Most people experience chickenpox at an early age, when it does not cause any particular harm to health and, as a rule, passes without complications. However, in adulthood and, especially, during pregnancy, the disease can lead to serious consequences (developmental defects, miscarriage, premature birth). And for the woman herself, chickenpox can pose a serious danger, as it can provoke pathological disturbances in the functioning of vital systems and organs, for example, the heart, brain, kidneys.
How can you get chickenpox during pregnancy?
Chickenpox is a common name for an infectious disease that can rightfully be considered a “children’s disease.” Caused by a virus from the herpetic group - Varicella Zoster. Chickenpox is a very contagious disease, so almost everyone gets it in childhood, after which a strong immunity to the infection is formed for life.
Women during pregnancy have an increased risk of getting chickenpox of two types:
- acute “classic” chickenpox;
- exacerbation of infection in the body with the appearance of symptoms of herpes zoster.
The source of active viruses is a sick person, often a child. It is not contagious for the entire period of illness, but only 24 hours before the appearance of the rash and another calendar week after the last element of the rash appears on the skin (this is easy to track if you smear new spots with brilliant green every day).
After this, the person, even if the rash itself has not yet gone away, is not contagious to the people around him. The virus cannot be transmitted from a third party (one who has been in contact with a sick person, but is healthy himself).
The pathogen is transmitted through the air - it is contained in the exhaled aerosol of a sick person. Varicella Zoster can be actively transported with air currents over long distances, including through ventilation systems. But the virus is viable under normal conditions for only 10-15 minutes. And ultraviolet radiation (including sun rays), various disinfectants, and high temperatures have a detrimental effect on the pathogen.
The incubation period from the moment of infection can be up to 21 days - this is the time for which quarantine is imposed when an acute episode of the disease is detected in a group.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
Thus, you can become infected with chickenpox only through direct contact with a sick person (usually a child) on the eve of the rash and for another week after the last elements appear. To do this, it is enough just to be within walking distance of the patient.
Is chickenpox dangerous for a pregnant woman if she has already had it?
After suffering from chickenpox, the body usually develops lasting immunity to this disease for life. That is, if you were ill as a child, then you have nothing to worry about. Cases of reinfection with chickenpox are known, but they are extremely rare.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, but does not remember whether she had chickenpox as a child, she can get tested to find out if she has antibodies to this disease in her body. According to existing statistics, antibodies to chickenpox are detected in 90% of women who undergo such testing.
Is it possible to get sick again?
After suffering from chickenpox, a person develops lifelong immunity to the disease and special antibodies of the Ig G class circulate in the blood. In addition, the virus itself remains in the body - it “hides” in nerve cells.
Weakening of the immune system, which is typical during pregnancy, can lead to an exacerbation of the disease, chickenpox, but in a different form - in the form of shingles. Pregnant women with HIV infection and blood diseases are especially at risk.
In addition, during pregnancy there are often cases when a woman, after contact with a sick child, becomes ill again in the same “childish” form. This may be due to the following circumstances:
- In childhood, chickenpox was confused with another infection, but in fact the girl did not have it. For example, rickettsial infections are accompanied by the same rash on the body.
- Chickenpox was suffered in a very mild, erased form, which did not lead to the formation of good immunity to the infection.
- If a girl has had chickenpox in the first six months of life, the likelihood of a weak immune response is also high due to the immaturity of all systems and organs.
- There are diseases that lead to severe immunodeficiency during pregnancy, for example, HIV.
When is the risk greatest?
The worst thing is to get sick a couple of days before giving birth, then the risk for the child becomes simply enormous. The baby may be born stillborn or with chronic chickenpox. However, even in such cases, modern medicine minimizes the risks for mother and child by delaying childbirth.
The long-awaited day for the expectant mother is moved forward a certain amount of time, and the patient herself is treated. In cases where it is simply impossible to delay childbirth, doctors, shortly before it begins, inject the woman with a dose of immunoglobulin, which prevents the death of the child. But at the same time he does not protect him in any way.
Is contact with chickenpox dangerous?
Contact with infection is dangerous for a pregnant woman in the following cases:
- If the girl has never had an infection or it occurs in a very mild form.
- If there was close communication in the period before the appearance of the rash two days or during the period of active appearance of new elements.
- If immunity is reduced due to the presence of other serious diseases.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
In most cases, a pregnant woman, even after prolonged contact with a patient, remains healthy due to her immunity, which was formed in childhood after an episode of illness.
Features of the manifestation of the disease
The disease begins to progress after the patient’s body is infected with type III herpes virus.
Varicella zoster virus
The pathogen is transmitted primarily by airborne droplets or through household liquids. The first signs of the disease appear on average within several days (sometimes up to 3 weeks) after infection.
Symptoms of the disease
The list of early symptoms of chickenpox includes the following:
- general deterioration of health;
- loss of appetite;
- temperature increase;
- headache.
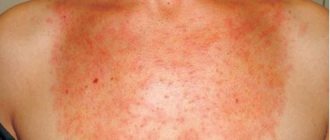
Chickenpox symptoms range from fever, headache and abdominal pain to loss of appetite. But first of all, in classic chickenpox a rash appears
A couple of days after the first signs appear, the skin becomes blistered with a clear liquid. Every day the number of rashes increases. The peak is reached approximately 5-7 days.
Chickenpox stages
The key danger of chickenpox in the case of pregnant patients is that the latter’s immunity in most situations is seriously weakened, which is why the disease occurs with moderate or severe severity and is accompanied by an increased intensity of adverse symptoms. The possibility of complications cannot be ruled out. They will be discussed in the following sections of the publication.
Main symptoms in early and late stages
The chickenpox virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, so it first enters the respiratory tract, and then into the blood and lymph. Only after this the body temperature begins to rise, lethargy, weakness, chills appear - signs similar to colds. The main manifestations of infection during pregnancy are as follows:
- Temperature increase . Usually observed only in the first few days of the disease. As soon as the rash appears, the temperature drops. In addition to this, pregnant women note a decrease in appetite, nausea and even vomiting.
- Rashes appear that itch . Most often, the first papules appear on the scalp, on the face. There is never a rash on the feet and palms. At the beginning, a slight redness (spot) appears, then a bubble forms in its place, after which it opens and a crust forms.
- After the latter disappears, white spots are visible in this area for some time; they disappear after a couple of weeks without leaving a trace. Typically, elements of the rash appear in groups after some time, so all stages of the disease can be found in one person at once.
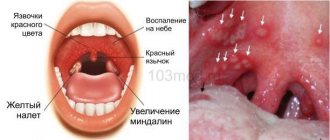
- Damage to mucous membranes. Spots, characteristic blisters and crusts can be found on the surface of the epithelium on the gums, soft and hard palate, and tonsils. In this case, symptoms similar to stomatitis arise - it hurts to eat. If the vaginal mucosa is affected, itching, burning, and discharge appear.
There are also atypical variants of the course of the disease, which is more dangerous during pregnancy. They are as follows:
| Erased form | In this case, only individual elements of the rash are detected, there is no temperature or other symptoms. Often the disease in this manifestation is not diagnosed |
| Bullous | Instead of the usual small bubbles, large ones appear - up to 2-5 cm in diameter, along with this, temperatures and other symptoms are more pronounced |
| Hemorrhagic | Set if the blisters fill with blood |
| Gangrenous | The blisters fill with pus, areas of tissue death appear, all this is accompanied by a very high temperature |
| Generalized | Areas of necrosis appear not only on the skin, but also on internal organs. Extremely severe variant of the disease |
How does the disease manifest itself in a pregnant woman?
A pregnant woman can feel the first signs of the disease within 14-21 days from the moment the virus is introduced. This is how long the incubation period lasts after a pregnant woman comes into contact with a patient with chickenpox.
You need to know that you can become infected from a person within two days from the onset of the rash, and within a week after the last addition of vesicular elements.
The main symptom of the disease is a characteristic rash. It appears approximately on the second or third day after an intoxication syndrome reminiscent of a cold. First, a small reddish spot forms on the skin, and then a bubble with liquid appears in its place. Vesicles can be localized in various areas of the skin and visible mucous membranes. New lesions form approximately every 3-4 days. The phenomenon is accompanied by severe itching. In addition, it is noted:
- violation of general condition;
- temperature increase;
- stomach ache;
- aches in muscles and joints;
- deterioration of appetite and sleep;
- headache.
The severity of the disease directly depends on the person’s age . The older the patient, the stronger the severity of symptoms and the more severe the process.
Consequences of chickenpox during pregnancy depending on trimester
The danger of this “childhood” infection largely depends on the form in which it occurred during gestation, as well as on the period at which it was transferred. There is evidence that in every fourth case of chickenpox during pregnancy, the virus is transmitted to the child - through the placenta, through the air or ascending through the cervical canal when the vaginal mucosa is affected.
The consequences of the infection may be as follows:
- Chickenpox was suffered in the first trimester - up to 12 weeks. In approximately 5-7% of cases, the virus will reach the child. In this case, chickenpox syndrome develops - underdevelopment of the limbs, atrophy of the nerve cells of the brain, and various eye defects. All this is fraught with disabling consequences for a child with physical and mental disabilities.
- In the middle of pregnancy - from 12 to 20 weeks. Such deviations occur in no more than 2% of children.
- At the end of pregnancy and before birth or within 24 hours after it. If a woman gets chickenpox at this time, her antibodies do not yet have time to form and reach the child. This greatly increases the likelihood that the baby will get sick - neonatal chickenpox occurs. The condition can be life-threatening for the baby, as it is often accompanied by the development of pneumonia, inflammation of the brain and liver.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
It should be borne in mind that the exacerbation of a chronic infection in the form of herpes zoster does not affect the child’s health - the mother’s antibodies protect the baby. The only dangerous cases are when a woman becomes infected for the first time in her life during pregnancy.
Chickenpox in early and late pregnancy poses a danger not only to the fetus, but also to the woman. The point is the possible consequences of infection for a woman’s body. The following is possible:
- stopping the development of pregnancy;
- miscarriages at different stages and premature births;
- pneumonia (pneumonia) in the pregnant woman herself.
Pneumonia is especially dangerous. The likelihood of their development is high due to compression of the lungs from the abdominal cavity by the growing uterus. Pregnant women quickly develop respiratory failure, and mortality can reach up to 40-50%.
Watch this video about the consequences of chickenpox for mother and child:
Complications and possible risks to the fetus
You should know about the symptoms of the disease
Statistics say that chickenpox very rarely affects pregnant women. But it is worth noting that everywhere there are exceptions. Let's look at the complications of chickenpox by trimester to study all the possible risks.
The first trimester of pregnancy is the most difficult period. In the first 12 weeks, all the organs of the unborn child necessary for normal development are formed. The mother's placenta is not yet fully formed, so all kinds of viruses, infections and bacteria can penetrate and disrupt the normal physiological development of the embryo. However, chickenpox infection is very rare. If we talk about the fact that a viral disease has developed in the fetus, then there can be several outcomes: death of the embryo in the early stages, miscarriage, underdevelopment of organs, damage to the central nervous system, deformity. Only with an ultrasound examination in the second trimester can one learn about the development of the fetus. The mother may be faced with the choice of medical abortion.
The second trimester of pregnancy is called the “golden period”. Toxicosis recedes, the tummy is not so noticeable, and the woman feels generally good. During this trimester, the placenta is fully formed. This means that the baby is completely protected from all kinds of viruses. And even if chickenpox is severe, the virus does not threaten the baby.
If chicken pox “caught” a pregnant woman in the third trimester, then it is necessary to pay special attention to this issue. The body of the expectant mother simply does not have time to form a “healthy” immune system. The baby can become infected both in the womb and during labor. How is this dangerous for a child? First of all, he may develop congenital chickenpox, which is quite complicated. It affects internal organs, the central nervous system, and skin. If you provide timely medical intervention (passive immunization), the risk of having a completely healthy baby increases by as much as 60%.
Read: Is it possible to suddenly quit smoking during pregnancy: expert advice
Diagnosis of the disease
Typically, the diagnosis of chickenpox is not difficult and is established based on the nature of the rash and the presence of contact with a sick child. If necessary, the following methods can be used:
- PCR . For analysis, the contents of the vials in which the virus is detected are collected.
- ELISA . Allows you to detect the presence/absence of antibodies in a woman’s blood - this way you can judge whether she has previously had chickenpox, whether she is currently in the acute or subacute period. Class G immunoglobulins are found in everyone throughout life who has ever had an infection in any form.
How is prevention carried out?
If the expectant mother has a history of chickenpox, preventive measures are not required. Even direct contact with the patient is not dangerous for her. But in the case where there is no immunity to this disease, it is necessary to try to prevent infection in the following ways:
- avoid long stays in rooms with a large number of people (especially in groups of children);
- eliminate contact with a person who shows signs of a cold and skin rash;
- a child in the family who has not had chickenpox should be vaccinated;
- The vaccination should be given to the mother herself, but only after childbirth.
If all recommendations are followed, the risk of developing the consequences of chickenpox during pregnancy will be minimal. The best option for preserving the health of your baby is planning a pregnancy. The woman gets the opportunity to undergo a full examination and vaccination against infections. Such a competent approach saves the expectant mother from many problems during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Treatment of chickenpox during pregnancy
Usually the infection is uncomplicated, so proper treatment at home is sufficient. Only atypical and complicated forms are subject to inpatient care. The following groups of drugs are used (combinations, regimens and dosages at the discretion of the attending physician):
- antipyretics - usually based on ibuprofen;
- to relieve itching - antihistamines, for example, Loratadine, etc.;
- antiviral - based on acyclovir;
- interferons - to increase your own immunity in the fight against infection;
- sedatives - tea with chamomile, mint, valerian.
In each case, the question of the need for passive immunization with chickenpox immunoglobulin is decided.
If you get chickenpox on the eve of giving birth, you should try to delay it for several days (3-4) so that the woman’s body develops immunity to the virus - this way it will be possible to protect the newborn.
If at the time of birth a woman is found to have rashes in the thighs and perineum, the issue of performing a caesarean section is decided.
If the mother gets sick immediately after giving birth, the baby is isolated until the end of quarantine - for at least 21 days.
Treatment of rashes
This is one of the important aspects of chickenpox treatment. The recommendations are as follows:
- You should avoid baths, saunas, and hot baths, so as not to provoke wetting and the addition of a secondary infection.
- It is better to wear clothes made from natural materials and change them at least once a day.
- It is important to treat all rashes. If they are on the skin, ordinary brilliant green (1% alcohol solution) or potassium permanganate (10% alcohol solution) will do. There is no need to touch those elements that have already dried - only new elements are processed.
- If ulcers have formed (especially on the mucous membranes), it is necessary to rinse several times a day with a solution of potassium permanganate (aqueous or alcoholic, weak). You can also treat them with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- If there are rashes on the genitals, it is recommended to do sitz baths with furatsilin, and also apply sea buckthorn oil. If there is a lesion in the vagina, use tampons based on it.
- If there are eye lesions, it is necessary to instill 30% sodium albucid up to 4-6 times a day.
Diet
Often the state of general intoxication is accompanied by suppression of appetite and the appearance of nausea and vomiting. And if aphthae have formed in the mouth, any meal becomes painful. The following is recommended:
- exclude fatty, fried, smoked, salty, spicy foods;
- cook exclusively by steaming, boiling or stewing;
- Dairy products, stewed vegetables, lean meat, eggs, teas and compotes are useful.
What to do if you suspect chickenpox?
If during pregnancy the expectant mother exhibits primary symptoms of chickenpox, then you should immediately report them to your doctor managing the pregnancy. If possible, you should go to the hospital on the same day, where doctors will prescribe treatment, which most likely will consist of taking Acyclovir.
In cases where certain complications such as difficulty breathing, fever or cough are added to the general symptoms of chickenpox, you need to call an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself.
You need to look at how you feel, since pneumonia with chickenpox develops quite quickly, so it is very important to start treatment in the first days, or better yet hours, after symptoms are identified. In all other cases, when the condition becomes critical, you should immediately call an ambulance.
When can you plan a pregnancy after chickenpox?
If the infection takes a woman by surprise while planning a pregnancy, then she should refrain from conceiving for another two to three months after chickenpox. This time is necessary to restore immunity and eliminate the effects of drugs used for treatment on the fetus.
If pregnancy occurs earlier than this period, chickenpox is not an indication for termination. In these cases, all women are recommended to undergo screening at 10-12 and 20-22 weeks using expert-class devices, and, if indicated, to perform amniocentesis.
Possible consequences for mother and child
Consequences for mother and baby
General information
As noted, during pregnancy the disease being studied today can take on atypical forms. About them in the table.
Table. Possible atypical forms of chickenpox in pregnant women
| Forms of the disease | Peculiarities |
| Hemorrhagic | The fluid contained in the blisters includes blood. Coughing up blood, vomiting blood, as well as nosebleeds and other adverse effects are possible. |
| Gangrenous | In addition to the blisters characteristic of chickenpox, dry crusts appear on the skin, which later progress into ulcers. |
Hemorrhagic form of chickenpox
According to average statistical data, more than 30% of pregnant patients with chickenpox develop a complication such as herpetic pneumonia. This secondary disease is characterized by a very severe course and requires qualified medical intervention. Otherwise, the consequences can be catastrophic, even fatal.
The list of possible complications also includes the following:
- miscarriage in the early stages;
- violations of the formation of the baby’s skeletal system;
- developmental disorders of the main sense organs;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- formation of rough scars on the skin of the mother and fetus;
- intrauterine death of a developing fetus;
- infection of a child with congenital chickenpox;
- various pathologies that provoke developmental disorders of the baby after his birth.
The dangers of chickenpox in pregnant women
The list of complications and, in general, the level of danger of chickenpox for mother and child vary depending on at what stage of pregnancy the woman fell ill. Thus, during the third trimester, this disease poses virtually no significant threat and proceeds in the same way as in non-pregnant patients. Information regarding the first two trimesters requires more detailed study.
The disease is especially dangerous in the 1st and 2nd trimesters
Chickenpox in the first trimester
During the first 12 weeks, the formation of the main organs and tissues of the future baby occurs. That is why absolutely any disease during this period poses an increased danger. The placenta as such remains underdeveloped, read – unable to provide adequate protection for the developing child.
First trimester of pregnancy and chickenpox
According to statistics, infection of the fetus occurs extremely rarely, but if intrauterine chickenpox does begin to progress, it will not go away without a trace with almost 100% probability.
The consequences can be very diverse: from disruption of the development processes of tissues, organs and systems to severe pathologies of the nervous system, various deformities and even intrauterine fetal death.
Chicken pox in the 1st trimester will affect the baby
The condition of the fetus is assessed using ultrasound methods. If a specialist identifies severe pathologies and deformities that pose a danger to the fetus or can significantly worsen the quality of life of the baby after birth, the question of artificial termination of pregnancy will be raised.
Ultrasonography
There is no confirmed information about the relationship between chickenpox and the likelihood of natural miscarriage or miscarriage.
Chickenpox in the second trimester
Chickenpox in the second trimester
After the 12th week, the likelihood of the fetus becoming infected with chickenpox is almost completely eliminated. By this point in time, the placenta is already able to provide adequate protection to the developing fetus, which reduces the risk of developing various complications to almost 0.
After 12 weeks, the risk to the baby’s health decreases
If you get chickenpox in the second trimester, undergo an ultrasound to assess the baby's condition and provide personal reassurance.
Basic diagnostic methods
The doctor rarely has to doubt the diagnosis, because the rash and other accompanying symptoms are very characteristic. However, when compiling a medical history, he will try to find out:
- whether you have been in contact with anyone who has chickenpox (if so, who are they);
- how long the contact lasted;
- what is the state of your immunity, as well as the immunity of your immediate family;
- whether the disease is accompanied by additional complications.
When examining the patient, the doctor must exclude other similar diseases (for example, parasitic vesicular rickettsiosis or generalized lymphopathy, etc.).
Also, the nature of the rash will be completely different in case of shingles or an allergy to some kind of bites.
If the doctor needs to obtain reliable confirmation of the diagnosis, he may refer you for special laboratory tests:
- to detect tissue antigens, paired blood sera will be subjected to serological tests;
- to detect the virus itself, an RTGA is done;
- to detect whether there are active antibodies against the pathogen, you will need RSC;
- The skin rash (its elements) can be examined under a light microscope using silvering reagents.
The doctor will also recommend additional tests for you. They will help make sure that your child is not affected in any way by the infection.
The occurrence of chickenpox in itself is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy, but it is better to find out that everything is in order and calm down.
Among the examinations include: ultrasound, chorionic villus biopsy, blood tests for markers of prenatal pathology, as well as cordocentesis or amniocentesis.
At what stage is infection dangerous during pregnancy?
Chickenpox poses a threat to the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy, up to the 20th week. The risk of developing abnormalities in the formation of the fetus before the 14th week does not exceed 1%, and from the 14th week to the 20th week the probability increases to 2%. From the 20th week until birth, chickenpox is not dangerous for the baby, since the formed placenta well protects the baby from all kinds of infections. This disease can threaten the health of the child if the mother becomes infected immediately before childbirth, 3-14 days. In such a situation, the development of congenital chickenpox is possible, which in 25% of cases ends in death for the little man.
Now imagine the situation. The eldest child fell ill with chickenpox, and I am pregnant and have never had this infection before. What to do in this case? We will look at this issue further.
Prevention
If a woman preparing to be a mother doubts whether she had chickenpox as a child, she should be tested for antibodies during pregnancy planning. If they are absent, it is extremely important for a woman to be vaccinated against smallpox.
A pregnant woman should not have contact with children as a source of infection. At this time, visiting schools, kindergartens, and mass children's events is undesirable. The disease has a long incubation period and the patient may not know that she is already a carrier.
If forced contact with patients in the first three days, an injection of immunoglobulin is required.
What Dr. Komarovsky says about chickenpox in pregnant women, and how dangerous the disease is for the expectant mother and baby, we learn from the video:
Chicken pox is not a dangerous disease, and in most cases it occurs without complications. But during pregnancy, complications may arise that will result in serious, sometimes irreparable, consequences for the unborn baby.
Features of chickenpox treatment in the case of pregnant women
Basic information about the features of the treatment of chickenpox in pregnant patients is given in the table.
Table. Chickenpox treatment
| Features of the course of the disease/pregnancy | Treatment procedure |
Normal course | If chickenpox occurs without complications and does not pose a threat to the mother and fetus, no specific treatment is used. In such situations, we limit ourselves to treating the blisters with brilliant green or another suitable remedy (as recommended by the doctor). Important! As a rule, chickenpox rashes are very itchy. Of course, you can’t scratch them - you can get infected. To get rid of itching, you can, for example, use calamine lotion. If the infection occurred during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy or on the eve of delivery, the doctor may prescribe immunoglobulin injections. |
Severe course | If chickenpox takes an atypical form and/or causes serious complications, more serious treatment will be required. As a rule, special antiviral drugs are prescribed, for example, acyclovir. This is used exclusively before the 20th week of the period and only during the first day after the initial symptoms of chickenpox are identified. If the above rules are not followed, the use of acyclovir will not give any positive results and, moreover, will harm the baby. |
Important! During pregnancy, a woman should take double responsibility for her health. Any uncontrolled self-medication is strictly prohibited - drugs to combat chickenpox are prescribed only by a qualified doctor.
To better understand the procedure for detecting symptoms of chickenpox during pregnancy, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the information below.
So, you have contracted chickenpox. The first thing you need to do is go to an appointment with the doctor managing your pregnancy. In the absence of complications and a serious threat to the fetus, treatment will most likely be limited to treating the rash with brilliant green or another remedy recommended by the doctor.
It is imperative to see a doctor if you are infected with chickenpox.
The decision regarding the need to use additional medications is made only by the doctor and only after a thorough examination of the patient and a comprehensive assessment of possible risks.