Scurvy was once considered a “sailor’s disease,” due to the fact that sailors ate exclusively canned food.
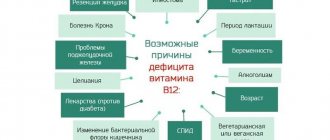
But these days, deficiency (complete vitamin deficiency) or hypovitaminosis (partial deficiency) of ascorbic acid can occur in the following situations:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- infectious diseases.
The fact is that the treatment of infectious diseases , as well as pregnancy and breastfeeding require increased amounts of vitamin C.
Causes of the disease
Previously, it was generally accepted that scurvy was an infectious disease, since it developed in isolated places such as ships, prisons and besieged fortresses and affected large numbers of people at once. Only in 1932 was it possible to find out what causes the disease scurvy. It has been proven that the main reason for the development of the disease is poor nutrition, or more precisely, a lack of vitamin C. This element plays an important role in the synthesis of collagen, which, in turn, is the basis for connective tissues.
History of scurvy
The symptoms of the disease were first mentioned in the records of the ancient Egyptians, dating back to 6 thousand BC. e. And as a disease it was described by Hippocrates.
The benefits of citrus fruits for patients
The healing properties of citrus fruits, containing high levels of vitamin C, against scurvy were confirmed back in 1507 by the Portuguese navigator Pedro Alvares Cabral. However, this did not protect other people from numerous deaths. This was primarily due to the lack of communication and slow dissemination of information characteristic of that time. Thus, in the period from 1500 to 1800, more than 2 million people died from the disease.
Peter I adopted the traditions of Holland and demanded that citrus fruits be included in the diet of the Russian navy. In Germany, meanwhile, they practiced eating sauerkraut at sea, and in the USA - cranberries.
James Lind was the first physician to conduct an experiment in 1747 and officially confirm the benefits of citrus fruits for patients with scurvy. However, this did not convince leading doctors
that era. They were sure that the disease was caused by digestive problems that developed as a result of a poor diet. They offered carbonated drinks as medicine to activate the gastrointestinal tract.
Members of Napoleon's army during the siege of Alexandria in 1801 successfully prevented scurvy by eating horse meat. After this, this product entered the diet of French soldiers.
.
Misconceptions and new assumptions about the disease continued to appear until the 20th century. The medical society concluded that scurvy was caused by waste products of bacteria that lived in meat, especially canned meat.
A major discovery was made in 1907 when Norwegian doctors Axel Holst and Theodor Fröhlich investigated the disease beriberi, which results from a lack of vitamin B1. They conducted tests on guinea pigs. The animals were fed grain and flour. This diet has previously caused beriberi in test pigeons. Imagine their surprise when the pigs showed symptoms of scurvy. Before this, it was believed that only humans were susceptible to this disease. The ability to study the disease in animals has greatly advanced research.
In 1927, Norwegian biochemist Albert Szent-Györgyi was the first in history to isolate ascorbic acid from the adrenal glands. And in 1932, American researcher Charles Glen King finally proved the connection between vitamin C and scurvy.
What is gum scurvy?
Scurvy is a disease that progresses due to insufficient vitamin C (ascorbic acid) in the human body. This, in turn, leads to disruption of the production of a protein such as collagen, which is responsible for the reliability of the walls of blood vessels and the elasticity of connective tissues. As a result, there is a gradual destruction of cartilage and bones, and a decrease in the functionality of the bone marrow.
Scurvy of the gums leads to the necrosis of the bone bed of the teeth, which is why they begin to rot and, as a result, fall out. It is related to the category of bleeding diseases, due to a lack of iron in the body. Often the disease can be caused by other forms of vitamin deficiency.
Scurvy manifests itself with a long-term, about six months, absence of vitamin C in the diet. Primary signs of the disease make themselves felt after two months from the date of the last use of this vitamin.
To maintain normal concentrations of the vitamin in the human body, you should constantly consume foods that contain it. That is why this disease is so common among sailors and people who, for some reason (climate or lack of funds), do not have the opportunity to constantly consume the vitamin.
Nowadays, absolutely anyone can get scurvy, especially those individuals who do not want or cannot provide themselves with sufficient intake of ascorbic acid. It is worth noting that this disease is quite long-lasting. The disease period lasts from one month to a year.
Symptoms of the disease
In the initial stages, it is very difficult to recognize scurvy, unless the patient has had episodes of prolonged fasting. The first symptoms may appear after 1-2 months
after the cessation of ascorbic acid intake into the body. They are expressed by the following characteristics:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- pallor;
- emaciation;
- pain in the limbs.
In the future, the manifestations of the disease are more specific and easier to identify. They consist of such phenomena as:
If treatment is not started on time, the patient's condition may worsen. Ulcers, hemorrhages and fractures may occur as a result of thinning bone tissue
. The patient also becomes vulnerable to infectious diseases. All these complications without taking proper measures can result in death.
Treatment and prevention of scurvy
The disease is treated with a diet that is tailored individually for each patient. The patient’s diet must include foods high in vitamin C. These, for example, include:
In severe cases of illness
the patient is prescribed injections of the missing element. It is also recommended to refrain from physical activity. Treatment lasts for 2-3 weeks.
To prevent the development of scurvy, you need to eat right. Even infants can be susceptible to this disease if they are fed low-quality formula or if their nurse does not consume enough ascorbic acid.
Symptoms of scurvy are primarily caused by fragility and increased permeability of blood vessels, since impaired collagen formation reduces the strength of the vascular wall. The main symptoms of scurvy are:
- the appearance of a hemorrhagic rash (pinpoint or extensive hemorrhages on the skin);
- bleeding gums;
- mobility of teeth (up to their loss);
- pain in the limbs, joints;
- tendency to bleeding (nasal, from the oral mucosa);
- deterioration in general health, increased fatigue;
- decreased immunity.
Treatment of scurvy
Depending on the severity of the disease, bed rest or rational general rest is recommended. Foods rich in vitamin C are prescribed (bell peppers, boiled potatoes, tomatoes, cabbage, green onions, radishes, milk, lemons, oranges, apples, black currants). It is also recommended to take vitamin C concentrates, rosehip infusion, and vitamin C-rich juices (tomato, blackcurrant, orange, etc.), especially if there is an insufficient amount of vegetables and fruits. In the treatment of scurvy, synthetic ascorbic acid is widely used orally, 500-1000 mg daily or parenterally (subcutaneously and intravenously) in the form of a 5% solution of 3-5 ml for 10-20 days. Careful gum care is necessary; To speed up the resorption of infiltrates, it is recommended to use baths and irradiation with the mountain sun.
Forms
Based on the severity of clinical symptoms, the following forms of the disease are distinguished.
- Subclinical stage
- the appearance of low-specific symptoms of hypovitaminosis C (fatigue, emotional irritability, decreased mobility, periodic bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth or eating solid foods). - Scurvy 1st degree of severity.
Characteristic: muscle weakness; - increased fatigue;
- muscle pain during physical activity (especially during long walking);
- pain when chewing;
- bleeding gums;
- scurvy gingivitis (redness and swelling of the gums);
- scurtain purpura (pinpoint hemorrhages appearing on the flexor surface of the joints).
- Scurvy grade 2.
It is characterized by: excruciating muscle pain; - inability to walk for long periods of time and self-care;
- darkening and peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of a large number of rashes on the skin, ulcers may form;
- The gums become blue and bleed easily. Teeth become loose.
- Scurvy grade 3
(extremely serious condition): hemorrhages under the skin (with the formation of hematomas), in the kidneys (with the development of gross hematuria (the patient urinates with a large amount of blood)), in the lungs (hemoptysis occurs); - gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) becomes gangrenous (with the death of gum tissue);
- tooth loss;
- bone fractures;
- swelling;
- stomach ache;
- bloody stool;
- extreme exhaustion of the body. Bone fractures, swelling, abdominal pain with bloody stools, and infectious complications also occur.
It should be noted that this classification currently has more historical than clinical value, since grades 2 and 3 of scurvy are extremely rare in modern practice.
Symptoms
The first signs of scurvy appear within three months of ascorbic acid deficiency. Symptoms include weakness, dizziness, easy fatigue, irritability, drowsiness, pain in the leg muscles and joints. However, these same signs can mean a number of other diseases, so for an unambiguous diagnosis it is still recommended to consult a doctor.
More typical signs include bleeding gums, dark purple bruises under the skin in different parts of the body, pain when chewing, increased salivation, pale or bluish mucous membranes, weak stools and dehydration.
At the final stage, in the absence of proper treatment, vitamin C deficiency leads to internal hemorrhages in organs, kidney and lung failure, and even death.
Causes
- The main and only reason for the development of scurvy is the absence (or deficiency) of vitamin C in the human body. Most often, this occurs when the principles of a rational and balanced diet are not followed (eating monotonous food, insufficient consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables).
- In modern practice, the disease occurs in extremely poor or asocial segments of the population, on long-distance expeditions, as well as in secure institutions (prisons, less often - the army). Also, outbreaks of scurvy occur during wars, in besieged cities.
Diagnostics
- Diagnosis of scurvy is not difficult and is based on: an analysis of the patient’s complaints and anamnesis of the disease (when the symptoms of the disease appeared, what is the reason for their appearance, how the manifestations of the disease have changed over time);
- analysis of the patient’s life history (here the key role is played by clarifying the patient’s nutritional characteristics);
- general urine and blood tests (detection of changes characteristic of anemia and inflammatory processes).
To exclude other diseases that have similar symptoms (for example, blood diseases), the patient is first prescribed high doses of vitamin C - this is both a diagnostic method and at the same time treatment.
Complications and consequences
- Currently, complications of scurvy practically do not arise, since complications such as bleeding, multiple organ failure (severe nonspecific stress reaction of the body, developing as the final stage of acute diseases and injuries), sepsis (blood poisoning), are characteristic of scurvy stages 2–3 (and they are almost never found nowadays).
- Mild hypovitaminosis C and grade 1 scurvy for adult patients, as a rule, resolve without critical consequences.
Classification of pathology
The clinical picture allows doctors to distinguish three degrees of the disease: mild, moderate and severe. In the first case, the patient experiences slight weakness and fatigue. The skin turns pale. The gums bleed moderately.
The average degree of pathology is accompanied by muscle pain. The skin takes on a dirty blue tint. Teeth begin to loosen and fall out. Numerous ulcerations form around the hair follicles on the arms and legs.
Severe degrees lead to hemorrhages in the pericardium and pleural cavity. Hemarthrosis of the joints forms, and areas of blood accumulation appear in the muscle tissues. Ulcerative stomatitis, complicated by gingivitis, develops in the oral cavity. The clinical picture is complemented by arterial hypertension.