Mother's milk is created by nature for feeding babies. It has a unique composition, it contains many useful substances that are very important for the growth and development of the child. However, in some cases it is necessary to either limit or completely stop breastfeeding. Lactase deficiency is a diagnosis that excludes the possibility of breastfeeding newborns. Today, pediatricians are passing a similar verdict on more and more children. But is it always justified? After all, this pathology was previously considered quite rare. And its symptoms are similar to the manifestations of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in infants. So what's the difference?
- 2 Video “What is lactase deficiency” - Komarovsky
- 3 Forms
- 4 Reasons
- 5 Symptoms and signs
- 6 Diagnosis of lactase deficiency in newborns
- 7 Treatment options
7.1 Photo gallery of baby formulas
Definition of disease
First, let’s clarify and define the concepts of “lactose” and “lactase”. This is important for understanding the essence and specifics of the disease.
Lactose is called milk sugar. Since a newborn has a special need for it - lactose is vital for the active growth and development of the child - mother's milk contains a lot of it.
Lactose promotes:
- replenishment of energy costs;
- improvement of the brain and central nervous system of the newborn;
- activating the body’s absorption of crumbs of calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc;
- normalization of the functioning of the digestive organs.
After lactose enters the baby’s stomach, it is broken down into simple monosaccharides - glucose and galactose, which are absorbed by the child’s body.
Lactase is an enzyme that helps break down lactose into simple monosaccharides: sucrose and galactose.
The breakdown of lactose occurs with the participation of a special enzyme - lactase. It is actively produced in newborns, since infants feed only on milk, which, accordingly, must be digested normally.
That is why lactase activity is very high up to one year, and then gradually decreases as the amount of breast milk consumed by the child decreases and “adult” food is introduced into his diet.
As a rule, the baby's body produces enough lactase so that the lactose supplied with mother's milk can be broken down and absorbed.
But sometimes the enzyme is not produced in sufficient quantities. Then unprocessed lactose enters the intestines, which leads to the appearance of signs of lactose intolerance.
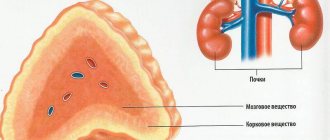
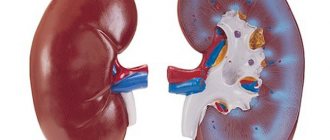
Lactase deficiency refers to a condition in a child’s body when his digestive system is unable to break down and absorb lactose due to too little production of the lactase enzyme. Often this pathology occurs in premature babies. It can also be a consequence of other diseases, such as gastroenteritis, celiac disease, ascariasis, etc.
Treatment
LN therapy has its own characteristics depending on the age of the child. The basic principles are based on the correct organization of breastfeeding, diet selection, optimization of lactose breakdown and prevention of complications.
How to treat lactose intolerance in infants? To maintain breastfeeding, infants are prescribed lactase replacement therapy.
As an example, drugs for lactose deficiency in infants: Lactazar, Baby Doc or Lactase baby. As a rule, the course of treatment lasts up to 3-4 months of the baby’s life and is canceled when his intestines begin to independently produce lactase. These drugs are safe and effective, have proven themselves and are in demand. When purchasing these drugs, you must be very careful due to the increasing incidence of counterfeiting.
To facilitate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and improve the functioning of the pancreas, the following drugs can be prescribed: Creon, Mezim or Pancreatin.
Probiotics will help stabilize the intestinal microflora and normalize peristalsis. It is very important that these preparations do not contain lactose.
To eliminate acute symptoms of FN, manifested by disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea, colic, etc., antispasmodics and remedies for diarrhea and bloating are prescribed.
Forms
There are three forms of the disease.
- Hereditary. In infants it is a congenital pathology. Symptoms of hereditary lactase deficiency appear almost immediately after the birth of a child and in severe form. In this case, lactose is detected in the urine. If you eliminate lactose from your diet, the symptoms will completely disappear.
- Secondary. It is very common and can appear at any age, including the newborn period. The disease occurs as a result of intestinal diseases (gastroenteritis, colitis, etc.) or after operations, for example, for stomach ulcers.
- Primary. Mostly occurs in those who are predisposed to a gradual decrease in the amount of lactase production as they age.
If we are talking about congenital lactase deficiency, when the child’s body does not produce lactase at all, then such cases are very rare. There are no more than five hundred precedents worldwide. More often, lactose intolerance is caused by some other disorders in the child’s body.
Forecasts
With primary congenital LI, you will have to follow a diet and undergo enzyme replacement therapy all your life. Transient LI in premature infants usually resolves after the third month of life. Secondary LN is eliminated as the underlying disease is cured and lactase synthesis is restored.
A child with lactase deficiency is seen by a pediatrician and pediatric gastroenterologist. The effectiveness of treatment can be judged by the elimination of gastrointestinal problems, weight gain in accordance with age norms, reduction of carbohydrates in feces and normal physical development.
Causes
In babies born prematurely, the enzyme system is not fully matured to break down all the lactose that comes with mother's milk. The active production of lactase in children is very often reduced due to treatment with antibiotics, feeding with inappropriate milk formulas, and also due to intestinal infections, especially viral ones. In addition, signs of lactase deficiency may appear due to improper feeding.
These are all causes of secondary, acquired lactase deficiency, which is temporary and goes away after the main problem disappears. And most often this form of the disease occurs in children.
Lactase deficiency in newborns can develop:
- If the baby was born ahead of schedule. In such a situation, the enzyme simply has not yet begun to be produced, because the process of its formation begins only at the 24th week of pregnancy. In a premature baby, lactase deficiency is detected from the first days.
- If the baby has a history of a genetic predisposition to the disease.
- If there has been the development of another pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. It is worth noting that the disease can occur due to allergies, infection in the intestines, enterocolitis or helminthic infestations.
- If the feeding regimen was not followed. In such a situation, dysbacteriosis develops, and it becomes a provocateur for disruption of lactase production.
Very often, the causes of the disease remain unknown, so doctors prescribe preventive treatment to make the baby’s life as easy as possible.
Apart from primary, all other types of lactase deficiency do not pose a mortal danger. But the disease can lead to digestive problems in the child and the development of associated pathologies.
It is important to know how the disease manifests itself in order to identify it as quickly as possible and begin treatment.
Symptoms
Since a lack of lactase causes lactose intolerance, its symptoms appear when consuming foods containing milk sugar. Whole milk is the main source of lactose, and it is its consumption that causes indigestion in people with LI.
How does lactase deficiency manifest in a baby, and what symptoms signal a threat to the health and life of the baby? Let's talk about this in more detail.
Symptoms of lactase deficiency are as follows:
- frequent, loose and foamy stools with a characteristic sour odor;
- less often - constipation;
- frequent regurgitation;
- flatulence, bloating;
- constant rumbling in the intestines, colic;
- tearfulness, increased excitability.
Alarming symptoms:
- vomiting after feeding;
- significant lack of weight according to the norms or severe weight loss;
- baby's refusal to eat;
- dehydration;
- lethargy or excessive restlessness.
The more lactose enters the body, the more severe the symptoms of LF appear.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner, then against their background the baby may develop:
- Dysbacteriosis – due to changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora.
- Changes in the central nervous system caused by endogenous intoxication and deficiency of minerals and vitamins. Possible manifestations include convulsions, sleep disturbances, delayed psychomotor development, muscle hypotonia, attention deficit disorder, hyperactivity and vitamin D deficiency rickets.
Symptoms and signs
Clinical symptoms of lactase deficiency are manifested in lactose intolerance and characteristic symptoms, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
In newborns the disease is characterized by:
- foamy, loose stools or, conversely, lack of independent bowel movements;
- bloating, flatulence;
- increased colic;
- regurgitation;
- weight loss (or the child may not gain weight);
- symptoms of dehydration;
- atopic dermatitis.
There is no relationship between the severity of symptoms and the level of lactase production. But in some patients there is a clear direct dependence of symptoms on the dosage of lactose.
Signs
Regardless of the cause of the disease, its symptoms are usually the same.
Stomach upset. The baby walks “big” much more often. The stool is liquid, foamy, and has a sour smell.
Weight loss. Is your child gaining weight poorly, or maybe losing it? In this case, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Colic. Immediately after eating, the baby begins to cry and does not calm down for a long time. Even the most proven remedies do not help. The easiest way to identify the disease is to take a stool test and determine the amount of carbohydrates in it. For newborns this value should be below 0.25%.
Diagnosis of lactase deficiency in newborns
Several tests are performed to confirm lactase deficiency. But, unfortunately, among them there is no one who could guarantee the correctness of the diagnosis and at the same time not cause harm to the child.
The following analyzes are carried out:
- stool is checked for carbohydrate levels and its acidity is determined;
- the hydrogen content in the exhaled air is checked after a lactose load (such an analysis is not carried out for children under three months);
- lactose content in urine is determined;
- Enzyme activity is checked using a small fragment of the small intestinal mucosa (it is taken using a biopsy);
- A biochemical analysis of the intestinal microflora is also performed.
In addition, additional measures are taken to establish the underlying cause if the disease reoccurs, for example, allergies, celiac disease, etc.
Diagnostics
If LN is suspected, a number of examinations are carried out.
Dietary diagnostics
Breast milk and infant formulas are completely excluded from the baby’s diet and replaced with low-lactose or lactose-free formulas. When symptoms of FN disappear, the diagnosis is confirmed.
The advantages of this method include its accessibility, and the disadvantages are the difficulties of switching to a new diet.
Analysis of stool for sugar content and acidity
A pH shifted towards acidity (below 5.5) may indicate lactase deficiency. Carbohydrates in the stool (above 0.25%) can confirm the diagnosis.
The disadvantage of this type of diagnosis is that unformed microflora and intestinal dysfunction can give a false positive result.
Exhalation hydrogen test
When lactulose ferments in the large intestine, hydrogen is released, which is then absorbed into the blood and removed from the body with exhaled air. An increased concentration of hydrogen during exhalation indicates excess lactulose as a consequence of lactase deficiency.
Lactose loading study
It is practically not carried out in infants, since certain conditions must be met to perform the study. Taking into account the possible incomplete digestion of lactose in infants, this method can only indicate functional LN.
Blood glucose testing is carried out on an empty stomach; you should not eat for 10 hours before the test. After the first sampling, the patient is given a lactose solution to drink, and two hours later another sample is taken. In the intestines, lactose is broken down into glucose, which is absorbed into the blood. Normally, the blood sugar level should double (compared to the first sample taken on an empty stomach). With hypolactasia, lactose is not broken down and glucose levels do not change or increase slightly.
Small bowel biopsy
This diagnostic method gives the most reliable results, but the invasiveness of the method and its complexity limit its use in pediatrics. It is used mainly in cases of suspected congenital LI.
Treatment options
Increasing lactase production with manifestations of congenital deficiency due to drugs is possible only for children born much prematurely.
If secondary lactase deficiency occurs, then medications that contain bacteria that produce lactase should be used. You can use enzyme preparations by adding them to the formula or to some expressed milk, and give them to the baby before feedings.
In mild cases, the baby is switched to eating lactic acid products, such as yogurt, kefir, acidophilus and others containing fructose.
In more severe forms of the disease, it is necessary to completely exclude milk from the child’s diet. Then low-lactose mixtures containing buckwheat and rice flour, malt extract, almond or soy milk, and immobilized enzyme preparations are prescribed.
In addition, studies have shown that some representatives of normal intestinal microflora (for example, lacto- or bifidobacteria) are able to break down lactose and promote its absorption by the body. This means that probiotics can also be used to treat lactase deficiency.
Photo gallery of baby formulas
Belakt mixture with buckwheat flour
“Baby” mixture with rice flour
Hypoallergenic mixture "Nutramigen"
“NESTOGEN” low-lactose mixture
Alfare mix from Nestle
Infant formula “Friso” Low-lactose formula “Bellakt”
Nutrilon mixture with soy content
When choosing a formula, you should definitely consult with a specialist who will select a mixture with the necessary set of ingredients specifically for your child.
What are the possible consequences of the disease?
In the absence of specific treatment for fermentopathy, lactase deficiency can lead to the development of the following disorders:
- weakened immunity;
- dehydration of the body as a result of massive loss of fluid due to incessant diarrhea;
- development of dysbacteriosis;
- creating favorable conditions in the intestines for the growth of putrefactive microflora;
- reduction in the intensity of absorption of minerals, primarily calcium;
- violation of peristalsis.
During the neonatal period and up to 1 year, the most dangerous complication of the development of this type of fermentopathy is the threat of dehydration (dehydration) of the child’s body.
Recommendations for parents
In most developed countries, pediatricians do not diagnose lactase deficiency if the child is gaining weight normally and has no signs of dehydration. In such a situation, the reason for bowel dysfunction in infants is most likely that breastfeeding is not properly organized.
In the gastrointestinal tract of infants, low-fat milk (foremilk) is broken down and absorbed less well than fatty and nutritious hind milk. If a child constantly receives only the front portion of milk, which serves mainly as a drink, then disturbances in the processes of digestion and bowel movements begin.
Neonatologists and breastfeeding specialists unanimously claim that in almost all cases when a child has symptoms of lactase deficiency, his condition can be improved in a few days only by adjusting the diet and feeding regimen.