunction with the others. However, they are serious and require monitoring and urgent action.
The first symptom of a bruise is swelling at the site of the impact and short-term pain. Then, depending on the damaged tissue, they can gradually increase in size. The result is constant intense pain, which causes dysfunction of the muscles in the affected area. The lesion is significantly enlarged relative to the original one.
- First. This is a slight bruise. Minor skin injuries in the form of abrasions and scratches that do not require special treatment.
- Second. It is characterized by rupture of muscle tissue, the appearance of swelling, hematoma and severe pain.
- Third. In this case, muscles, tissues and tendons are already damaged. This degree of injury is diagnosed more often with dislocations.
- Fourth. Noticeable swelling forms, internal organs suffer, so hospitalization is required for a more accurate diagnosis of the bruise.
When diagnosing a bruise, it is very important to distinguish it from a fracture. The latter injury is more serious. It is a partial or complete violation of the integrity of cartilage or bone, which is accompanied by damage to the surrounding soft tissue. A bruise should not be confused with an open fracture. In this case, the bone is visible and there is bleeding. A closed fracture may well not be recognized, because it has symptoms similar to a bruise. They can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- the pain syndrome during a fracture only intensifies over time, and during a bruise, on the contrary, it gradually subsides;
- swelling in case of a bruise appears immediately, and in the case of a fracture only after 2-3 days;
- damage to the integrity of the bone prevents you from leaning on it due to sharp acute pain;
- when the bone is displaced, one can visually observe the deformation of the limbs and even a change in their length compared to healthy ones.
Severity of injury
In order to understand how to respond to what happened to a person, it is important to assess the severity of the injury. Concussion is usually classified into 3 degrees of severity:
- First degree (mild concussion). A slight fainting state is observed, and all manifestations disappear after 25-30 minutes. The following symptoms are possible: loss of consciousness for several seconds or minutes; nose bleed; nausea (sometimes vomiting); headache.
- Second degree (concussion of moderate intensity). In this case, loss of orientation lasts from 30 minutes to several hours. The first symptoms are an inadequate reaction; fog in the eyes and tinnitus; loss of concentration in space and time; absent-minded look.
- Third degree (severe concussion). The following symptoms are observed: loss of consciousness; signs of concussion; general weakness; excessive sweating; pale skin; loss of appetite; disturbing dream.
Mild and moderate concussions do not require special treatment procedures. When the action of provoking factors is eliminated and rest is ensured, the body is fully restored no later than in 10-12 days. Typically, recovery occurs much faster. In case of severe injuries, vascular damage and internal hematomas are possible, and therefore a set of diagnostic studies is necessary to assess the real state of the brain. You may need specialized treatment.
One of the most severe injuries from impacts is cerebral contusion. In case of severe injuries, focal tissue damage is possible with the occurrence of hemorrhages and vascular compression. Depending on the degree of damage and the location of the lesion, paralysis, loss of sensitivity, speech impairment, and other serious disorders are possible. In the future, this pathology can cause epilepsy. The symptoms of a brain contusion are in many ways similar to the signs of a concussion, and therefore, in case of severe injuries, an examination is necessary to differentiate these types of lesions.
Don't worry and believe in the best.
Knowing what a concussion is and what to do in this case, you will never be at a loss if you have to help someone or even yourself. In the event that a concussion in an adult is accompanied by loss of consciousness, your main task is to properly place the victim before the ambulance arrives, and not allow him to stupidly die due to elementary asphyxia.
A concussion in an adult can also be accompanied by long-term memory loss and memory lapses. Patience, time and faith will help overcome these consequences. A concussion in a child is a more common occurrence. According to statistics, this happens, unfortunately, to every third child under the age of 16.
And while the signs of a concussion are more pronounced in an adult, they may not be as pronounced in children. And this is the difficulty of diagnosis; parents should pay more attention to what happened. Grown-up children should also be explained what to do in the event of a concussion and what not to do if the situation happens somewhere far from adults - while riding a bike or hiking.
Classification of mild brain injury
According to the domestic classification, traumatic brain injury (TBI) is divided into mild, moderate and severe. Mild TBI includes concussion and mild brain contusion. While domestic and foreign authors generally agree on the understanding of severe TBI, there are differences regarding mild TBI.
American authors group head trauma into severe (severe), moderate (moderate) and moderate (mild). Some American authors divide moderate head trauma, in turn, into mild (minor) and minimal (minimal). A minimal head injury corresponds to a concussion according to the Russian classification, and a mild head injury corresponds to a brain injury resembling a mild contusion according to the Russian classification.
In the following, we will use the term “mild brain injury” (MTBI), since the term “mild TBI” is inappropriate in this situation, since the size and extent of brain damage are of greatest importance, while cranial trauma plays only an indirect role.
Rehabilitation at home
A decoction of motherwort, mistletoe and mint herbs softens the effects of a concussion.
- a collection of motherwort, mistletoe and mint herbs (in equal proportions), as well as lemon balm (3/4 doses) are brewed with boiling water and allowed to brew for several hours. The product is consumed 3 – 4 times a day, half a glass at a time;
- mix valerian, mint, lemon balm and hops and pour boiling water for 20 minutes. The decoction is drunk at night;
- Bee pollen, which is consumed in a course for 1 to 2 months, accelerates recovery.
If there is a disturbance in brain activity due to a concussion in a child or adult, consultation with a doctor is required. Mild injuries can be treated at home. The patient is provided with complete rest and lack of physical activity.
Home treatment
After the team of doctors arrives and provides primary care, a decision is made on whether the patient should be hospitalized or treated at home. Mild to moderate concussions are most often treated at home. Usually, its duration is 8-12 days.
During home treatment, the following measures are taken:
- ensuring peace and full, long sleep;
- use of folk remedies for sedative purposes;
- following a gentle diet with a predominance of dairy and plant foods with a significant limitation in the consumption of table salt;
- exclusion of watching TV, reading, using a computer;
- sports and physical activity are completely excluded;
- Listening to light music is allowed, but without using headphones;
- The room is provided with optimal temperature and regular ventilation.
When treating a concussion at home, the following folk remedies have a positive effect:
- An infusion from a medicinal collection - motherwort, mint, mistletoe (50 g each) and lemon balm (30 g). The mixture is poured with boiling water (250 ml) and infused overnight. Use 70 ml 3-4 times.
- An infusion of a mixture of mint, hop cones, lemon balm (1 part each) and valerian root (2 parts). Everything is mixed and poured with boiling water at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 200 ml of water. Drink 250-300 ml per 1 procedure.
- An infusion of the mixture – dubrovnik, horsetail, thyme (1 part each), shepherd’s purse, mistletoe, yarrow (2 parts each). The raw materials are poured with boiling water and infused for 8-10 minutes. Drink 1 liter of infusion during the day.
You can speed up the effect of tissue restoration with the help of bee pollen. It is taken 10 mg 3 times a day. The course of such treatment is 8-10 days. When using folk remedies, it should be taken into account that the treatment of concussion is unacceptable using alcohol infusions. Alcohol in any form is strictly prohibited.
How to help the victim?
The first step is to call an ambulance, even if the victim himself refuses, claiming that he is already better. Delay often leads to subsequent difficulties in carrying out diagnostic measures.
But giving any painkillers or other medications before the doctors arrive is strictly prohibited. In the best of circumstances, pharmacological agents will only blur the overall clinical picture. But in a more serious scenario, they will only harm a weakened body.
It is better to start with the last point, which provides for mandatory bed rest in the safest possible environment. Moreover, it is extremely important not just to send a person to sit without unnecessary movements, but to move him to a horizontal position, limiting his mobility.
Recommends applying cold to the head. A heating pad with ice water, pre-wrapped in a towel, is best suited for these purposes. If you don’t have ice on hand, even a simple cold compress from a rag will do.
You will also have to make sure that the victim’s head is slightly higher than the body itself. Open a window to allow fresh air to enter.
When, during the initial examination, it turns out that the patient is unconscious, the first task of those around him is to bring him to his senses. Having shifted the person to his side, it is worth going for ammonia. A cotton swab is moistened with its solution and then brought to the victim’s nose.
If the patient constantly falls into an unconscious state, then it is better to leave him to continue lying on his right side, bending his left arm and leg 90 degrees. The head should be directed towards the floor. This will ensure complete intake of air into the lungs, as well as prevent tongue retraction or suffocation due to uncontrolled release of vomit.
You should not give the patient any alcoholic drinks “for courage,” as this will only increase the already significant load on the cardiovascular system. Even if the doctors who arrived at the scene diagnosed a mild concussion and refused hospitalization, this does not mean that the person is allowed to return to their usual pace of life.
You will have to give up any physical activity for a while, and also not watch TV or strain your eyes when working with a computer. If you follow such a simple rehabilitation program, you will be able to recover in about a few weeks.
But in most cases, for final confirmation of recovery, you will have to undergo auxiliary instrumental diagnostics. This can be either computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
A concussion can lead to serious consequences. If an injury occurs, a person is advised to immediately contact a medical specialist to undergo a comprehensive examination. Each person is recommended to familiarize themselves not only with the rules for providing assistance at the pre-medical stage, but also with key actions that can harm a victim with such an injury. If you suspect this injury, it is strictly prohibited:
- Feed and water the victim;
- Change the position of the patient’s body until the emergency medical team arrives;
- Independently use medications in any of the existing forms;
- Shake the victim, slap him in the face and attempt to independently bring him to consciousness.
Any of the above actions will cause a negative reaction from the body of the affected person, and will lead to the development of serious consequences.
Diagnosis of post-concussion syndrome
There are no clear criteria for PS. PS can develop in mentally healthy patients with no psychological abnormalities in the premorbid period, but it is more common in individuals who had any neurotic symptoms before the injury. Factors such as high-risk work, home or financial problems, and the desire to receive material or other compensation play an important role in the development of PS and its prolongation.
The role of MRI in the diagnosis of PS has not yet been determined. Symptoms of the disease may appear in patients without any changes on CT and MRI.
Features of the problem
In general, a concussion is recognized as a fairly mild type of temporary damage to brain tissue. When there is a strong mechanical impact on the skull in the form of a blow or bruise, the brain, by inertia, hits the cranial walls. As a result, short-term ischemia, compression of nerve fibers, and tissue swelling can occur, which causes the manifestation of characteristic symptoms.
It should be noted that numerous studies have not found significant tissue or vascular damage or structural changes in the brain, and this is considered an important feature of concussion. All small changes are reversible and disappear on their own when the cause disappears. A slight stretch is observed in the nerve fibers, which causes a delay in some reflexes.
Despite the reversible nature of the lesion and complete self-healing within 9-12 days, one cannot be too calm about the phenomenon in question. A concussion can have varying degrees of severity, and therefore a temporary disruption of the blood supply to tissues cannot be ruled out. If the necessary measures are not taken and when exposed to a number of provoking factors, serious brain dysfunctions are possible, which can cause complications.
What to do after a concussion
The recovery period after injury lasts from one to three weeks. In elderly patients and people suffering from other diseases, the treatment process may be delayed. In order for the patient to return to a full life as quickly as possible, during sick leave he must follow the following recommendations:
- follow the schedule for taking medications prescribed by the doctor;
- refrain from listening to music, watching movies, working on the computer, reading and activities that require visual concentration, such as small crafts, crossword puzzles, online games, etc.;
- maintain bed rest, avoid sudden movements;
- do not be nervous, exclude the possibility of any, even the most minor stress;
- get as much rest as possible - sleep and rest in this case are the best medicines;
- follow a diet, eat foods rich in vitamins, refrain from “heavy” foods such as fatty meats, mushrooms, etc., since the body spends too much energy to digest them;
- regularly ventilate the room, since fresh air not only promotes a speedy recovery process, but also alleviates symptoms;
- eliminate sources of bright light - it irritates the eyesight;
- talk on the phone as little as possible (ideally, don’t talk at all);
- Do not play sports under any circumstances, avoid any activity.
As an aid, with the permission of the attending physician, you can use relaxing herbal decoctions and other folk remedies - this will certainly help the patient with a concussion and alleviate his condition.
How does the brain react?
The brain is located in the skull, surrounded on all sides by brain fluid. The fluid protects the brain from hitting the skull bones. But with sudden falls or bruises, this mechanical protection is not enough and the brain is injured and reacts in one way or another, disrupting the functioning of the organ.
Usually these phenomena are reversible.
The characteristics of each stage occurring in the brain have not been determined by modern doctors even today. However, most doctors argue that the phenomenon leads to disruption of the normal functioning of nerve cells. After all, with a concussion, their nutrition deteriorates, tissue layers shift, and communication between centers is lost. As a result, tiny hemorrhages, microbruises, and swelling appear. Unfortunately, even MRI does not show such changes.
What is the danger of TBI?
The consequences of head injuries can be different, so treatment for a concussion must be complete and comprehensive.
With bruises and skull injuries, the following may be observed:
- sensitivity to alcohol, infections, which can cause mental disorders,
- constant attacks of migraine, dizziness, gradually increasing with physical activity, sudden movements,
- hot flashes to the head, after which blanching of the skin is observed (this symptomatology can manifest itself on only one side),
- increased fatigue, problems with concentration,
- irritability, mood swings,
- attacks of aggression, rage,
- convulsions, epileptic seizures,
- anxiety, constant neuroses, depression, insomnia,
- Hallucinations, delusions, and
- sometimes there are disturbances in thinking or memory, apathy and disorientation,
- in some cases, trembling of the limbs is possible.
As a rule, psychotherapy has no effect. And treating a concussion with narcotic painkillers - Codeine or Morphine - can cause addiction. A possible way out of the situation may be complete control of the patient and therapy in a hospital setting.