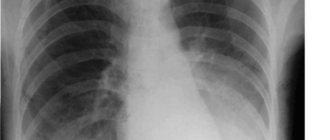
The forced recumbent state of elderly patients, cardiac pathology leads to stagnation of blood in the small pulmonary circle in the circulatory system, in the venous outflow. If treatment is not started in time, pulmonary edema may occur, which can result in death.
Pulmonary congestion is a life-threatening condition that is associated with insufficient ventilation of the lung tissue as a result of stagnation of blood in the lungs. Often stagnation is caused by forced inactivity of older people, chronic diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Causes of congestion
Along with elderly people over 60 years of age, those at risk for pulmonary pathology include patients who have undergone operations, injuries, and those in the terminal stage of oncology. According to statistics, death occurs from stagnation in more than half of cases. Especially if the stagnation is caused by a condition such as pulmonary embolism.
The forced recumbent state of elderly patients and concomitant cardiac pathology leads to stagnation of blood in the small pulmonary circle in the circulatory system and disruption of venous outflow. The physiological mechanism is that first the venules expand, which causes compression of the pulmonary structures, then the transudate finds its way into the intercellular space and edema occurs. All this disrupts gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen cannot enter the blood in sufficient quantities, and carbon dioxide cannot be removed from the body.
Thus, impaired pulmonary ventilation and physical inactivity in the elderly are the main factors in the development and progression of stagnation. Under the influence of microorganisms, for which stagnation is a favorable environment for reproduction, pneumonia (pneumonia) begins. At the sites of fibrous tissue formation, pneumosclerosis occurs, affecting the structure of the pulmonary alveoli and bronchi. If treatment is not started in time, pulmonary edema may occur, which can result in death.
The disease may also be associated with heart failure, under the influence of the following factors:
- cardiomyopathy, pathology of the heart structure;
- hypertensive crisis;
- renal failure and vascular sclerosis;
- poisoning with chemicals through the respiratory system, taking medications, injuries.
Forecast
With lung lesions affecting large areas, especially in elderly bedridden patients, the risk of death is very high and reaches 70%. To prevent such an outcome, it is necessary to begin conservative treatment at the first symptoms indicating pulmonary congestion in bedridden patients. Moreover, immediately consult a doctor; self-medication will only worsen the condition of the elderly patient.
The general prognosis for hypostatic pneumonia in the active phase depends on the depth of pathological processes in the lungs, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases. The sooner pneumonia is diagnosed and adequate therapy is prescribed, the better the overall prognosis for recovery will be.
Symptoms of stagnation
Initially, symptoms are similar to pneumonia. In many cases, early diagnosis is difficult. Along with the examination and listening to breathing, body temperature is measured, blood tests are taken and an x-ray of the lungs is taken. Both diagnosis and treatment, as well as the prognosis of stagnation, depend on how the body is able to cope with pathogenic microflora. In cases with reduced functions of the immune status, the disease can occur as early as the 3rd day.
Elderly people are susceptible to congestion after a few weeks and its symptoms are as follows:
- the temperature background is stable, rarely outside the normal range;
- rapid breathing with symptoms of tachycardia;
- the sick person speaks intermittently, feels anxious, and breaks out in a cold sweat;
- a cough appears with exudate, then with blood, bloody foam;
- patients complain of increased fatigue and weakness, it is difficult for them to lie on a low pillow (when sitting, the symptoms of shortness of breath gradually disappear);
- upon examination, the skin is pale, the nasolabial triangle is bluish in color, there are signs of swelling of the lower extremities;
- Pleurisy and pericarditis may occur against the background of hypoxia and pathological processes of insufficiency.
If the first symptoms of respiratory failure associated with the lungs appear, then urgent medical attention is needed.
Symptoms of this disease
How severe the form of the disease can be can be judged by the form of the disease that preceded the development of pneumonia, and by the extent to which inflammation affects the body.
Symptoms include the following:
- Increased or normal body temperature;
- Cough with sputum mixed with pus;
- Sputum production mixed with blood;
- Fatigue and decreased performance;
- Severe shortness of breath.
In the early stages of the disease, any symptoms will be the result of underlying diseases. A person who has had a stroke has difficulty remembering and breathing. If the patient has heart problems, heart failure may develop.
Treatment approaches
At any stage of the disease, treatment is best done in an inpatient setting. In difficult cases - in the intensive care ward or in the intensive care unit. To increase breathing volume, an oxygen mask or artificial respiration apparatus is prescribed.
During hospitalization, the patient is prescribed an X-ray of the lungs, an ECG, and an ultrasound of the heart. A clinical blood test and biochemistry show signs of an inflammatory process: an increase in ESR, leukocytes, a positive C-reactive protein reaction.
Establishing the cause of stagnation should be the main focus of therapy. If the symptoms are caused by problems with heart failure, then the attacks are stopped and a complex of cardiotherapy is prescribed.
Regardless of the source of the disease in the lungs, a group of antibacterial therapy is prescribed to suppress the pathogenic effects of microbes on the lung tissue. To these are added agents that reduce the thickness of sputum.
It is important to treat a cough, not suppress it. Treatment is carried out using mucolytics, herbal preparations, extracts of coltsfoot, plantain, thyme, which are recognized as the most effective phytotherapeutic agents. Diuretics and vitamins are required to enhance the immune response to pathogenic microflora in an elderly person.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that congestive pneumonia does not have specific symptoms, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to make an accurate diagnosis. As a rule, diagnostic measures consist of two stages. First of all, a physical examination of the patient is carried out with the collection of a personal history and clarification of the current clinical picture.
- blood sampling for general and biochemical analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- sputum collection for microscopic examination;
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the pleural cavity;
- ECG;
- EchoCG.
Based on the results of the diagnostic program, the doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis and, therefore, prescribe effective treatment.
Prevention of pulmonary congestion
To avoid congestion in the lungs, a patient who is forced to constantly stay in bed must make as many movements as possible. If it is not possible to do them yourself, then resort to the help of caregivers. It is useful to turn over every 4 hours, change body position, and sit down. You should not sleep on low pillows or be motionless for a long time, which weakens the functions of breathing and chest movement.
A physical therapy specialist can teach simple exercises that will help avoid pathology in the elderly and bedridden. Active independent breathing is important, and for this you can suggest inflating a balloon and breathing through a cocktail straw into a glass of water. Such exercises help enrich the bronchi and lungs with oxygen and expand the range of motion of the chest, including the diaphragm. Congestion in the lungs in the initial stage is eliminated only by activity.
Of particular importance is a diet rich in protein and carbohydrates, multivitamins, which will give vital energy to the cells. You can use medical cupping, mustard plasters, physiotherapy and active massage with tapping.
Regardless of the causes of the disease, those who are bedridden should drink hot tea with lemon and honey. It will help dilate blood vessels, strengthen their walls, and resist the formation of sputum.
It is necessary to use every opportunity to organize prevention in order to avoid more serious consequences.
/ Table of contents:
Congestive pneumonia is called inflammation of the lungs, which is not the main disease, and occurs mainly in older people (60 years and above) and in patients forced to remain in a supine position for a long time.
The diagnosis of pneumonia is made when there is inflammation of the lung tissue. In the case of primary pneumonia, inflammation occurs due to colds
.
Secondary or congestive pneumonia has an etiology of hemodynamic disturbances.
The patient experiences shortness of breath
,
cough
with
sputum
temperature
rises
effusion
may form (fluid accumulates in
the pleural cavity
).
These are the main and most obvious symptoms of the disease. vary
depending on the stage and extent of the disease .
There may not be a temperature. The cough may be accompanied by mucous or purulent sputum, and possibly hemoptysis. Often the disease is accompanied by exudative diathesis. Characterized by severe weakness and inability to bear loads. Congestive pneumonia especially weakens the body in old people. With existing heart and vascular diseases, pneumonia may be accompanied by heart failure.
impaired consciousness in stroke survivors
and
respiratory arrhythmia
.
Congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients can begin already in the first days of observing movement restrictions. In such cases it is considered early. If limited movement of the patient occurs between two and six weeks, this is late secondary pneumonia
.
A whole therapeutic complex is used in the treatment of this disease
.
Antibiotics
combined with
bronchodilators
, to which, when indicated, cardiac
glycosides
.
The patient is prescribed diuretics
, and
a chest
and back massage is performed.
Exercise therapy and inhalations
are indicated to support and consolidate the result of treatment .
If necessary, puncture of the pleura or pericardium
.
Congestive pneumonia treatment
suggests, first of all, an underlying, primary disease.
They also determine the choice of medications
. After the elimination of the underlying pathology, secondary congestive pneumonia has a much more optimistic treatment prognosis.
Treatment of congestive pneumonia in the elderly is aimed at activating the motor mode, normalizing lung ventilation and relieving the inflammatory process by taking appropriate medications. One of the most common diseases is congestive cardiac pneumonia, which occurs against the background of heart disease.
What is the danger of this disease, and why is the prevention of congestive pneumonia so important? This disease develops mainly in patients who have a history of other serious illnesses. Both congestive pneumonia in the elderly and congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients can lead to decompensation of the existing condition and cause death.
.
Death from congestive pneumonia, despite the methods of treating it available to doctors, occurs quite often
. The main reason is late diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the disease is difficult
for several reasons.
The main ones are the low-specificity of the clinical picture,
mildly expressed symptoms, as well as
the predominance of manifestations of the patient’s underlying disease
, which draw attention to themselves.
- To accurately prove congestive pneumonia, radiographic examination is necessary. It will allow you to control the degree of transparency of the lung field, detect foci of darkening, focal and linear shadows.
- Pleural effusion can be diagnosed using ultrasound. ECG data is also taken into account during diagnosis.
- In a blood test, the disease is manifested by an increased ESR. This is how congestive pneumonia is usually diagnosed in old people.
- When examining sputum under a microscope in patients with secondary pneumonia, hemosiderin-containing cells are detected.
Timely research is the key to successful treatment of the disease.
This is why
the prevention of congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients and people over the age of 60 important
The disease is classified according to the characteristics of its occurrence.
- Community-acquired pneumonia is formed due to a weakened body when exposed to pneumococcus.
- Long-term care pneumonia – occurs during prolonged forced immobility of the body, when it is exposed to bacterial pathogens.
- Nosocomial pneumonia - occurs under the influence of gram-negative and gram-positive bacilli, mainly Staphylococcus aureus.
Preventive measures
forced bed rest
for a long time .
Congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients has a disappointing prognosis.
Therefore, preventive measures
cannot
.
You should change it as often as possible
position of the patient's body.
Any active exercises that the patient can perform, including breathing, are indicated.
An important factor in preventing diseases such as congestive pneumonia is massage.
It can be cupped or percussion. Massage the chest area.
Application of mustard plasters and various compresses help prevent the development of the disease
People suspected of having this diagnosis
, a complete fortified diet should be provided.
The prognosis for congestive pneumonia is considered relatively unfavorable. The disease, taking an advanced form, is accompanied by the formation of necrotic foci in the lung tissue.
Abscesses form and multilobar lung damage occurs.
Therapy for the disease is selected strictly individually
, taking into account all the features of its course and associated factors
Congestive pneumonia rarely occurs on its own. Usually, an insidious illness appears against the background of some serious illness, significantly complicating its course. Unfortunately, in some cases, this disease causes the patient's premature death.
It is generally accepted that congestive pneumonia is the lot of elderly patients. Indeed, older people get sick more often. However, young people can also get this disease, for example, with cardiovascular pathology, oncology, after a stroke, serious traumatic brain injury or spinal surgery... The disease develops with a long-term fixed position of bedridden patients. In the elderly, the cause of congestive pneumonia may be different: old, weakened people sometimes breathe shallowly, as a result, the diaphragm does not contract as it should. In this case, the occurrence of congestive pneumonia is not excluded even in walking patients. How does the disease manifest itself and what are the treatment algorithms for congestive pneumonia?
Often the disease begins without fever, cough and chills, which are characteristic of lobar or focal pneumonia. At first, there is severe weakness, shortness of breath, a feeling of incomplete exhalation, sweating, and coughing. In other diseases, similar symptoms are also not uncommon. However, if symptoms persist after prolonged bed rest, an x-ray should be taken if possible. Unfortunately, patients consult a doctor when wheezing and sputum appear. The lungs are often not audible at all, since fluid has accumulated in them due to swelling of the bronchial mucosa and lung tissue. The fluid appears due to the fact that blood plasma, passing through the vessels, accumulates in the lung tissue and pleura. The algorithm for removing liquid is as follows. If there is little liquid: about 500 ml, at the level of 7-8 ribs, then it usually resolves itself, exiting through the lungs with wet breathing or through the pores due to sweating. When there is a lot of fluid, it is pumped out through a puncture in the chest. Sometimes this operation is performed on an outpatient basis.
The process of development of congestive pneumonia is sluggish and the course of this disease is usually unnoticeable. Therefore, it is not always possible to accurately diagnose. The disease progresses differently, but recovery takes the same time, within 5-6 months.
Treatment of this disease should always be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, as bacterial infection may occur. Then the doctor necessarily prescribes antibiotics. Algorithm for treatment with medications for coughing, as well as for better sputum discharge: taking bronchodilators (as prescribed by a doctor) for a month; in case of stagnation due to cardiovascular pathology, trengal is taken to improve blood flow, and digitalis is taken to strengthen the heart muscle. Diuretics are also prescribed to remove excess fluid from the body and reduce swelling.
After treatment, you can continue with herbs. Pharmacies sell ready-made syrups, elixirs, breast mixtures, and you can prepare medications using folk recipes.
Place 2 tablespoons of elecampane roots in an enamel ladle and pour 1.5 cups of boiling water, cook for 30 minutes over very low heat, covering the container with a lid. Afterwards, cool the broth, strain and add enough honey so that the broth tastes sweet with a hint of bitterness. Take the resulting syrup 1-2 tablespoons before meals. This syrup will improve sputum discharge.
Thyme or thyme helps very well. Pour 2 tablespoons of herbs into 0.5 liters. boiling water Strain and drink three times a day, half an hour after meals.
You can prepare a remedy called urbech. Take 1 kg of flaxseed, 1 kg of walnut kernels, mix and grind the mixture in a coffee grinder. After grinding, a viscous mass is obtained. This mass should be stored in a cool place. Before taking, take 1 tablespoon of the mass and 100g of butter. Mix and bring to a boil. Then add a spoonful of honey. After cooling, keep the cooled mass in the refrigerator until hardened. Then spread the urbech on bread and eat it with tea for breakfast or whenever you want. Tasty and healthy.
To treat congestive pneumonia, it is very important to perform breathing exercises. Complexes developed by Strelnikova or Buteyko help well. A detailed description of these complexes can be found in the books of these authors, on Internet pages in health magazines. For example, you can use the following exercises:
Take a deep breath, hold your breath and exhale slowly (perform the exercise for 1-2 minutes);
Raise your arms up as you inhale, then lower them sharply with the sound “ha!” exhale (execution time 1-2 minutes);
Inflate balloons twice a day, start doing the exercise from 1 minute, increase to 5 minutes;
Blow air through a tube inserted into a glass of water.
Bedridden patients need to have a massage every 2-3 hours: turn the patient on his stomach and lightly tap on the back, bypassing the heart area for 3-5 minutes, then massage in the chest area.
Nutrition during this period should be complete and varied. It is recommended to eat 30-50g of butter and fatty brisket per day. Exclude only spicy and salty foods. There are no other restrictions. It is also necessary to drink more fluids. It is advisable to give slightly acidified drinks: fruit drinks, jelly, compotes, rosehip decoction. On average, a patient should drink up to 1.5 liters per day along with first courses. This rule especially applies to older people. Drinking is necessary to remove harmful substances from the body. After all, any infection is an intoxication in which decay products, in particular bacteria, are absorbed into the blood. This is why people lose weight, lose their appetite, and develop anemia.
Know that congestive pneumonia is a disease that is easier to prevent than to treat.
Pulmonary congestion in bedridden patients is considered a life-threatening condition. It is caused by stagnation of blood or fluid in the lung tissues as a result of low mobility. Congestion in the lungs is accompanied by edema and bedsores. If the patient is not treated promptly, this condition can lead to death.
Breathing exercises
Special exercises can improve lung ventilation, normalize blood circulation, strengthen the respiratory system, and remove accumulated mucus.
Breathing exercises for the prevention of pneumonia can be performed by patients from 3 years old, if there are no contraindications. Contraindications include:
- elevated temperature;
- pulmonary hemorrhage;
- immunodeficiency;
- heart/respiratory failure;
- rapid heart rate (more than 100 beats per minute for adults);
- hypertonic disease.
Classes should be conducted in a well-ventilated room.
Several times a day, you should take a drainage position - position your head and chest area so that they are lower than the level of your torso and legs. You need to stay in this position for 2-5 minutes. At the same time, it is useful to carry out vibration and drainage massage - stroking and gentle tapping.
To improve sputum discharge, perform the following exercises:
- Starting position (hereinafter – i.p.) – hands on shoulders. As you inhale, move your elbows up and to the sides. As you exhale, lower your elbows and press them to your chest.
- I.p. - lying on your back. A deep breath is taken, and at the same time the arms are spread to the sides. As you exhale, your knees are pulled towards your chest.
- I.p. -lying on your right side, right arm under your head, left arm extended along your body. As you inhale, move your left arm back, and as you exhale, return to the starting position. Repeat 2-3 times on each side.
- I.p. - lying on your back. As you inhale, stand on your feet and raise your pelvis, while exhaling, return to the starting position.
Exercises from the author’s breathing exercises method by A.N. can also be used. Strelnikova.
Causes of congestion in the lungs
Lung congestion is mainly observed in people over 60 years of age. Persons who have undergone various injuries and operations are also at particular risk. According to medical statistics, in bedridden patients, pulmonary congestion leads to death in 40-50% of cases.
The causative factor of pulmonary congestion in elderly patients is a forced recumbent position and concomitant cardiac disease. This condition leads to stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circle and disruption of venous outflow. Why is this happening? First, the venules expand and put pressure on the pulmonary structures. After this, the transudate enters the intercellular space and causes swelling. As a result, gas exchange is disrupted and insufficient oxygen enters the blood. Carbon dioxide leaves the body.
Due to these disorders, congestion occurs in the lungs. For many microorganisms, stagnation is considered a favorable condition for reproduction. Therefore, most patients are diagnosed with pneumonia, that is, pneumonia. In this case, pneumosclerosis forms on the fibrous tissue, which destroys the structure of the bronchi and alveoli. Without treatment, the prognosis is disappointing: in 70-80% of cases, pneumonia ends in death.
In most cases, the causative agents of pneumonia are bacteria such as mycoplasma, chlamydia and pneumococcus. Is it contagious for older people? Yes, because their immune system is weakened and the body is not able to resist pathogenic bacteria.
Lung congestion can also occur due to impaired kidney function. In this case, the fluid is not completely removed from the body and penetrates into the lung tissue.
Prevention
The main prevention measures for congestive pneumonia are:
prevention, detection and relief of diseases of the chest organs, against the background of which congestive processes may occur in the lungs;- when forced to remain in a lying position for a long time - breathing exercises;
- to give up smoking;
- strengthening the body’s immune system and strengthening the body as a whole;
- regular physical activity;
- regular preventive examinations with a pulmonologist and therapist, even in the absence of complaints.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of pulmonary congestion can occur as a result of a bacterial infection, asthma, bronchitis or diffuse emphysema. Clinical signs may worsen after stroke.
At the initial stage of development, patients experience attacks of dry cough. Over time, coughing attacks intensify, and mucopurulent sputum streaked with blood appears. An increase in body temperature in patients is not always observed. As the disease develops in some elderly patients, the temperature can reach 38-39°C. With bilateral pneumonia in a bedridden patient, the temperature reaches 40°C.
Lung congestion also manifests itself in the form of rapid and difficult breathing. An accompanying symptom is shortness of breath. As congestion develops, shortness of breath appears at rest. In old age, symptoms such as:
- slowness;
- fog;
- lethargy;
- loss of appetite;
- vomit;
- nausea;
- pain syndrome in the abdomen.
The patient's general condition deteriorates sharply. Attacks of dizziness and severe fatigue appear. Under no circumstances should such symptoms be ignored. The consequences can be life-threatening.
As a result of reduced oxygen levels in the blood, the functioning of internal organs is disrupted. When listening to the patient with a stethoscope, wheezing and gurgling are heard. The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of development of the disease. In some cases, the patient may experience increased heart pressure, sticky sweat, pale skin, and a feeling of fear.
The accumulation of fluid in the lungs significantly complicates the treatment of any pathology. When existing chronic diseases worsen, the body's ability to fight bacterial infections decreases.
Why is congestive pneumonia dangerous?
The danger of congestive pneumonia lies in the complications that this disease can bring. Complications of hypostatic pneumonia include:
- Pulmonary edema
- Inflammation of the pleura
- Breathing problems
- Lung abscess
Each of these complications can lead to death, since in older people, especially with existing chronic diseases, the body's defenses are already depleted.
Medical therapy
What to do if a bedridden patient has symptoms of pulmonary congestion?
In this case, the patient must be provided with medical assistance, otherwise the inflammatory process may spread to the second lung.
Drug treatment includes antibiotic therapy and taking symptomatic medications that help get rid of secondary pathology.
Protected penicillins, fluoroquinolones and cephalosporins are used as antibiotics. For atypical pneumonia, Metronidazole and Erythromycin are prescribed.
To avoid serious consequences, treatment is carried out in a hospital, where the patient is under the strict supervision of a doctor. This allows you to monitor changes in the condition and promptly change the course of treatment if bacteria become accustomed to antibiotics. The most effective antibiotics for treating pneumonia are Ampicillin, Azithromycin, Amoxicillin and Cefuroxime.
As an auxiliary therapy, treatment can be carried out with folk remedies. At the initial stage of the development of pneumonia, it is recommended to prepare a medicinal decoction of anise with honey. It has expectorant properties. To prepare the decoction you will need to pour 2 tbsp. l. anise 200 ml water. Place the container on the fire and bring to a boil. Add 1 tbsp to the prepared broth. l. honey Take small sips throughout the day.
A decoction of cherry stalks will help remove serous fluid. Pour 1 tbsp. l. stalks with 1 glass of water. Bring the broth to a boil. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
This video talks about mucus in the lungs:
An herbal mixture of licorice, juniper, steelhead and lovage is effective. To prepare the recipe, you need to mix all the ingredients in equal proportions. Pour 1-1.5 tbsp. l. collecting 200 ml of water. Place the container on the stove. Boil the broth for 5-7 minutes. Take small sips throughout the day.
Treatment with folk remedies should only be carried out in consultation with the attending physician.
The occurrence of pneumonia in bedridden patients is usually caused by bed rest, when a person is forced to remain motionless for a long time. At risk are people who have suffered a stroke, traumatic brain injury, those suffering from cardiovascular pathology and those who, due to their incapacity, are forced to stay in bed for a long time.
In the category of elderly patients, the stagnant form can be detected even with active movement, and this is due to the fact that in old, weakened people the diaphragm stops contracting, and breathing becomes shallow. And this is already fraught with congestion in the lungs.
Prevention of pneumonia in children
Prevention of pneumonia in children has its own peculiarities. Due to his age, a child cannot always correctly assess his condition and describe it to adults. And means for prevention must be chosen with special attention and care so as not to cause harm. To prevent disease in children, maximal strengthening of the immune system is of primary importance.
Basic preventive measures:
Vaccinations
- Vaccinations against influenza, pneumococcal infection, and hemophilus influenzae. Timely vaccination against serious diseases makes the body more protected against pneumonia pathogens.
- Physical activity. Balanced physical activity keeps the body in good shape and develops the muscular system. A parent can play sports with their child and become a good role model.
- Fortification. Taking vitamins is beneficial at any age. For children, there are special vitamin complexes with a high content of microelements necessary for a growing body.
- Walks. It is recommended to walk with your child at least twice a day, avoiding hypothermia. Fresh air increases your chances of not getting sick.
- Inhalations with natural herbs (chamomile, coltsfoot, licorice root).
- Hardening. The procedure begins gradually with hardening the legs, the water temperature is gradually reduced from 34 to 25 degrees.
- Massage. Thanks to massage, children not only develop correct posture, but also activate blood flow and strengthen their immune system.
- Treatment of chronic diseases. Chronic pathologies have a secondary effect on the likelihood of pneumonia, so it is important to prevent their exacerbations.
Due to prolonged lying down, infants are at risk of developing congestion in the lungs. Against the background of impaired pulmonary blood flow, ventilation of the lungs is disrupted, causing the appearance of viscous sputum. In such conditions, bacteria develop quickly and lead to pneumonia. Therefore, the attention of relatives to the condition of young children at home should be especially close.
Preventive measures for infants:
- Fresh air. It is important to maintain a cool temperature and humidity in a child's room.
- Water. Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus. Juices and fruit drinks are used as an alternative to water.
- Physical activity. When moving, sputum is separated faster and in larger volumes.
The above recommendations reduce the likelihood of contracting pneumonia, strengthen your general condition and minimize the adverse effects of colds and inflammation.
Symptoms of congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients
At first, the disease develops without any characteristic signs. Chills, cough and fever, characteristic of focal and lobar forms, are absent. At the same time, the patient may complain of weakness, a feeling of incomplete inspiration and shortness of breath.
All this makes it extremely difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, since malaise in bedridden patients is not a rare deviation. Therefore, if the listed symptoms persist for a long time, the patient should undergo an X-ray examination (do), because often recognition of the disease occurs already at the stage of the appearance of sputum and wheezing in the lungs. Untimely attention to congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients leads to a long fight against it (from 5 to 7 months).
Treatment of pneumonia in bedridden patients with medications
In order to prevent the development of complications, treatment of congestive pneumonia should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician. Complication means the penetration of a bacterial infection. For the treatment of congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients, a specialist also prescribes procedures for pumping out accumulated water (in severe cases). Complex action drugs have a beneficial effect on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and diuretics accelerate the removal of fluid from the body.
Fluid that has accumulated in large quantities in the lungs is pumped out through a puncture made in the chest. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not cause pain, since the muscle layer between the ribs is very thin.
Relief occurs almost immediately - the patient begins to breathe deeply. If it is impossible to transport the patient to a medical facility, the puncture can be performed on an outpatient basis. Remember that when the disease is congestive pneumonia in bedridden patients, the treatment prognosis is favorable if you seek medical help in a timely manner (protracted forms are less responsive to treatment).
Measures to prevent pneumonia in bedridden patients
- To improve blood flow to the patient's lungs and reduce shortness of breath, he should be provided with a semi-sitting position. To do this, place several pillows at the head of the bed.
- In order to prevent pneumonia in bedridden patients, they can be given a therapeutic massage by lightly tapping the back and chest without affecting the heart area. It is carried out for 3 – 5 minutes several times a day. Massage is of great benefit to patients bedridden due to injuries, but it is contraindicated for patients suffering from angina pectoris and cardiovascular failure.
- To develop lungs, you can inflate children's balloons. Perform this action in the morning and evening, starting from 1 - 2 minutes and gradually reaching 5.
- Air from the lungs can also be blown out through a tube into a glass of water.
Treatment
Treatment of congestive pneumonia is complex and includes the following measures:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- breathing exercises and exercise therapy course;
- special food.
Breathing exercises for pneumonia
In most cases, treatment of such patients is carried out in a hospital setting; therapy with folk remedies at home is ineffective and can lead to the death of the patient.
Drug therapy includes taking the following drugs:
- antibiotics - they are prescribed exclusively on an individual basis, the dosage regimen and dosage are strictly prohibited from changing;
- diuretics;
- mucolytics;
- expectorants;
- antipyretics (if necessary);
- antiviral;
- vitamin and mineral complex;
- to improve the metabolism of the heart muscle and cardiac glycosides (for heart failure);
- immunomodulatory.
As for additional treatment methods, the patient may be prescribed the following:
- breathing exercises;
- back massage;
- oxygen therapy;
- exercise therapy exercises;
- inhalation.
In more complex cases and if conservative treatment methods are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe bronchoscopy or bronchoalveolar lavage.
Causes
The causes of congestive pneumonia lie in the difficult passage of blood in the pulmonary circulation. In addition to hemodynamic pathologies, impaired functionality of the lungs and bronchi is observed. With insufficient ventilation of the lungs, a large amount of thick sputum enters the bronchi, which is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. The causative agents of this disease are most often streptococci, pneumococcus, staphylococcus and other bacterial agents. Congestive pneumonia usually originates in the lower part of the right lung. Sometimes it can be bilateral, which makes its treatment much more difficult.