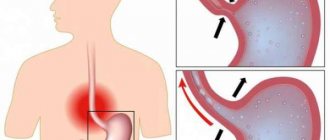
A pathology such as duodenogastric reflux (there is no code in ICD-10) is detected in 15% of seemingly healthy people. This is a disease of the digestive tract, which is characterized by the reflux of bile acids and duodenal enzymes into the stomach. The disease very rarely occurs on its own. In most cases, the development of duodenogastric reflux occurs as a result of other diseases, such as gastritis, ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, but there are many other reasons.
Duodenogastric reflux (DGR)
Physiological duodenogastric
Duodenogastric reflux
(
DGR
) - reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach.
Acceptable spelling: duodeno-gastric reflux.
Incorrect names:
duodenal gastric reflux, duodenal reflux, gastric reflux, gastroduodenal reflux
.
Duodenogastric reflux occurs in 15% of healthy people. At the same time, duodenogastric reflux is often a syndrome that accompanies many diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract: chronic gastritis. peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
If the contents of the duodenum are thrown not only into the stomach, but also into the esophagus, then such reflux is called duodenogastroesophageal.
Duodenogastric reflux existing for a long time leads to the development of reflux gastritis. stomach ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
In the clinical picture of severe duodenogastric reflux, there is a high frequency and severity of pain and dyspeptic syndromes, a yellow coating on the tongue, and diffuse abdominal pain on palpation. Duodenogastric refluxes are very often combined with pathological gastroesophageal refluxes (Pakhomovskaya N.L. et al.).
pH-gram of the patient’s stomach body, duodenogastric refluxes at night and in the morning (Storonova O.A. Trukhmanov A.S.)
Acidity index and the number of duodeno-gastric refluxes in healthy people
The table shows average quantitative estimates of acidity and duodenogastric reflux in “healthy” people (without complaints of gastroenterological problems and without any subjective sensations) (Kolesnikova I.Yu. 2009):
Source: https://www.gastroscan.ru/handbook/117/361
Gastro reflux symptoms
The clinical picture of GERD is varied. There are esophageal and extraesophageal symptoms.
Esophageal symptoms of gastro reflux:
- heartburn (burning sensation behind the breastbone);
- regurgitation (passive leakage of stomach contents);
- belching (entry of air into the oral cavity, as well as sour and bitter contents);
- chest pain;
- odynophagia (pain or discomfort when food passes through the esophagus);
- dysphagia (impaired swallowing);
- nausea and vomiting;
- “wet pillow” symptom (as a manifestation of regurgitation).
Extraesophageal gastroreflux symptoms are divided into otorhinolaryngological, bronchopulmonary, cardiological, and dental.
The most common GERD-associated manifestations of the respiratory system are bronchial asthma, chronic pneumonia, recurrent and chronic bronchitis, otitis and sinusitis, apnea and even sudden death syndrome.
Cardiac manifestations of GER are characterized by pain masquerading as angina. Such pain usually occurs in a horizontal position of the body. The development of arrhythmias is also possible. Dental manifestations include erosion of tooth enamel and the development of caries.
The most striking and specific symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease is heartburn.
Bulbit, gastroduodenitis and duodeno-gastric reflux
Published: June 29, 2020 at 12:16 pm
Many people are familiar with stomach problems. When a doctor diagnoses “gastroduodenitis and bulbitis,” a lot of questions arise. In this article we will try to understand all the little things related to this terrible problem.
Gastroduodenitis and bulbitis are diseases that affect the duodenum. These are infectious diseases that are accompanied by inflammatory processes not only in the intestines, but also in the stomach. Gastroduodenitis and bulbitis occur for many reasons: unhealthy diet, bad habits, and constant stress. Bulbitis can be acute and chronic.
Main symptoms and treatment of gastroduodenitis
The symptoms of this disease can be confused with problems in the gastrointestinal tract:
- pain in the stomach after eating;
- nausea;
- Pain is felt when pressing on the abdomen.
- heartburn;
- bloating;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- bad breath;
- surface. It occurs without any significant violations of the integrity of the cells, but is accompanied by atrophy of the upper layer of the mucous membrane;
- erosive. In this case, it is customary to talk about disorders of the mucous membrane that are located on its surface;
- catarrhal DGR. It causes hyperemia, swelling and inflammatory processes;
- give up tobacco products;
- do not consume caffeine;
- take all medications only on the recommendation of a doctor;
- Causes of duodenogastric reflux
- Degree of development of duodenogastric reflux
- Traditional methods of treating GHD
To cure gastroduodenitis, you must adhere to a strict diet. You should consult a doctor immediately to prevent the disease in the early stages.
In this case, the pain is localized in the epigastric region, as a rule, these are cramping sensations. Sometimes it goes to the navel. Treatment of the disease bulbitis takes a long time. Therapy includes a healthy lifestyle, quitting smoking and alcohol, and following a diet.
Duodeno-gastric reflux, bulbitis - compatible concepts
Duodeno-gastric reflux is the source due to which stomach diseases occur. The main symptoms include a yellow coating on the tongue, sharp and aching pain in the abdomen, constant heartburn and belching. This disease can only be detected through a comprehensive examination. You should not treat duodenogastric reflux on your own; it is better to consult a doctor immediately. He will prescribe the necessary antibiotics. To prevent the onset of the disease, you must carefully monitor what you eat. The most important thing is to avoid smoking.
There is no specially developed diet yet, but there are well-known recommendations for the treatment and prevention of duodeno-gastric reflux and bulbitis. This means eating food frequently in small portions, not overeating, walking more in the fresh air, not wearing tight-fitting clothes (so that there is no pressure on the abdominal cavity), giving up bad habits. If left untreated, gastritis will occur.
Remember the main rule - your health depends on how much you take care of it. It is necessary to fight not the symptoms of the disease, but its cause. Then everything will be fine with you.
Source: https://zhkt.guru/bulbit/gastroduodenit-1
This pathology develops as a result of a number of reasons, among which the following stand out:
Anatomical features. Since the reflux of contents is associated with dysfunction of the pylorus of the duodenum, this condition may be caused by congenital pathologies. For example, weakness of the sphincter muscles, which does not hold the organ in the desired position, causing duodeno-gastric reflux.
Tumors. Changes in the muscle girdle under the influence of a neoplasm can provoke the development of GHD, since it entails disturbances in the functioning of the duodenal sphincter.
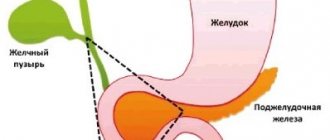
Diseases. In the presence of a number of diseases - pancreatitis, hepatitis, hiatal hernia, cholecystitis, gastritis - the patient may develop duodenogastric reflux. This disease also occurs after surgery on the gastrointestinal tract.
The first occurs among half of the patients. It is characterized by the release of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach cavity without the manifestation of additional symptoms. In the second degree, we can talk about a number of serious diseases that appear in 40% of patients. The third degree of duodenogastric reflux is characterized by an acute condition in which all symptoms are most acute.
Any disease needs proper treatment, and although GHD is not a disease, but a condition, it cannot be ignored. Usually, to restore the patient’s body, complex therapy is used, aimed at eliminating the root cause that caused this condition (in particular, treatment of the stomach). Medical recommendations include not only medications (prokinetics, antibiotics), but also mandatory dietary adjustments.
So, the patient will have to exclude fatty, salty, sour, smoked, flour and chocolate from the diet. Instead, you need to eat steamed foods, dietary fish, white meat, vegetable soups, porridge and sweet fruits.
In addition, when treating duodenogastric reflux, the patient must:
From the short video below you will learn how a colonoscopy is performed and what the disease looks like from the inside.
Source: https://zhivotbolit.ru/zheludok/chto-takoe-dgr-1077.html
Contents: [hide]
Diagnostics
Duodenogastric reflux (treatment includes medication) is a disorder that needs to be diagnosed. With the help of an examination, it is possible to establish the cause of the symptoms.
Duodenogastric reflux is the responsibility of a gastroenterologist - a doctor who specializes in identifying and treating diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). If visiting this specialist is not possible, you can contact a therapist.
Before prescribing a diagnosis, perform the following steps:
- Survey. The doctor asks questions regarding symptoms and concomitant diseases.
- Measuring indicators. The specialist pays attention to blood pressure, pulse, temperature.
- Inspection. The doctor examines the patient's skin.
- Palpation. The specialist palpates the abdominal cavity to determine the location of the pain.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing GDR are listed in the table.
| Name | Description |
| Complete blood count (CBC) | A study that is always prescribed. The analysis is used to assess a person's health status. The result sheet indicates the value of various indicators (hemoglobin, red blood cells, etc.). Types of analysis:
Blood from a vein or finger is used as a biomaterial. The result preparation period is 1 working day. The cost of analysis is from 300 to 1000 rubles. |
| General urinalysis (UCA) | The study allows us to identify various diseases. Urine is used as a biomaterial. Liquid collection steps: 1. Purchase a sterile container in advance from a pharmacy chain. 2. Wash with warm water. If soap or other detergent is used, rinse it off thoroughly. 3. Flush some urine into the toilet, then, without stopping urination, collect the liquid in a container. 4. Close the container and deliver it to the laboratory. Collected urine can be stored for no more than 2 hours at a temperature of 5 – 20 degrees. For analysis, you need to collect the morning portion of liquid (accumulated in the bladder at night). The result sheet indicates the volume, color, and smell of the biomaterial. Additionally, pay attention to foaminess, transparency, and density. They also indicate acidity (pH), the number of indicators (erythrocytes, leukocytes, etc.). The result preparation period is 1 working day. The cost of analysis is from 300 to 500 rubles. |
| Coprogram | Examination of stool to diagnose diseases of the digestive system. Stages of collecting biomaterial: 1. Purchase a sterile container from a pharmacy chain. 2. Wash with warm water. If detergent is used, rinse it off thoroughly. 3. Have a bowel movement after waking up in the morning. It is better to do this not in the toilet, but in a separate container. 4. Take a stool sample that is not in contact with the walls of the container and transfer it to a sterile container. 5. Deliver the container to the laboratory. The maximum shelf life of feces in the refrigerator is up to 12 hours.
The result preparation period is up to 4 working days. The cost of analysis is from 500 to 800 rubles. |
Duodenogastric reflux is a condition that requires hardware diagnostics. An examination is ordered to prescribe effective treatment. Hardware diagnostic methods are listed in the table.
| Name | Description |
| pH meter | The method involves measuring acidity in the gastrointestinal tract. Types of pH measurements:
The procedure is prescribed for various gastrointestinal diseases - ulcers, gastritis and more. The study involves the introduction of a flexible probe into the gastrointestinal tract. It is equipped with measuring electrodes. The probe is inserted through the oral or nasal cavity. The cost of the procedure is from 2000 rubles. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity | The method is based on the influence of ultrasound waves. They are reflected from the tissues, returned to the sensor, and received on the monitor in the form of a black and white picture. The procedure is performed using the transabdominal method. Stages of abdominal ultrasound: 1. A person undresses to the waist and lies down on the couch. 2. The medical professional lubricates the skin of the abdominal cavity with a special gel, which improves visualization. 3. The worker moves the sensor over the skin. During the examination, the physician may ask the person to hold his breath and roll over to the other side. 4. The person wipes the skin and receives a result sheet with a description of the study. Ultrasound is performed in 10–30 minutes. The cost of the study is from 1000 rubles. |
| X-ray of the abdominal cavity | The study is based on X-ray radiation.
2. Contrast radiography. Before the photo is taken, a contrast agent is injected into the person's vein. The medication improves visualization. The substance spreads through the bloodstream and slightly stains the organs. Among the advantages, a high level of visualization and the ability to detect tumors are noted. Disadvantages: duration (the study can take up to 2 hours), side effects are allowed (head pain, weakness, etc.). The cost of the procedure is from 1000 rubles. |
| Fibrogastrod-wodenoscopy (FGDS) | The procedure involves examining the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum using an endoscope. The method is informative and allows you to detect many gastrointestinal diseases. FGDS usually does not cause pain to a person. Therefore, the procedure is carried out without the use of drugs. But it is possible to use painkillers. Stages of FGDS: 1. If necessary, local anesthesia is administered (blocking pain impulses in the area of study) or anesthesia (the person falls asleep and does not feel anything). 2. The patient is asked to lie on the couch on his left side. 3. A ring is inserted between the teeth to prevent clamping of the tube. 4. An endoscope is inserted into the mouth, which you must try to swallow. 5. When the device reaches the stomach, the compressor straightens the walls of the organ using air. 6. An electric suction cleanses the stomach of its juice and bile. 7. The doctor examines the condition of the organs. 8. The endoscope is removed. If necessary, during FGDS additional biomaterial can be taken for biopsy. When carrying out the procedure, you should follow all the specialist’s recommendations, pay attention to your breathing (it should be slow), and do not be embarrassed by copious amounts of saliva. The duration of FGDS is no more than 20 minutes. The cost of the study is from 2000 rubles. |
| Electrogastroenterography | Another name is electrogastrography. The method involves studying the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure is carried out by recording the biopotentials of various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Using electrogastroenterography, gastrointestinal motility can be assessed. Stages of the procedure: 1. A person lies down on a couch. 2. 3 electrodes are attached to the abdomen (pre-lubricated with conductive paste). 3. Registration is carried out within 60 minutes. 4. The electrodes are disconnected, a break is taken for 1.5 hours, during which time the person must eat. 5. When the break is over, the electrodes are reattached and the study is repeated. The total time required for electrogastrography is up to 3 hours. The cost of the study is from 4000 rubles. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | The method is based on X-ray radiation. The result is three-dimensional images of the organ being examined. Unlike a conventional X-ray, a tomograph is more informative; from the images you can determine not only the presence of a pathological focus, but also identify its location. If improved visualization is needed, the person will be given a contrast agent before the test. Stages of performing a CT scan of the abdominal cavity: 1. The patient lies down on the couch. 2. The table takes a position that corresponds to the beginning of the study area. To ensure that the image is layered, CT scans start from the diaphragm. 3. When the scan is completed, the person is allowed to stand up. The duration of the procedure reaches 40 – 60 minutes. The cost of a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is from 2500 rubles. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | The procedure is based on electromagnetic radiation. The method depends on the type of tomograph: 1. Open. The person lies down on a couch over which the apparatus is located. The table takes a position corresponding to the study area. 2. Closed. The patient lies down on a couch, which slides into the tomograph. The method is not suitable for people with a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia) and weighing more than 120 kg. If necessary, the person is given a contrast agent before the test. The duration of the procedure is from 40 to 60 minutes. The cost of an MRI of the abdominal cavity is from 4,000 rubles. |
| Biopsy | A procedure performed to obtain a biopsy (tissue sample) from the gastrointestinal tract. A biopsy is required if a tumor is suspected. After the biomaterial is taken, it is sent to the laboratory for research. The cost of a biopsy is from 1000 rubles. |
Before the examination, it is necessary to follow the preparatory rules. They will be recommended by a specialist, depending on the list of procedures.
It is impossible to single out one diagnostic method and say that it is better than others. Most often, the doctor prescribes an examination, which includes several procedures. Diagnostic costs may vary. It all depends on the list of procedures, city, organization. Therefore, the price must be clarified in a specific clinic.
There is a possibility of free diagnostics. To do this, you need to go to a clinic with a compulsory health insurance policy (CHI).
Causes of duodenogastric reflux
Reflux can be caused by diseases such as chronic stomach ulcers and chronic gastritis. GHD is not considered a disease as it does not have a detrimental effect on the entire digestive system.
However, a person with GHD experiences some discomfort. In addition, factors influencing the rapid development of GHD are the progression of symptoms of diseases such as gastritis and duodenitis. Gastritis is a consequence of dysfunction of the human duodenum, partial or complete damage to the epithelial tissue of the stomach. Gastroduodenitis is the cause of the occurrence and development of a disease such as duodenogastric reflux.
One cannot help but mention the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, which is also one of the causes of the occurrence and development of GHD:
As already noted, reflux does not have pronounced symptoms. The symptoms of the disease coincide with the symptoms of gastritis and ulcers, in fact, the consequence of which is duodenogastric reflux. The symptoms of reflux are quite difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of other digestive diseases, but there is a list of characteristic signs:
The disease can develop in both adults and children. When the first signs of the disease are detected, the patient is given a referral to a radiologist who takes an X-ray of the stomach. Most doctors will complete this process without making any extra efforts. When signs of illness are detected in children, the child is diagnosed using acoustic contrast testing of the stomach or filling hollow organs with apple juice.
Duogenogastric reflux of the second degree is characterized by the fact that the contents of the duodenum enter the stomach in large quantities, thereby causing other diseases. Statistics show that the second degree of development is observed in 10% of patients suffering from this disease. The third stage of development is the most acute symptomatology of the disease. It is observed in the remaining 51% of patients with this disease. In addition, it is worth saying that along with duodenitis, a disease such as gastroduodenitis, which has the following symptoms, often occurs:
It should be noted that the symptoms of gastroduodenitis are in many ways similar to the manifestations of a disease such as gastritis, and have the following “general” symptoms:
Mild disorders of the digestive system include superficial gastritis and reflux. However, the consequences that can occur after gastritis are much more serious (duodenal ulcer) than after duodenogastric reflux.
Return to contents
The treatment of the disease should be carried out by a doctor who has a sufficiently high qualification; it is such a specialist who is able to establish an accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time and prescribe an effective course of treatment, which will be carried out through physiotherapy. Physiotherapy is a series of therapeutic procedures and exercises, the implementation of which will lead to a significant strengthening of the abdominal press. These therapeutic measures can be carried out both as preventive and problem-correcting measures.
Treatment using herbs is called herbal medicine. It is worth noting that herbal medicine is the safest way to treat GHD. Perhaps the most effective folk remedy is the use of a decoction of St. John's wort leaves. The preparation method is quite simple, you need to chop the leaves, pour boiling water over them and let it brew. That's the whole process. Good luck with your treatment!
Source: https://ozheludke.ru/drugoe/dgr-zheludka-chto-eto-takoe.html
What is this?
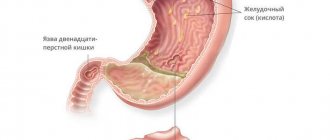
Duodenogastric reflux is a condition in which the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. As a result of the pathology, the alkali located in the duodenum is thrown into the stomach. The mucous membrane begins to be affected, which then creates inflammatory processes. They are called reflux gastritis. It should be noted that approximately 13% of the population suffers from this condition, and these are mainly adults.
Stages and types
In the typology of destructive processes, 4 types of reflux are distinguished:
- superficial, only the cells of the mucous membrane are affected;
- catarrhal, accompanied by an inflammatory process;
- erosive, foci of atrophy form on the mucosa;
- biliary, when the outflow of bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum is impaired.
There are 3 degrees of development of duodenogastric reflux:
- The first degree of GHD is a moderate process. This phase is characterized by the discharge of a small amount of the contents of the duodenum. Irritation of the gastric mucosa manifests itself in an unexpressed way. About 50% of people may experience this problem.
- The second degree is characterized by the introduction of a large amount of alkaline medium. At this stage, the development of an inflammatory process is often observed, which leads to new gastrointestinal diseases. This degree of disease occurs in 10% of people.
- The third degree is a pronounced process, which is accompanied by pain, nausea, and vomiting. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, the patient complains of heaviness in the stomach. An examination by a specialist makes it possible to record a clear clinical picture of the development of pathology.
The danger of duodenal gastric reflux is that the disease can cause ulcers to appear on the gastric mucosa. This occurs as a result of mixing bile and pancreatic juice, which form an aggressive environment, destroying the mucous membrane.
If duodenal gastric reflux is neglected, it can lead to serious consequences (peptic ulcer, digestive system disorders).
Symptoms
It should be noted that doctors generally do not consider GHD as a separate disease, believing that its symptoms are similar to stomach diseases. Some unpleasant symptoms may occur after playing sports or during sleep. In general, this condition does not have any clear signs. As with diseases of the stomach and intestines, these are characterized by:
A differential diagnosis is usually prescribed to distinguish duodenogastric reflux from any other gastrointestinal disorders. Basically, radiography, ultrasound and fibrigastroduodenoscopy are done to make the diagnosis as accurately as possible.
Treatment methods
In addition to traditional methods of treating GHD, the patient can also turn to traditional medicine. Typically, taking herbal tinctures and decoctions gives positive results. They have a beneficial effect on the gastric mucosa and improve digestive processes in the body. The prognosis for this condition is favorable if treated by a qualified doctor. As a rule, measures aimed at treating duodenal gastric reflux give a positive result.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of such an unpleasant disease as duodeno-gastric reflux, it is necessary:
- regulate your diet;
- avoid overeating;
- promptly seek help from specialists if problems arise with the digestive system;
- do not self-medicate and take medications only under medical supervision;
- engage in physical therapy and perform exercises to strengthen the abdominals and muscle corset.
Be healthy!
Gastric GHD: what is it?
Many people ask the question, GHD of the stomach - what is it?
Duodenogastric reflux, or DGR for short, is a disease in which the contents of a person's duodenum enter the stomach. The disease is insidious in that it has virtually no symptoms, but the disease can manifest itself during sleep or during physical activity.
The disease can be “earned” if you eat poorly, eat rarely and in large portions (office workers are often guilty of this), and fast food lovers are also at risk.
The following factors also significantly influence the development of the disease:
Symptoms of duodenogastric reflux
And perhaps one hundred percent symptom of duodenogastric reflux is an unpleasant odor coming from the patient’s mouth. This symptom is a sign of the evacuation function of the stomach, and this process occurs as a result of abuse of carbohydrate foods. Often all this is accompanied by the release of bile into the stomach, and this process is called duodalogastric bile reflux. In general, the result of the appearance of the disease is a process in which the pressure of the duodenum increases, and at the same time the chronic stage of duodenitis develops.
Often the detection of this disease occurs unintentionally:
Gastro symptoms
GERD affects both men and women equally often and is difficult to treat. The most striking and specific symptom of gastrointestinal tract is heartburn with or without penetration of stomach contents into the oral cavity.
The clinical picture of GERD is diverse and includes esophageal and extraesophageal symptoms.
Distinctive symptoms of heartburn due to gastrointestinal illness:
- “chill” at the bottom of the throat;
- burning and stinging in the throat;
- bitter or sour taste in the mouth;
- lump in the throat;
- nausea and stomach pain.
Frequent attacks of heartburn can lead to irritability, insomnia, anorexia, and chronic aspiration of stomach contents into the respiratory tract. Signs of chronic aspiration: cough, hoarseness, sore throat.
Also, gastrointestinal disease (Gerb) may be accompanied by pain when swallowing; esophageal bleeding; pain in the chest area; an unpleasant taste in the mouth that does not go away even after brushing your teeth.
Due to constant throat irritation, patients with GERD may develop chronic pharyngitis or laryngitis. At the same time, symptoms characteristic of the listed diseases are added (pain when swallowing, swelling of the throat, intoxication).
Degree of development of duodenogastric reflux
Currently there are three degrees of development. In order to identify a disease and find out the degree of its development, doctors take a number of diagnostic measures, which were discussed just above. Typically, the disease of the first degree is characterized by the fact that a small part of the duodenal contents is thrown into the stomach cavity. This degree of development of the disease is observed in 49% of patients.
Treatment of GHD
The most effective method of treating GHD is the use of complex therapy, the result of which should be the elimination of the main causes of duodenogastric reflux. In order for the course of treatment to be most successful, the patient should radically change his lifestyle at the time of health-improving operations, namely:
However, physiotherapy alone will not work, so the doctor, in addition to the physiotherapeutic course, prescribes the patient some types of medications, such as prokinetics, anthrocytes and antibiotics that limit the supply of histamine receptors.
Traditional methods of treating GHD
In addition to medical intervention in the treatment of the disease, the patient must consider and follow a fairly strict diet, carry out a number of additional therapeutic measures using various types of folk remedies. When treating GHD, the patient must completely exclude the following types of foods from his diet:
Instead of the above categories of products, it is recommended to consume fruits, vegetables, berries, pureed vegetable soup, fish, chicken, milk and dairy products. The diet subsequently allows you to stabilize and normalize the functioning of the patient’s digestive system.
Traditional methods of treating GHD include the use of various types of herbal tinctures, which can significantly speed up the patient’s recovery process.
Causes of the disease
The causes of duodenogastric reflux are not entirely clear. This disease can be caused by a disruption of the nerve signals entering the duodenum and bile ducts (hence, reflux occurs in patients after gallbladder removal). In addition, it occurs with excessive relaxation of the pylorus, changes in its motility or peristaltic force.
Duodenogastric reflux can be caused by gastric hyperplasia or blood stasis. In addition, the composition of the bile entering the stomach affects the secretion of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the activity of the protective mechanisms of the gastric mucosa, which further aggravates the problem and complicates treatment.
Duodenogastric reflux causes:
It should be noted that these symptoms do not appear immediately, but as the disease develops.
Treatment
Unlike acid, changes in diet or lifestyle are usually ineffective in preventing or treating gastric reflux. It is most often treated with medication or surgery. Many treatments also reduce acid reflux. This is important because the two conditions often occur at the same time and lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Drugs that decrease the relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, such as baclofen, have been shown to reduce duodenal gastric reflux, especially in patients who are refractory to inhibitor treatment.
Medicines used in the treatment of gastric reflux include bile acid sequestrants, particularly cholestyramine, prokinetic agents to move material from the stomach to the small intestine more quickly, preventing reflux.
Drugs for duodenogastric reflux
Menthol;
Lanreotide;
Somatostatin;
Angiopeptin;
Hormone antagonists.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid.
A prescription medication that helps reduce the frequency of symptoms and severity of stomach pain associated with bile reflux. However, duodenal gastric reflux does not cure.
- Bile acid sequestrants. Doctors often prescribe bile acid sequestrants, which interfere with bile circulation. Research shows that they are less effective than other treatments. Side effects such as bloating can be serious.
- Inhibitors. Protonix®, Prilosec®, Prevacid®, AcipHex®, Nexium® are prescription drugs. They are often prescribed to block acid production, but they do not have a clear role in treatment.
- Medicines to lower cholesterol levels. Questran®, Colestid®, help the body eliminate bile.
- Cisapride (Propulsid®). Eliminates or significantly reduces bile reflux in children. The product was removed from the US market due to side effects.
- Promoting agents. Used to improve gastric emptying, therefore reducing the amount of bile that can leak back.
Surgery
Doctors recommend surgery if medications fail to relieve severe symptoms or if there are precancerous changes. Some types of operations are more successful than others. Be sure to discuss all the pros and cons with your doctor.
Options:
- Diversionary surgery (Roux-en-Y). A procedure that is a type of weight loss surgery. Recommended for people who have previously undergone gastric surgery with removal of the pylorus. With Roux-en-Y, surgeons place a new connection to allow bile to flow further into the small intestine, away from the stomach.
- Antireflux surgery (fundoplication). The part of the stomach closest to the esophagus (fundus) is sutured around the lower esophageal sphincter. The operation strengthens the valve. There is little evidence of the effectiveness of surgery for duodenogastric reflux.
Integrative therapy
Integrative therapy has not been clinically proven to effectively treat duodenogastric reflux. Therapy used to treat gastritis may be effective.
Watch the video, doctor's advice
Treatment at home
This disease can be easily treated on your own by following a diet and using folk remedies. Duodenogastric reflux is not a complex disease - it is rather a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to illness in the future. Before this happens, take responsibility for your health into your own hands.
Diet
An important step in treatment is changing eating habits. A sensible diet minimizes the symptoms of duodenogastric reflux and helps improve the functioning of the digestive system.
- Margarine, lard, and lard should be excluded from the diet; it is better to replace them with olive oil. Butter can be eaten in limited quantities (it is very important not to fry anything with it).
- Avoid smoked and fried foods.
- You can eat lean poultry, but you should avoid fatty meats and fatty products (for example, duck, goose, pork, offal, pates).
- For fish, choose low-fat varieties: cod, trout, pollock. Canned fish should be excluded from the diet.
- The diet limits processed cheeses.
- Eliminate strong coffee, cocoa, and strong tea from drinks.
- As for carbohydrates, wheat-rye bread or wholemeal bread, durum pasta, and brown rice will be healthy for you.
- You should minimize the consumption of chocolate, cakes, and cakes with rich creams.
- Vegetables that are contraindicated include cucumbers, all types of cabbage, green beans and citrus fruits. Hot spices (curry, red pepper) can be used in limited quantities.
- The diet completely prohibits carbonated drinks. Alcohol in small doses is not contraindicated.
Phytotherapy
Treatment with medicinal herbs, roots, honey and other folk remedies gives an amazing effect, which in many ways exceeds the effect of medical procedures. After all, it is best to improve the functioning of the body in natural ways - this will help eliminate side effects.
Yarrow, chamomile and St. John's wort
These three herbs are the three “pillars” on which the health of our digestive system is built. They can treat many diseases - gastritis, heartburn, indigestion, nausea, dysbacteriosis and, of course, duodenogastric reflux. Mix yarrow, chamomile and St. John's wort in any proportions (that is, take the ingredients “by eye”), pour boiling water over them, and make delicious tea with honey. You need to drink this drink every morning and evening.
Herbs for bilious vomiting
If the disease has worsened so much that you have not only pain, but also vomiting bile, treat with fume grass. You need to make infusions from it (2 tablespoons of the plant per half liter of boiling water, keep covered for 1 hour). Take 50 ml of infusion every 2 hours until vomiting and pain subside. Then move on to treatment with chamomile, yarrow and St. John's wort (as described in the previous recipe).
The root of marshmallow is no less effective. You need to make cold infusions from it - that is, pour cold water over the plant at the rate of 2 tablespoons of crushed roots per half liter of water. The mixture should be infused for 5-6 hours. Take it in small portions throughout the day until the bilious vomiting stops.
Flax seed
Treatment with flaxseed is effective for heartburn, gastritis and all types of reflux (including duodenogastric reflux). It envelops the gastric mucosa, protecting it from the negative effects of bile salts. Pour a tablespoon of seeds with cool water (about 100 ml) and wait until they swell and mucus comes out from the seeds. This mixture should be drunk on an empty stomach before meals. Additionally, treat with other plants that would support duodenal motility.
Plants for peristalsis
Mix the following herbs:
From this mixture you need to make warm infusions - 1 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs, cover with a lid, strain after 20 minutes and drink. For taste, you can add honey to the drink. Drink the medicine 3 times a day an hour after meals.
Rue also has a stimulating effect on duodenal motility. It can be brewed instead of tea. But the easiest way is to simply chew 1-2 leaves of the plant every time after eating.
Source: https://nmed.org/duodenogastralnyjj-reflyuks-lechenie.html
Source: medservice26.ru
Diet
Proper nutrition is important for the treatment of the disease. The diet for duodenogastric reflux was not specially developed; it is based on generally accepted principles of nutrition for gastrointestinal diseases.
Black bread, coffee, chocolate, onions, garlic, and tomatoes are excluded from the diet. They reduce the tone of the gastric sphincter of Oddi. You should avoid cabbage, sour apples and other foods that increase the acidity of gastric juice.
During snacks, it is allowed to take crackers and dry crackers, which promote the outflow of bile. You should also exclude spicy, fried, and canned foods.
The menu should include vegetarian soups, vegetable and fruit dishes, bran bread, low-fat cottage cheese, juices, yoghurts, and mineral water.
It is better to eat lean meat, fish, vegetables, fruits, cereals and dairy products. A complete list of permitted and prohibited products can be obtained from a gastroenterologist. Basically, treatment tables No. 1 and No. 2 are prescribed, recommended for gastrointestinal diseases.
There should be 5 or 6 small meals per day. After eating, it is better not to bend over or do other movements associated with abdominal tension. You should avoid wearing clothes that are tight around the waist to avoid increasing intra-abdominal pressure.