Joint arthropathy is joint problems that are not associated with rheumatic diseases. They are usually caused by improper functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems, internal organs, metabolic disorders, allergic reactions, infections, etc. Arthropathy is difficult to detect: it has many types and symptoms, which often overlap with other similar diseases. That is why in case of pain, difficulty moving, or inflammation of the joints, it is important to quickly contact a rheumatologist and conduct research.
Why does arthropathy occur?
The most common causes of arthropathy include:
- infections that appear in the human body due to chlamydia, salmonella, and E. coli;
- damage to small blood vessels;
- diseases of the cardiac, respiratory, digestive systems;
- chronic inflammation of cartilage and bone tissue in psoriasis;
- acute allergic reaction;
- rubella, meningitis and other infectious diseases;
- hyperthyroidism, diabetes and other endocrine problems;
- improper metabolism.
Expert opinion
Marina Igorevna Kozhbukh, traumatologist
There are forms of arthropathy that do not depend on the listed causes. Doctors are accustomed to blaming their appearance on bad heredity and calling them “idiopathic.” Traumatic arthropathy is also classified separately. It is formed due to injuries received.
Alleged reasons for development
The hereditary factor apparently plays a role in the occurrence of this pathology, since 70% of patients with this diagnosis have the HLA-B27 antigen. The second etiological factor is a previous infectious disease. Reactive arthropathy develops two to four weeks after onset:
- chlamydial genitourinary infection;
- one or another enterobacteriosis (salmonellosis, dysentery, yersiniosis, etc.);
- tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia of chlamydial or mycoplasma nature.
If the pathogen is not found, a diagnosis of “unspecified reactive arthropathy” is made. The immune system produces specific antibodies to the antigens of the above-mentioned microbes. People who are carriers of HLA-B27 have a cellular protein structure similar to the antigens of pathogenic microorganisms. As a result, the action of the synthesized antibodies is directed towards infectious agents and the body’s own cells.
Antibodies with antigens form immunocomplexes that are deposited on the synovium of the joints and cause inflammation of the tissues that form the joint. Males between the ages of twenty and forty are more susceptible to the disease.
Don't miss: Psoriatic arthropathy
Types and symptoms
The manifestation of the disease directly depends on its type. We will briefly list the main ones and tell you in more detail about arthropathy of the leg joints.
- Allergic
It is recognized by pain in the joints and signs of allergies: itching, swollen lymph nodes, skin rashes, shortness of breath.
- Parasitic-infectious
Develops due to rubella, brucellosis, chickenpox, viral hepatitis, meningitis, HIV. These diseases can provoke symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, polyarthritis, arthralgia and myalgia. You can cope with them if you get rid of a specific infection or parasite.
- Endocrine
Associated with hormonal imbalances and excess weight. It often torments obese women with crunching, stiffness, pain, and swelling of the small joints of the feet. There are also signs that are unique to diabetes and other endocrinological diseases.
- Hereditary, Reiter's syndrome
This terrible term refers to damage to the joints, organs of vision and the genitourinary system by chlamydia, salmonella and other pests. With Reiter's syndrome, patients first suffer from an acute genitourinary infection, then from an eye infection, and after a month and a half, joint problems are added. Unpleasant sensations and characteristic symptoms may appear in the knee, ankle or foot.
- "Vasculitic"
When small blood vessels are damaged, the tissues located next to the vessels swell and painful sensations occur periodically.
- Associated with diseases of internal organs
The joints hurt a lot, the shape of the nails and fingers may change.
- Reactive arthritis
Cartilage and tissue react to oncology, leukemia or endocrine disorders with knee pain.
- Pyrophosphate
Most often diagnosed. Due to improper metabolic processes, calcium salts settle on the cartilage. This happens after infections and joint injuries.
It is difficult for an ordinary person to notice these symptoms in time and recognize a certain type: there are too many details to take into account. It is much easier to detect common signs and contact a specialist for a detailed diagnosis.
Common symptoms of arthropathy include:
- swelling and inflammation;
- asymmetrical joint damage;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain, often paroxysmal;
- heaviness and other difficulties when walking;
- accumulation of fluid inside the joint;
- redness and swelling of the toes, purple-bluish skin;
- fever and generally feeling unwell;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
Diagnostics
If you have the above symptoms and suspect an infection, you should immediately consult a doctor and get laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis. The doctor must identify the cause of the development of oligo- and monoarthritis. There are certain exclusion criteria:
- septic arthritis;
- spondyloarthritis;
- crystalline arthritis;
- streptococcal arthritis;
- Lyme disease.
Etiological diagnosis is also used, including the following set of methods:
- Immunological. The presence of chlamydia antigen and corresponding antibodies is detected.
- Morphological. The morphological structures of the pathogen are studied (immunofluorescent analysis, staining of preparations).
- Cultural. Chlamydia is isolated (laboratory animals, chicken embryos, cell cultures are used).
- Molecular biological. Involves studying the DNA of the pathogen.
- Examination (bacteriological) of feces and urine.
Features of leg joint arthropathy
Knee arthropathy
These are progressive negative changes in the bones and cartilage that sometimes lead to lifelong lameness and severe deformity of the knee. One knee usually becomes inflamed after injury, but in most cases, inflammatory processes affect both knees at the same time.
Knee arthropathy is caused by thyroid problems, diabetes mellitus, brain tumors, encephalitis, and spinal cord lesions. Children additionally have infections, allergies, and genetic disorders. Reactive arthritis (reactive arthropathy of the knee joints) is a consequence of previous infections, chlamydia. Symptoms of genitourinary and eye diseases are added, rashes similar to psoriasis are added, and the temperature rises.
Regardless of the cause, the knee can hurt if it is heavily loaded, if you stay in an upright position for a long time, or if you put pressure on it. It may become deformed, swell, become larger, heat up and turn red.
Ankle arthropathy
It occurs rarely, but sometimes leads to attacks. Cartilage tissue can be destroyed due to endocrine disorders, leukemia, age-related changes, calcium deficiency, psoriasis, and heredity. It is recognized by painful sensations at night, during physical activity, holding the body in one position for a long time, as well as by stiffness, deformation, redness and swelling.
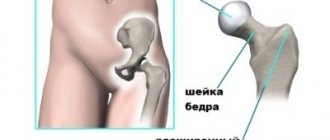
Hip arthropathy
The disease also usually develops after an infection, but is more common in children. It occurs in four stages:
- inflammation leads to thinning of the cartilage;
- Erosion develops on the bone tissue, fluid accumulation causes swelling of the joint;
- The gluteal and thigh muscles atrophy, cysts appear;
- The articular surfaces fuse together, complete immobilization occurs.
Arthropathy of large joints, such as the pelvis, differs in symptoms, it depends on the form, but among the common ones are pain with sudden movements, swelling, stiffness after rest and sleep, discomfort can spread to the groin and buttocks. When reactive arthropathy of the hip joint is detected, the child initially faces only symptoms of conjunctivitis, then inflammation of the urethra joins it. In adults, it’s the other way around: vision and genitals may not give signals, and the joints immediately rebel.
For prevention purposes
Primary prevention of psoriatic arthropathy does not exist today, since the causes of the disease are not known.
To stop the development of pathology, the patient must maintain a normal weight, lead an active lifestyle, avoid stress, viral and bacterial infections, eat a balanced diet, and take vitamin D.
In addition, there are the following methods of preventing the disease:
- Splinting. With the help of splints, the joint can be given the correct position, the inflammatory process can be controlled, and joint erosion can be reduced.
- Hydrotherapy. Exercises performed in water help strengthen joints and maintain their function.
- Cold and hot compresses. If they are applied one by one to the affected joints, they relieve pain and remove swelling.
It is necessary to alternate physical activity and rest, do not overload the joints, if necessary, use aids for movement, for example, canes, carts, they help reduce the load on the joints.
Compliance with all these rules will reduce the risk of disease progression and improve the quality of life.
How is the treatment carried out?
Complex therapy is used. You will need to take the following prescribed by your doctor:
- antimicrobials;
- immunostimulants and immunomodulators;
- NSAIDs;
- if inflammation is severe, hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Be sure to also eliminate the disease that caused the development of arthropathy. If it is not an infection, but endocrine disorders, hormones are added; if it is a blood disease, chemotherapy is added. To relieve symptoms, injections can also be made into the joint, or a solution of glucose or lidocaine can be injected inside.
The use of folic acid and vitamins saves you from the risk of complications and consequences of drug therapy.
After a course of medications, it is recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures. These are UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, paraffin treatment or electrophoresis, ultrasound, ozokerite. Ideally, you should relax in a sanatorium and take advantage of the services of mud therapy, massage, physical therapy, and take sulfide and radon baths.
A special situation arises when the mobility of the knee joints is severely limited and the tissues are seriously deformed. This is an indication for surgery, a gentle diet, bed rest and a special recovery program.
Forecast
Favorable with timely prescribed therapy. In the absence or inadequately selected treatment, chronic pathology is possible. The disease takes on a subacute course with frequent periods of exacerbation. Patients who have a genetic predisposition to reactive arthritis are most susceptible to this complication. The disease does not lead to the development of contracture (complete immobility of the joints). The patient may still experience pain and some stiffness. With concomitant eye damage, in severe cases, vision loss occurs.
Looking for a good doctor? Make an appointment with the best rheumatologist or orthopedist in your area.
295
Orthopedist