Syphilis is a curable infection that is sexually transmitted. If detected, treat the disease immediately, otherwise ignoring the disease will lead to death.
The infection is rare among women in Russia. In 2014, 25.5 cases of infection were found per 100,000 people, according to a study by the State Scientific Center for Dermatovenereology and Cosmetology.
Russian doctors detect syphilis during pregnancy in the 1st and 2nd trimester. Most often, the disease is detected in minor mothers, foreign citizens and in women who were not observed in antenatal clinics.
What is syphilis and why is it dangerous?
Syphilis belongs to the group of infectious microbial diseases that occur in a chronic form. The main cause of the pathology is infection with Treponema pallidum, a bacterium of a specific shape that has a number of special properties. Mostly women become infected through sexual contact, which makes syphilis one of the sexually transmitted infections (a group of STDs).
Important
Of all these diseases, syphilis is the most dangerous and severe, because it leads to damage to many tissues and organs of the woman herself, and is also transmitted in utero to the fetus, leading to serious problems for the child and congenital infection.
The infection is characterized by an undulating and recurrent course, with periods of attenuation of symptoms and the appearance of a wave of new, more dangerous and serious ones. From the moment of infection, treponema pallidum penetrates the blood vessels, spreading through the bloodstream to all organs and tissues, also affecting the reproductive sphere, placenta, and fetus. The activity of the parasite will persist for a very long time; without treatment, it lives in the body for years, gradually leading to irreversible phenomena. Even during periods of latent disease, it never ceases to be dangerous for the patient himself and the people around him.
Classification of infection: features during pregnancy
Depending on the time of occurrence, the disease is divided into acquired and congenital. If we are talking about acquired syphilis , it develops after unprotected sex with an infected partner. Congenital syphilis is formed when the mother is infected during pregnancy with transmission of the infection during gestation or childbirth.
By stages, the infection is divided into:
- an incubation period lasting from 3 to 4 weeks, there are no symptoms during this period, Treponema pallidum actively multiplies and affects the genitals and internal organs.
- the stage of primary syphilis, which occurs during the first 45 days from the moment of infection,
- secondary infection, this is a period of up to 2-4 years from the moment of infection,
- tertiary syphilis, lasting up to 5-15 years from the moment of infection.
Features of infection
Syphilis infection occurs through sexual contact with a sick partner; domestic infection is unlikely and has not been confirmed by doctors . During pregnancy, a woman can infect her fetus with syphilis in utero, since treponema can penetrate the placenta. The most dangerous period for a child to become infected is the second trimester, and the most dangerous period is the presence of a secondary period of infection in the mother, as well as the period during the first three years from the moment of infection.
Each stage has its own typical manifestations that are worth knowing about.
Symptoms of syphilis in women during pregnancy
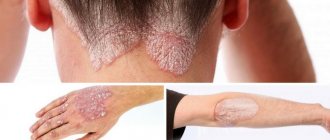
At the first stage, during primary infection , a specific syphilitic picture is formed - the formation of hard chancre . A small round or elongated reddened area is formed, which has a painless erosion in the center, which then turns into an ulcerative defect, reaching a size of 2 cm. The edges of the wound are raised, the discharge from its surface is scanty, and a crust can often form.
Important
Such a chancre does not cause any pain; it usually develops in the area where the treponema has invaded. For women, this is the vagina or cervix, clitoris or vulva.
Such formations are detected less frequently due to the fact that they are invisible to the eye in the vagina or on the cervix. It is also possible for chancre to form in other atypical areas - the mouth or rectum, mammary glands, legs or arms. When a formation appears, regional lymph nodes enlarge, they are enlarged and painless. The period lasts up to 6-7 weeks.
With secondary syphilis, rashes develop in the genital area and body skin, and hair loss is typical. Internal organs and the nervous system are affected, the duration of this period is up to 2-3 years. Gradually, syphilis becomes latent, when there are no rashes on the skin, the activity of the infection decreases, but the internal organs are invariably destroyed.
With tertiary late syphilis, damage to the liver and heart, nasal cartilage and nervous system is typical, and death occurs from complications of neurosyphilis. Such manifestations are rare today; the disease usually does not progress to such a state.
Manifestations during pregnancy are typical, but may be somewhat brighter and last longer. Tertiary syphilis practically does not occur in pregnant women; against its background, pregnancy is almost impossible due to serious lesions of the genitals with the absence of ovulation and multiple adhesions in the pelvis.
note
The most common option is the presence of latent syphilis during pregnancy, when there are no manifestations, the woman feels healthy and bears the fetus.
The infection is detected during tests, which requires immediate consultation with an obstetrician, venereologist and additional specialists. This is due to the characteristics of the infection and the risk to the fetus.
How dangerous is syphilis during pregnancy: signs, treatment, prevention
Syphilis during pregnancy is a serious problem, since the disease can provoke premature birth and subsequently lead to dangerous pathologies in the child. Therefore, expectant mothers are required to undergo a test to detect this disease, which will allow timely treatment.
If this disease is detected, the question of the need to terminate the pregnancy is raised. In most cases, this is not necessary - the disease can be cured without consequences for both the expectant mother and the fetus.
By the way, half of women infected with syphilis learn about their disease during pregnancy when appropriate screening is carried out. However, in some cases abortion is recommended.
This happens if a woman becomes pregnant while already infected.
Syphilis symptoms during pregnancy
If the mother previously suffered from syphilis and successfully treated it, then she is recommended to become pregnant no earlier than 3 years after the “healthy” conclusion.
The more time passes from the moment of treatment, the greater the chance of carrying and giving birth to a healthy baby, since the likelihood of relapse of the disease and infection of the fetus is minimal.
Before planning a pregnancy, you should definitely be tested for syphilis and, if necessary, undergo preventive treatment.
The signs of this disease in expectant mothers are no different from the symptoms of other patients. This disease can occur latently, without showing certain signs, or violently. Most often, pregnant women are diagnosed with a latent form of syphilis. Symptoms of syphilis depend on the stage of the disease.
Stage 1
The main symptom is a hard chancre in the place where the treponema has entered the body.
This is a firm, painless ulcer that usually appears in the perineum, cervix, vulva or penis, rectum or mouth - where the virus enters the body.
The ulcer goes away on its own within a few weeks. This indicates that syphilis has moved to the next stage.
Stage 2
Lymph nodes throughout the body become inflamed and enlarged. A characteristic rash may appear on the skin or mucous membranes. If it appears on the scalp, then hair loss is possible. Wide condylomas or growths appear on the skin, which serve as a source of infection.
When such changes occur, the risk to the fetus increases significantly, and there is almost no chance of maintaining the pregnancy. The fact is that at this stage, treponema - the causative agent of syphilis - enters the blood, so all organs and systems of the body are under attack.
Gradually this leads to irreversible changes.
Stage 3
It is characterized by dangerous pathological processes that affect many internal organs. The heart and liver are most often affected. The nervous system is also under attack, which leads to disruption of the functioning of other organs.
This stage of the disease is incompatible with pregnancy; there is no point in trying to save the fetus at this stage, since, most likely, the child will die anyway.
In addition, the third stage of syphilis is considered the last and often leads to death.
Diagnostics
To detect syphilis during pregnancy, several tests and samples are prescribed at once. This will allow you to accurately determine whether a woman is infected. Screening (MR or RF) is usually prescribed. The disadvantage of the analysis is that it is often false positive during pregnancy. If a woman receives such a result, she undergoes RPGA and RIF tests.
If both tests are negative, the doctor concludes that the expectant mother is healthy.
If one of the two tests also showed a positive result, then either the woman has an early stage of the disease, or the test also turned out to be false positive - although rare, this does happen. Then additional tests are prescribed: immunoblotting, RIBT, ELISA.
They will help clarify the clinical picture. If the screening and the results of both tests are positive, then a diagnosis of syphilis is made, since false positive results in all three cases are excluded.
It must be remembered that the Wasserman reaction is not the most accurate diagnostic method, since during pregnancy women often show a false positive. So don't panic when you see this result.
Consequences of syphilis for pregnancy
Syphilis does not go away without a trace in pregnancy; usually in early pregnancy, Treponema pallidum leads to miscarriages up to 14-16 weeks, and there are also high chances of stillbirth and premature birth . During pregnancy, the condition suffers, the functions of internal organs and tissues are disrupted, which threatens placental insufficiency, intrauterine infection of the fetus and the birth of a child with manifestations of congenital syphilis, developmental defects, or outwardly normal, but with persistently positive blood reactions. Laboratory indicators reveal pale treponema in the child’s body, transmitted to him from the mother.
For a long time after treatment for syphilis, the chances of problems with pregnancy and the birth of a sick baby are high. This depends on the timing of when the woman became infected with syphilis and the amount of therapy she received. The child usually becomes infected after the 5th month of pregnancy, although earlier episodes are also possible.
Infection without treatment
Without treatment, pregnancy after syphilis can have significant complications. That is why, thanks to modern diagnostics, it is possible to identify syphilis in pregnant women in the early stages and begin urgent treatment, which will prevent the risk of pathological changes in the body of the mother and fetus, as well as reduce the risk of pathologies and miscarriage.
It is also worth noting that syphilis in pregnant women is often detected after hospitalization in the maternity hospital. And, according to statistics, more than 67% of patients with late diagnosed treponemal infection did not register with antenatal clinics and did not undergo the examinations and tests required for all pregnant women according to the observation schedule.
In such situations, when syphilis is diagnosed in pregnant women during childbirth, the risk of developmental defects in the fetus or pathologies in the early period of the newborn is quite high. That is why, at present, registering pregnant women is strictly mandatory. Indeed, in cases where the diagnosis is confirmed, modern therapy makes it possible to maintain pregnancy after treatment for syphilis. And, as statistics from recent years show, pregnancy after treated syphilis proceeds without pathologies with regular observations and examinations by obstetricians and gynecologists.
Consequences of syphilis for the fetus and child
Syphilis is even more dangerous for the embryo and developing fetus. First of all, in the early stages there are miscarriages with pregnancy fading , and before 30 weeks there is a high risk of stillbirth . This is associated with multiple lesions of the internal organs of the fetus, lesions of the lung tissue, liver and spleen, and kidneys.
Important
Under the influence of treponema, the lung tissue in the fetus undergoes degeneration, forming foci of infiltration and compaction, which leads to disruption of the formation of alveoli and their filling with epithelial cells. Such lungs will not be able to fully open during the first inhalation.
No less dangerous for the fetus is insufficiency of the placenta, which, under the influence of treponema, shrinks and thickens, its vessels sharply narrow, which leads to chronic hypoxia of the fetus and its death. Children usually die in utero, but if they survive, a diagnosis of congenital syphilis is made.
Clinical manifestations for congenital syphilitic infection are very specific; they are not similar to all other diseases. Based on the presence of certain symptoms, a doctor may suspect syphilis in the fetus even without tests. The most typical of them include:
Hochsinger infiltration, specific skin lesions that form around 7-8 weeks of a baby’s life. The epithelium in the area of the palms and feet, nasolabial triangle, and buttocks thickens and turns red, acquiring a polished, shiny appearance. These zones lose their elasticity, scars and cracks form on them, and the epithelium peels.
- syphilitic pemphigus, blisters appearing on the palms and soles, as well as similar elements in the area of the legs and torso. There is turbid content inside the bubbles; they gradually merge into larger elements, forming crusts and opening erosions that bleed.
- syphilitic rhinitis, which develops by the 4th week of a child’s life. The mucous membranes of the nose are affected, breathing becomes difficult, which leads to problems with breastfeeding. Gradually, the lesion affects the bone and cartilaginous part of the nose, which leads to deformation of the nose and disruption of its basic functions.
- the formation of osteochondritis is a violation of bone growth and bone deformation, which is revealed by radiography. At an advanced stage of the disease, false paralysis can form, in which the damaged limbs are flaccid, they are practically not used during the activity of the baby.
- the development of meningitis, inflammatory lesions of the meninges, manifested in the form of convulsions and hydrocephalus, strabismus and paresis. In parallel with these symptoms, the doctor notes deformation in the area of the skull bones, the predominance of the brain over the facial area, and protrusion of the frontal tubercles.
- the formation of choreoretinitis, the formation of special inclusions and plaques in the fundus.
- hair loss with the formation of alopecia.
Identifying even a couple of these signs already allows you to make a diagnosis of congenital syphilis and begin active treatment of the baby.
In addition, the specific Hutchinson triad . It manifests itself in any variant of the course of infection in the mother, and allows you to accurately and without doubt determine congenital syphilis in the child. This complex includes three mandatory symptoms that are detected in all infants with congenital syphilitic lesions:
parenchymal keratitis is a complete or partial clouding of the cornea, affecting both eyes at once. Possibly from completely reversible to total, with complete blindness.
- damage to teeth with dystrophic processes in their rudiments, which, when erupting, manifests itself in the formation of screwdriver or barrel-shaped shapes.
- swelling of labyrinthine origin, occurring as a late symptom of congenital syphilis. It can manifest itself in the period from 7 to 14 years, and initially the episodes of hearing loss are temporary, gradually turning into irreversible damage.
The consequences can last for a long time, and syphilis may occur at an early age. It starts in the period from 1 to 2 years, and there may also be variants of congenital late syphilis with its manifestation in the period of 5-6 years, while positive tests for syphilis are recorded, although there may be no symptoms at all.
Spiral bacteria
Retaining the ability to maintain its vital functions, the spirochete successfully reproduces in tissues of different structures and purposes, but they are vital and can remain in them for a long period in the form of spirillary/high pathogenesis or in the L-form (cyst, grains).
- The L-form of the spirochete state is very resistant to the effects of medications and often becomes detectable only in the stage of late or latent form of syphilis.
- And, conversely, the spirillary form of treponema corresponds to the primary, secondary fresh and/or recurrent stages of the syphilitic disease.
- During this period of the disease, a transformation of the body's immunoallergic reaction mechanism occurs, as a result of which infiltrates are formed in organs and tissues, and a little later - infectious granulomas.
This, in turn, will first lead to the appearance of scars, and in the process of granuloma disintegration - to death for the patient, since granulomas usually affect important organs and tissues.
Syphilis already at an early stage of its development in the body affects the health of the nervous system. First, affecting the meninges and blood vessels (the period of early neurosyphilis), then acting destructively on the cells of the gray matter, causing manifestations of dementia (stage of progressive paralysis).
At the same time, it disrupts the conductive ability of the pathways in the spinal cord, which subsequently destabilizes the function of organs in the pelvic area.
Syphilis during pregnancy
The picture of the onset of the disease against the background of the onset of pregnancy has its own characteristics in light of the possible impact on the health of two people: the mother and the unborn child.
Syphilis in pregnant women is detected by the presence of typical symptoms, or goes hidden. In the second case, serological tests can show the presence of the disease, giving a positive test for syphilis during pregnancy.
The disease itself can be acquired through sexual contact or have a congenital form due to untreated or insufficiently treated syphilis, which the mother had.
What are the consequences of infection of the fetus with syphilis if syphilis and pregnancy proceed in parallel, but in different directions: pregnancy serves to create a new life, and syphilis, on the contrary, destroys it?
- First of all, the presence of this sexually transmitted disease, up to 25% of cases, ends in miscarriage (usually within 12-16 weeks);
- stillbirth of the fetus or premature birth is also possible;
- 40–70% of cases result in manifestations of syphilis in a child at an early stage or over time.
Immediately after birth, the baby will show early symptoms of syphilis, a congenital form. Characteristics here: prematurity of the fetus, with clearly affected skin. The baby may have rhinitis (runny nose) from the first days; the bones, nervous system, liver, and lungs are affected.
The child will gain weight much more slowly, lag behind in development, sometimes with an undeveloped sucking function. Due to disorders of the nervous system, such children are more restless, they have poor sleep, increased tearfulness with hysterical attacks.
It should be remembered that for a child affected by syphilis, pneumonia poses a mortal danger.
- Manifestations of the late stage of the congenital form of syphilis will become noticeable after 2 years of the child’s life, although more often they appear from 7 to 14 years of age, without obvious signs of the disease in an earlier period of life.
- The most common signs of the presence of a late stage of congenital syphilis are: damage to the organs of vision, organs of hearing and dental diseases.
- However, due to widespread damage to organs and tissues, all of them can be negatively affected by syphilis.
Classification of the disease and etiological aspect of syphilis
Syphilis is characterized by a wave-like course with recurrent exacerbations. Immediately after the spirochete penetrates, it is quickly transported by blood vessels to various tissues and organs.
Like most diseases caused by infections, syphilis has an incubation period. When the disease has not yet manifested itself. This period can last from 4 to 5 weeks.
It is replaced by the stage of primary syphilis with the following symptoms: a specific syphilitic rash or chancroid, a raised area of redness, it is also called primary syphiloma; Erosion appears at the site of chancre/syphiloma; erosion turns into an ulcer, up to 1-2 cm in size, on the surface of which a crust can form.
The location of the chancre is the place where treponema pallidum has entered the body. This is a kind of mark.
Such places can be: in men - the inner layer of the foreskin, the neck of the glans, the head, the body and the base of the penis; in women - cervix, vagina, vulva, clitoris.
Due to the hidden nature of the genital cavities, these symptoms are less noticeable in women.
But ulcers of chancroid can also appear in other places, such as: the rectum, oral cavity, lips, tongue, tonsils, fingers and toes, and mammary glands. The condition of primary syphiloma or chancroid can become more complicated due to repeated infection.
In the absence of treatment, regression of primary syphiloma occurs, and a scar may form. Simultaneously with this process, the lymph nodes enlarge and this process can continue for 6 to 7 weeks.
- After the primary comes secondary syphilis, which is characterized by profuse rashes on the skin (roseolous, papular, vesicular, pustular syphilis), on any part of the body and on the genitals, in some cases, hair loss, the patient may experience attacks of low fever, feelings of fatigue, frequent headaches, sore throat (sore throat).
- All areas affected by the rash carry an infection, so not only sexual, but also any physical contact is unacceptable, especially if there are lesions on the skin of a healthy person or he touches the rash with his mucous tissues.
- But the main changes occur inside the body - syphilis affects internal tissues and organs, as well as the nervous system.
Which can lead to the development of signs of such types of syphilis as: visceral and neurosyphilis. In general, secondary syphilis and the processes that arise from it occur within 2 to 4 years.
Then the disease hides - the hidden period of its course begins. Skin rashes disappear and the process of organ damage stops. The transition to the latent period of the disease is possible “thanks” to treatment.
Syphilis can go into a latent period, during which the patient is less infectious and there are no clinical symptoms, but serological reactions remain positive.
This sign of recovery is doubtful. This is just the “calm before the storm.”
And this “storm” is called late or tertiary syphilis, when the heart, liver, nervous system and musculoskeletal system become affected by the disease. This period can last from 5 to 15 years.
- Affected vital organs critically affect the patient’s condition; he may experience attacks of mental disorders, progressive blindness, serious neurological problems, heart diseases; everywhere on the skin you can see what the consequences of refusal of professional therapy lead to.
- It is not uncommon for the disease to develop and transform into the form of neurosyphilis, which can last for many years and even decades, if physically the patient can survive this period of long, terrible torment.
- At this time, it is already too late to talk about options and hopes, since on the horizon for those who have not treated syphilis there is only one prospect - a painful and quick death.
- All of the above stages of syphilis in the context of pregnancy are important for cases where a woman who had fallen ill long before considered the attenuation of the disease as recovery and recklessly became pregnant, without taking into account the huge negative consequences.
After all, we are talking about the relative danger of infecting an unborn child with syphilis. The child becomes infected in the womb of a pregnant woman and the most likely period for transmission of the disease is the time of secondary syphilis, that is, in the first three years after the mother’s illness.
Accounting and treatment of syphilis in pregnant women
To diagnose syphilis in a timely manner, a potential mother must first of all register at an early stage of pregnancy and undergo screening for the presence of the disease.
Analysis for syphilis in pregnant women: norm and explanation
During pregnancy, all women are tested for this infection three times during the entire period. This allows, in case of infection, to promptly identify a similar problem and begin its active treatment. Research is carried out upon registration, then once in the second trimester and in the third. A negative result indicates the absence of treponema and antibodies to it, but to make a diagnosis of syphilis, positive serological tests are required - the presence of antibodies to treponema. All types of tests are divided into two large groups:
- Non-treponemal
- Treponemal.
The first group ( non-treponemal tests ) always give positive results in the presence of syphilis, but can also give positive results against the background of some other infections or pathologies. They are used to determine the activity of the process and monitor the cure. When the treponema is successfully removed from the body, they become negative.
note
The classical diagnosis of syphilis (Wassermann reaction) often produces errors, and therefore it is replaced by more accurate and sensitive tests.
The second group ( treponemal tests ) have high specificity and sensitivity; they give positive results only against the background of syphilis. However, after an infection they can remain positive for the rest of their lives, which will indicate a process suffered in the past. The level of antibodies to treponema is determined by ELISA with the determination of IgM and IgG, and the first group indicates a recent infection and an acute process. It is also indicated to carry out other research methods that clarify the presence of treponema and antibodies to it.
The diagnosis is made if one test from the first group and at least 2 tests from the second are positive.
If the results are questionable, the studies are repeated after 1-2 weeks. We recommend reading: Diagnosis of syphilis: tests and their interpretation
Diagnosis of syphilis
1. Physical and gynecological examination to identify characteristic clinical signs.
2. RMP - microprecipitation reaction now serves as a screening method for diagnosing syphilis. RMP is performed for all pregnant women three times during pregnancy, at registration, at 30 weeks (when you go on maternity leave) and at 34-36 weeks. If the RMP is negative, then there is no syphilis. If the RMP is positive, then further examination is carried out using the ELISA method.
3. ELISA - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used to identify protective antibodies that the body has produced in response to the introduction of a pathogen. The result will be the CP indicator (antibody density coefficient): - positive (above 1.1) A positive result can sometimes be seen in crosses: weakly positive - ++ (CP 1.2-2.5), positive - +++ (CP 2.6- 3.5), sharply positive - ++++ (KP 3.6 and higher). - doubtful (0.9 - 1.1) - negative (less than 0.9) A specific ELISA test for syphilis will remain positive almost forever, only the concentration of antibodies will change. During pregnancy, the density coefficient becomes particularly important, since this indicator is used to evaluate the effectiveness of preventive or therapeutic medications and adjust the duration of treatment.
Other studies are rarely used.
Treatment of syphilis during pregnancy
If a primary or secondary process is detected during pregnancy, in order to avoid extremely dangerous and severe processes in relation to her own body and the body of the fetus, at least two courses of treatment are necessary. The first will be the main one, it is carried out only inpatiently, as soon as the diagnosis of syphilis is established. The second is carried out for the purpose of prevention on an outpatient basis or also in a hospital.
Detection of syphilis during the first and second trimester leads to treatment at the time of diagnosis, then at 20-24 weeks. Penicillin antibiotics are usually used in therapy , and if there is intolerance, ceftriaxone . It is these drugs that are active against Treponema pallidum and do not have dangerous effects on the fetus.
Treatment tactics for syphilis vary depending on the timing of gestation. Before 4 months of pregnancy, medications of the durant series are used, which are eliminated from the body for a long time, and after this period those that are eliminated much faster and more actively are used. So, up to 18 weeks, bicillin (1, 3 or 5) or penicillin is used, courses are selected depending on the drug. After 18 weeks, only penicillin or cephalosporins are prescribed.
After the initial course of treatment, in order for the infection to harm the child as little as possible, it is also necessary to undergo a course of therapy to sanitize the fetal body. It is carried out from the 20th week of gestation, provided that:
- specific treatment was carried out before pregnancy or in the first trimester, after which the tests became negative.
- completed the main course of therapy before 18 weeks of gestation.
Prophylactic penicillin is prescribed, the course is selected by the doctor. After such a two-stage treatment, the infection stops in its development, does not develop from primary secondary syphilis and complications, changes on the skin and damage to internal organs disappear. Thus, the threat to the health of a pregnant woman is eliminated and she ceases to be infectious to others.
Important
Thanks to modern treatment regimens for syphilis, if it is detected in the first two trimesters, congenital syphilis in the fetus can be completely prevented. Detection of an infection will not be an indication for termination of the desired pregnancy, but after birth the child will be examined for the presence of infection and will be monitored for a long time.
Childbirth when a woman has syphilis
If the diagnosis was first made during pregnancy, the woman is treated in an infectious diseases hospital or observational department of a specialized maternity hospital, and childbirth also takes place in the observational department, in a separate ward. The rules for managing childbirth are the same as under normal conditions, and the delivery option is chosen taking into account indications from the mother and fetus; natural birth or cesarean delivery do not in any way affect the possibility of fetal infection or their prevention.
Important
After the birth of the placenta, it is necessary to carefully examine it; flabbiness and fragility; large areas of degenerative phenomena threaten to violate the integrity of the organ, and then it is possible to leave a portion of the placenta in the uterine cavity.
If there is any doubt that the placenta is intact, the mother is given anesthesia and manual inspection of the uterine cavity is performed. Pieces of the umbilical cord and placenta are sent for histological diagnosis. This will confirm infection of these organs and also determine infection in the fetus.
Syphilis and childbirth
Childbirth in a patient with syphilis is carried out according to general rules. The type of delivery (conservative or surgical) is chosen depending on the obstetric situation. The type of delivery does not affect the activity of the infectious process and the likelihood of infection of the fetus.
After birth, a thorough examination of the placenta is performed. Specific changes in the placenta (flabbiness, fragility, large size and foci of degeneration) lead to its easy damage; the integrity of the membranes can easily be damaged and a piece of the placenta will remain in the uterus. Therefore, the placenta is examined; if its integrity is in doubt, a manual examination of the uterine cavity is performed under general anesthesia.
Then pieces of the placenta and umbilical cord are taken for histological examination. Some sources recommend testing cord blood for syphilis, but if the mother has a reliably positive reaction to syphilis, this is pointless. Up to a certain point, the blood of the mother and fetus is “common”; the child will also have a positive reaction to syphilis.
Infection with syphilis before pregnancy: what to do?
If a diagnosis of syphilis is made before pregnancy, when a course of full treatment has been completed, the risk of transmission of treponema and infection to the fetus is progressively reduced. The longer the period from illness to conception, the lower it will be. According to doctors, after 2-3 years the risks to the fetus become minimal, since at this time a complete cure for syphilis is achieved. If pregnancy occurs earlier than this period, based on the results of blood tests in the pregnant woman, in order to prevent congenital infection in the fetus, the doctor may prescribe preventive therapy for the woman.
Therapy is carried out during the 20-24th weeks of pregnancy, this is the time when the placenta is already fully formed and treatment at this time will be most complete. The child will receive the entire required amount of drugs through the placenta. During pregnancy, such a woman is no longer contagious or dangerous to others, and she can give birth in any maternity hospital of her choice. At the same time, she must have in her hands all the documents confirming the diagnosis and the full course of treatment.
Diagnostics
First of all, to determine infection, blood tests are taken from the finger and vein, and the spinal cord. There are 2 types of screening for pathogens:
First of all, to determine infection, blood tests are taken from a finger and a vein.
- MR. The presence of antibodies 1:2 and 1:320 indicates infection. At a late stage, the indicators are small;
- P.B., R.W. “-” indicates that the pathogen was not detected. “++”—infection is unlikely; additional diagnostic measures are required. “+++” - most likely the pathogen is present in the body. “++++” - a pathogenic microorganism has been detected in you. Antibodies after examination 1:2, 1:800 indicate infection.
Examination to detect pathology:
- PCR. If your test results are positive, you are most likely sick. Minus - you are healthy. This examination cannot give a 100% answer about infection. It is necessary to undergo additional tests;
- REEF. Detects the presence of a pathogenic microorganism in the early stages of development. “+” - you are infected. “-” - healthy;
- RPGA. Detects pathology at any stage. An indicator of 1:320 indicates that you have been infected not so long ago. High numbers indicate long-standing infection;
- ELISA. Prescribed as an additional analysis to determine the stage. “+” speaks of infection or illness before conception;
- RIBT. Prescribed when a false test result is suspected;
- Immunoblotting. Diagnoses congenital Lewis in children.
There are a number of factors that can cause survey results to be false. These include the period of gestation. Therefore, pregnant women are subject to examination 2 times. If the disease is still detected, the patient is hospitalized.
The consequences of infection during pregnancy are quite unfavorable.
Typical situations for syphilis during pregnancy
There are several typical situations when a woman has syphilis detected before pregnancy. Tactics regarding mother and fetus are somewhat different:
- If the infection was relatively recent, but before pregnancy, and the woman received the full course of treatment, her tests still remained positive and she was not removed from the register for this infection. During pregnancy, she undergoes tests every trimester, but the volume of tests is greater than in healthy women. In the 20-24th week, preventive treatment is carried out to protect the fetus. After birth, the baby must be examined for syphilitic infection.
- If a woman has been infected for a long time, and non-treponemal tests (indicating early treated syphilis) remain positive, testing for infection is monitored once every trimester during pregnancy. During the 20-24th week of pregnancy, a woman is given preventive therapy. In these cases, planning and preliminary additional treatment of syphilis is recommended, and after the baby is born, it must be examined for syphilis.
- if the infection is long-standing, currently during pregnancy non-treponemal tests show negative results; during pregnancy they are repeated at least 3-4 times. If all tests are negative, no treatment is necessary. If at least one of the tests is positive, a preventive course of therapy is carried out to prevent infection in the baby. After birth, the child then needs to be tested for syphilis.
note
All doubtful situations are resolved in favor of treatment and benefit to the fetus.
Preventative treatment
Specific treatment
If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the pregnant woman should be hospitalized in a dermatovenerological hospital for treatment. Treatment is often carried out with antibiotics of the penicillin group: novocaine and sodium salt of Penicillin, Bicillin, Extensillin, Retarpen.
In the case of primary syphilis, treatment lasts a couple of weeks, in the case of tertiary syphilis – a couple of years.
For expectant mothers who have positive blood test results for syphilis after treatment before pregnancy, and for those who were treated during pregnancy, an additional preventive course of treatment is prescribed to prevent congenital syphilis.
This course is prescribed at the 20th week of pregnancy or immediately after the main course (if it was not completed before the 20th week). Treatment is carried out with Penicillin salts or Erythromycin (in the presence of penicillin intolerance).
This treatment is necessary not only for the mother, but also for the baby; it does not pose a threat to the fetus.
When children are born who were born from sick mothers who have not completed full courses of treatment and prevention, they are given a preventive course of treatment - they are given antibacterial drugs.
At the moment, there are no specific recommendations in what situation a pregnancy should be terminated with syphilis. Current methods of treating syphilis make it possible to prevent congenital syphilis by identifying the disease in the mother in the early stages of pregnancy.
If syphilis is detected later, it is no longer possible to terminate the pregnancy, and treatment should be carried out for both the pregnant woman and the baby. So, if the pregnancy is desired, then it is possible to preserve it, subject to mandatory treatment of the disease.
Those women who have previously been completely cured of syphilis have a chance of giving birth to a healthy baby without undergoing additional preventive treatment.
In the first trimester
All pregnant women are required to be tested for the presence of the syphilis virus in the body.
Diagnosis of syphilis in a child: exclusion of intrauterine infection
If congenital syphilis is suspected, a whole range of examinations of the child is necessary. It is important to study general data about the mother and her state of health, the duration of the infection in herself and the courses of treatment carried out. Based on the information received, the doctor selects tactics in examining the newborn, based on certain options:
- the pregnant woman did not undergo treatment or did not complete the therapy: the child is examined to identify signs of congenital infection. If they are detected, treatment begins immediately. All types of tests are carried out, taking blood 7-10 days after birth. According to indications, cerebrospinal fluid is also collected to diagnose neurosyphilis. After analyzing all the data obtained, the child is prescribed medications.
- The pregnant woman was treated for syphilis, was observed by a doctor, and received all courses of treatment. The baby will be examined by an ENT doctor, a neurologist, an ophthalmologist, and a bone x-ray will be taken. If at least one sign of congenital syphilis is detected, diagnosis is indicated as for adults.
Until one year of age, a child is registered with specialists as being at risk due to intrauterine infection . Specialists will frequently and carefully examine him, noting the dynamics in his development and possible signs of the disease. At the age of three months, screening for infectious lesions is carried out, the child is examined by specialists, and tests for syphilis are carried out. If positive test results are detected, treatment for syphilis is applied, but if only external signs are identified, control is carried out after another 3 months. If the tests are negative, another examination per year is required. If there are no signs of infection, the child is removed from the register for congenital syphilis; if signs remain, further monitoring is carried out, prescribing drug treatment if necessary.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
15, total, today
( 59 votes, average: 4.25 out of 5)
Stripe on the stomach during pregnancy
Blood in urine in adults, children and pregnant women: causes and diagnosis