ABSCESS, or abscess, is a focal purulent inflammation, which is characterized by the formation of a cavity filled with pus, consisting mainly of white blood cells (leukocytes), blood serum and debris of destroyed tissue. There is, however, a less common type of abscess, the so-called. cold abscess, in which no inflammatory reactions occur. A regular, or purulent, abscess can be located in any tissue of the body, for example in the center of a bone. In the latter case, it is called Brodie's abscess. More common are appendicular, peritonsillar and subdiaphragmatic abscesses, abscesses of the lymph nodes, mammary glands, liver, and lungs. Abscesses also include boils, carbuncles and felons.
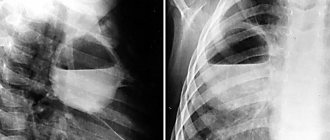
Subphrenic abscess
formed as a result of infection of any abdominal organs. Common causes are a ruptured appendix, a perforated stomach or duodenal ulcer, or a liver abscess. A subdiaphragmatic abscess forms between the liver and the diaphragm, almost always on the right, while the body temperature rises and the number of leukocytes in the blood increases. Pain sensations are mild or absent. Fluoroscopy data showing elevation of the diaphragm are of great importance in diagnosis.
How does it appear?
Typically, an abscess arises against the background of various infections entering the body. In the area that is filled with pathogenic bacteria (burn, splinter, wound, cut), ordinary inflammation begins. This is an absolutely normal reaction of the body, aimed at protection, and it is needed to destroy foreign microorganisms.
Symptoms of ordinary inflammation are:
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the damaged area;
- swelling of the area.
However, a normal process can take on a severe form and become pathological - it is at this moment that an abscess appears.
Treatment
Purulent abscesses, regardless of their location, are opened and drained as soon as the presence of pus is established. Various forms of drainage are used, but the least painful and most effective is the use of a rubber drainage tube. Most abscesses should be opened under general anesthesia. Local anesthesia is unsuitable in such cases, as it does not allow proper examination of the abscess cavity. The contents of cold abscesses have to be sucked out, since their opening creates the risk of secondary infection.
What's the prognosis?
Most small abscesses, such as boils, go away on their own. The prognosis for abscesses that are treated inpatiently is also favorable. Complications of abscesses are quite rare and are more common with a suppressed immune system. Complications in this case include worsening or spread of inflammation to adjacent areas of skin or soft tissue, which can lead to the formation of lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, arthritis, osteomyelitis and endocarditis; and very rarely, the spread of infection through the blood with the development of sepsis. Recurrence of infection is another possible complication that may occur after a certain period of time.
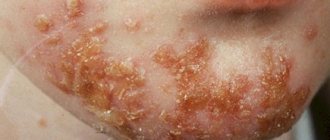
Boils, carbuncles and panaritiums
Boils are localized abscesses located in the skin or subcutaneous tissues. They form on the hairy parts of the body. The infection usually enters the tissue through the hair follicles. Furunculosis is often observed in patients with diabetes and is usually caused by staphylococcus.
A carbuncle affects a larger area of tissue and has several exit holes, rather than just one, like a boil. Carbuncles most often form on the neck and, unlike boils, are caused not by staphylococci, but by more virulent bacteria.
As soon as the presence of pus is detected, carbuncles and boils should be opened. Sometimes the formation of pus in a boil can be prevented with hot lotions and the administration of chemotherapy.
Felons are infectious processes localized in the fingers. Starting in the soft tissues of the finger, they open outward through a very narrow passage; sometimes they spread deeper and involve the bone; inflammation of the periungual bed is called paronychia. They are usually caused by staphylococcus, which penetrates through cracks in the skin. Symptoms include pain, tenderness to the touch, slight swelling and mild fever. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and, if pus is detected, the panaritium is urgently opened to prevent damage to the nearby bone.
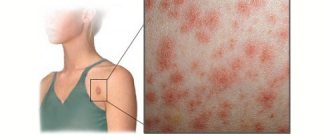
Causes and mechanisms of skin abscess.
Like any purulent disease, a skin abscess occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the body’s protective barriers and the penetration of pathogenic agents (bacteria or viruses) into it. Bacteria that cause the melting of skin tissue and the formation of a capsule filled with purulent masses are part of us, but under certain conditions and an increase in their number they can be activated. A large number of such organisms exist on our mucous membranes: the oral cavity, nasal cavity, mucous membranes of the eyes, genital organs, and some are located in our intestines, both large and small. It can be quite difficult to identify the causative agent of an abscess, and the effectiveness of treatment sometimes depends on this. The variety of bacteria that cause purulent inflammation is very large; we will consider only those that are most often encountered in surgical practice.
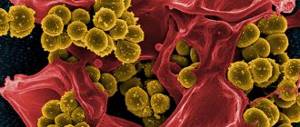
- The overwhelming majority of skin abscesses are caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Recent studies show that Staphylococcus aureus is detected in 27.6% of cases of skin abscess detection, and is almost always sown in pure culture, without accompanying flora. 47.4% were abscesses identified in the upper half of the body (abscesses of the face, neck, axilla and chest), the main cause of which was Staphylococcus aureus. Some of the subgroups of staphylococcus are not sensitive to many antibiotics, which makes treatment difficult.
- Proteus mirabilis is one of many microorganisms that live in the large intestine and are isolated during stool microscopy. This microorganism is often the cause of abscesses of the lower half of the body, although it is not a permanent inhabitant of the skin.
- Quite often, the cause of skin abscesses is Escherichia coli; this microorganism is part of us and is part of the intestinal flora, but under certain conditions and decreased immunity it can cause severe and sometimes fatal diseases.
- Some drugs can cause sterile abscesses that resemble skin cellulite.
- Some diseases may be complicated by the occurrence of abscesses (pharyngitis, ingrown nails, paraproctitis, Crohn's disease, osteomyelitis, orchiepidymitis, amoebiasis, donovanosis, phthiriasis...)
What it is?
Psoas abscess is an inflammatory purulent process that occurs in the thickness of the iliopsoas muscle. What is this? This muscle consists of several components:
- Psoas major muscle.
- Psoas minor muscle.
- Iliacus muscle.
Its direct purpose is as follows: it connects the spine and pelvic bones with the femurs. The muscle is also involved in flexion of the spine and legs at the hip joint.
Why psoas abscess? From the Latin name of the iliopsoas muscle - m. iliopsoas. Accordingly, for certain reasons, inflammation will develop in it, complicated by purulent discharge.
Pathogenesis of purulent-inflammatory disease
An abscess occurs either in dead tissue, where autolysis processes occur (self-dissolution of cells under the influence of enzymes), or in living tissues exposed to the aggressive effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
When an infection enters the body, the immune system is activated. The main “defenders” are leukocytes (neurophilic, basophilic). 6-8 hours after the introduction of the infectious agent, neurophils move from the vascular bed to the mucous membranes. With the help of chemoattractants, neurophilic leukocytes penetrate to the inflamed lesion.
In the initial stage of the purulent process, the affected area is infiltrated (soaked) with inflammatory fluid and leukocytes. Over time, under the influence of neutrophil enzymes, the tissue undergoes melting, forming an internal space filled with exudate. The pus in the cavity is lysosomal enzymes from the remains of neurophils. The walls of a soft tissue abscess eventually form a two-layer pyogenic membrane. It prevents exudate from spreading to neighboring anatomical structures.
READ ALSO: Pimples after acne (holes) - how to remove on the face, in the middle, photos, remedies, dimples from blackheads
Symptoms of the disease
Let's imagine the main symptoms of psoas abscess:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Feeling of discomfort in the groin area, as well as the front of the thigh.
- Pain in the lower back.
- When straightening the leg, pain is felt in the hip joint.
- High body temperature, chills, fever.
The person will complain of constant pain in the left or right side of the lower abdomen. Pain syndrome can be felt in them at the same time. Often there is discomfort in the front of the thigh. With a certain spread of infection, it spreads to the groin area. This feels like muscle tension in the thigh area. As for the groin, the patient will notice as if there is an accumulation of some substance.
When walking, you may also feel pain that radiates to the back area. Fever and high temperature are common signs of an active inflammatory process in the body.
The condition is dangerous because the clinical picture in most cases is blurred. Especially when the patient is taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, with which the person is trying to numb the pain. The patient may be observed by a neurologist for a long time, while the cause of the pain syndrome is determined incorrectly.
Varieties
An abscess (according to ICD-10 code L02) can occur in absolutely any soft tissue. Taking into account exactly where the abscess formed, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Abscess of muscles or subcutaneous fat. This is the most common type of pathology. The prerequisite for its development is almost always a minor trauma to the skin.
- Peritonsillar type. It is formed in the tissues surrounding the tonsil and is usually a consequence of purulent tonsillitis.
- Retropharyngeal view.
- Liver abscess. A serious complication of acute infectious pathologies of the abdominal cavity.
- Purulent process in the lung. It often becomes a consequence of pneumonia or the penetration of foreign objects into the bronchi.
- Brain abscess. One of the most severe types of the disease, the prognosis for it is usually unfavorable.
- Purulent processes in the pelvic organs. This is often a consequence of chronic infections of the female reproductive organs.
- Abscess of intestinal loops.
- Pathology of the appendix. Appears as a complication of simple appendicitis.
- Lung abscess.
The classification of acute and chronic types of pathology also includes peripheral and central types of the process. In addition, ulcers can be multiple or single, depending on the number of infectious foci.
In reality, this list is far from complete and shows only the most common types of the disease.
Diagnostics
If the abscess is located directly under the skin, long-term diagnosis is not required. The doctor identifies superficial abscesses by typical signs of inflammation. With a superficial abscess, diagnosis is needed to identify the causative agent of inflammation - and, therefore, an abscess; for this purpose, a purulent smear is examined.
Deep abscesses cannot be recognized or detected during external examination. For example, if an abscess has formed in the kidneys or lungs, the doctor will only be able to recognize and differentiate it from other diseases using imaging techniques. These include:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT).
In addition to imaging to diagnose an abscess, complete blood tests are taken. The doctor examines the blood for signs of inflammation and antibodies responsible for inflammation.
An increase in the number of leukocytes and an increase in eosinophils, an increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein in the blood are additional signs of an abscess.
Psoas abscess in ICD-10
In the International Classification of Diseases, this abscess is designated by code M60.0 - “Infectious myositis.” This is a muscle disease (M60-63), a soft tissue disease (M60-79), as well as pathologies of connective tissues and the musculoskeletal system (M00-M99).
Psoas abscess in ICD-10 is a type of infection of the deep layers of soft tissue. In addition to it, pyomyositis (an acute primary bacterial infection of skeletal muscles) is identified in the M60.0 group. Psoas abscess is named in the classifier as an abscess of the psoas major muscle. It is also defined as an infection of the muscle sheaths.
Causes of the disease
As medical statistics show, most often such inflammation develops in patients over 30 years of age. Its most common cause is Staphylococcus aureus. In some cases, the causative agents may be intestinal and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, hemolytic streptococci.
These are the main causes of psoas abscess. In this case, the infection spreads from the primary source to the iliopsoas muscle. Accordingly, pathogens reach it through lymphatic and blood vessels.