Autoimmune thyroiditis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland of autoimmune origin. Unfortunately, every person who encounters it is forced to follow a special lifestyle and diet. Autoimmune thyroiditis has many limitations. But it is possible to make a balanced diet.
What can you eat with this disease? And what not? What should the menu be like? This and much more will be discussed now.
Briefly about the disease
Before we talk about the basics of a diet for autoimmune thyroiditis, we need to discuss the specifics of this disease.
It manifests itself in a violation of immunological control. The body of a person suffering from this disease produces antibodies to the thyroid tissue, as well as to thyroid peroxidase (this is the main enzyme of hormones) and thyroglobulin (a protein that accumulates in the structural and functional unit of the thyroid gland).
This violation leads to inflammation. This, in turn, causes the destruction of gland cells. The result is hypothyroidism.
What does the diet include? The most important thing is to limit or completely eliminate foods that can increase autoimmune reactions and inflammation; in addition, it is necessary to enrich the diet with foods that can restore the intestinal microflora. Since it is its change that is the key factor in any autoimmune disease.
Do I need to take iodine to prevent thyroid diseases?
Many “health stores” and a number of pharmacies, including online, sell dietary supplements “for the thyroid gland” that contain iodine and other ingredients. In many of these supplements, the amount of iodine exceeds the daily norm not only several times, but even several hundred times, which is actually dangerous to health. Taking too much iodine can lead to even greater thyroid dysfunction. In such cases, autoimmune thyroiditis often worsens.
It has also been noted that those who take iodine additionally due to a possible lack of it in the area where they live are more likely to experience dysfunction of the thyroid gland due to an overdose of iodine preparations, especially in people who have some kind of gland dysfunction . Of course, it is advisable for these people to take iodine, but the daily dose should not exceed 500 mcg.
There is one more disadvantage: there are no clear recommendations on the amount of iodine intake (as well as other minerals and vitamins), since over the last decade the old norms have been radically revised. For example, it is believed that an adult needs 150 mcg of iodine per day, pregnant women should receive 220 mcg, and during lactation - up to 290 mcg of iodine per day. In the past, the amount of iodine recommended for supplemental intake was significantly higher.
Strictly prohibited products
Under no circumstances should you eat foods high in refined carbohydrates, as well as foods that contain Omega-6 – polyunsaturated fatty acids.
These foods are the most likely to promote inflammation. Because the body, assimilating them, produces so-called oxidants - oxidizing agents that destroy cells and support inflammation. In addition, they contribute to dysbiosis, obesity, diabetes and the development of intestinal and breast cancer.
Here is a list of foods that are prohibited from consumption:
- Grape seed oil.
- Wheat germ.
- Rapeseed, peanut, soybean, cottonseed, corn and sunflower oils.
- Pumpkin seeds.
- Rye, oats, lentils, chickpeas.
- Wheat.
- Sesame.
Omega-6 predominates in all of the above.
Ban on vegetables, cereals and more
Of course, the short list above is not all that you will have to give up when following a diet for autoimmune thyroiditis.
A ban is imposed on dairy products. After all, proteins and casein may not be completely digested, and this will create an additional burden on the gastrointestinal tract.
Trans fats should not be consumed either. Namely:
You should also not eat starchy vegetables, which include:
Some experts claim that nutrition for autoimmune thyroiditis also involves avoiding cereals, grains and legumes. Doctors believe that gluten should be eliminated first of all from your diet. In other words, patients are recommended to follow a gluten-free diet.
Patients are also advised to avoid nuts, seeds and nightshade vegetables. But opinions on the need to follow such a diet for autoimmune thyroiditis are contradictory. If you wish and after consulting with your doctor, you can try to stick to it for 2-3 months, and then draw conclusions regarding its effectiveness. The main thing is to monitor the dynamics of antibodies to thyroglobulin.
Gluten-free diet
Although gluten-containing foods are not the cause of Hashimoto's disease, they can trigger an autoimmune response in some people. This leads to inflammation and tissue destruction. Gluten is part of every wheat flour product and can be found in many products. You should avoid:
- Wheat.
- Barley.
- Cookie.
- Cakes.
- Pizza.
- Pasta.
- Bread
Gluten-free alternatives to regular flour products are available, although they can be expensive. For people suffering from Hashimoto's disease, the best thing to do is try a gluten-free diet and see if it relieves symptoms. With autoimmune thyroiditis, diet and lifestyle must change. If you continue to drink milk and a bun every day and eat fried potatoes in the evenings, the situation will not improve.
Dishes that will cause harm
Before listing the permitted foods for autoimmune thyroiditis, it is necessary to highlight a separate list of those foods that are strictly prohibited. This:
Supplements for AIT
what supplements to take for AIT
I have been studying nutritional supplements and how they affect the body in AIT for several years now. I chose the best ones in my opinion.
I took all these dietary supplements and I know for sure that they help with autoimmune thyroiditis. That is, this is not just blah blah blah, like many theorists, but is based on personal experience.
- selenium (lowers antibodies)
- folate
- vitamin C (no more than 500 mg per day)
- vitamin D (studies show a clear link between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune diseases. We are deficient, but it is better to get tested to know for sure)
- Omega-3 (for the balance of omega acids in the body)
- Magnesium (thyroid hormones)
- Zinc (thyroid hormones)
- Pepsin (increases acidity, in our case it is reduced)
- Milk thistle (for the liver and gastrointestinal tract)
- Iron (we have iron deficiency everywhere)
- Food enzymes (help digest food, help with leaky gut syndrome)
- Probiotics (beneficial bacteria) can be Saccharomyces boulardii.
- Glutamine (restores intestinal walls)
What to include in your diet
It is highly recommended to build your menu based on products containing Omega-3 (fatty acids). Their consumption helps correct dysbiosis and reduce inflammation.
Their sources are products of plant and animal origin:
The meat of animals and birds is also allowed, but only those that have been fed on grass. It's difficult to find such a product. But cows, in any case, feed on plant feed throughout the entire spring-summer period. So it’s better to make a choice in favor of beef.
Fish must also meet certain requirements. You need to buy one that has lived in natural conditions - in the ocean or in the sea. Artificially fed fish contains too much Omega-6.
Allowed fruits and vegetables
Continuing to talk about how to eat with autoimmune thyroiditis, we need to mention fruits and vegetables, the consumption of which is allowed. The list is as follows:
In general, vegetables that do not contain starch are allowed. You should also include fiber and fruits (except bananas) in your diet, as their consumption will help reduce inflammation and improve peristalsis.
Products prohibited for consumption
There are foods that can aggravate the disease by negatively affecting hormone production. One of the first on this list are products containing soy. It contains isoflavones, which slow down the formation of enzymes that convert the T4 hormone to T3.
In addition to soy, the following products are contraindicated:
- sugar, coffee, cocoa, strong tea, which promote the production of cortisol and adrenaline - hormones with a negative effect on the thyroid gland;
- fresh cabbage, radishes and rutabaga - these products contribute to the formation of goiter, they become safe only after heat treatment;
- peanuts, horseradish, spinach, peaches, pears and strawberries, citrus fruits - for the same reason;
- canned food, smoked meats, spicy dishes and marinades;
- fried foods, fatty saturated broths, jellied meat and fish;
- alcohol and energy drinks;
- sweets in limited quantities;
- foods rich in iodine (in particular, seaweed);
- fish caviar, seafood;
- any fast food.
Thyroid diseases are the most common reason for visiting an endocrinologist. Chronic thyroiditis of the thyroid gland - what is it and how to treat it?
How to treat the thyroid gland at home, read here.
Is pregnancy possible with autoimmune thyroiditis? Here https://gormonexpert.ru/zhelezy-vnutrennej-sekrecii/shhitovidnaya-zheleza/autoimmunnyj-tireoidit-i-beremennost.html all about how pregnancy goes with this disease and what consequences can be expected for the mother and fetus.
Vitamins
They need to enrich your diet. Here are the vitamins that are really important to take for autoimmune thyroiditis:
Is it possible to eat cabbage if you have thyroid diseases?
Among the supplements “for the thyroid gland” are the so-called goitrogens, or goitrogens, which suppress the function of the thyroid gland. On the one hand, they are recommended for hyperthyroidism. On the other hand, endocrinologists and nutritionists warn that in case of hypothyroidism it is necessary to avoid goitrogens, and especially those types of food that contain them. Very often, a goitrogenic substance is called anything that can lead to goiter - an enlargement of the thyroid gland. Most often this is the so-called group of cruciferous vegetables and soy products.
Cruciferous vegetables include cabbage, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, kale, radish, bok choy and a number of other vegetables. They are rich in substances that are credited with anti-cancer properties. However, these substances can disrupt iodine metabolism and suppress the production of thyroid hormones. This does not mean that people with thyroid dysfunction should avoid these vegetables. On the contrary, different types of cabbage and radish are very healthy. It is suggested that it is necessary not to overindulge in the amount of these vegetables in the daily diet, especially in the presence of hypothyroidism.
There is no exact data on what maximum portion of cruciferous vegetables is permissible so as not to harm the thyroid gland. Typically, experiments are carried out on healthy people using inflated amounts of vegetables or products made from them. In addition, the variety of vegetables makes it difficult to determine their overall impact. Most often, a negative effect is observed in people suffering from certain metabolic disorders and in older age. Taking 1-2 kg of raw vegetables, especially cabbage vegetables, to improve health is not justified.
In general, there are no clinical studies on the actual harm or benefit of cruciferous vegetables for thyroid function.
Macro- and microelements
When adhering to the correct lifestyle and diet for autoimmune thyroiditis, you must not forget about the need to include in your diet foods that contain macro- and microelements necessary for the body. Especially the following:
These substances normalize microflora. Namely, the quality of digestion, absorption and synthesis of vitamins depends on it.
Treatment for Hashimoto's disease
Many doctors who diagnose thyroid disease may prescribe hormone therapy and continue testing thyroid hormone levels until they return to normal. First of all, Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an immune problem. Until the immune system stabilizes, the body will be at risk of further autoimmune attacks.
The full range of treatment options should include further research into what caused the disorder in the first place, as well as hormone therapy. You need to follow a special diet for autoimmune thyroiditis. Those with Hashimoto's disease must make dietary and lifestyle changes to eliminate aggravating stressors that could lead to chronic immune dysfunction.
When the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormone, hypothyroidism occurs, which affects the body's metabolism, so weight gain is often associated with thyroid problems. The good news for people with Hashimoto's disease is that the condition can be completely controlled with the right diet and taking Levothyroxine. This remedy is the first line of defense against hypothyroidism because it mimics the hormone (thyroxine) produced by the thyroid gland.
For those who have abandoned the gluten-free diet
Above we talked about what you can and cannot eat with autoimmune thyroiditis. It must be said that the menu will be especially varied for people who decide not to follow a strict gluten-free diet. Their diet is more varied:
From the listed products you can create a very diverse, balanced and non-repetitive menu. With autoimmune thyroiditis, you can eat tasty and nutritious food.
Diet for autoimmune thyroiditis of the thyroid gland
Thyroiditis does not require strict dietary restrictions. The menu, on the contrary, should vary, but be balanced. It is necessary to regularly consume foods containing iodine and selenium. The optimal caloric content of the daily diet is from 1400 to 1900 kcal. Calorie intake less than 1200 kcal leads to progression of thyroiditis, weight loss and deterioration of health.
Prohibited Products
Excessive gluten consumption can provoke unwanted autoimmune reactions. Therefore, if you have thyroiditis, it is recommended to follow a gluten-free diet. The largest amount of gluten is found in cereals, so for thyroiditis the following are prohibited:
- wheat, oats, rye;
- bakery products;
- bran;
- pasta;
- breading;
- ready-made breakfasts.
Also, in case of autoimmune inflammation, it is necessary to exclude the following products:
- boiled, smoked sausages and frankfurters;
- products with high soy content;
- marinades;
- semi-finished products;
- fast food;
- chocolate, ice cream, marshmallows and other sweets;
- canned food (peas, beans, corn, pineapples);
- fish roe, crab sticks;
- cabbage family vegetables: radishes, cabbage, turnips;
- sauces, spices, seasonings, bouillon cubes;
- strong coffee, tea, kvass, industrial juices, soda, alcohol.
Since iodine is considered one of the provocateurs of reactive hypothyroidism, in case of autoimmune thyroiditis its consumption should be limited and should not exceed 50 mcg per day.
Healthy food
The diet for thyroiditis is selected by the doctor taking into account the severity of the pathology and the presence of other diseases. In case of AIT of the thyroid gland, the diet should be dominated by foods saturated with fatty acids, selenium and calcium. To get rid of extra pounds, a person with thyroiditis must adhere to the principle of separate nutrition. It is recommended to consume light foods separately from dishes that are difficult for the body to digest.
The following products are considered the most useful:
- fresh vegetables;
- fruits and unsweetened berries;
- lean meat;
- chicken and quail eggs;
- fish fat;
- pumpkin and flaxseed oil;
- all types of seafood;
- mushrooms;
- cheese, cottage cheese, sour cream, yoghurts (for thyroiditis it is recommended to buy natural fermented milk products);
- millet, buckwheat, rice;
- seeds and nuts that have not been heat treated;
- potato;
- beans and corn.
Also, for endocrine and autoimmune disorders, it is necessary to regularly drink fresh vegetable juices (especially beetroot and pumpkin), green tea, since such drinks contain antioxidants. For thyroiditis, it is recommended to include them in the diet every 2 days.
With thyroiditis, stress and emotional instability are prohibited. To strengthen the nervous system during AIT, you can drink decoctions and infusions based on herbs with a calming effect 2-3 times a week.
Dietary recommendations
The diet is less effective than drug therapy, but it stabilizes the functioning of the thyroid gland and improves the functioning of the endocrine system. Nutrition for thyroiditis involves following the following recommendations:
- you need to eat 5-6 times a day, portions should not exceed 200 g;
- permissible daily dose of calories – from 1500 to 1800;
- It is recommended to consume carbohydrates and proteins separately;
- fats must be combined with vegetables;
- drink at least one and a half liters of bottled water per day.
Since complex carbohydrates are the main energy resource for thyroiditis, carbohydrate-free diets are strictly prohibited.
For AIT, it is necessary to consume at least 200 mg of selenium per day, since its deficiency leads to iodine intolerance.
Healthy recipes
Nutrition for AIT of the thyroid gland can be varied and interesting, the main thing is to find recipes. The following dishes can be used as base dishes for thyroiditis:
- Oatmeal with prunes. Add 100 g of dry oatmeal to 250 ml of boiling milk, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. When the porridge has cooled a little, you can sweeten it slightly and add finely chopped prunes.
- Vegetarian borscht. To prepare you will need 2 liters of water, beets and carrots (150 g each), potatoes (250 g), cabbage (200 g), onion, 2 cloves of garlic, sour cream, herbs, salt and spices. Throw chopped potatoes and cabbage into boiling water. Next, fry the onion and garlic (in vegetable oil) in a preheated frying pan. When the onion turns golden, add grated beets and carrots to the pan and fry for another 5-7 minutes. Place the finished roast in a pan, add salt and spices and cook for another 10 minutes. When serving the soup, it is recommended to add a little sour cream and fresh herbs.
- Vinaigrette with squid. Necessary ingredients: boiled squid (180 g), beets (150 g), carrots (50 g), pickles (130 g). The products must be cut into cubes or strips, salted, seasoned with sunflower oil mixed with lemon juice.
Supplements and Drinking
Many people are interested in what they can season their dishes with if they have to follow a diet. Well, it is allowed to use unrefined vegetable oils in small quantities. The most benefits can be obtained from avocado, flaxseed, sesame and olive.
Walnut oil is also useful. By the way, it is allowed to be consumed. Walnuts have an ideal balance of Omega-3 and Omega-6 acids.
You can drink green tea with ginger or lemon, rosehip decoction, still water, and also natural juices.
Special benefits of cherries
It is necessary to talk about it separately. The fact is that these red berries are rich in compounds that have antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects. The flavonoid quercetin alone is worth it!
The ellagic acid contained in cherries also benefits (it destroys cancer cells while preserving healthy ones). Just 200 grams of berries per day is enough to reduce the level of uric acid in the blood.
But you should only eat those berries that grew on trees that were not fed with pesticides.
Diet
It is recommended to switch to 6 meals a day. This will prevent you from feeling hungry during the day. A sample menu might look like this:
Advantages and disadvantages
Of course, restrictions are always bad. But since health problems arise, you need to adhere to a certain lifestyle. diets.
A diet for autoimmune thyroiditis involves giving up simple carbohydrates, and this is a minus. Many patients find it difficult to tolerate this. The second disadvantage is that this diet is expensive for many people. It involves eating seafood, and not all of it is cheap.
However, there are also undoubted advantages. Namely:
Diets that help with autoimmune thyroiditis
There is currently no form of nutrition that can help every patient with autoimmune thyroiditis equally. It is important to find the right individual nutrition. In one person, gluten contributes to the disease, in another - grains in general, in a third - milk protein, which is not tolerated and aggravates the disease, in a fourth - carbohydrates with a high glycemic index, which lead to worsening of symptoms, in a fifth - a lack of vital substances from - due to a lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet, for the sixth - all together.
In this case, it is necessary to find a diet that optimally takes into account the needs and food intolerances of each individual patient.
The following forms of nutrition or combinations thereof may be tested. It's best that each of these diets be supplemented with plenty of fruits and vegetables:
- Gluten-free diet
- Grain-free diet
- Sugar free diet
- Glyx diet (food system with low glycemic index)
- Paleo diet (possibly especially for autoimmune diseases)
- Dairy-free diet
Gluten-free diet for autoimmune thyroiditis
Many people with Hashimoto's thyroiditis also suffer from food intolerances, especially gluten intolerance. The official statement is that only people with proven celiac disease should avoid gluten. In reality, however, there are other forms of gluten intolerance besides celiac disease that are unfortunately often ignored, such as celiac disease-independent gluten sensitivity. If a patient with autoimmune thyroiditis suffers from this form of intolerance and if he is not on a gluten-free diet, then his recovery will be impossible!
Gluten is part of the protein in grains. A gluten-free diet avoids gluten-containing grains such as wheat, spelt, rye, barley, einkorn and even oats, as well as gluten-containing products such as bread, pastries and pasta. All other food groups can be consumed, including gluten-free grains (corn, rice, millet) and pseudo-grains (quinoa, buckwheat, amaranth).
A study of 2,232 patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis found that 76 percent believed they were gluten sensitive, resulting in constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, reflux, headache, fatigue and other symptoms. Many of these symptoms also relate directly to autoimmune thyroiditis.
However, once these people started following a gluten-free diet, 88 percent of this group felt better. Their digestive symptoms improved, their energy levels increased, they suddenly lost weight, and their mood also improved.
If there is improvement on a gluten-free diet, you can check to see if wheat alone is causing the individual problems. You can try eating other grains that contain gluten (spelt, rye, oats, etc.) and watch for symptoms. After all, there are other problematic substances in wheat, and gluten does not always lead to intolerance. Since a wheat-free diet is not as difficult as a gluten-free diet, it's worth a try!
Grain-free diet for autoimmune thyroiditis
Some people with chronic inflammatory diseases may do better on a diet that removes all grains, including gluten-free and pseudograins. So if you still don't feel any improvement with a gluten-free diet, you may want to test this form of eating for yourself.
However, often it is simply a matter of consuming too many grains and causing problems. Especially when it comes to gluten-free foods, the menu often consists primarily of gluten-free bread, gluten-free baked goods, gluten-free pasta, as well as rice, polenta and quinoa. And this is instead of eating vegetables, fruits and salads as often as possible. Therefore, small quantities of pseudocereals are not a problem in many cases.
Cereals are often an important source of selenium, and patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis in particular depend on a good supply of this trace mineral. They often suffer from selenium deficiency or respond to selenium by improving symptoms, since the trace element can reduce antibody titers. Therefore, taking selenium for autoimmune thyroiditis is necessary in any case. To do this, use nutritional supplements (the usual dose is 200 mcg).
However, there are also non-cereal sources of selenium. A great example is Brazil nuts, which have the highest selenium content of any food. Just 15-20 grams of Brazil nuts may be enough to provide the indicated 200 mcg of selenium. “Maybe” because the actual selenium content, as usual for natural products, always tends to fluctuate.
Best Sources of Selenium:
- Brazilian nut
- halibut
- tuna
- oysters
- sardines
- lobster
- liver
- grass fed beef
- sunflower seeds
- eggs
Lifestyle
Lastly about this. The lifestyle with this disease changes dramatically, and this is caused by the symptoms of the disease.
Doctors strongly recommend limiting yourself to the following:
In any case, before refusing anything or limiting yourself in anything, you need to consult your doctor.
What is thyroiditis of the thyroid gland and how is it treated?
Thyroiditis is a concept that includes a group of disorders associated with inflammation of the thyroid gland. The group of diseases is based on thyroid abnormalities. Previously, it was believed that thyroiditis was associated with a lack of iodine in food and water, but it has now been proven that it is an autoimmune disease of genetic origin.
- Classification of thyroiditis
- Causes of the disease and its clinical manifestations
- Diagnosis of thyroiditis
- Treatment of thyroiditis
- Thyroiditis in children and adolescents
Classification of thyroiditis
The disorder is classified depending on the characteristics of clinical manifestations and type of development.
Types of illness:
- spicy;
- subacute (lymphocytic, pneumocystis, granulomatous);
- chronic (Riedel's goiter, Hashimoto's thyroiditis).
In addition, thyroiditis is divided into forms:
- Latent, that is, hidden. The thyroid gland is of normal size, its functions are not impaired.
- The hypertrophic form is accompanied by the appearance of a goiter of the thyroid gland, the organ is noticeably enlarged in size, and nodular thyroiditis develops. Depletion of the gland leads as a consequence to hypothyroidism.
- The atrophic form is characterized by a decrease in the size of the gland and a decrease in the production of hormones.
Causes of the disease and its clinical manifestations
The cause of acute forms of thyroiditis of the endocrine gland can be radiation therapy used for treatment, irradiation, mechanical trauma or hemorrhage into the thyroid gland. Often the cause of the disease is an infection, viral or bacterial.
The long-dormant chronic form begins to manifest itself after viral diseases, radiation or drug abuse; the resulting nodular goiter sharply reduces the quality of life.
Clinical manifestations of thyroiditis depend on the form of the disease.
Only such a decoction will trigger REGENERATION of the thyroid gland
The goiter will disappear in 3 days! This remedy has become a sensation in the treatment of the thyroid gland!
Symptoms of thyroiditis in acute, purulent form:
- Pain in the thyroid area, starting with a slight tingling sensation and subsequently developing into severe pain when swallowing and turning the head.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Constantly high temperature, febrile state.
- General weakness.
Symptoms of thyroiditis in acute, non-purulent form:
- rapid pulse;
- weight loss;
- tremor;
- sweating;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- swelling;
- dry hair and skin;
- discomfort in the gland area, pain when touched.
Symptoms of the subacute form:
- enlarged gland;
- pain in the neck;
- red neck due to strong blood flow to this area;
- high body temperature;
- lymph nodes do not enlarge.
A disease such as chronic thyroiditis (Riedel's goiter) may not manifest itself for a long time; the first symptoms of the disorder are a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing. Over time, the voice becomes hoarse and breathing becomes impaired. The diffuse goiter that appears can be easily palpated.
Subsequently, the patient begins to be bothered by the following manifestations:
- headache;
- noise in the hearing organs;
- vision problems;
- arrhythmia.
Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis is almost impossible to identify before the first symptoms appear:
- discomfort in the gland area;
- lump in throat;
- unpleasant feeling when swallowing;
- muscle weakness;
- joint pain;
- high pressure;
- tachycardia;
- sweating
Diagnosis of thyroiditis
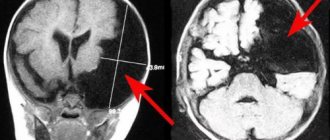
Since the disease in its chronic form does not produce pronounced symptoms, the endocrinologist pays attention to the family history. If family members suffer from autoimmune diseases, such as Riedel's thyroiditis, the doctor advises the patient to undergo a full laboratory examination, including the following procedures:
- Biopsy of gland tissue.
- Ultrasound to determine the tissue structure, shape and size of the gland. Ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of diffuse changes in the gland using special echo signs.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones.
- Immunogram.
Treatment of thyroiditis
Treatment is selected depending on the form and complexity of the disease. If the thyroid gland is hyperfunctional, thyreostatics, such as Thiamazole or Mercazolil, are prescribed; to reduce the negative effect of drug therapy on the heart, patients are prescribed beta-blockers.
Taking anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs reduces the production of antibodies that destroy gland tissue.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Indomethacin;
- Voltaren;
- Methindol.
Treatment of thyroiditis is carried out in a complex manner; this is the only way to achieve a good result. Along with anti-inflammatory drugs, thyreostatics and adrenoblockers, endocrinologists prescribe vitamins, drugs necessary to restore immunity and adaptogens. When endocrine gland function decreases, patients take hormone replacement therapy.
Subacute thyroiditis is treated with glucocorticoids, which reduce the effects of inflammation of the endocrine gland, reduce pain, and relieve swelling. Patients with subacute thyroiditis also take Prednisone, which belongs to the group of steroid drugs.
The acute form of the disease does not allow surgical intervention; radioactive iodine is also contraindicated. The disease in its acute course is treated with beta-blockers (Propranolol). If the acute form is combined with goiter and neoplastic processes in the tissues, then an operation called thyroidectomy is performed.
Riedel's thyroiditis requires not only treatment, but also adherence to a certain diet, in which the daily dose of calories should not be lower than 2000 kcal. Reducing calorie intake can lead to poor health.
Nutritionists recommend the following products:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- nuts;
- greenery;
- seafood;
- lean meats;
- buckwheat
To prevent the development of osteoporosis, patients need calcium.
Thyroiditis in children and adolescents
Thyroiditis in young children and adolescents during puberty is uncommon; an enlarged thyroid gland, neck pain radiating to the ear and back of the head may indicate an acute period of the disease that requires immediate medical intervention.
The subacute form affects children during viral exacerbations, this is autumn and winter. The cause of the disease can be a common flu. The following infections are considered to be the causes of the disease in children:
- malaria;
- sarcoidosis;
- streptococcus.
Signs of subacute thyroiditis in children:
- low-grade fever;
- pain in the area of the endocrine gland;
- weakness;
- pain when turning the neck and swallowing.
The acute phase of the illness lasts up to seven weeks, while laboratory blood tests show high levels of thyroid hormones and a decrease in thyrotropin, and the uptake of radioactive iodine is also very low.
Signs of the disease disappear as T3 and T4 levels normalize in the blood. A sign such as an enlarged and swollen gland can bother you for a long time. The recovery phase is characterized by a picture of hypothyroidism with a decrease in T4, an increase in thyrotropin and an increase in iodine uptake. Hypothyroidism has been bothering me for about six months.
Therapeutic measures to relieve the symptoms of subacute thyroiditis in children consist of therapy with salicylic or pyrazolone drugs. Patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs: Indomethacin, Naproxen. In severe cases, glucocorticoids and adrenergic blockers are used to relieve the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Children with subacute thyroiditis are advised to eat a diet that includes pureed and liquid foods. Children's nutrition should be rich in protein and iodine. Children need dairy and fermented milk products rich in calcium. Meals are fractional, in small portions.
Patients in the acute phase of the disease are advised to reduce physical activity to a minimum; ideally, patients should remain in bed.