Why do they arise?
The main cause of papillomas is the human papillomavirus. Infection with it occurs unnoticed and more often than not people do not suspect that they are carriers of the infection.
According to the latest data, HPV of various types is present in the body of a third of the world's population, with the exception of infants and the elderly (according to other sources, every 9 out of 10 people are infected with HPV).
Activation of the virus and, accordingly, the growth of papillomas and the development of other diseases occurs in the following cases:
- With a significant weakening of the immune system.
- Under the influence of harmful factors, which include smoking, alcohol abuse, and taking certain medications.
- Exacerbations of gastrointestinal diseases, influenza.
- With long-term use of oral contraceptives.
- It has been noticed that most papillomas on the body occur in people who lead a promiscuous sex life.
Risk factors for papillomavirus infection ↑
- Sexual behavior: frequent change of partners, unprotected sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraception.
- Presence of partners who are carriers of HPV infection.
- Internal factors: decreased immunity due to illness, pregnancy, vitamin deficiency.
- Concomitant sexually transmitted diseases: herpes, thrush, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc.
- Bad habits: taking drugs, drinking alcohol, smoking, etc.
- Imbalance of vaginal microflora.
- Visiting places with high air humidity: swimming pools, baths, beaches, etc.
Prevention of infection is the observance of a number of recommendations by people
Thus, you need to be careful with scratches and cuts - “gateways” for infection, and picky in sexual relations. And most importantly, since the infection can recur repeatedly against the background of reduced immunity, it is necessary to monitor its maintenance, protecting yourself and your loved ones from stressful situations and illnesses.
Human papilloma: types - simple, plantar, flat, filiform, pointed
After introduction into the body and activation, the human papillomavirus leads to changes in the skin and mucous membranes, but not only that. A number of diseases dangerous to human health may appear. This will depend mainly on the type of HPV present in the body.
As you already know, papillomas are caused by several types of viruses, and doctors can guess from the location and external features of skin growths what type of HPV they are dealing with.
Simple. They have several names - vulgar or ordinary. They appear on the body when several types of HPV are introduced and develop in the body. More often these are 26-29, 41, 63, 77 (digital designation of varieties of human papillomaviruses is used - author's note).
Vulgar papillomas are often classified as benign formations. The process of its formation begins with a slight burning and tingling sensation in the affected area of the body, then, at this place, you can notice the growth of a spherical tumor.
After some time, the surface of this uneven formation becomes rough. The color changes from flesh-colored to darker. The growth of a simple papilloma starts from 1 mm and in rare cases reaches a centimeter in diameter.
Most often, such papillomas are localized in adults on the fingers, the spaces between them and on the back of the hand. Vulgar papillomas are often found in children, and a common localization of neoplasms is the knee area, which is associated with the fact that a small child moves crawling on all fours when playing and becomes infected through the slightest cracks in the skin.
Ordinary papillomas can be single or multiple. With multiple growths, daughter formations are formed near the maternal focus.
Plantar. When people are infected with HPV types 1, 2 and 4, papillomas may appear on the soles of their feet. These formations are easily confused with calluses, but plantar papilloma has a number of signs:
- The formation has all the external characteristics of vulgar papilloma.
- Pain appears, intensifying when the papilloma is compressed by tight shoes or pressure when walking.
- There is no skin pattern on the affected area. On calluses, the skin pattern is preserved, the callous surface is quite smooth.
Papillomas on the sole can collapse on their own, which is often observed in young children. Often small bubbles form around the first lump, which over time transform into papillomas (mosaic papillomatosis - the medical term).
Flat. This type of growth has a characteristic feature - they protrude 2 mm above the skin. Flat papillomas are round in shape, often elongated, oval. Typical places of growth are the face, the area near the lips, the upper chest, and the external genitalia. In girls and women, they are often diagnosed in the cervix.
Nearby flat papillomas can merge with each other and then they become very visible on the body. The color of these formations rarely differs from the rest of the skin tone or may be slightly darker.
Thread-like. Papillomas that grow on a thin stalk and have an elongated, elongated shape are referred to in medicine as filamentous or acrochords. They are caused by HPV types 7 and 2. At the beginning of the growth of this formation, you can notice a small bump on the skin, which gradually stretches out and hangs down.
Acrochords predominantly grow in people after 40 years of age, regardless of their gender. Most often they are located on the upper eyelids, neck, under the arms and mammary glands, in the groin area. Thread-like formations are prone to injury, since the thin leg can easily be caught by clothing or careless movements.
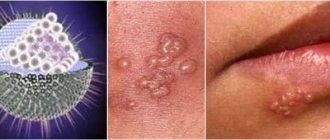
Pointed. Pointed papillomas or condylomas are papillary formations, they are located both individually and in whole groups. As they grow, they merge with each other and during this period their surface visually resembles a cockscomb, the color of the formations ranges from flesh-colored to bright pink.
Genital warts are caused only by types of HPV that are sexually transmitted. That is why these papillomas are found on the genitals, in the anus, in the perineum and groin. In men, condylomas often affect the penis or grow inside the urethra. In women, papillary formations involve the vagina and cervix.
Condylomas acuminata grow very quickly, merging and extensive encroachment of healthy tissue is sometimes observed within a few days. This type of skin formation is prone to relapses after treatment. Often, tests can also reveal concomitant infections - mycoplasmosis, chlamydia.
Features of papillomas on the sole
Three types of viruses can provoke the development of HPV on the sole. These will be No. 1, 2, 4. After the infection has entered the body, the incubation period lasts for several months. First, a small growth will form, which will be surrounded by a rim.
Later, the same formations may appear side by side, but slightly smaller in size. They will resemble bubbles. In this case, mosaic damage to the epithelium is diagnosed, which is provoked by a certain virus.
Especially formations on the sole:
- their appearance provokes pain;
- discomfort appears when walking;
- When wounds form, ulcers may develop.
When such papillomas appear in children, they very often go away on their own. Their structure is similar to calluses, but upon closer examination, differences can be found.
The appearance of flat neoplasms is promoted by types No. 3 and 10. They will have a pink or yellow tint. They are similar in shape to a circle, but sometimes they are found with many angles. When they form, the following may be observed:
- pain;
- itching;
- redness and increased temperature in the damaged area of the skin.
It is necessary to prevent infection from entering through the resulting tumor.
HPV: types of papillomas - squamous and inverted
Here in the video, you can find out the features of oncogenic types of papillomavirus and their treatment:
HPV types are usually divided according to the risk of possible oncogenic lesions of the skin and internal organs. Highlight:
- HPV with a high cancer risk are types 16, 18, 45, 36.
- HPV with an average degree of cancer risk – 31, 35, 33, 58. 51, 52.
- HPV with a low degree of oncological risk (non-oncogenic) – 11, 44, 43, 42, 6.
Non-oncogenic types of the virus most often cause benign growths - papillomas on the skin.
Squamous . This kind of papilloma occurs as a result of the proliferation of squamous epithelium of the skin. It is most often formed in older people and is characterized by slow growth. In younger people, it can form in areas of the body that are subject to constant trauma.
Squamous cell papillomas are both formations on a thin stalk and tumors that have a wide base and a rounded shape. At the beginning of its growth, the papilloma is mobile, its color is whitish, flesh-colored or dark brown, and its size can reach one and a half to two centimeters.
With constant injury, it can become inflamed, as a result of which the cells mutate and can degenerate into cancer and a squamous cell type of cancer occurs.
Inverted . This papilloma (transitional cell) is detected relatively rarely, and has its own characteristics of occurrence and development, these include:
- Specific localization - this type of papillomas affects only the nose and its paranasal sinuses. The formation often grows in the maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, and ethmoidal labyrinth.
- The lesion is unilateral, that is, the papilloma grows on one side of the nose, but it can be either single or multiple.
- Germination of papilloma into bone structures, which leads to destruction of the walls of the orbit, palate, sinuses, and skull bones.
- Relapse of the disease 5-10 years after effective treatment.
Inverted papilloma leads to severe nasal congestion, the appearance of bloody discharge or nosebleeds.
If the tumor reaches a significant size, then the deformation of the facial skeleton and the displacement on the affected side of the eyeball are visually determined. In 5% of cases, the long-term course of the disease in the absence of adequate therapy leads to the degeneration of papilloma into a cancerous growth.
What you need to know about HPV
Photo of papilloma on the body
Are papillomas dangerous? To a certain extent, yes. The level of danger depends on a number of constituent factors. Regarding some situations, we can say for sure that the virus is dangerous. In others, there is no threat from HPV.
To determine the danger of papillomas, we first advise you to understand what papilloma is and what the characteristics of the virus are.
- In most cases of sexually transmitted infections, what problems are found? That's right, HPV. Human papillomavirus accounts for about 80% of all cases.
- Papilloma poses minimal danger during primary infections at a young age. The body is quite strong and continues to develop. Therefore, in approximately 75% of cases, after 1-2 years, warts resolve on their own. The older the person infected with the virus, the less likely it is to resolve on its own.
- Getting infected with HPV and having it are not the same thing. The virus can “sleep” in the body for many years without making itself felt. The disease involves the appearance of warts themselves on the body.
- What are papilloma and why are they dangerous? Many will say that there is a possibility of degeneration into cancerous tumors. But in fact, in carriers of the virus, precancerous processes are found in less than 1% of all cases. That is, the likelihood of encountering cancer due to HPV is extremely low.
- Why is papilloma dangerous? The fact that it occurs with virtually no symptoms when infected. This greatly complicates the search for the root cause of the disease.
- Another feature is its direct dependence on the immune system. If your immune system works well, this virus will be completely safe. You can only detect its presence by taking tests. If the immune system leaves much to be desired, then the fight against warts will be much more serious. Until you normalize the effective functioning of the immune system, warts will appear again and again.
- Warts can form on the skin, mucous membranes and inside the body. It is not uncommon to find papillomas of the anus, papilloma in the stomach or on the genitals. Affecting the anus, urethra, cervix or oral cavity, growths can cause much more serious problems.
Important addition: How to get rid of condylomas using folk remedies, features of treatment and prevention
Where do papillomas grow?
Single or multiple papillomas can be detected on any part of the body. Naturally, growths on the face cause more inconvenience, but papillomas on closed areas of the body are often injured by rough clothing.
Due to the peculiarities of the development of the virus and the structure of the skin, several localizations of papillomas are distinguished, these are:
- Natural folds on the body are the armpits, groin area, lower abdomen if you are overweight. In women, the formation of flat and thread-like papillomas often occurs under the mammary glands.
- Hands, skin of the face, neck, back and abdomen. On the face, flat and simple papillomas are often localized near the mouth, near the eyes, and on the eyelids.
- The genitals are where genital warts most often grow.
- Internal organs - bladder, stomach, intestines.
- Feet.
See photos of a century affected by the human papillomavirus
Viral growths can also be in the oral cavity, bladder, internal genital organs, and in the ducts of the mammary glands. Papillomas are detected in the esophagus, larynx and trachea. Growths in the throat area lead to a narrowing of the lumen of this channel and then signs of respiratory failure develop.
What does papilloma look like on the skin of the penis: papilloma on the penis
Papillomas are considered benign formations, but under the influence of negative provoking factors they can degenerate into malignant tumors; this process takes from several months to several years.
Here you can see papillomas growing on the mucous membrane of the mouth on the tongue:
How to remove papillomas on the face at home?
At home, simple and time-tested local preparations are widely used. The use of such medications is usually safe and does not require a prescription for purchase in pharmacy chains.
Salicylic acid for papillomas
Salicylic acid solution is a common remedy for various skin diseases. Viral changes in the epithelium require careful contact with alcohol-containing substances.
To remove papilloma, salicylic acid is used in two versions:
- Alcohol solution (from 2%) . Papillary growths are blotted with salicylic alcohol several times a day for 14 days.
- Salicylic liniment (60%) . The ointment is applied to the affected areas, covered with a bandage and secured with an adhesive plaster.
Before applying salicylic ointment, the skin is thoroughly cleaned and steamed. This is necessary to achieve maximum therapeutic results.
The instructions for using salicylic ointment contain virtually no contraindications other than individual intolerance.
Ointments and creams for warts and papillomas on the face
Unfortunately, hardware techniques do not get rid of the true cause of papillomatous rashes - HPV infection. Given the current somatic status of the patient, neoplasms appear again. To stop the viral activity of strains, drug therapy using local and systemic drugs is used.
The main groups of drugs are antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs, along with the prescription of vitamins and antitumor drugs.
Popular pharmaceutical products are local preparations for removing papillary lesions on the face:
- Aldara cream:
- Stefalin for papillomas on the face;
- Pianping 999 is a popular Chinese ointment;
- Viferon is an antiviral immunomodulatory ointment;
- Cryopharma is a freezing drug;
- Verrucacid is a solution based on oil and alcohol with a cauterizing effect for local application;
- Supercleaner is an effective natural-based product;
- Feresol is a means for cauterizing papillomatous lesions;
- Zinc paste for drying and disinfection;
- Betadine ointment is antibacterial and drying.
Various plasters, herbal and homeopathic preparations, and essential oils are suitable for the face.
It is important to coordinate any treatment with your doctor:
- Firstly, it is impossible to independently determine the nature of the neoplasms.
- Secondly, if there is a risk of malignancy, treatment should be careful, aimed at suppressing the cancer process.
Benign formations: warts, condylomas and papillomas - what is the difference?
Activation of different types of HPV can lead to the appearance of three different benign formations on the skin: warts, genital warts and papillomas.
These formations have both significant differences and some similar characteristics. Comparing the appearance and growth characteristics of growths on the body will help you more likely to independently determine the type of benign growth.
Warts . The appearance of a wart on the body can be determined by some external features of this growth, these include:
- The tumor size is up to 1 cm in diameter.
- Clarity of external boundaries, density on palpation and surface heterogeneity.
- Irregular shape, which is more close to round.
- Color ranges from light gray to almost black.
Features of the location. Warts occur in people mainly on open areas of the body, especially those that are subject to frequent injury. These are hands and fingers, knees, elbows, scalp.
The virus that causes warts is almost always transmitted through household contact, that is, through handshakes or, less often, through the use of certain things - towels, gloves. Most often diagnosed:
- Vulgar warts - in 70% of cases. Simple warts are also detected in 20% of adolescents and children of primary school age.
- Plantar – detected in 30% of patients with warts.
- The flat type of warts is diagnosed in 4% of patients with this type of papillomas.
“Butcher’s warts” are classified into a separate group; they are detected in people whose specialties are related to the processing of fish or meat.
Papillomas . Let's look at how papilloma looks and develops. Papillomas are skin growths that are soft to the touch, extending from the body on a thin stalk or having a flat base.
The virus that causes the growth of papillomas thrives in a humid, warm environment and therefore can easily become infected in baths, saunas, and swimming pools.
At the beginning of their growth, papillomas cause some burning and tingling in the upper layers of the skin, then at this place you can notice the formation of a small lump. Gradually, this growth stretches and lengthens, its dimensions vary from 0.2 mm to 1-1.5 cm in diameter.
The color of papillomas is most often flesh-colored, grayish or yellowish. These tumors grow more often in older people, but often affect the skin of young people. Unlike warts, papillomas prefer to grow on closed areas of the body - under the armpits, mammary glands, in the groin area, on the inner thighs.
Papillomas usually begin to grow during long-term treatment of infectious or somatic diseases, as well as in people with weakened immune systems. A single formation leads to the formation of others and then papillomatosis occurs.
Condylomas. Genital warts appear on the mucous membranes only under the influence of certain types of HPV, which are transmitted in the only way - sexually.
Most often, these growths are localized in the genital area and near the anus, less often in the oropharynx. Condylomas are papillary growths; individual elements can merge with each other and then a tumor appears that resembles a cockscomb.
It is easy to detect condylomas on the external genitalia if you pay close attention to your health. It must be remembered that the mucous membrane is normally always smooth, and the appearance of roughness, bumps, and bumps on it is a reason to seek a diagnosis at a medical institution.
Prevention and diagnosis of papillomavirus
In order to prevent papillomavirus, you should periodically visit a specialist for examination or just a basic examination. This is especially true for those who have already been exposed to neoplasms on the skin and may have even undergone a course of treatment.
If, at the end of treatment, the lesions were still active, then their changes should be closely monitored.
The main requirement is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. During pregnancy, you should follow your doctor's advice.
Diagnosing the disease is not difficult. As a rule, this occurs through an external examination by a specialist (dermatologist, oncologist or gynecologist) of the surfaces of the body, especially if the skin has already been subjected to similar nuances.
To study the activity of the virus in the body in more detail, various methods are used, including:
- Polymerase chain reaction (determination of the DNA of the virus itself in any material);
- Colposcopy (careful examination of the cervix using a drug that magnifies the image almost 30 times);
- Cytological examination of the cervix (examination of scraping of the mucous membrane under a microscope);
- Digene-Test (high-precision examination).
In addition, the usual method of interviewing the patient to get a complete picture is valid, since knowing what causes the growths to appear, one can paint a picture based on some of the person’s actions.
How is HPV transmitted?
HPV can be transmitted in several ways:
- sexual,
- from mother to fetus during childbirth,
- contact – through cracks and abrasions on the skin.
Contact does not have to be direct; often the virus remains on personal items - towels, razors, washcloths, toothbrushes. It is possible to become infected with HPV in hairdressing salons, beauty salons, and medical institutions - insufficient disinfection of instruments leads to infection with various types of pathogenic microorganisms.
Diagnosis of the disease
The doctor examines the tumor and evaluates its appearance on the ABCDE scale (asymmetry, uneven edges, uneven color, variability and size more than 6 mm). Knowing what malignant papilloma looks like, he can, with a high degree of probability, determine the presence of an oncological process during an examination.
During the biopsy, damage to the growth occurs. It can increase the likelihood of papilloma degenerating into cancer. Therefore, they try not to prescribe a biopsy to make a diagnosis. The doctor monitors the tumor and, if there are many dangerous factors, recommends removing it. After the surgical procedure, the removed tissues must be examined to determine the presence of cancer cells and the extent of damage to the nevus. Histological examination allows for an accurate diagnosis.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Stretching the seminal canal
Why is papilloma dangerous for women, children and men?
The virus can be detected through several tests and examinations. Based on them, the doctor selects treatment, and the woman must be constantly examined in order to catch in time the activation of the proliferation of the microorganism, which is the prevention of cancer.
Many people think about the treatment and removal of papillomas only in connection with the occurrence of a cosmetic defect on the skin. But such a change is dangerous only from the aesthetic side; you need to be more careful about another consequence - the degeneration of papilloma into a cancerous formation.
Frequent injuries to growing papillomas and their inflammation contribute to this complication. If a growth develops in the throat, vocal cords and trachea, breathing function deteriorates, bleeding and suffocation are possible.
Papillomas in women not only disrupt reproductive function, but can also be transmitted to the child. Usually the virus enters the baby directly into the mouth and then papillomas grow in the oropharynx, interfering with breathing and voice formation.
A man who has papillomas on his body and genitals can transmit the virus to his sexual partners. The risk of HPV transmission through towels and other objects cannot be excluded, and then the risk of infection arises for children and relatives living nearby.
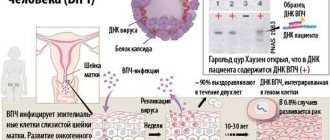
Mechanism and causes of pathology development
Skin formations that arise at the site of localization of the human papillomavirus are called papillomas, and the disease itself is called papillomatosis. This concept includes several types that differ in appearance, place of formation and type of HPV. When diagnosing papilloma - it is not difficult to understand what it is, you can translate it: papilla is a nipple, oma is a tumor, that is, literally it is a tumor in the form of small papillae.
It is quite simple to become infected with this virus - just a slight contact with an HPV carrier is enough and the viral cells begin to quickly penetrate under the upper layer of the dermis of a healthy person. The greatest risk of infection is in people with damaged skin; even a microcrack that is invisible to humans is enough for this to happen.
HPV is a simple virus, has a spherical shape and is characterized by a high ability to penetrate epithelial cells. Invading the cell nucleus, the virus begins to actively multiply, thereby provoking pathological proliferation of epithelial cells. The virus is not always activated immediately after entering a human cell; sometimes decades can pass before external manifestations and other symptoms appear, and this directly depends on the state of the human body.
Sometimes papillomas appear in only one area, but when immunity decreases, the growths can spread throughout the body. The high viability of viral cells allows them to withstand low and high temperatures, some antiseptics, acids and lipid solvents. That is why infection can occur not only from person to person, but also from household objects.
The greatest risk of HPV infection is in public places - transport, baths, gyms, clinics.
Since the human papillomavirus can remain latent for a long time, there is practically no chance of identifying the site of infection and the carrier of the infection. Since papillomatosis occurs when immunity decreases, the following are considered provoking factors:
- Colds and infectious diseases.
- Exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Nervous overstrain.
- Excessive physical overload.
- Having bad habits.
- Promiscuous sexual life, a large number of sexual partners.
There are several main ways of infection with the papilloma virus:
Touching an infected person (even if he has no manifestations of papillomatosis).- By household means, for example, through personal hygiene items.
- Through sexual contact (HPV accounts for approximately 10% of all sexually transmitted infections).
- From an infected mother to her child through amniotic fluid or during childbirth through the genital tract.
To reduce the risk of contracting the papilloma virus, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, not use other people's towels, razors and other items, and, of course, have one sexual partner and use protection during sexual contacts.
Treatment
Treatment for HPV must be mandatory. Modern medications are not able to completely remove the virus from the body, but they are necessary in order to transfer the pathogen to a dormant state in which there is no infection and no diseases develop.
Papillomas on the body are removed using different methods; in addition, several groups of drugs are used to reduce viral activity.
Is it possible to remove papillomas?
Papillomas on the body are removed by conventional surgery, using a laser, electrocoagulation, or radio wave therapy. The choice of method for cutting off a papilloma depends on its location, size, number of formations, and the presence of a stalk.
Conservative treatment
Drug treatment consists of a course of use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antiviral agents that can stop the reproduction of the virus. These are Izoprinzin, Allokin alpha, Groprinosin.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Immunity enhancing agents.
The course of treatment with human papillomavirus drugs can be repeated several times based on the results of the analysis. The goal of antiviral therapy is to completely suppress HPV activity.
Folk remedies
In addition to basic therapy, traditional medicine can be used. You can prevent further growth and, in some cases, destruction of papilloma by lubricating these growths with celandine juice, castor oil, dandelion juice, garlic and sour apple.
Naturally, such removal of papillomas will take a lot of time and is effective in most cases when combined with the simultaneous use of antiviral drugs.
Preventive actions
Preventing the appearance of papillomas on the body consists of sufficient personal hygiene, timely treatment and healing of all minor cuts on the body.
You must follow the rule of using only your own towel, manicure sets, combs, and shoes. When having sexual intercourse with untested partners, you should always use condoms, and after an intimate act, take a shower and thoroughly clean the genitals, because it takes time for the virus to penetrate the epithelium.
Source: https://gidmed.com/onkologiya/lokalizatsiya-opuholej/kozhnyj-pokrov/papilloma.html
How to treat papillomas on the face?
Clinicians recommend removal of papillomatous lesions of any location, but the skin on the face is most prone to injury and scarring. Hardware techniques today remove pathological epithelial growths as safely and without complications as possible.
After the papilloma is removed, it is sent for histological examination to assess the degree of potential cancer risks.
Use the following hardware removal methods:
- Laser excision of growth . Under the influence of the laser, the moisture in the papillary growths evaporates, the vessels stick together, eliminating bleeding. The method is safe and highly effective. The downside is the high cost of laser papilloma removal.
- Cryodestruction . The method is based on the influence of liquid nitrogen, which freezes the tumor, after which it self-amputates after a few days.
- Radio wave destruction . Destruction of papillary growth using radio waves. The method is characterized by short-term rehabilitation, quick recovery and painlessness.
- Electrocoagulation . Removal involves excision of the growth using electric current of varying intensity. Despite the safety, accessibility and bloodlessness of the method, patients always experience pain. The average price for electrocoagulation of papillomas is here.
If malignancy or conglomerative arrangement of papillomas, condylomas or warts is suspected, the doctor may decide to remove the tumors with a scalpel or chemically.
The main advantages of hardware treatment are:
- availability,
- short recovery period,
- relative painlessness.
Treatment of flat papillomas on the face
Treatment of flat papillomas is carried out preferably with local drugs along with laser excision. Other methods are ineffective. If there is a risk of malignancy, doctors can use the scalpel method.
Effective drugs against flat papillomas are:
- Kolomak - exfoliates dead epidermal cells;
- Solcoderm - dries and separates the wart from the skin;
- Cryopharm - suppresses the growth of viral cells by freezing tumors.
There are many pharmaceutical drugs for the treatment of any type of neoplasm, but it is important to use medications only after consulting a doctor.
Key therapy techniques
After you understand what papilloma is, you should understand how to get rid of it. Modern medicine offers several effective methods:
- Surgical removal. Recently, surgical intervention is used only on those tumors that are located in internal organs, for example, in the uterine cavity. The procedure is performed under anesthesia, and therefore is fraught with complications.
- Laser burning. Many beauty salons offer such procedures. Removal is carried out quickly and painlessly. The beam burns out the tumor layer by layer. The likelihood of bleeding and infection is completely excluded, since the laser seals the blood vessels. This technique is often chosen in situations where the growth is located on visible parts of the body. It is allowed to remove several papillomas at once in one procedure.
- Cryodestruction. The essence of this technique is to expose the papilloma to liquid nitrogen, which instantly destroys it. The advantage of this method is the low likelihood of relapse. Single large tumors are often removed by cryodestruction. As the growth heals, a crust forms in its place, which falls off on its own.
- Electrocoagulation. With this method of treatment, the growth is exposed to electric current, which leads to its death. Using electrocoagulation, a large papilloma is burned in one session. A dry crust remains on the skin, which disappears on its own over time. You cannot tear it off, as this can cause infection of the wound.
- Chemical exposure. This technique treats multiple papillomatosis localized in a small area of the body. Formic acid is most often used for the procedure. Several sessions are required to completely remove the tumor. After such removal, there is a high risk of rapid relapse, so drug therapy is required.
- Use of medications. This technique appears to be effective in the early stages of the disease. First of all, the specialist prescribes antiviral drugs: Cycloferon, Panavir, Viferon and some others. After the virus can be transferred to a latent state, agents are used to remove the growth. Super celandine and its direct analogs are the most effective. The medicinal composition is applied directly to the tumor. After some time, it dies off, leaving no scar underneath.
The means of restoring the full functioning of the body’s immune system will help speed up the treatment process. For this purpose, doctors often prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes. Proper nutrition, exercise, giving up bad habits and frequent walks in the fresh air will help improve the body's protective properties.
It is strictly forbidden to remove papillomas on the skin mechanically. This often causes bleeding and infection of the wound. As a result, concomitant diseases develop that threaten not only human health, but also human life.
Danger of papillomas
Papillomas on the body are not as harmless as they seem at first glance. In the absence of proper treatment, the virus provokes the development of serious complications:
- Due to the influence of pathogenic microflora, papillomas develop into malignant neoplasms. This often leads to the appearance of metastasis, which threatens human life.
- Growths localized on the mucous surface of the larynx make breathing difficult. This can lead to a dry cough and asthma attacks.
- When tumors are injured, bleeding may occur. The likelihood of infection of an open wound increases.
- Growths located in the vaginal area often cause the development of diseases of the genitourinary system.
To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to establish the causes as early as possible and begin treatment of the disease. Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Types of papillomas
Their shape and localization characteristics will depend on which strain of the virus caused the formation of papillomas. The following types of growths are distinguished:
- Simple or vulgar.
- Flat.
- Plantar.
- Thread-like.
- Pointed.
- Squamous.
- Inverted.
- Breast papillomas.
- Growths in the throat.
- Papillomas in the cervix.
- Growths on the tongue.
- Neoplasms in the urethra.
Defects located on visible areas of the skin cause psychological discomfort to a person. To prevent their growth, it is necessary to begin therapy immediately. A dermatologist can tell you everything about papillomas and choose the right strategy to combat them.
Simple
They appear after the activation of HPV types 26, 27, 28, 29, 41, 63 or 77. Initially, mild discomfort appears on the skin. A small tumor gradually forms. Tiny tubercles quickly develop into papillomas of impressive size. They often reach 1 cm in diameter. The surface of the growth gradually becomes rough and begins to darken.
Most often, such papilloma appears in the area of the palms or between the fingers. In men, they are often located on the penis. Growths can be either single or group.
Flat
Their distinctive feature is their subtle elevation above the skin level. Such growths have an oval shape. Outwardly, they resemble flattened cones.
The appearance of papilloma of this type is a consequence of HPV types 10, 28 or 49 entering the human body. They are often found on the face, in the upper part of the sternum, and on the genitals. The skin around the growth becomes inflamed and itchy. The causes of papillomas lie in a sharp decrease in the protective properties of the body.
Plantar
New growths on the foot can easily be confused with calluses. To carry out competent therapy, it is necessary to understand what this type of papilloma looks like. Outwardly, it resembles a vulgar growth, has no skin pattern, and its surface is smooth.