If a person has low white blood cells, this can be a sign of many diseases. This condition is medically called leukopenia. It leads to a sharp drop in immunity. Leukocytes are otherwise called white blood cells. They are responsible for neutralizing pathogens, parasites and toxins. These cells protect our health. A person suffering from leukopenia begins to get sick more often, as his body loses the ability to resist infections.
Leukocyte function
Leukocytes or white cells are blood cells. They are very important for the formation of immunity. These blood elements play a protective role. If pathogenic microorganisms enter the body, white blood cells recognize foreign protein substances. White cells quickly find bacteria and viruses, surround them, and then digest and destroy them. When fighting an infection, a large number of leukocytes die. To compensate for their deficiency, the hematopoietic system produces more and more white cells. Therefore, in infectious inflammatory diseases, an increase in leukocytes is often observed.
However, in some pathologies, low white blood cells are observed. What does this indicator mean? This sign indicates that a person’s body’s defenses are weakened. In a patient with leukopenia, the risk of infection by bacteria, viruses and other dangerous microorganisms sharply increases. If a decrease in white cells in the blood is observed constantly and over a long period of time, then the person begins to get sick more often due to a decrease in immunity.
Possible reasons
Leukocytes are white blood cells that are necessary to fight infection, bacteria and viruses.
They play a major role in the functioning of the immune system and resistance to various diseases. If the level of these cells deviates from the normal limits in one direction or another, this result must be analyzed and corrected. If we talk about the reasons, we can distinguish three main ones, from which “ramifications” already occur, including diseases:
- Insufficient amount of substances that are necessary for the synthesis of leukocytes.
- Disappearance of leukocytes in the blood structure.
- Problems with bone marrow function.
Leukopenia indicates the development of a disease. Its presence provokes the fall of white cells. There are several reasons that cause this condition. Let's talk in more detail about each of them.
Leukopenia is caused by temporary or permanent exposure to exo- or endogenous factors. Most often, violations are provoked by:
- lack of substances necessary for full leukopoiesis;
- rapid destruction of protective cells;
- defective maturation, decreased synthesis, failures in differentiation;
- diseases or ingestion of certain substances.
Leukopenia is a laboratory term. It indicates general disorders in the body. To normalize the protective functions of the immune system, it is necessary to lead to physiologically altered indicators. This can only be done in one way - by finding the cause of the displacement and eliminating it.
Substance deficiency
The synthesis of all blood cells requires almost the same substances. Among them are vitamins (B1, B6, B9, B12, C). The most important minerals are copper, iron, cobalt, minor ones are iodine, manganese, zinc. Arachidonic acid, amino acids, and selenium are also required. Almost all of them enter the body with food. With serious violations of the diet, a deficiency of microelements develops.
As a rule, with nutritional disorders, blood counts drop slightly (to the lower limit of normal). Deviations are combined with each other (for example, there is not enough leukocytes, erythrocytes, hemoglobin at the same time). If the disruptions are not caused by serious diseases that impair the absorption of nutrients, leukopenia can be easily corrected with diet.
All types of blood cells are synthesized in the bone marrow. This is their main reservoir in the body. If necessary, the formed elements of the blood come out, mature, and are sent into the blood to perform their functions. Malfunctions of the leukopoietic system occur when:
- intoxications - acute and chronic, significant (heavy metals), less dangerous (alcohol consumption, nicotine addiction, drug addiction);
- oncological diseases - the activity of the bone marrow decreases; when tumors metastasize, its tissues are simply replaced by atypical structures;
- congenital pathologies - myelocathexis, Kostmann's disease;
- taking medications - some medications suppress the activity of hematopoiesis, including the production of leukocytes (chemotherapeutic agents, interferon).
As a rule, if the problem lies in the improper functioning of the bone marrow, the deviations in blood cell counts are significant. They persist for a long time and do not change when following a diet.
Leukocytes are the first to rush to attack pathogenic agents. They concentrate in the area of the “entry gate” of infections, allergens, and toxins. Cells of one type redirect others here. With local changes, significant losses of protective bodies are possible, which affects the test results. Deviations are also possible in case of serious bacterial and viral infections that persist in the body for a long time (influenza, hepatitis, pneumonia). Intoxication with poisons also provokes the rapid destruction of leukocytes. With their regular intake into the body, the blood picture changes significantly.
Colliding with pathogenic microorganisms causes the immune system to work more actively, and the bone marrow to produce protective cells en masse. However, with prolonged or too intense development of the pathology, internal reserves may be depleted, which is manifested by leukopenia. This happens when:
- oncopathologies;
- viral lesions (cytomegalovirus, influenza, hepatitis, herpes, measles, rubella, HIV);
- complications of bacterial infections (pneumonia, sepsis, tuberculosis);
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland with an excess of hormones;
- parasitic infestations (worms, chlamydia, trichomonas);
- autopathologies (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis).
The level of leukocytes is also affected by the condition of the liver and spleen. These organs are capable of not only destroying, but also depositing blood cells and producing important enzymes.
The most striking example of the effect of therapeutic agents on immune activity is chemotherapy. The drugs used to treat cancer can not only destroy tumors, but also suppress the activity of the immune system and slow down the release of protective cells from the depot.
Leukopenia can develop with long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (painkillers), antispasmodics, and barbiturates. Cytostatics and interferon have a direct immunosuppressive effect. Often, a deficiency of white cells is detected during therapy with antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and antibacterial drugs.
Minor leukopenia may not manifest itself for a long time. Even with significant deviations, there are no specific symptoms. Health problems are manifested by signs of a disease that has caused a shift in the leukocyte formula. Serious deviations are most often accompanied by:
- pain and dizziness;
- chills, weakness, drowsiness;
- changes in body temperature with sudden changes;
- constant low-grade fever;
- deterioration of the skin and mucous membranes (dryness, cracks, rashes).
Symptoms may vary individually. Often, a deficiency of leukocytes manifests itself through frequent colds, viral and bacterial infections, and furunculosis.
The main reasons that lead to low white blood cells (leukopenia) in the blood in adults include:
- Medicines, toxic substances;
- Autoimmune diseases (killer cells destroy their own healthy tissue);
- Congenital pathologies with reduced bone marrow function;
- Myelofebrosis (bone marrow damage);
- Acute viral infections;
- Oncological diseases;
- Systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Chemotherapy for oncology;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Vitamin deficiency, deficiency of B vitamins;
- Deficiency of microelements (copper, zinc, iron, iodine, cobalt);
- Intoxication;
- AIDS, HIV;
- Worm infestations;
- Congenital diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- Diseases of the liver, spleen.
Reasons for a decrease in leukocytes in a child’s blood:
- Radiation sickness;
- Anaphylactic shock;
- Hereditary diseases;
- Bone marrow lesions;
- Acute form of leukemia (blood cancer);
- Bacterial and viral infections (flu, chickenpox, whooping cough);
- Sepsis.
Now you know the reasons for low levels of leukocytes in the blood in adults and children, but how leukopenia manifests itself can be found out below.
Key clinical signs that your blood has a low white blood cell count:
- In the first days, hyperthermia is observed (in particular, in children up to – 38 degrees), accompanied by chills;
- General weakness, lethargy;
- Pain in the joints;
- Decreased or complete lack of appetite, weight loss;
- Pustules on the skin of the trunk, face, limbs;
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), heart pain;
- Increased projection of the spleen, liver;
- Enlarged tonsils, lymph nodes;
- Hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- Dizziness, headache.
Leukopenia can also be asymptomatic, in which case it is discovered by chance during testing.
How to detect leukopenia
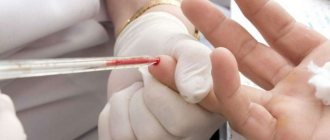
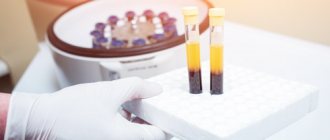
You can find out the number of leukocytes in the blood by taking a routine clinical blood test. Using this study, not only the white cell count is determined, but also the hemoglobin level, the number and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
It is important to remember that white blood cells are divided into several types. The following types of white blood cells are distinguished:
- lymphocytes;
- monocytes;
- neutrophils;
- basophils;
- eosinophils.
If the results of a general blood test reveal that leukocytes are low or high, then an additional diagnostic test is prescribed. This is a blood test for the leukocyte formula. It shows which type of white cells is increased or decreased.
To understand what low white blood cells mean, your doctor may order additional tests for infections, cancer, and thyroid hormones. This helps to identify the cause of leukopenia.
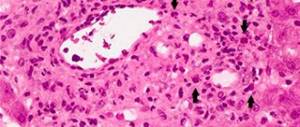
Bone marrow dysfunction
Since all subgroups of leukocytes are created and mature until they are released into the blood in the bone marrow, any damage to this organ leads to a drop in the blood test results. We are talking not so much about physical injuries, but about factors of internal origin.
There may be many such pathologies, we will note only the main ones:
- Intoxication. Moreover, this can be either simple poisons, alcohol, nicotine, food poisons, or complex ones - heavy metals, arsenic, medicinal poisons.
- Autoimmune damage, in which the body destroys its own cells, mistaking them for a disease-causing agent.
- Congenital diseases. The occurrence of leukopenia is provoked by certain genetic diseases that affect the normal functioning of the bone marrow and the production of leukocytes (myelocathexys, Kostmann's syndrome).
- Treatments carried out. A low white blood cell count can be caused by the treatment of certain serious diseases (cancer tumors, viral hepatitis).
- Replacement by tumor. Metastasis of the tumor to the bone marrow leads to the destruction of leukopoietic tissue and its replacement with tumor tissue. Leukopoietic tissue is responsible for the generation of new leukocytes, and its deficiency is immediately reflected in a drop in blood test values.
- Chemotherapy, taking interferon - all this is necessary for severe damage to the body, but it affects the functioning of the bone marrow.
It should be remembered that such bone marrow pathologies are extremely rare, therefore, with a small decrease in leukocytes, it is too early to sound the alarm.
Normal indicators
The normal level of leukocytes in the blood for adults (both men and women) is 4-9 x 109 g/l. In children, the white blood cell count is usually always higher. For a child under 6 years of age, the leukocyte count is considered to be from 5 to 15 x 109 g/l, and for children under 12 years of age - from 4.5 to 13.5 x 109/l. With age, this figure decreases.
If a patient's white blood cells are low, doctors recommend taking a repeat test or undergoing a more detailed hematological study. Sometimes a deviation from the norm is temporary and can be caused by random reasons. If a decrease in white blood cells is observed constantly, then doctors talk about leukopenia. Next we will look at the main reasons for this phenomenon.
Main causes of leukopenia
Low white blood cells in an adult or child are not always associated with pathology. If the analysis shows a slight deviation from the norm, this may be caused by taking certain medications. This deviation is observed during a course of treatment with antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as medications for thyrotoxicosis. Leukopenia of drug origin is considered physiological, it is not associated with diseases. However, a decrease in leukocytes should be reported to your doctor; it may be necessary to adjust the dosage or discontinue the medication.
It often happens that leukocytes are low due to pathology. Leukopenia is not a separate disease, but can be a symptom of various ailments. The reasons for this deviation can be divided into the following groups:
- lack of substances that affect the production of leukocytes;
- death of white cells or a decrease in their number in the bloodstream during infections and poisonings;
- disruption of the hematopoietic system;
- diseases of internal organs leading to leukopenia.
Let's take a closer look at each of these factors.
Poor nutrition
It often happens that a person is completely healthy, but his white blood cells are low. What does it mean? Due to insufficient or irrational nutrition, the body may develop a deficiency of substances necessary for the normal functioning of the hematopoietic system. These include the following vitamins and microelements:
- folic acid;
- iodine;
- iron;
- copper;
- zinc;
- vitamins B1 and B12.
All these substances affect the formation of white blood cells, and their lack can cause leukopenia. If this condition is caused by eating disorders, then the situation can be corrected quite easily. It is necessary to include in the diet foods rich in the above substances, this will lead to normalization of leukocyte levels. It is also useful to take vitamin and mineral complexes.
Pregnancy and decreased white blood cell levels
Normally, during different periods of pregnancy, a slight increase in the level of blood leukocytes may occur. This condition is called physiological leukocytosis. It is due to the need to provide additional protection for the fetus growing in the uterine cavity. A significant portion of leukocyte cells, after the formation of the placenta, migrate into its vessels, where they are deposited until birth.
If during pregnancy a decrease in the level of leukocytes is recorded in blood tests, this cannot in any case be the norm. Such pregnant women are subject to a thorough examination, which begins with a repeat general blood test.
If the results reveal leukopenia, you need to look for the cause of this syndrome. It can be associated both with pregnancy and any harmful influences. The prolonged existence of leukopenia during pregnancy will inevitably lead to weakened immunity, which poses an immediate threat to the normal development of the fetus.
Infections and chronic poisoning
If an infection enters the body, white blood cells rush to fight the foreign agent. White cells are sent from the blood to the lesion, which is located in the tissues. In this case, leukocytes are formed in sufficient quantities, but their number in the plasma is significantly reduced.
Often, when bacteria invade the body, there is an increase in the number of white cells. This is due to the fact that the hematopoietic system produces protective elements in increased quantities to fight microbes. However, there are cases when a person is sick with an infectious pathology, but at the same time low leukocytes in his blood are detected. What does it mean? This phenomenon is observed with viruses, as well as with parasitic diseases (chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, helminth infestation). When trying to destroy infection and parasites, a large number of leukocytes die.
White blood cells can fight more than just infection. They also neutralize toxins entering the body. When consuming low-quality products, poor environmental conditions or smoking, the body constantly receives toxic and harmful substances. White blood cells strive to destroy and digest toxins. In this case, a considerable number of white blood cells die.
Hematopoietic disorders
The most dangerous cause of leukopenia is a violation of the formation of white cells. This is always associated with serious illnesses. A decrease in the production of leukocytes is noted:
- in case of severe poisoning with chemical compounds (toluene, lead, benzene, arsenic);
- bone marrow tumors;
- radiation sickness;
- HIV infections;
- diseases of autoimmune origin;
- treatment of oncological diseases using chemotherapy;
- genetic disorders (Kostman syndrome, myelocathexis).
In these diseases, the production of white blood cells by the bone marrow is inhibited, which becomes the cause of leukopenia.
Internal illnesses
With diseases of the liver, spleen and endocrine system, the patient may experience low leukocytes in the blood. What does it mean? In some cases, this is one of the initial symptoms of pathology. Diseases of the liver and spleen lead to the accumulation of white blood cells in the affected organs. As a result, the content of white cells in the blood decreases.
Leukopenia is also observed in diseases of the thyroid gland. Endocrine pathologies negatively affect the composition of the blood and can cause the destruction of white cells.
Decreased white blood cells in women
Sometimes in healthy women, when taking a blood test, low white blood cells are detected. What does such a deviation mean and why does it occur? The physiological causes of leukopenia are varied:
- Some women experience pain during menstruation and take large amounts of analgesics during their menstrual periods. Excessive and uncontrolled use of such drugs can lead to leukopenia.
- White blood cells may decrease when hormonal levels change. Therefore, a decrease in the number of white cells is often observed in women taking birth control pills with estrogen.
- Leukopenia occurs in patients following an overly strict diet to lose weight. In this case, the body creates a deficiency of vitamins and minerals necessary for the normal functioning of the hematopoietic system.
These reasons are not dangerous. When medications are discontinued and nutrition is normalized, leukopenia disappears.
During pregnancy, an increase in the number of white cells is more common. But sometimes during gestation the analysis shows low white blood cells. What does this deviation from the norm mean? If the patient is healthy, then this may be a sign of vitamin deficiency or overwork. You should definitely pay attention to such a violation and undergo a course of treatment. Leukopenia is very dangerous during pregnancy. A woman’s body is defenseless against infections that can affect the development of the fetus.
We tell you everything about low levels of leukocytes in the blood of women
Leukocytes include white blood cells that are able to react to foreign cells that come from outside, neutralizing their activity. There are 5 types of leukocytes, each of which has its own function and role in the body.
For example, lymphocytes, equipped with a large network of receptors, are able to notify other leukocytes of a health threat, which causes the entire immune system to become active. Neutrophils destroy pathogenic microorganisms, sacrificing their own lives.
In addition, white blood cells are able to accumulate information about the microbes they have encountered. Such cellular memory is passed on through genes to future generations, which allows for the formation of innate immunity.
The level of white blood cells is determined using a blood test.
For a complete study of these cells, it is important to know not only their total number, but also their qualitative composition, expressed as a percentage of the total leukocyte mass.
In some cases, white blood cells may be low, indicating the presence of leukopenia . In what cases does this pathology develop in women and how to deal with it, we will find out further.
Leukocyte level: norm and deviations
Regardless of gender, the average level of leukocytes in a healthy person is in the range of 4-9×/l. However, in women there may be minor errors associated with hormonal changes in the body. Normal indicators, depending on age, have the following values:
- 18-25 years - the peak of puberty, when hormonal levels are stable and the body is initially configured for procreation - 4.5-10.5 × / l;
- 25-35 years – period of hormonal changes, especially in the presence of pregnancy – 3.5-9.5×/l;
- 35-45 years – the most active period of a woman’s life – 4.5-10×/l;
- 45-55 years - the period of menopause, during which sex hormones cease to be produced, which signals the decline of reproductive function - 3.3-8.8 × / l;
- 55-65 years – decline of all vital functions that regulate hormones – 3.1-7.5×/l.
The older a woman gets, the fewer white blood cells are produced by the bone marrow. The normal indicator shifts towards the lower limit.
During pregnancy, there is most often a natural increase in leukocyte levels, which is explained by the activation of the immune system in order to protect the fetus from the negative influence of the environment.
Decreased test results may indicate a malfunction in the body that occurs due to hormonal changes.
Usually this phenomenon is short-term and short-lived, so it does not require specific intervention, but should be fully monitored by a doctor.
Leukopenia in children
The white cell count in the blood of children is usually higher than that of adults. But there are cases when children’s leukocytes are low. What does it mean? If this phenomenon is observed in infancy, then most often the granulocytes in the blood test are low. This is one of the varieties of white bodies. This feature is due to the fact that infants have antibodies in their bodies that come with mother’s milk. They protect the baby from infections. This condition does not require treatment and does not affect health.
If white blood cells are low in the blood of an older child, this may be due to infection. Leukopenia is observed in the following diseases:
- measles;
- rubella;
- hepatitis;
- paratyphoid;
- brucellosis.
Often, at the slightest cold, parents give their children antibiotics. Uncontrolled use of antibacterial agents also leads to low white blood cells in the child.
Leukocytes in the blood are low in women: reasons, what does this mean? - Diagnostics
Leukocytes include white blood cells that are able to react to foreign cells that come from outside, neutralizing their activity. There are 5 types of leukocytes, each of which has its own function and role in the body.
For example, lymphocytes, equipped with a large network of receptors, are able to notify other leukocytes of a health threat, which causes the entire immune system to become active. Neutrophils destroy pathogenic microorganisms, sacrificing their own lives.
In addition, white blood cells are able to accumulate information about the microbes they have encountered. Such cellular memory is passed on through genes to future generations, which allows for the formation of innate immunity.
The level of white blood cells is determined using a blood test.
For a complete study of these cells, it is important to know not only their total number, but also their qualitative composition, expressed as a percentage of the total leukocyte mass.
In some cases, white blood cells may be low, indicating the presence of leukopenia . In what cases does this pathology develop in women and how to deal with it, we will find out further.
Symptoms
A decrease in leukocytes entails a deterioration in the body's resistance to various diseases. A person begins to catch colds more often and get foodborne illnesses. He has weakness and fatigue. An unreasonable increase in temperature is often observed. The lymph nodes may become enlarged and the tonsils in the throat may grow.
Every person’s body contains microorganisms that, under normal conditions, do not cause any illness. This is a candida fungus, a herpes virus and papillomavirus. However, with leukopenia they are activated and become pathogenic. Such microorganisms are called opportunistic. With a decrease in leukocytes, patients often experience candidiasis of the genitals or oral cavity, herpetic rashes and warts on the skin.
Why is it dangerous?
Leukocytes are those cellular elements of the blood that are responsible for maintaining the first links of immune surveillance in the body. Therefore, if a low level of leukocytes is recorded according to the results of a blood test, this indicates a microbial threat to the body. Deprived of leukocytes, it becomes defenseless against many pathogenic and even conditionally pathogenic representatives of the microbial world.
This is manifested by a frequent incidence of colds, a protracted and complicated course of any infectious processes. A favorable background is created for the proliferation of fungi on the surface of the mucous membranes, skin and its appendages, as well as such dangerous infections as tuberculosis, herpes viruses, Epstein-Barr and other common pathogens.
Leukocytes are immune cells that are the first to appear at the site of inflammation
Treatment
If leukopenia is caused by taking medications, you should consult your doctor about reducing the dosage or replacing the drug.
If there is a decrease in white blood cells associated with poor nutrition, you need to pay attention to your diet. You need to eat as many foods as possible rich in folic acid, B vitamins, iron and copper. These include:
- lean meat;
- seafood and fish;
- cheese;
- buckwheat dishes;
- apples;
- leaf crops;
- Brussels sprouts and cauliflower;
- legumes;
- walnuts;
- liver.
It is useful to supplement the diet with regular intake of vitamin and mineral complexes.
In more complex cases, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. It is important to remember that leukopenia is not a separate disease. A decrease in white blood cells is only a symptom of many pathologies. There is no specific drug that can increase the number of white blood cells. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a course of therapy for the disease that caused leukopenia.
How to increase white blood cells
A low white blood cell count is not a disease, but just a symptom that must be correctly assessed. Therefore, what to do with it should be decided exclusively by a specialist, taking into account the reason. You should not take any medications to improve immunity or leukopoiesis stimulants on your own. Such treatment can only do harm. The only thing that can help resolve the situation with a natural temporary decrease in leukocytes is compliance with the following rules:
- Dynamic monitoring of the patient. A natural or physiological decrease in leukocytes goes away on its own after a short period of time. If this does not happen, the patient needs a detailed examination;
- Refusal of bad habits and elimination of any toxic effects on the body (antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents, harmful production and work conditions);
- Dosed physical activity and active lifestyle. Involves sufficient exposure to fresh air and adequate physical activity;
- Enhanced diet and balanced nutrition. The diet should have a variety of foods and contain sufficient amounts of vitamins and proteins.
Leukopenia is not a harmless condition. But even it can be easily corrected if the right approach to eliminating it is chosen.
What the patient needs to remember
If a person has low white blood cells, this negatively affects the immune system. Therefore, the patient needs to protect himself from infections, poisoning, as well as from intestinal parasites.
A patient with leukopenia must adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid contact with people suffering from infectious diseases.
- During flu epidemics, use a gauze bandage and take immunomodulators and vitamins.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
- Eliminate home-canned foods from your diet to avoid contracting botulism.
- Do not eat expired products.
- Meat and fish dishes must be thoroughly cooked.
- Drink water and milk only when boiled.
Leukopenia cannot be ignored. It is necessary to consult a doctor, find out the cause of the decrease in white cells and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment.