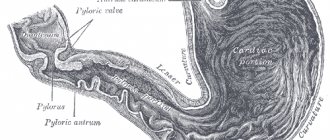
When is the procedure indicated?
The examination is carried out if diseases and pathologies are suspected that may pose a serious danger to the patient. In most cases, barium X-ray of the stomach allows you to confirm or clarify the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
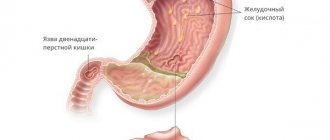
Suspicion of the formation of gastric and duodenal ulcers
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (DPC) leads to the periodic appearance of ulcers. It can take years to develop and cause serious harm to health. Using a barium X-ray of the stomach, the specialist finds the ulcer and evaluates its size, shape and other parameters, as well as establishes the stage of the disease and detects accompanying symptoms.
Detection of a malignant process in an organ
If the development of a malignant process is suspected, an X-ray of the stomach with barium is recommended without fail, since the consequences of the disease can be deadly for the patient. In the photographs, the cancerous process looks like a defect in the mucous membrane. Often, after a barium X-ray of the stomach, an endoscopic examination is performed and a sample of the tumor is taken for laboratory testing.
Diverticulosis and other deformities of the gastric walls
To diagnose wall protrusion (diverticulosis), a barium X-ray of the stomach requires additional preparation. After administration of the contrast agent, the patient alternately lifts the upper and lower parts of the body so that the contrast fills the entire organ cavity. On a barium X-ray of the stomach, small diverticulosis looks like an ulcer, but has a horizontal level and a neck.
Any inflammation of the stomach
Foci of inflammation in the stomach can appear as a result of various processes. Including peptic ulcers or oncology. An X-ray of the stomach with barium allows you to find the source of inflammation and, based on indirect signs, determine its cause.
Swallowing dysfunctions
Dysphagia, or swallowing dysfunction, is often expressed by the patient complaining of the inability to swallow food and its accumulation in the esophagus. In this case, the patient cannot always accurately indicate the location of the obstacle. Therefore, barium radiography of the stomach is used to accurately localize the pathology.
Pain in the abdominal area or navel area
Pain in the navel and abdominal area may indicate the development of malignant processes in the stomach and duodenum. Therefore, with such symptoms, the specialist often refers the patient to an X-ray of the stomach and duodenum with barium.
Indications and contraindications
Ulcers
X-ray examination of the abdominal cavity is an inexpensive and accessible diagnostic method. Radiation exposure is minimal. The procedure helps to quickly exclude (or confirm) serious diseases. Recommended in the following cases:
- suspicion of the presence of ulcerative pathology in the patient;
- for diseases of an inflammatory nature;
- the probable presence of tumors of benign or atypical etiology;
- during possible deformation processes.
X-ray of the stomach is prescribed when a certain clinical picture develops: sudden weight gain or loss, constant pain in the epigastric region, frequent occurrence of heartburn, blood in the stool.
Diagnosis is carried out according to the doctor’s recommendations; you will first need to visit a gastroenterologist. The procedure has some contraindications, they are characterized as absolute and relative.
What can be detected with radiography?
If a barium stomach x-ray is performed correctly and with proper patient preparation, the examination can provide enough comprehensive information to make a diagnosis in most cases. At the same time, to detect a particular disease, a specialist evaluates a number of parameters.
Gastric lumen disorders
Disturbances in the lumen of the stomach may indicate the development of a malignant process or diverticulosis. If the lumen of the stomach is narrowed on a barium X-ray, diffuse fibroplastic cancer is possible. With diverticulosis, on a barium X-ray of the stomach, the lumen appears larger than it should be normally.
Abnormal placement of the stomach
Gastroptosis (prolapse of the stomach) is often diagnosed with an abdominal wall hernia or diaphragmatic hernia. The disease is clearly visible using barium X-ray of the stomach.
Niche symptom
A niche is a shadow of a contrasting mass that fills a defect during an ulcer or the development of a malignant process. Depending on the location of the defect, an X-ray of the stomach with barium distinguishes between a contour and a relief niche. In the first case, the silhouette of the defect is visible from the full face, in the second - in profile.
The lack of filling is visible in the image as a dark area
A dark area on a barium x-ray of the stomach indicates that there is a place where the contrast could not reach. As a rule, this happens with atrophic gastritis or tumor.
How to diagnose stomach cancer in the early stages?
Detecting the disease at the earliest stage allows oncologists to choose the most effective treatment.
If unusual symptoms appear or if there is a noticeable and unmotivated deterioration in your health, you should always contact a medical facility.
The doctor must describe all your sensations, indicate the time of their appearance and increase.
Based on the examination and questioning, the doctor prescribes the necessary tests and instrumental examination methods to more likely confirm or exclude cancer.
Particular attention to your health and the appearance of unusual symptoms should be paid to those people who already have or have had stomach polyps, peptic ulcers, and chronic gastritis.
Anemia is also considered a precancerous disease. Patients with these diagnoses need to undergo control examinations of the body at least twice a year.
How should a patient prepare for the procedure?
Since the patient needs time to prepare for a barium stomach x-ray, it is best to start a few days before the examination. The first step is to exclude from the diet foods that cause increased peristalsis and gas formation. 8 hours before the examination you should completely abstain from food. To relax the stomach before the x-ray and prepare it for filling with barium, the doctor may recommend taking a special drug half an hour before the examination. Contrast is administered orally a few minutes before the procedure. When a double contrast examination is required, after the patient has prepared for a stomach x-ray and taken barium, he will need to drink a gas-forming mixture.
Palpation
Palpation or feeling a tumor with your fingers is one of the most ancient methods of medical examination. In the early stages, it is unlikely that a stomach tumor can be palpated; this is only possible when the tumor is approximately the size of a walnut.
In order to correctly carry out such a diagnosis, other conditions must be met, these are:
- The patient's stomach should not be full of food. Therefore, palpation is carried out before meals; you can first take a laxative.
- Palpation is performed in several positions. The patient alternately takes a position on the left and right side, on the back. Palpation is also necessary while standing.
- Palpation of nearby organs. Tumors in the projection of the stomach can also come from the liver, pancreas, and spleen.
Cancerous tumors usually do not cause pain on palpation; their edges are uneven and lumpy to the touch. The neoplasm can be either soft or dense, almost hard. It is more difficult to detect tumors located on the posterior wall of the organ by palpation.
When is x-ray prohibited?
An X-ray of the stomach with barium is a safe examination, but since it is done using ionizing radiation and a contrast agent, the method has a number of contraindications.
Hematopoietic disorders caused by pathological conditions of the bone marrow
Ionizing radiation can worsen the disease. Therefore, if hematopoiesis is disrupted, an X-ray of the stomach with barium is not performed.
Cataract
When X-raying the stomach with barium, the radiation dose does not exceed permissible limits. However, with cataracts, even a limited amount of ionizing radiation may be enough to have a negative effect on the condition of the lens.
Malignant neoplasms of the bronchi and lungs
The examination is contraindicated if the patient is undergoing radiation or chemotherapy treatment.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, even minor radiation can have a detrimental effect on the development of the fetus. Therefore, X-rays of the stomach with barium are contraindicated for expectant mothers.
Childhood (before the onset of puberty)
In childhood, the body reacts poorly to exposure to even small doses of ionizing radiation. Therefore, doctors refer children for an X-ray of the stomach with barium only if absolutely necessary.
CT scan
CT diagnostics involves obtaining layer-by-layer images of an organ. When carrying out this diagnostic method, the thickness of the walls of the stomach, the degree of spread of the cancer tumor throughout all layers of the organ, the size and location of the tumor are assessed.
Computed tomography can additionally be performed with a contrast agent, this facilitates the identification of pathologically altered lesions.
PET-CT
PET-CT is an innovative diagnostic method that stands for positron emission tomography. The method is based on the introduction of a radioactive tracer into a vein. This indicator reacts to increased metabolism and therefore reaches sites where cancer cells accumulate.
PET-CT allows us to determine functional changes at the cellular level, which helps to recognize the cancer process at the earliest stage of its development in the stomach.
PET imaging is also necessary to clarify the pathways of gastric cancer metastasis; secondary lesions with this diagnostic method are also detected at the very initial stage of their development.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI diagnostics are carried out using a special tomograph. The principle of receiving data from the device is based on the interaction of radio frequency pulses and magnetic fields.
Photo of stomach cancer diagnosis using MRI
The patient must first drink a contrast agent. After preparation, it is placed in a tomograph and several images are taken; the procedure takes about 30 minutes. Clear images obtained in three projections make it possible to identify all changes in the organ.
In addition to the stomach itself, the nearest lymph nodes and nearby organs are examined.
Examination of stool and vomit for occult blood
A fecal occult blood test determines a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. This method is used as an additional examination to confirm gastric disease.
Before collecting stool, the doctor must warn the patient about following a diet and avoiding certain medications. A reliable positive test is considered if the blood shows a two-time analysis.
Examination of vomit is carried out whenever possible. Usually a guaiac test is performed, which even shows traces of blood.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is usually prescribed to patients when the diagnosis of stomach cancer is established.
Such a study is necessary to identify secondary lesions in the abdominal cavity and pathological changes in the lymph nodes.
When performing laparoscopy, it is also possible to take changed pieces of tissue for histological examination.
Laparoscopy does not present certain difficulties during the procedure.
After anesthesia, a minimal incision is made on the side of the abdominal wall, the same size as the laparoscope. At the end of the laparoscope there is a miniature video camera, with the help of which the entire internal image is displayed on the monitor screen.
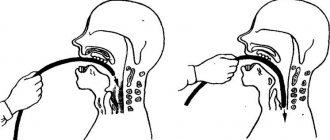
Endoscopy
Endoscopy for stomach cancer is a gastroscopy. Using an inserted endoscope, the doctor carefully examines the organ cavity and determines the form of cancer based on endoscopic signs.
These signs include the size of the formation, its location in the stomach cavity, the presence of ulcerations, the clarity or blurring of the boundaries of the pathological change.
Modern devices allow you to leave all the data in the computer, which in the future makes it possible to accurately determine whether the tumor is growing and whether it can be treated.