Laryngitis and pharyngitis are common diseases that affect the upper respiratory tract. Knowing what laryngitis and pharyngitis are, what is the difference between these two diseases, how to treat each of them, is important for adequate therapy.
Related articles:
The use of antibiotics for laryngitis in children - rules of administration Symptoms and treatment of acute laryngitis Preparations for inhalation for laryngitis with a nebulizer Treatment of voice loss due to laryngitis Effective antibiotics for laryngitis in adults and children
What is laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammatory process in the larynx that appears against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, measles, whooping cough, and scarlet fever.
Acute laryngitis develops quickly and goes away after two weeks. But the chronic form lasts from 14 to 60 days.
Symptoms of laryngitis
The onset of the disease is abrupt with general good condition. The temperature increases to 38.5–39 °C. A person has a burning, tickling, scratching sensation in the throat and discomfort when swallowing. Laryngitis is accompanied by headache.
The ligaments swell and the sonority of the voice disappears. The airways narrow, making it difficult to breathe. A cough without sputum becomes wet. Afterwards, purulent sputum disappears.
The laryngeal mucosa is red. Blood appears from the inflamed capillaries. For this reason, purple spots and thickening of the vocal folds appear on the membrane.
Reasons for appearance
The acute form of the disease rarely progresses as an independent disease, but acts as a sign of acute respiratory viral infection. In this case, the mucous membranes of the nose and pharynx are also susceptible to inflammation. Less commonly, the lower respiratory tract is involved in the process.
The primary cause of the development of the acute form is respiratory viruses. The disease is also caused by streptococci and staphylococci. Bacteria live on the mucous membrane, but do not cause disease. Activated under the influence of the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- inhalation of harmful fumes, gas and dust;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- thermal irritation;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Chronic laryngitis progresses for the following reasons:
- overstrain of the vocal cords;
- frequent laryngitis;
- sinusitis;
- chronic inflammation of the trachea.
Internal factors include:
- metabolic disorder;
- weakening of the immune system.
How does laryngitis differ from pharyngitis, sore throat and tracheitis?
The basis of each of these pathologies is inflammation of the mucous membrane of a particular organ. Laryngitis, unlike pharyngitis, as mentioned above, is characterized by inflammation of the larynx. The main symptom is hoarseness, since the vocal cords are often involved in the process. Depending on the complexity of the disease, complete loss of voice is possible.
Sore throat or tonsillitis is a pathological process in the pharyngeal tonsils. And pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx. Tracheitis affects the lower respiratory tract - the trachea.
One of the main reasons for the development of double pathology is a weakened immune system. When pharyngitis occurs, the body's immune cells cannot cope with the inflammatory process, as a result of which the infection goes down and damages the tonsils and vocal cords, provoking the development of laryngitis or tonsillitis.
If, at the time the infection spreads, adequate treatment is not prescribed, or the patient does not fully comply with medical recommendations, the inflammatory process may descend even lower and affect the tracheal mucosa. This disease is called tracheitis and is characterized by a painful, dry cough and a feeling of tightness in the chest.
What is the difference between laryngitis and pharyngitis and other diseases?
What is pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, characterized by itching and pain in the throat.
It occurs in both acute and chronic forms.
Symptoms of pharyngitis
Main signs of the disease:
- itchy throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- inflammation of the upper cervical lymph nodes;
- impotence;
- temperature rise to 37.5 °C;
- redness of the back of the throat.
A person feels a sore throat and a lump in his throat. Cough without phlegm and persistent. Patients are irritable and nervous. Sleep disturbance occurs.
Reasons for appearance
The main factors causing pharyngitis are:
- inhalation of cold or polluted air;
- hypothermia;
- smoking.
The disease progresses due to exposure to bacteria:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- pneumococci.
Pharyngitis is caused by influenza viruses, adenoviruses or fungal infections. Due to the transition of the infectious process from the source of inflammation, the disease progresses with sinusitis, rhinitis and dental caries.
Dr. Phil will tell you everything you need to know about pharyngitis in this short video:
Acute pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis is a fairly rapidly developing disease that occurs immediately after contact with a provoking factor. Depending on the cause, bacterial, viral, fungal, traumatic and allergic forms are distinguished. In addition, those forms of the disease that arose as a result of the irritating effects of any substances from the external environment act as a separate subgroup.
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis are primarily represented by a feeling of slight soreness and soreness in the pharynx. This is especially noticeable during the swallowing process. Severe dryness and burning with the same localization are added. There is an increase and the appearance of pain in the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes. A nonproductive cough may develop. The patient indicates a deterioration in general health, his body temperature rises, a headache and a feeling of weakness appear. Upon examination, you can see pronounced redness and swelling of the pharyngeal area, as well as the appearance of plaque in some places.
Acute pharyngitis can be complicated by the spread of the pathological process to the bronchi or larynx with the trachea. In addition, without proper treatment, it can become chronic or develop paratonsilar or retropharyngeal abscesses.
What is the difference between laryngitis and pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis differs from laryngitis in the location of the infection. Differences between the two diseases:
- With pharyngitis, a person remains able to work, as the temperature rises to 37.5 °C. With laryngitis, the temperature increases to 38.5–39 °C.
- Pharyngitis is caused by viruses, while laryngitis is caused by bacteria.
- With proper therapy, you can recover from pharyngitis in a week. Symptoms of laryngitis will begin to go away on the tenth day of therapy.
- Coughing with laryngitis occurs immediately. With pharyngitis, they appear on the third day due to pain in the throat.
If symptoms occur, it is advisable to seek help from a doctor.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The causes of diseases can be colds, viral, bacterial or fungal infections. Pharyngitis, as a rule, does not appear on its own. You already know about this. Laryngitis, on the contrary, can be an independent disease. The cause of pharyngitis is an untreated runny nose, in which mucus flows down the back wall of the larynx. Pathology can occur against the background of an illness or after it (with whooping cough, scarlet fever). Even caries can cause inflammation. Laryngitis is caused by inhalation of dirty air, dust, and household fumes. The disease appears due to infection by viruses or bacteria. It is possible to determine what exactly caused the illness only through laboratory tests.
The diseases pharyngitis and laryngitis also differ in symptoms. Both inflammations are accompanied by pain and sore throat. With laryngitis, hoarseness occurs; in some cases, a person cannot utter a word. Pharyngitis is often accompanied by high fever. A cough with laryngitis is more like a barking cough; if the inflammation has spread to the trachea, sputum is produced. Pharyngitis is characterized by a dry, non-productive cough that occurs due to irritation of the lymphoid tissue. A runny nose may also occur, which usually does not happen with inflammation of the vocal cords. Depending on the symptoms of laryngitis or pharyngitis, the appropriate treatment is chosen.
General in the treatment of throat diseases
Treatment of a throat infection is indicated only after identifying the causative agent:
- bacterial infection - antibiotics;
- pathogenic viruses – antiviral medications;
- fungal infection - antifungal drugs.
Infectious diseases require symptomatic treatment. It helps to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms and alleviates the general condition of the patient.
7 simple rules if someone at home is sick
Given the difference in the location of the infection, the cure for the disease in adults is largely similar. Eliminate pharyngitis and laryngitis with:
- Inhalation with hot steam or nebulizer: Dexamethasone, Lazolvan, calendula, St. John's wort. Thanks to these actions, swelling and mucus are eliminated.
- Resorption of tablets with an analgesic effect: Stopangin, Septolete, Lizobakt.
- Instillation of nasal drops with a softening effect: Pinosol, Miramistin, Thuja oil.
- Warming up: warming compresses, mustard plasters on the chest, foot baths.
- Spray: Inhalipt, Lugol, Yox, Cameton, Hexoral.
- Rinse: chamomile, Furacilin, sage.
Before using medication for pharyngitis or laryngitis, it is advisable to consult an ENT specialist.
Differences in the treatment of pharyngitis and laryngitis
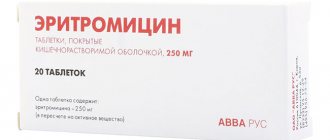
Among the differences in therapy will be voice rest for laryngitis. For aphonia, healing lasts one and a half months. The doctor prescribes antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Erythromycin, Cefazolin.
In the treatment of laryngitis, inhalations occupy an important place, and for pharyngitis, rinses. This is the main difference.
If your voice is hoarse, you should not talk for the first 2–3 days. It is useful to perform special gymnastics.
Folk remedies for the treatment of pharyngitis and laryngitis
It is possible to overcome the disease at home. In addition to complex therapy, doctors advise using traditional medicine recipes. When treating pharyngitis at home, you can get rid of symptoms after 3 days, and from signs of laryngitis after 5 days.
Gargles
Popular recipes:
- Pour 3 tablespoons of onion peel into 1 liter of boiling water and boil for 3 minutes. Rinse your throat 5-6 times a day with lukewarm, strained broth.
- Pour 2 tablespoons of mint into 0.5 liters of boiling water. Wait until it cools down and perform the procedure 5 times a day.
- If your voice is too dry, combine 0.5 liters of beet juice and 2 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar. Use the resulting medicine for procedures four times a day.
- Pour 1 liter of boiling water over dried apple leaves. Rinse with the resulting drug 5-6 times a day.
3 best recipes for gargling
Infusions
- Stir cherry juice with currant juice and pour in 1 tsp. honey Serve warm throughout the day.
- Boil 2 tablespoons of raisins in 0.2 liters of water and add 1 tablespoon of chopped onion to the finished broth. Drink 2 spoons three times a day.
- Pass the onion through a press, add a cup of liquid, add a spoonful of sugar. Simmer the mixture over low heat until the onion softens. Use 1 spoon throughout the day.
Nasal drops
Use peach, rosehip or olive oils. Place 3 drops in each nostril. Preheat to body temperature.
Steam inhalations
For sessions, use hot infusions in a saucepan. Wrap yourself in a sheet and inhale the vapors through your nose and mouth until the liquid cools. Do not lean too close, otherwise the patient will get burned.
For procedures take:
- ground eucalyptus leaves;
- onion or garlic passed through a press;
- sea salt and clove oil.
Proper nutrition
With laryngitis and pharyngitis, immunity is reduced. This is due to a lack of vitamins.
Therefore, it is important for patients to eat properly. It’s worth changing your diet and sticking to the following principles when eating food:
- eat food often, but in small portions;
- refuse to eat too hard foods, as such food scratches the throat;
- food is not too hot and too cold;
- Avoid eating spicy, salty and smoked foods.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis develops on the inner mucous membrane of the pharynx and is expressed in the presence of an inflammatory process on the walls. Pharyngitis has the following symptoms:
- Sore throat.
- Dry cough.
- There may be an increase in body temperature.
The disease pharyngitis also occurs against the background of respiratory diseases: ARVI, rhinitis and others. During the development of pharyngitis, inflammation appears on the back wall of the inner lining of the pharynx.
With the development of a runny nose, the infection may move from the nose to the pharynx, which will become a provoking factor for the onset of pharyngitis.
Pharyngitis can be avoided by adhering to the following simple rules:
- Do not eat cold food or food with hot, sour or salty spices (vinegar, pepper, horseradish, mustard).
- Stop smoking - it causes dryness of the mucous membranes of all surfaces of the throat, including the pharynx.
- Avoid mechanical injuries to the pharynx by chewing food thoroughly.
- Food should be warm, preferably with a predominance of liquid and semi-liquid food (mashed soups are ideal, as well as thin porridge for the prevention of pharyngitis).
Pharyngitis disease
Treatment of pharyngitis
- Pharyngitis is treated by rinsing, you can use either water with a small spoon of soda or salt, or using decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs.
- When using lozenges and lozenges, pharyngitis will be cured faster, and there will be significantly less discomfort in the throat due to their moisturizing and softening effect.
- Inhalations, both using a nebulizer and using improvised means (steam), have proven themselves in the treatment of the disease. You need to inhale medicinal vapors through your mouth and exhale through your nose, so more of the medicinal solution will settle on the throat.
- It is possible to instill vegetable oils in case of severe discomfort associated with dry mucous membranes.
- Drinking medicinal teas based on decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs also has a positive effect in treating the disease.
In general, the nature of the diseases is similar, only the location of the source of inflammation differs: pharyngitis develops in the pharynx, and laryngitis develops in the larynx and vocal cords. The treatment of these diseases also consists of the same procedures, with some nuances.