Bacterial vaginitis: symptoms and treatmentJava script is disabled in your browser, you need to enable it or you will not be able to get all the information on the article “Bacterial vaginitis and symptoms”. Category: Women's diseases
Bacterial vaginitis - main symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Swelling of the labia
- Itching in the vagina
- Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes
- Painful urination
- Pain during intercourse
- Redness of the genitals
- Vaginal discharge with a fishy odor
- Bleeding during intercourse
- Feeling of fullness in the pelvic area
- Feeling of heat in the pelvic area
Bacterial vaginitis (syn. bacterial colpitis) is an inflammatory disease that affects the organs of the female reproductive system, which occupies one of the leading places in gynecology. It is worth noting that pathology often develops during the period of pregnancy.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention and prognosis
The fundamental reason for the development of the infectious-inflammatory process is the penetration and reproduction of pathogenic agents into the vagina. In addition, hormonal imbalance and failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules are also among the predisposing factors.
In the clinical picture, such a sign as an increase in the volume and change in the consistency of vaginal discharge comes to the fore. Symptoms also include itching and burning in the genital area, frequent urge to urinate, and deterioration in general condition.
Establishing a correct diagnosis requires a wide range of laboratory tests, which are necessarily supplemented by a gynecological examination and instrumental procedures.
The treatment regimen for bacterial vaginitis, regardless of the etiological factor, is only conservative in nature - it consists of oral medication and local use of medicinal substances.
Description of the disease
Damage to the inner surface of the vagina by pathological flora or injury to it leads to the development of an inflammatory reaction - vaginitis, another name for colpitis. When the process is localized inside the vagina and in the area of the outer labia, vulvovaginitis is diagnosed. Damage to the clitoris and lips major and minor – vulvitis. Often, both forms of pathology are diagnosed at once.
Colpitis is a common diagnosis in gynecological practice. This is due to a large number of pathological microflora that affects the female organs.
ICD-10 code: acute vaginitis - N76.0 ; subacute and chronic vaginitis - N76.1 .
Normally, the internal environment of the vagina is not sterile. There are many beneficial lactobacilli on the mucous membrane. Their waste products increase acidity, as a result of which the bacteria that penetrate inside die. The number of these lactobacilli may decrease, reducing local immunity. This promotes the pathological growth of conditionally beneficial microorganisms and increases the risk of STIs.
It is characterized by pronounced edema, hyperemia and increased temperature in the localization of the lesion. Pinpoint hemorrhages and ulcerations may be observed on the mucous membrane. The type of discharge changes depending on the nature of the pathogen. The disease is accompanied by itching, pain, and burning.
It is diagnosed in women of any age, including girls of early childhood. Vaginitis is more often detected in sexually active women who have a large number of partners, and in women with reduced immunity. According to statistics, residents of large cities are more susceptible to colpitis. It is assumed that this is due to poor ecology.
The diagnosis is not life-threatening and is often easily treated. The STIs that led to its occurrence are dangerous. Some viruses are difficult to eliminate and lead to a number of dangerous complications. In severe cases, inflammation progresses to the chronic stage.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid getting vaginitis, you should adhere to the following principles:
- When having sexual intercourse with unfamiliar men, be sure to use a condom;
- use Miramistin after accidental intercourse with a new sexual partner;
- choose soft care products for intimate hygiene;
- systematically wash your face and change your underwear;
- change pads regularly during menstruation, at least every 4 hours;
- monitor hormonal balance during menopause;
- treat women's diseases, including ovarian diseases;
- give preference to natural fabrics when choosing underwear;
- do not abuse alcoholic drinks and sweets;
- provide a balanced diet.
According to a number of doctors, relapses of vaginitis occur in those women who constantly experience stress. With systematic stress, the immune system is weakened. Plus, when you are depressed, you often want to eat sweets, the abuse of which causes an imbalance in the vaginal environment. Glycogen is an excellent nutrient medium in which fungus develops.
Timely diagnosis and a competent approach to treatment will help you quickly get rid of the pathological condition and prevent relapses.
Reasons for development
Inflammation does not occur on its own. Often, nonspecific vaginitis occurs as a result of the penetration of viruses or bacteria. Allergic reactions, hormonal imbalance, dysbacteriosis, disruption of the glands, exacerbation of chronic pathologies can provoke and accelerate the process.
Common causes of infectious colpitis are as follows:
- failure to maintain intimate hygiene;
- washing too often;
- improper use of tampons, pads and other intimate hygiene products;
- use of vaginal preparations, spermicidal gels and other products;
- use of drugs that reduce immunity: antibiotics, corticosteroids;
- unprotected sex;
- unbalanced diet;
- disruption of the circulatory system;
- chronic vaginitis;
- other systemic pathologies.
Poor hygiene is one of the main factors in the spread of bacteria. Due to improper washing, bacteria from the anus enter the vagina. Common pathogens in such conditions are Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and mycoplasma.
Important! To avoid the spread of opportunistic gastrointestinal flora into the vagina, it is necessary to monitor personal hygiene. It is necessary to wash the external genitalia in the direction from the pubis to the anus.
Due to the use of certain medications, local immunity decreases. This leads to the death of beneficial microorganisms that protect against pathogenic flora. The result is an overgrowth of opportunistic bacteria and fungi. This leads to candidiasis, a common cause of diagnosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bacterial vaginitis
Like many infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, colpitis has specific and pronounced symptoms. The first manifestation indicating the occurrence of such a disease is profuse vaginal discharge, which can be:
- white or yellow;
- cream or transparent;
- mucous or purulent;
- thick or liquid;
- with blood impurities;
- with or without an unpleasant odor.
Sexual intercourse or showering can increase the amount of discharge.
Against the background of this symptom, the following symptoms of bacterial vaginitis develop:
- pain and bleeding that occurs during sexual intercourse;
- itching and pain in the vagina, intensifying during the process of urination;
- swelling of the labia;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- feeling of fullness and heat in the pelvic area;
- the appearance of a weak or pronounced smell of “rotten fish”;
- scratching the external genitalia, which leads to injury;
- an increase in the volume of lymph nodes located in the groin area.
Signs of bacterial colpitis in children are presented:
- copious purulent discharge that has a greenish tint and leaves behind crusts;
- redness of the external genitalia, as well as the skin in the area of the inner thighs;
- pain when urinating;
- false urge to defecate;
- an increase in the volume of regional lymph nodes.
In addition, this disease in women, adolescents and girls is often accompanied by general malaise and a slight increase in temperature.
Symptoms
Acute colpitis is a common reason for visiting a gynecologist. This is due to severe symptoms and manifestations that cause women discomfort. The main complaints with which people consult a doctor are the following:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- redness of the affected areas;
- change in the nature of cervical mucus: color, consistency, smell and quantity change;
- burning;
- discomfort caused by swelling of the mucous membrane;
- discomfort during sex;
- pain when urinating;
- menstrual irregularities.
Normally, vaginal discharge does not have a strong odor, is transparent or white, and is released in small quantities. With colpitis, their character and volume changes. Patients complain of an unpleasant odor and copious foamy green or yellow discharge. They can also detect bloody inclusions. Severe tissue irritation manifests itself as ulceration and contact bleeding.
Various rashes may form. For example, herpes manifests itself as a vesicular rash.
Many patients complain of menstrual irregularities. The volume of menstrual blood increases, periods are painful, with a significant deterioration in the general condition.
Painful urination indicates damage to external organs and involvement of the urethra in the process.
During sexual intercourse, the irritated epithelium is injured, causing pain and discomfort.
In some cases, there may be no complaints, which indicates a chronic course.
Methods for detecting the disease
Even one symptom is cause for concern. But more often than not, all the signs of pathology appear in combination. If you suspect a disease, you should make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible so that he can diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment.
Women come for examination with complaints of discomfort in the genitals, as well as pregnant women: upon registration, in each trimester and before delivery.
An important point is to differentiate vaginitis from other diseases.
To do this, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts laboratory tests, and analyses. The main study is microscopy of vaginal smears stained with Gram stain. The specialist identifies mobile microorganisms, takes into account their morphotypes, and looks to see if there are leukocytes.
To determine the cause of the pathology, the doctor may prescribe laboratory tests. With vaginitis, the smear contains:
- bacteroides;
- Klebsiella;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- gardnerella;
- fusobacteria.
For diagnosis, the acidity of vaginal discharge is sometimes determined. Normally the environment is acidic. When the pH is above 4.5, vaginosis is diagnosed.
An amine test is carried out. To do this, take a special substance - potassium hydroxide. It is mixed with vaginal secretions. If a fishy smell appears, then the woman suffers from vaginosis. The doctor prescribes general urine and blood tests to assess the presence of a secondary infection.
Additional tests for suspected vaginitis:
- cultural;
- serological;
- immunoenzyme;
- DNA diagnostics.
Course of the disease
Depending on the duration of vaginitis and the clinical picture, it is divided into three forms:
- acute – initial stage. The main difference is the pronounced symptoms. It manifests itself as abundant discharge, characteristic of the colonized microflora. Patients complain of pain, itching, burning. They are accompanied by deterioration of health, weakness, increased body temperature;
- subacute – transition from acute to chronic form. Often occurs at least 2 weeks after infection. At this stage, the bright symptoms fade away and there is no obvious clinical picture. The general condition and body temperature are normalized. The amount of mucus decreases, but the unpleasant odor and color remain. Unpleasant symptoms are preserved, but less pronounced;
- chronic – the most severe stage. Develops in the absence of proper treatment, reduced immunity or ineffective therapy. It is characterized by an undulating course: a long “silent” period followed by exacerbation. This form is more often complicated than others by the involvement of other organs and persistent dysfunction of the affected tissues.
Important! Many girls learn about the presence of the disease during an examination with a gynecologist. This is due to the absence of specific symptoms. To prevent them, you should visit your doctor regularly.
Disease prevention measures
It is important for a woman to exclude factors that provoke the proliferation of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora on the vaginal mucosa. For specific bacterial vaginitis, the only preventative measure is protected sex with one partner.
For a non-specific form there are more rules.
- know about chronic diseases and treat them on time;
- exclude self-medication;
- do not douche;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- wear underwear made of cotton fabric;
- do not overuse sanitary pads;
- exclude casual intimate relationships;
- give up IUDs and oral contraceptives.
Statistics show that most cases of bacterial vaginitis occur in intimate areas, but other options cannot be excluded. It is impossible to foresee everything, but the rules listed above can reduce the risk of disease.
Popular articles:
|
Classification according to the nature of inflammation
Depending on the pathogen, the body’s reaction to it and clinical manifestations, the diagnosis is classified according to the nature of the inflammation. The following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Infectious - the impact of pathogenic microorganisms irritate tissues, and their waste products contribute to the development of a local reaction, which is accompanied by the separation of purulent mucus. Often the cervical canal and uterine cavity are involved in the process. When carrying out etiotropic therapy, symptoms decrease until complete recovery. According to the ICD-10 classification, this type of disease also includes bacterial and fungal vaginitis.
- Allergic - an allergen that gets on the epithelium triggers an immune response. This is accompanied by a local reaction. Liquid, transparent, odorless discharge may appear.
- Candida – occurs due to excessive growth of the Candida fungus and a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria. It manifests itself as a white or yellowish cheesy coating, itching and burning.
- Vaginitis in pregnant women - due to hormonal changes, they are susceptible to the growth of pathogens. The flora may spread into the amniotic fluid.
- Atrophic – a consequence of age-related changes and endocrine disorders. It affects women of elderly and senile age, after menopause, when involution of the mucous surface occurs (postmenopausal). It is also diagnosed in young patients with ovarian diseases and endocrine pathologies.
Bacterial vaginitis is a pathological condition of the mucous membranes of the vagina of a non-inflammatory nature, resulting from a change in the composition of its normal microflora, namely an excessive concentration of anaerobic opportunistic microorganisms and a significant decrease in the number of lactic acid bacteria.
1. Symptoms 2. Causes 3. Treatment 4. During pregnancy
Symptoms
The symptoms of bacterial vaginitis vary greatly depending on the reason for which this type of disorder occurred.
- Abnormal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Redness and swelling of the vaginal mucosa.
- An abundance of white discharge, and sometimes even mixed with blood.
- Feeling of pain in the lower abdomen.
- Burning sensation when urinating.
- Itching occurs inside the vagina and on the external genitalia.
- Experiencing discomfort during sexual intercourse and decreased libido.
However, it should be noted that some women may not experience symptoms of bacterial vaginitis at all. And in such cases, they are discovered purely by chance during preventive examinations by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
In case of abnormal vaginal discharge, characterized by an unusual color, unpleasant odor, irritating effect on the skin, including those characterized by abundance, you should consult a doctor. After all, vaginitis symptoms, manifested by itching sensations, can occur at any time of the day, even at night. In addition, it can negatively affect your intimate personal life.
Moreover, vaginitis symptoms often spread to the skin of the buttocks and thighs. Itching, burning, and purulent discharge occur. And in older people, dryness of the vaginal mucosa is observed due to age-related changes occurring in the body.
How is candidiasis colpitis treated?
Bartholinitis is acute here
Causes of atrophic colpitis /bolezni/kolpit/atroficheskij-kolpit.html
Causes
The causes of bacterial vaginitis can be very diverse. There are quite a large number of them. This may be taking antibacterial drugs. Many people know that taking antibiotics greatly harms the body and leads to intestinal dysbiosis, but few know that taking them can also lead to vaginal dysbiosis.
Colpitis can also be caused by hormonal imbalances. In most cases, this occurs as a result of disruption of the endocrine system and the use of incorrectly selected contraceptives. Diabetes mellitus can also cause bacterial vaginitis. If there is a malfunction of the immune system, this can lead to the development of colpitis. Great attention should be paid to women's health if the structure of the genital organs is disturbed. Colpitis can also develop in the presence of various blood diseases.
Treatment
The variety of manifestations of bacterial vaginitis explains the lack of standard treatment regimens. The decision on the need to prescribe medications is made by the gynecologist.
Since the disease is based on two main triggers - a violation of the vaginal biocenosis and, as a consequence, the proliferation of unwanted flora - any treatment regimen should be aimed at eliminating them. When choosing a treatment method, the presence of concomitant diseases of a hormonal, neuroendocrine or inflammatory nature is taken into account. If necessary, the treatment plan includes measures to correct these conditions.
Treatment of bacterial vaginitis includes two main stages and depends on how pronounced the clinical picture is:
- Elimination of opportunistic flora using antibacterial therapy
- Restoration of vaginal biocenosis
Antibacterial agents are selected by the attending physician. They are used in the form of suppositories, gels, ointments, tablets and solutions. In the presence of chronic inflammation or a bright clinic, antibiotics can be used. Antibacterial agents are prescribed after studying the sensitivity of the vaginal microflora to them. Antibiotics should be avoided during pregnancy.
The most popular drugs in the treatment of bacterial vaginitis are Metronidazole and its derivatives, Ofor, Fluomizin. Vaginal suppositories and gels (Metronidazole, Neomycin, Clindamycin, Hexicon, etc.) are used both as monotherapy and in combination with other drugs. For irrigation of the mucous membrane, solutions of lactic and boric acids, Chlorhexidine, etc. are used. At the next stage of therapy, the necessary conditions are created to restore the normal number of lactic acid bacteria in the vaginal environment with the help of eubiotics, probiotics with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Femilex suppositories containing lactic acid help restore the pH of the vagina.
The effectiveness of the treatment is assessed after 6-10 days. The criterion for cure is the restoration of the normal ratio of microorganisms in the vaginal environment, confirmed by the results of laboratory research.
Therapy for bacterial vaginitis in pregnant women has its own characteristics. In the first trimester, antibiotic therapy is contraindicated. Exclusively local remedies are used.
Systemic drugs are prescribed in the second trimester of pregnancy in parallel with local therapy. The choice of medication is made only by a gynecologist. The second stage of therapy is similar to that in non-pregnant patients.
A large number of antibacterial drugs with different spectrums of action can cause an incorrect independent choice of treatment method, which is the danger of self-medication of bacterial vaginitis.
There are no specific methods for preventing bacterial vaginitis. Currently, these are considered to be proper personal hygiene, the absence of promiscuity, normalization of the gastrointestinal tract, and the elimination of hormonal and immune changes in the body.
Restoring the normal biocenosis of the vaginal environment is the key to women's health and a favorable pregnancy outcome. An annual visit to the gynecologist will help maintain women's health.
Bacterial vaginitis is not a sexually transmitted disease and is not transmitted sexually.
During pregnancy
Bacterial vaginitis during pregnancy is very insidious and is fraught with many pitfalls. In a smear of vaginal discharge, pathogenic microorganisms may be detected that exceed the permissible level, but at the same time, the woman may not present absolutely any complaints characteristic of vaginosis. Recently, it has been generally accepted that it is not worth treating such women, but simply observing the dynamics of development. It is likely that the vaginal microecosystem will restore itself with the help of pregnancy hormones without medical intervention. But such women are temporarily at increased risk due to possible premature rupture of the membranes. They should visit their gynecologist more often and have a home kit for quickly diagnosing amniotic fluid leakage.
The second category of women is with heavy vaginal discharge. The most difficult in terms of diagnosis. Primarily because during pregnancy, physiological secretions increase, which can cause unreasonable anxiety and treatment. If there is excessive leucorrhoea during pregnancy, a differential diagnosis should be made between bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and leakage of amniotic fluid. Since leakage in the vast majority of cases is the result of bacterial vaginosis, women at risk should have a test system at home to monitor the integrity of the membranes in order to exclude this pathology first - as the most dangerous. The only home system recommended by the European Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists today is the Amnishur test. Its accuracy is 99.8% and surpasses many laboratory diagnostic methods.
Tweet
Pin It
Diagnostics
The doctor can see the first signs of damage during a gynecological examination and based on the patient’s complaints. After identifying a pathological reaction, it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological study of smears and perform tests. Material is collected during the inspection. Afterwards, the type of flora and sensitivity to antibiotics are determined within a few days.
If it is not possible to determine the infection using the bacteriological method, the blood is examined for the presence of specific antibodies and viral DNA particles.
Diagnosis of allergic vaginitis is carried out after identifying the allergen.
Atrophic, and colpitis in pregnant women, requires a study of hormonal levels and determination of the amount of female hormones in the blood.
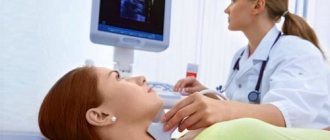
Ultrasound is used to determine signs of inflammation in the uterine body and identify neoplasms.
How is the diagnosis made?
A gynecologist can tell that a woman is sick with vaginitis or colpitis only on the basis of an examination. But since a large number of pathogens can provoke the disease, they need to be identified in order to prescribe the correct treatment. To do this, before taking antibiotics (local or systemic), the doctor prescribes the following studies:
- Bacteriological culture of vaginal discharge: allows you to isolate most microbes - both nonspecific and specific. During the study, it is also possible to determine which antibiotics the causative bacterium is sensitive to;
- PCR study. It allows you to isolate some microorganisms that are not detected by culture. These are chlamydia, urea and mycoplasma. The PCR method can determine all microorganisms, but this is usually not done due to the high cost of such a complete study.
The doctor will also prescribe an ultrasound of the genital organs to exclude further spread of infection to the uterus and tubes.
Treatment
After diagnosis, the doctor determines what to do next, how to treat the disease, what medications and suppositories to use. He is the one who draws up the treatment plan. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the main symptoms and normalize the microflora. The following stages of treatment are distinguished:
- Etiotropic - after a bacteriological examination, the patient is prescribed medications that are effective against the identified microorganisms. Depending on the course of the disease, they can be of general or local action. They use various groups of antibiotics, tablets, antifungals, suppositories, antiseptics and antiviral drugs. It is important to complete the full course of medication without interrupting it.
- Symptomatic – reduces clinical manifestations. For this purpose, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and antihistamines are prescribed to relieve itching, swelling and hyperemia. They act locally, thanks to which the desired result is achieved faster.
- Restorative therapy is aimed at restoring the mucous membrane and microflora of the vagina. For this purpose, regenerative substances are prescribed, often for local use, and lactobacilli.
- Replacement therapy - if the disease occurs due to hormonal imbalance, the woman is prescribed estrogens.
Physiological therapeutic methods are also used. Patients are prescribed various procedures: douching, magnetic therapy and others. They promote faster recovery and shorten the rehabilitation period.
Treatment of bacterial vaginitis
As mentioned above, at the first symptoms of vaginitis, a woman should seek medical help from a gynecologist as soon as possible. The medication regimen will not be considered within the framework of this article - it must be prescribed by a doctor, and self-medication in this situation is unacceptable. However, below we will talk about some traditional medicine recipes that can be an excellent addition to the main treatment prescribed by a doctor, as well as the basic principles of successful treatment of bacterial vaginitis.
- Treatment of both sexual partners
As already mentioned, bacterial vaginitis is a typical female disease. But, in no case should we lose sight of the fact that a man is a carrier of this disease. That is why, if a woman notices one or more symptoms of vaginitis, both partners should see a doctor: the man – a urologist or venereologist. And treatment is also necessary for both sexual partners - otherwise the woman, immediately after recovery, may be re-infected.
- Restrictions for the period of treatment
Doctors strongly recommend that sick people completely abstain from sexual intercourse during treatment in order to avoid permanent infection of each other. As a last resort, if there is no possibility or desire to refuse sexual intercourse, it is imperative to protect yourself with a condom. Otherwise, the entire effect of the treatment will be reduced to zero. The treatment does not last that long - about 10 - 14 days, so it is still worth giving up sex life. And, in addition, for the entire period of treatment, the sick person must completely stop drinking even low-alcohol drinks. And this restriction is introduced for a reason - those drugs that are most often used to treat bacterial vaginitis, in combination with alcoholic beverages, can become a severe blow to a woman’s body and lead to the occurrence of pathological irreversible processes.
Another very important stage in the treatment of bacterial vaginitis is the correction of all kinds of disorders of the female body’s immune system, as well as the treatment of all concomitant diseases that the woman has. If necessary, the gynecologist should refer the woman for a consultation with specialists and an immunologist.
Vaginitis during pregnancy
Hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy are a favorable background for colpitis. If microorganisms are detected, it is important to undergo etiotropic therapy due to the risk of infection of the fetus. This is especially dangerous in the first trimester. This can cause defects and serious condition of the newborn. A child may be born prematurely with various congenital defects. In severe cases, miscarriage and stillbirth may occur.
In the third trimester, the baby may be contaminated with pathogens during its passage through the birth canal. Less commonly, bacteria penetrate through the hematoplacental barrier and cause intrauterine damage to the child. A newborn is born weakened, with birth defects.
Important! Many medications are contraindicated during this period, which makes it difficult to determine how to treat the patient. But eliminating the pathological process during this period is extremely important.
A chronic course can lead to the spread of pathology to the cervix and blockage of the cervix. Because of this, problems arise with conceiving a child. Adhesions, which can form over a long period of time, complicate labor and lead to injuries and ruptures.
These are the most dangerous complications. Despite the fact that they are rare and often pregnancy with vaginitis proceeds normally, such pregnant women need careful medical monitoring for timely relief of dangerous conditions.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is necessary to carefully monitor your health, and if even minor symptoms appear, you should immediately undergo a diagnostic examination, especially since it never hurts to see a doctor once again.
To identify the causes, forms and varieties of the disease, the doctor must carry out several diagnostic measures.
- Visual examination of the external and internal genital organs. It will allow you to determine their condition, suggest the presence and cause of the disease. During the examination, the doctor will definitely take a smear for laboratory testing. And only after receiving its results, it is possible to accurately determine the forms and varieties of the disease.
- In case of frequently recurring manifestations of symptoms or if it is impossible to determine the cause of the disease with a simple examination and examination of a smear, the doctor may prescribe a more in-depth bacteriological examination , sending a smear for culture and cultivation of bacteria. This is necessary for a more detailed consideration of the analysis and establishment of an accurate diagnosis.
- In order to exclude more serious diseases, for example, a cancerous tumor, the doctor must take a scraping of cells from the mucous membrane of the cervix and send it for cytological examination.
- An ultrasound of the pelvic organs may also be prescribed to exclude complications in other areas of the genitourinary system.
When all the necessary parameters are established, and aspects that do not need to be paid attention to are excluded, the doctor will prescribe the necessary and rational treatment.