Home / Improving potency
Back
Published: 04/24/2020
Reading time: 7 min
0
3
- 1 Analogs
- 2 Analogue options
- 3 Why are eye drops prescribed?
- 4 Instructions for use
- 5 Instructions for use of ointment and drops
- 6 How to “get off” prednisolone?
- 7 How to reduce the dose for short-term use
- 8 Medicine “prednisolone”: what helps
- 9 Prednisolone ointment: what is it prescribed for?
- 10 Overdose
- 11 Side effects
- 12 The drug “prednisolone”: instructions for use
- 13 Application of the solution
- 14 Contraindications
- 15 Composition
- 16 Composition and release form
- 17 Terms of sale and storage
- 18 Pharmacological action
- 19 Price, where to buy
Analogue options
The active hormonal synthetic substance that is the basis of this drug can, in some cases, be replaced by analogues. Today, such options are offered in a fairly wide selection. This could include Russian and foreign medications that are equally effective and have a smaller list of adverse reactions.
This list includes:
- Menopred,
- Prednisone,
- Decotrine salt (in the form of 20, 25, 50),
- Prednisolone Nycomed and others.
Drug interactions
During a course of taking Prednisolone, signs of its interaction with other drugs may appear:
- barbiturates, drugs for the prevention and relief of epileptic seizures, rifampicin, antihistamines reduce the effectiveness of the drug;
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, amphotericin B can lead to severe hypokalemia;
- combination with sodium drugs can cause an increase in blood pressure and the formation of edema;
- simultaneous use with Paracetamol increases the likelihood of negative changes in the liver;
- tricyclic antidepressants when combined with Prednisolone often lead to an increase in the severity of mental disorders;
- taking the drug together with immunosuppressants negatively affects the immune system;
- Aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alcohol-containing drugs and alcohol increase the likelihood of ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract and associated bleeding;
- oral contraceptives increase the activity of Prednisolone, including its toxic properties;
- the drug reduces the effectiveness of anticoagulants, insulin and hypoglycemic drugs;
- combination with diuretics can lead to imbalance of electrolyte metabolism.
Be sure to read:
Eucalyptus oil - beneficial properties and contraindications
Prednisolone in high doses can cause undesirable consequences after vaccinations, including the possibility of replication of viruses contained in live vaccines.
You may be interested in an article about the healing properties and dangers of burnet.
There is also a useful article on treating rheumatoid arthritis at home.
Here you will learn about the treatment of polyarthritis of the fingers with folk remedies.
Why are eye drops prescribed?
Prednisolone is indicated for use in non-infectious inflammations of the eye affecting its anterior segment. Drops are prescribed for the development of an inflammatory process as a result of injury and surgery. The drug is used for the following eye pathologies:
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- blepharoconjunctivitis;
- irite;
- blepharitis;
- iridocyclitis;
- sympathetic ophthalmia;
- sclerite;
- keratitis;
- uveitis;
- episcleritis.
How to “get off” prednisone?
The treatment regimen involves a gradual reduction in dosage. To do this, the volume of the drug is reduced weekly by 1/8. A faster way out of the syndrome is achieved by using the product every other day, while simultaneously reducing its volume by 1/5. This requires stimulation of the adrenal glands. The patient is advised to use insulin and ascorbic acid.
During therapy for bronchial asthma, inhaled steroids are replaced at the final stage. In case of autoimmune pathologies, they switch to mild cytostatic medications.
Patients respond completely positively to the ointment and solution for external use. They note the absence of serious side effects, while confirming the effectiveness of the drug.
How to reduce the dose for short-term use
Stopping Prednisolone should be done gradually. It is usually recommended to reduce the dose by 1/8 each week. But after a short course, other methods of cancellation are possible. The doctor chooses the regimen depending on the individual characteristics of the patient.
We suggest you read How to bring a girl to a squirting orgasm
One option is to reduce the dose by 1/5 and at the same time take the drug every other day. This is the fastest way to stop treatment. It must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Therapy that supports the functioning of the adrenal glands is necessary. Insulin, ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol, and sometimes maintenance therapy with cortisol are prescribed.
A slower withdrawal of Prednisolone involves reducing the dosage by 10% every 4 days. When the amount reaches 5 mg, which is 1 tablet, reduce by ¼ tablet. If withdrawal symptoms occur with such a reduction, it is recommended to return to the previous dosage and after a few days try to reduce the dose again at a slower pace.
Another option for discontinuing Prednisolone is an injection of any long-acting hormonal agent. This method is effective only if treatment lasts less than 2 months. The injection is given after reaching a dose of 5 mg.
Withdrawal syndrome when taking Prednisolone is a dangerous condition. Abruptly stopping treatment may lead to severe adrenal insufficiency. Therefore, those who take this drug must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations.
Rules for using the product
If the patient has been diagnosed with indications for the use of Prednisolone ointment, the attending doctor selects an individual treatment course. The frequency and dosage of application of the medicinal composition cannot exceed the recommended value in the instructions for use. The doctor needs to convey to the patient all the features of using this drug, pointing out possible adverse reactions and complications in case of non-compliance with the recommended doses.
Medical specialists recommend using hormonal ointments in the smallest dosages. The duration of therapy should also be minimal. Regardless of what the ointment is used for, it is not necessary to use it more than three times a day. This drug belongs to the category of drugs whose effects are aimed at relieving acute conditions of the disease.
The medicine "prednisolone": what helps
Indications for the use of tablets and injection solution include the following systemic diseases:
- allergic pathologies; hay fever;
- rheumatic fever;
- inflammatory diseases of joints and tissues (osteoarthritis, synovitis, spondyloarthritis, tenosynovitis);
- multiple sclerosis;
- lung cancer (in combination with cytotoxic drugs);
- diffuse connective tissue abnormalities;
- sarcoidosis, pneumonia, fibrosis;
- minor chorea, rheumatic carditis;
- tuberculosis, meningitis;
- acute alveolitis, hypocortisolism;
- congenital adrenal hyperplasia;
- hepatitis, granulomatous thyroiditis;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- autoimmune pathologies, nephrotic syndrome;
- leukemia, anemia and other diseases of the circulatory system;
- cerebral edema;
- skin abnormalities of autoimmune and other etiologies (psoriasis, exfoliative dermatitis, eczema, etc.);
- eye diseases (keratitis, conjunctivitis, uveitis, choroiditis, keratitis, iridocyclitis, etc.) of an allergic or autoimmune nature;
- hypercalcemia, caused by cancer.
What else are Prednisolone tablets and injections prescribed for? Injections are given in emergency shock conditions. After a few days of administering the solution, patients are prescribed tablets.
Internal use of the drug is indicated for severe or chronic diseases (bronchial asthma, etc.). Injections and tablets are prescribed during transplantation to prevent implant rejection and to stop vomiting that occurs while taking cytostatics.
Features of using ointment for allergies
Systemic use is advisable for:
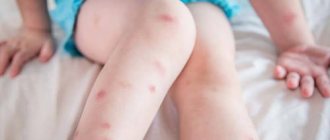
- allergic diseases (including food or drug allergies, toxicoderma, serum sickness, atopic/contact dermatitis, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, urticaria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Quincke's edema);
- minor chorea, rheumatic fever, rheumatic carditis;
- acute and chronic diseases that are accompanied by inflammation in the joints and periarticular tissue (synovitis, nonspecific tenosynovitis, seronegative spondyloarthritis, epicondylitis, osteoarthritis (including post-traumatic), etc.);
- diffuse connective tissue diseases;
- multiple sclerosis;
- status asthmaticus and asthma;
- lung cancer (the drug is prescribed in combination with cytostatics);
- interstitial diseases of the lung tissue (fibrosis, acute alveolitis, sarcoidosis, etc.);
- eosinophilic and aspiration pneumonia, tuberculous meningitis, pulmonary tuberculosis (as an addition to specific therapy);
- primary and secondary hypocortisolism (including after adrenalectomy);
- congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) or dysfunction of their cortex;
- granulomatous thyroiditis;
- autoimmune diseases;
- hepatitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hypoglycemic conditions;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs and blood (leukemia, anemia and diseases associated with damage to the hemostatic system);
- cerebral edema (post-radiation, developing with a tumor, after surgery or trauma; the annotation and Vidal reference book indicate that for cerebral edema, treatment begins with parenteral forms of the drug);
- autoimmune and other skin diseases (including Dühring's disease, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus, Lyell's syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis);
- eye diseases (including autoimmune and allergic; including uveitis, allergic ulcerative keratitis, allergic conjunctivitis, sympathetic ophthalmia, choroiditis, iridocyclitis, non-purulent keratitis, etc.);
- hypercalcemia developing against the background of cancer.
Indications for the use of injections are emergency conditions, for example, an acute attack of food allergies or anaphylactic shock. After several days of parenteral use, the patient is usually transferred to the tablet form of Prednisolone.
Indications for the use of tablets are chronic and severe pathologies (for example, bronchial asthma).
Prednisolone solution and tablets are also used to prevent transplant rejection and relieve nausea/vomiting in patients receiving cytostatics.
Eye drops are prescribed to relieve inflammation of a non-infectious nature affecting the anterior segment of the eye, as well as inflammation that develops after an eye injury or ophthalmic surgery.
Local use of Prednisolone is justified for the following eye diseases:
- iridocyclitis;
- uveitis;
- iritis;
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- keratitis (in particular, discoid and parenchymal; in cases where the epithelial tissue of the cornea is not damaged);
- scleritis;
- episcleritis;
- blepharitis;
- blepharoconjunctivitis;
- sympathetic ophthalmia.
The solution is administered intravenously, intramuscularly and intraarticularly.
The method of administration and dosage of Prednisolone (Prednisolone Nycomed, Prednisolone hemisuccinate) are selected individually by the attending physician, taking into account the type of pathology, the severity of the patient’s condition, and the location of the affected organ.
In severe and life-threatening conditions, the patient is prescribed pulse therapy using ultra-high doses for a short period of time. For 3-5 days, he is given 1-2 g of prednisolone daily by intravenous drip infusion. The duration of the procedure is from 30 minutes to 1 hour.
During treatment, the dosage is adjusted depending on the patient's response to therapy.
It is considered optimal to administer Prednisolone intravenously. For intra-articular administration, ampoules with Prednisolone are used only in cases where the tissue inside the joint is affected by the pathological process.
Positive dynamics are a reason to transfer the patient to tablets or suppositories with prednisolone. Treatment with tablets is continued until stable remission develops.
If it is not possible to administer Prednisolone intravenously, the medicine should be injected deep into the muscle. However, it should be borne in mind that with this method it is absorbed more slowly.
In the human body, the release of adrenal hormones into the bloodstream occurs between 6 and 8:00 am, so injections should also be given at this time. The entire daily dose is usually administered at once. If this is not possible, at least ⅔ of the prescribed dose is administered in the morning, the remaining third should be administered at lunchtime (at approximately 12:00).
Depending on the pathology, the dose can range from 30-1200 mg/day. (with its subsequent decrease).
Children aged from two months to 1 year are administered from 2 to 3 mg/kg. Dosage for children from one to 14 years of age is 1-2 mg/kg (as a slow, 3-minute intramuscular injection). If necessary, after 20-30 minutes the medicine is re-administered in the same dose.
If a large joint is affected, 25 to 50 mg of prednisolone is injected into it. From 10 to 25 mg is injected into medium-sized joints, and from 5 to 10 mg into small joints.
The patient is transferred to taking tablets, following the principle of gradual withdrawal of GCS.
If HRT is used, the patient is prescribed 20 to 30 mg of prednisolone per day. Maintenance dose - from 5 to 10 mg/day. For some pathologies - for example, with nephrotic syndrome - it is advisable to prescribe higher doses.
For children, the starting dose is 1-2 mg/kg/day. (it should be divided into 4-6 doses), maintenance - from 0.3 to 0.6 mg/kg/day. When prescribing, the daily secretory rhythm of endogenous steroid hormones is taken into account.
Recommendations regarding the use of drugs from different manufacturers are the same. That is, the instructions for Nycomed tablets do not differ from the instructions for tablets produced by.
The ointment is a means of external therapy. It should be applied to the affected areas of the skin in a thin layer from 1 to 3 times a day. An occlusive dressing can be applied to limited pathological lesions to enhance the effect.
When used in children over one year of age, the drug should be used for the shortest possible course. You should also exclude measures that enhance the absorption and resorption of prednisolone (occlusive, fixing, warming dressings).
Instillations of the drug are carried out 3 times a day, instilling 1-2 drops of solution into the conjunctival cavity of the affected eye. In the acute phase of the disease, the instillation procedure can be repeated every 2-4 hours.
For patients who have undergone ophthalmic surgery, drops are prescribed 3-5 days after surgery.
Glucocorticosteroid therapy is aimed at achieving maximum effect with the lowest possible doses.
The duration of treatment depends on the patient's diagnosis and individual response to treatment. In some cases, the course lasts up to 6 days; with HRT it lasts for months. The duration of external therapy using Prednisolone ointment is usually from 6 to 14 days.
The dosage for dogs and cats is selected individually depending on the indications.
So, for example, with infectious peritonitis, a cat should be given orally 1 r./day. 2-4 mg/kg of prednisolone, for chronic panleukopenia - 2 times/day. 2.5 mg each.
The standard dosage for a dog is 1 mg/kg 2 times a day. Treatment lasts 14 days. Upon completion of the course, you must take tests and be examined by a doctor. When discontinuing the drug, the dose for dogs should be reduced by 25% every 14 days.
Side effects
The medicine "Prednisolone", reviews and instructions indicate this, can cause negative reactions in the body:
- diabetes mellitus, erosive esophagitis;
- increased or decreased appetite;
- dizziness;
- adrenal dysfunction;
- nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure;
- hallucinations, stomach and intestinal ulcers;
- changes in corneal trophism, digestive disorders;
- slow wound healing, flatulence;
- headache, arrhythmia;
- disorientation, hiccups;
- depressive psychosis; bradycardia;
- hypokalemic syndrome, osteoporosis;
- increased intracranial pressure, acne;
- nervousness, skin rash;
- weight gain, tendon rupture;
- anaphylactic shock, convulsions;
- increased intraocular pressure, increased sweating;
- stretch marks, secondary eye infections, itching;
- growth retardation or delayed sexual development in children, withdrawal syndrome.
What are the consequences of incorrect use?
Effect on the body:
- Adrenal gland dysfunction.
- Diabetes.
- Gastrointestinal lesions: gastric and duodenal ulcers, perforation and bleeding, pancreatitis.
- Damage to the nervous system: reactions to long-term use vary: from euphoria to psychosis and depression.
- Increased blood pressure, intracranial and intraocular pressure.
- If prone to cardiovascular diseases, it causes arrhythmia, brachycardia, thrombosis, and slows down the formation of scars during a heart attack.
- Sudden loss of vision. When using the medicine in the head and neck area, the substance may be released in the lens of the eye.
- Allergic reactions up to anaphylactic shock.
- Decreased immunity.
Danger for children
Prednisolone for allergies for pediatric patients is used under the strict supervision of a pediatrician and pediatric allergist. Long-term use can cause serious developmental disorders: impaired growth, hormone production, delayed puberty.
When using ointment, diapers and diapers have a dressing effect and increase the amount of active substance that penetrates the bloodstream. Their use must be abandoned.
The course is prescribed as short as possible, and the dose is reduced to a minimum while maintaining effectiveness.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy, Prednisolone is used only as a last resort, when the life of the mother is threatened. It penetrates the placental barrier and can cause side effects in the child. Systemic forms (tablets and injections) in the third trimester threaten the fetus with adrenal atrophy, which will require replacement therapy.
It passes into breast milk, so breastfeeding should be discontinued.
The drug "prednisolone": instructions for use
The dosage, form and method of administration of the medication depend on the complexity of the disease, the effectiveness of therapy and the patient’s condition.
Prednisolone tablets are taken immediately after or during meals. The daily dosage according to the instructions is 0.025–0.05 g. The medicine is taken 2-3 times. Subsequently, the dosage is reduced to 0.005 g. You need to drink 4-6 times a day.
The maximum daily amount of the drug should not exceed 0.1 g, a single dose - 0.015 g. It is possible to increase the highest dosage to 0.3–1.2 g per day in especially severe cases. Prednisolone tablets are prescribed to children under 4 years of age based on their weight. The daily dosage is distributed as follows:
- Up to 4 years - 0.001 g/kg;
- 5–6 years - 0.02 g;
- 7–9 years – 0.025–0.03 g;
- 10–14 years - 0.025-0.04 g.
Prednisolone ointment: what it is used for, detailed instructions for use, analogues and reviews
Like all hormonal drugs, Prednisolone can provoke adverse systemic and local reactions. Despite its high effectiveness, it is not prescribed to some categories of patients. The drug is used only in dosages determined by the doctor after a series of biochemical studies.
Description of the drug
Prednisolone is a thick, white ointment without any specific odor. It is well absorbed by the skin, and the ingredients quickly penetrate into pathological areas. The product has a healing effect a few minutes after its application.
The hormonal drug is used to treat acute and chronic skin diseases. It eliminates almost all clinical manifestations of pathologies of allergic origin.
What does Prednisolone ointment help with:
- swelling and redness of the epidermis, caused by an inflammatory process;
- burning, pain, itching;
- large and small rashes;
- abundant exfoliation of the upper epidermal layer.
The drug is included in therapeutic regimens only by the treating specialist. He studies the patient's medical history and the results of biochemical tests. The dermatologist must take into account the degree of tissue damage and the stage of the pathological process.
Clinical and pharmacological group
Prednisolone cream is included in the clinical and pharmacological group of glucocorticosteroids for external use.
pharmachologic effect
Therapeutic effectiveness is based on the pharmacological properties of the drug component - prednisolone. This is a synthetic analogue of the hormone produced by the adrenal glands, but with a more powerful therapeutic effect.
The active ingredient has the following properties:
- anti-inflammatory. Prednisolone inhibits enzymes that stimulate the production of mediators prostaglandins, leukotrienes, bradykinins;
- antiexudative. The glucocorticosteroid prevents the accumulation of macrophages and leukocytes in inflammatory foci. It is the high concentration of these immune system cells that leads to the formation of edema;
- analgesic. Suppression of prostaglandin production causes a decrease in the severity of pain.
Under the influence of the synthetic hormone, capillary permeability decreases, which is increased by the released histamine. The activity of fibroblasts, secreting precursors of collagen and elastin proteins, decreases.
In addition to Prednisolone ointment, the therapeutic line includes eye drops used in ophthalmic practice. They are prescribed to patients with episcleritis, blepharitis, and blepharoconjunctivitis. Drops are used in the treatment of one of the most common eye pathologies - allergic conjunctivitis.
Release form and composition
Prednisolone ointment is produced by many domestic pharmaceutical factories. It is available in 10 and 15 g packaging in sealed aluminum tubes.
Secondary packaging is a cardboard box with instructions for use included. The ointment base is formed from the following additional ingredients:
- white paraffin;
- methylparaben;
- stearic acid;
- emulsifier;
- propylparaben;
- glycerin;
- purified water.
Auxiliary ingredients ensure maximum absorption of the glucocorticosteroid into inflammatory lesions. And due to paraffin, a protective film is formed on the surface of the skin. It prevents infection of affected tissues against the background of decreased local immunity.
Patients often ask doctors whether the ointment is hormonal or not. The active component prednisolone is a hormone obtained synthetically. Its presence in the composition determines not only the anti-inflammatory effectiveness of the ointment, but also a wide range of contraindications. Therefore, it is necessary to consult with your doctor about the safety of using Prednisolone.
Storage conditions and periods
The drug is stored in a dark place at a temperature of 5-15°C. Shelf life: 24 months. If the temperature regime is violated, the ointment delaminates, changing its color and smell.
This indicates the unsuitability of Prednisolone for treatment. After opening the tube, you must use its contents within a month.
Young children's access to the drug should be limited.
Indications and contraindications
Ointment with prednisolone successfully treats chronic pathologies that are aggravated under the influence of negative factors. It is prescribed to patients with localized neurodermatitis. In this case, the antiproliferative activity of the drug is used, which manifests itself in slowing down cell division.
The hormonal drug is included in treatment regimens when diagnosing the following diseases:
- contact, atopic dermatitis;
- discoid lupus erythematosus;
- psoriatic rashes (papules, plaques);
- dry and weeping eczema of any location;
- erythroderma;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- toxicoderma;
- acute urticaria.
Prednisolone is not prescribed to patients if there are microtraumas in the area (cracks, scratches, abrasions, cuts). It is prohibited for use during pregnancy and lactation. In pediatrics, the ointment is used to treat children older than one year.
Contraindications to therapy include syphilitic, tuberculous, and acne rashes. The hormonal agent is not intended to treat inflammation of fungal, viral, or bacterial origin.
Directions for use and doses
If allergic reactions develop, it is recommended to apply a thin layer of ointment to the area of swelling and rashes. The dosing frequency varies from 1 to 3 times a day. The duration of treatment with Prednisolone for allergies is 7-10 days.
For psoriatic plaques, the drug is used according to the dosage regimen determined by the doctor. It is applied in a thin layer to the area of skin affected by inflammation and lightly rubbed.
In the acute course of the pathological process, it is allowed to use the product under occlusive (airtight) dressings. This contributes to the maximum concentration of glucocorticosteroid in inflammatory foci.
Side effects and special instructions
With a long course of therapy, persistent dilation of small blood vessels in the skin, characterized by redness, is possible. In some cases, steroid-type acne forms. Violation of the dosage regimen causes swelling of the skin and increased skin itching.
According to the instructions for Prednisolone, ointment is not used to treat children for longer than a week. It can be mixed with cream to reduce dosages. If the drug is abruptly discontinued, the symptoms of the disease may worsen.
Prices and conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Prednisolone is not a drug dispensed from pharmacies with a doctor's prescription. Its average cost is 20 rubles. A new generation of ointments with similar therapeutic properties has appeared in the pharmacy assortment. They are combined with medications in various dosage forms - tablets, injection solutions, syrups, suspensions.
Products with the active ingredients hydrocortisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone have a similar pharmacological effect.
Contraindications
Prednisolone should not be taken if you are hypersensitive.
The medication should be prescribed with caution to patients suffering from the following pathologies:
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- peptic ulcer in acute or latent phase;
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa;
- esophagitis;
- diverticulitis;
- UC with threat of rupture of the intestinal wall or abscess formation;
- tendency to thromboembolism;
- recent surgery performed to create an intestinal anastomosis;
- acute and subacute phase of myocardial infarction;
- high blood pressure;
- systemic fungal infection;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- systemic osteoporosis;
- severe course of chronic heart failure;
- infectious diseases of various etiologies, both acute and recently transmitted, including contact with an infected person;
- active and latent forms of tuberculosis;
- increased and decreased thyroid function;
- obesity 3 and 4 degrees;
- 8 weeks before vaccination and 2 weeks after it;
- diabetes;
- mental illness;
- poliomyelitis, except bulbar encephalitis;
- lymphadenitis after vaccination with BSG;
- severe forms of renal and liver failure;
- immunodeficiency;
- hypercortisolism;
- severe muscle failure;
- kidney stone disease;
- hypoalbuminemia.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Adrenogenital syndrome: symptoms in newborns, congenital forms in boys, girls - salt wasting, virile, diagnosis and screening, treatment
Composition and release form
It is produced in the form of ointment, eye drops, tablets, solution for injection into a vein or muscle tissue. The medicine "Prednisolone", which helps for various indications, contains the active substance of the same name. Its share in solution is 30 mg per ml, in tablets - 1 or 5 mg, ointment 0.05 g.
Auxiliary components of the drug, depending on the form of release, are sodium pyrosulphide, stearic acid, propyl parahydroxybenzoate, nicotinamide and other components.
pharmachologic effect
The drug "Prednisolone", from which its effect is manifested, belongs to the corticosteroid group of drugs. This is a glucocorticosteroid agent that exhibits weak activity, which allows it to be successfully used for the treatment of many allergic, inflammatory and autoimmune pathologies.
Is Prednisolone hormonal or not? Doctors answer that the medicine is a hormonal agent for systemic or local use with an average duration of action. The active substance is an analogue of the hormone hydrocortisone, which is produced by the adrenal cortex.
The medicine stops or prevents the occurrence of allergies, suppresses the immune system, creates an anti-shock effect, and stops the inflammatory process.