Regular menstruation is the most important indicator of female sexual health, which depends on the hormonal balance in a woman’s body. To restore the menstrual cycle, doctors prescribe women Progesterone, a hormone responsible for the normal functioning of the reproductive system, the formation of the endometrium and the course of pregnancy.
A deficiency of this substance can cause the absence of menstrual periods in women and a number of other pathologies associated with the health of the reproductive system. Progesterone injections help cope with these problems.
Composition and mechanism of action of injections
Progesterone is a hormonal drug for inducing menstruation, which is sold in pharmacies in the form of ampoules for intravenous administration, tablets for oral administration, capsules for vaginal use or gel for external use. The main active ingredient is progesterone.
Progesterone is a steroid hormone produced in the female body by the ovaries. It interacts with special progestin receptors located on target cells. Progesterone binds to them and enters the cell, activating DNA and stimulating the production of ribonucleic acid. The substance can cause the following changes in a woman’s body:
- the endometrium begins to rapidly develop;
- ovarian functions are restored;
- a sufficient amount of glucose accumulates in the liver;
- the menstrual cycle is normalized;
- conditions are created for a favorable pregnancy.
Since it is the deficiency of this hormone in the female body that often causes amenorrhea, doctors prescribe progesterone by injection to induce menstruation quite often. However, it is impossible to start treatment with the drug without preliminary research, because excess progesterone in the body is just as dangerous as its deficiency.
Analogs
Thanks to pharmacists, today there are many drugs containing artificial or synthetic hormones. Only an experienced physician who understands the nuances of a particular drug can replace the drug in injections. Which form is best for the patient - progesterone tablets, injection solution, capsules or gel - will depend on many factors.
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (India)
Average cost:
capsules 100 mg (30 pcs.) – 366 rubles, 200 mg (10 pcs.) – 253 rubles, gel – from 242 rubles.
A drug with progesterone in the form of capsules for oral or intravaginal use, as well as in the form of a vaginal gel. The drug is prescribed to eliminate disorders caused by hormonal deficiency, to prevent miscarriage, in preparation for IVF, etc. Like progesterone injections to induce menstruation, both forms are used for MC problems.
The drug is available with different concentrations of the hormone: 100 or 200 mg per capsule, 80 mg per 1 g of gel.
The duration of the course and the method of administration to the body are determined individually.
Pros:
- The effect is similar to Utrozhestan, but costs less
- Helps with MC problems.
Flaws:
- Leaks, causes drowsiness, tachycardia
- May cause allergies because the capsules contain peanut oil.
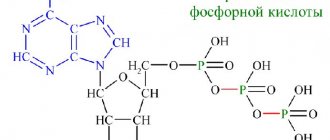
Dosage form: solution for intramuscular administration [oil] Composition:
1 ml of the drug contains:
active substance:
progesterone 10 mg or 25 mg;
Excipients
: medical benzyl benzoate 0.2 ml, olive oil up to 1 ml.
Description: Transparent oily liquid of light yellow or golden yellow color.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: gestagen ATC: G.03.DA Pregnin derivatives
G.03.DA04 Progesterone
Pharmacodynamics:
Hormone of the corpus luteum, has a gestagenic effect. By binding to receptors on the surface of cells of target organs, it penetrates into the nucleus, where, activating deoxyribonucleic acid, it stimulates the synthesis of ribonucleic acid. Promotes the transition of the uterine mucosa from the proliferation phase caused by follicular hormone to the secretory phase, and after fertilization creates the necessary conditions for implantation and development of a fertilized egg. Reduces the excitability and contractility of the muscles of the uterus and fallopian tubes, stimulates the development of the end elements of the mammary gland.
By stimulating protein lipase, it increases fat reserves, increases glucose utilization, increasing the concentrations of basal and stimulated insulin, promotes the accumulation of glycogen in the liver, increases the production of aldosterone; in small doses it accelerates, and in large doses it suppresses the production of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland; reduces azotemia, increases nitrogen excretion in urine. Activates the growth of the secretory section of the acini of the mammary glands and induces lactation. Promotes the development of normal endometrium.
Pharmacokinetics:
It is quickly and almost completely absorbed after intramuscular administration. Metabolized in the liver to form conjugates with glucuronic and sulfuric acids. The CYP 2C 19 isoenzyme is also involved in metabolism. The half-life is several minutes. Excreted by the kidneys - 50-60%, with bile - more than 10%. The amount of metabolites excreted by the kidneys varies depending on the phase of the corpus luteum.
Indications:
Amenorrhea, anovulatory metrorrhagia, endocrine infertility (including corpus luteum insufficiency), threat of miscarriage; oligomenorrhea, algomenorrhea (due to hypogenitalism); diagnosis of the formation of endogenous estrogens.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity; breast and genital cancer (as monotherapy); liver failure; pregnancy (II-III trimesters); tendency to thrombosis, acute forms of phlebitis or thromboembolic diseases; vaginal bleeding of unknown origin; failed miscarriage; porphyria. Carefully:
Diseases of the cardiovascular system, arterial hypertension, chronic renal failure, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, epilepsy, migraine, depression; hyperlipoproteinemia, ectopic pregnancy, lactation period.
Directions for use and dosage:
The drug is administered intramuscularly.
For bleeding associated with ovarian dysfunction
, prescribe 5-15 mg daily for 6-8 days; if the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity has been previously scraped, injections begin after 18-20 days (if scraping is impossible, they are administered during bleeding). During the treatment period, bleeding may temporarily increase (for 3-5 days); Severely asthenized patients must first undergo a blood transfusion (200-250 ml). After bleeding stops, therapy is continued for 6 days. If bleeding has not stopped after 6-8 days of treatment, further administration is not advisable.
With hypogenetalism and amenorrhea
administered after the use of estrogen drugs in the form of injections of 5 mg daily or 10 mg every other day, for 6-8 days.
With algodismenorrhea
treatment begins 6-8 days before menstruation, 5 or 10 mg daily, for 6-8 days.
With algodismenorrhea caused by underdevelopment of the uterus
, combined with estrogens at the rate of 10,000 units every other day for 2-3 weeks; then administered for 6 days.
For the prevention and treatment of threatening and incipient miscarriage associated with insufficient function of the corpus luteum,
- 10-25 mg daily or every other day, until the symptoms of a possible miscarriage completely disappear.
With a habitual abortion
administered before 4 months of pregnancy.
In case of corpus luteum deficiency
- 12.5 mg/day for 2 weeks from the moment of ovulation (if necessary - up to 11 weeks of pregnancy).
Diagnosis of the formation of endogenous estrogens
: 100 mg once.
Side effects:
From the nervous system:
drowsiness, headache, depression, apathy, dysphoria.
From the digestive system
: cholestatic hepatitis, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, calculous cholecystitis.
From the genitourinary system
: decreased libido, shortened menstrual cycle, intermediate bleeding.
From the senses
: visual impairment.
From the cardiovascular system
: increased blood pressure, edema, thromboembolism (including pulmonary artery and cerebral vessels), thrombophlebitis, retinal vein thrombosis.
From the endocrine system
: galactorrhea, alopecia, weight gain, enlargement, pain and tension of the mammary glands; hirsutism.
Allergic reactions
.
Local reactions:
pain at the injection site.
Overdose:
When using higher doses of the drug, side effects described in the corresponding section occur more often. If gestagen-dependent side effects occur, treatment with the drug should be interrupted and, after their disappearance, resumed in a reduced dosage. If necessary, carry out symptomatic treatment.
Interaction:
Reduces the lactogenic effect of oxytocin.
Reduces the intensity of the action of drugs that stimulate the smooth muscles of the uterus, anabolic steroids, gonadotropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland.
When used simultaneously with barbiturates, a decrease in the effect of progesterone is observed.
Special instructions:
No data.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.: During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions. Release form/dosage:
Solution for intramuscular administration [oily], 10 mg/ml, 25 mg/ml.
Package:
1 ml in neutral glass ampoules.
10 ampoules, along with instructions for use and a knife for opening ampoules or an ampoule scarifier, are placed in a cardboard box.
5 ampoules in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film. 2 contour blister packs with instructions for use and a knife for opening ampoules or an ampoule scarifier are placed in a cardboard pack.
Progesterone injections are a drug of synthetic origin that is used to eliminate various functional disorders of the reproductive system. Also, progesterone injections can be prescribed by a specialist to treat certain forms of infertility that occur in the fair half of the population and to restore the normal menstrual cycle.
During pregnancy, such injections can be prescribed when there is a threat of miscarriage, as well as when the natural level of progesterone in the body decreases. To determine the insufficiency of the hormone level in the blood, a woman needs to undergo certain tests on the twenty-third day from the start of her critical days. Only a laboratory blood test can give an accurate result about whether hormonal therapy is necessary.
Most often, drug injections are administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. The most common method is intramuscular injection, since this method is considered less painful. But subcutaneous administration of the drug is often accompanied by compactions and even hematomas. Progesterone in ampoules is available in the form of 1 and 2.5% solutions of one milliliter. After the injection, the drug is very quickly absorbed into the blood and its effect begins within an hour after administration.
Decomposing in the patient’s liver, the medicine is excreted from the body in the urine in the form of metabolic products. Before use, the ampoule with the medicine must be held in your hand so that the medicine has time to warm up. This action provides the oil composition with maximum absorption into the patient’s blood.
If crystals are visible when the ampoule is cleared, then it is advisable to first heat it in a water bath until completely dissolved, and then cool it to room temperature. The dosage of this drug is exclusively individual and should be selected only by a qualified specialist.
Based on the indications obtained as a result of laboratory tests, the specialist makes a decision on prescribing the drug. Let's consider the main indications for use:
- Natural lack of natural hormone levels in the female body;
- Bleeding that occurs and has nothing to do with menstrual periods;
- The drug can be prescribed to adjust the length of the menstrual cycle, and the specialist must first make sure that the woman is not pregnant;
- Heavy menstrual cycle;
- Low level of progesterone in the blood of the expectant mother;
- If there is a threat of miscarriage;
- If a woman has already had several unsuccessful attempts at pregnancy, which ended in spontaneous rejection of the fetus;
- Insufficient level of corpus luteum in the female body.
Any need for injections is determined only by taking a blood test. To reduce pain when using the drug, you must follow certain instructions. It is important to ensure that the specialist knows exactly how to inject the medicine.
In addition to indications for use, there are also instructions on contraindications, which include: breastfeeding, the last month of pregnancy, planned pregnancy, any cancer of the mammary glands and epilepsy. If any point is present, injecting the drug is strictly prohibited.
Experts strongly recommend not to self-medicate and prescribe the dosage of the drug, since such actions are fraught with unwanted side effects, which can ultimately have a very negative impact on your health.
According to the instructions, the drug should be used with extreme caution for patients who suffer from asthma, renal failure and tubal pregnancy. It is also prohibited to drink alcohol-containing drinks during treatment, as such interactions can significantly increase the risk of side effects and increase their severity.
Instructions for use of Progesterone in ampoules
The drug for intramuscular administration is absorbed into the blood instantly, so it acts very quickly. Doctors prefer 1% or 2.5% Progesterone injections.
Some women do not have the opportunity to go to a hospital for treatment or go to the clinic for injections every day to induce menstruation. What is their solution? Inject 1 percent or 2.5 percent injections yourself according to the instructions:
- warm the ampoule with the medicine in your hands to room temperature;
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap and wear latex gloves;
- take a clean cotton swab, soak it in alcohol, wipe the base of the ampoule, carefully open it, draw the liquid into the syringe;
- Using a new cotton swab soaked in alcohol or another antiseptic, wipe the injection site;
- With a quick, confident movement, insert the needle at a right angle into the gluteal muscle - into the upper right square;
- slowly inject the medicine into the muscle;
- After administering the drug, remove the needle and treat the injection site with a clean cotton swab soaked in alcohol.
Indications for use
Progesterone is more often prescribed to women when their periods are late or absent. Sometimes the indication for prescribing the drug is painful menstruation. There are a number of other ailments that Progesterone can help cure:
- systematic heavy or minor uterine bleeding, which is observed in the intervals between menstruation;
- heavy and prolonged menstruation;
- prolonged absence of pregnancy with regular sexual activity without contraception;
- miscarriages;
- various disorders of the reproductive system.
Progesterone can also be prescribed during pregnancy if a woman is at risk of miscarriage. The use of the drug is advisable up to 35 weeks of gestation.
What are the contraindications?
Since the drug is a hormonal drug, if used incorrectly it can cause harm to the body. Contraindications to the use of Progesterone for delay and other disorders:
- the presence of cancerous tumors on the reproductive organs or mammary glands;
- serious liver dysfunction;
- vascular diseases and cardiac disorders;
- tendency to allergies;
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- migraine;
- epilepsy and other neurological diseases.
Features of use (scheme, dosage, duration of therapy)
When your period begins when treated with Progesterone depends on a number of factors. The success of drug therapy is primarily affected by the level of hormone deficiency in the body. If the lack of progesterone is significant, the course of injections can last from 8 to 12 days. With a slight deficiency of the hormone, menstruation may begin within 3 days after the start of treatment. The results of therapy also depend on the individual characteristics of the patient, the duration of the delay and the correctness of dosage determination.
Regardless of when menstrual bleeding begins after using Progesterone, treatment cannot be interrupted. The duration of use of the product and its dosage are determined by the doctor.
If the deficiency is mild, the patient may be prescribed daily injections of a solution with a concentration of 1%. A more concentrated drug - 2.5% - is prescribed for a serious lack of pregnancy hormones. The duration of treatment in complex cases can be from 6 to 11 days.
When it comes to minor progesterone deficiency, doctors may prescribe the drug in tablets or capsules. Taking the medicine in this form is not acceptable for everyone: doctors say that the side effects when taking capsules or tablets orally are more pronounced.
Overdose and interaction with other drugs
Excess progesterone can be detrimental to a woman's health. If the dosage of the drug is too high, a woman may experience nausea, vomiting, dizziness, weakness and other disorders characteristic of intoxication of the body. If such symptoms appear, treatment should be stopped by informing your doctor.
Progesterone can enhance the effect of some drugs and weaken the effect of others. If the drug is taken simultaneously with anabolic steroids, oxytocin, anticoagulants, the effect of these drugs is weakened.
Progesterone enhances the effectiveness of systemic coagulants, drugs used to treat hypertension, immunosuppressants, diuretics, bromocriptine. Barbiturates reduce the effect of using Progesterone.
Side effects
When treated with Progesterone, adverse reactions may occur:
- blood pressure surges;
- decreased libido;
- slowing down metabolic processes;
- emotional disorders, mood swings;
- discomfort in the mammary glands;
- unnatural leucorrhoea;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting.
If these side effects occur, you need to tell your doctor about it. He will reduce the dosage, change the form of use of the drug, or suggest a similar remedy.
Indications for use
The hormonal remedy is designed to eliminate pathologies of the female reproductive system. It is used for:
- Amenorrhea
- Dysfunctional bleeding from the uterus
- Threat of miscarriage
- Infertility caused by insufficient production of the corpus luteum in the body
- Miscarriage due to deficiency of corpus luteum hormones
- Painful menstruation.
Progesterone is also prescribed for delayed menstruation, if the disorder is caused by insufficient hormones in the body.
Dosage of the drug and duration of therapy
As mentioned above, only the attending physician will be able to select the required dose after familiarizing himself with the results of the analysis, and, of course, the pathology for which it is used to treat. And, of course, it is first necessary to exclude the fact that the patient is possibly pregnant.
If a woman or girl has painful periods, then the first injection should be given seven days before the expected menstrual bleeding with a 1% solution. After several cycles, repeated injections can be performed.
If there is excessive blood loss during menstruation, progesterone is administered for 6-8 days in a row.
Progesterone injections to induce menstruation are given for seven days in a row with a 1% or 2.5% solution, in a volume of 0.5 to 1.5 ml. There is also a scheme for alternating injections, that is, they are administered every other day. With the help of such therapy, the woman’s body itself chooses the dose of the hormone to begin menstruation.
Every woman should take into account the fact that progesterone in their body may not behave as it should, and all this depends on her mood, the general condition of the body and individual characteristics.
Medicinal properties
The therapeutic effect of the drug is achieved due to the properties of the main component – the corpus luteum hormone.
After penetration into the body, progesterone changes the functioning of the uterine mucosa, transferring it to the secretion phase. Thus, it provides the necessary layer of the endometrium, in which the attachment of the egg is possible. After it is implanted, the substance promotes its proper development.
At the same time, the hormone eliminates excitability and contraction of the uterine muscles, which is very important for maintaining pregnancy, and activates the preparation of the mammary glands.
The effect of Progesterone on the secretion of gonadotropes depends on the dosage used: a small amount of drugs stimulates their formation, large doses inhibit it.
After injection, the hormone is instantly absorbed. It is transformed mainly in the liver, the remaining volume of the substance is retained in the subcutaneous tissue. The main active metabolite is pregnadiol.
Arrival of menstruation after injections
The main question that worries all women is “When will menstruation begin after therapy?” If the woman does not have any concomitant pathologies or abnormalities, and progesterone was used to normalize the menstrual cycle, then bleeding develops on the third or fifth day after completing the course of hormone therapy.
If your period does not come, you should immediately consult your doctor. After a thorough examination and additional tests, the doctor will identify a possible disease, which will be treated in a different way. And if nothing is found, an additional course of hormones is prescribed, after which menstruation should begin.
But each woman’s body is individual, and accordingly, the reaction to the introduction of a synthetic hormone can be different, usually this is reflected in the nature of menstrual bleeding.
In most cases, after completing the course of treatment, fairly scanty bleeding is observed. This indicates that the drug had an effect on the body, but the level of hubbub did not level out in sufficient quantities. Because of this, insufficient thickening of the endometrium occurs, and as a result, a small amount of menstrual flow.
It is possible that the development of a directly proportional situation, that is, too much discharge, but such a phenomenon is very rare. If this situation develops, excessive growth of the endometrium occurs, and this indicates that the hormonal levels have not leveled out. This phenomenon usually occurs if the doctor has chosen too low a concentration of the drug for treatment.
And it is very rare to encounter the development of painful periods. But usually this is not associated with the action of progesterone, and in the end it turns out that the problem lies in the condition of the woman’s reproductive organs.
What if it hasn't started?
If the course of treatment with injections is completed, but menstruation has not started, then you need to contact your doctor again.
Lack of menstruation may mean:
- the patient is pregnant;
- the delay is due to other reasons.
Normal well-being and functioning of all body systems, and above all the genital area, are possible with the interconnection of different organs. The hormonal balance is ensured by the participation not only of the presence of progesterone, but also of other hormones produced by:
- pituitary gland;
- hypothalamus;
- adrenal glands;
- thyroid gland, etc.
Only a complete and thorough examination
will show what caused the absence of menstruation - the presence of an ovarian cyst, problems with the pituitary gland, dysfunction of the thyroid gland or other pathology. Eliminating the cause will restore the normal menstrual cycle.
Latin name:
Progesterone
ATC code:
G03D A04
Active ingredient:
Progesterone
Manufacturer:
Dalkhimpharm, Alvils (RF), Farmak (Ukraine)
Conditions for dispensing from the pharmacy:
By prescription
Progesterone is intended for use in gynecology. It is used for problems with MC, treatment of infertility, treatment of pathologies caused by insufficient levels of hormones.
Side effects after progesterone injections
If the hormonal drug is used incorrectly, unwanted side effects may develop. Typically, this situation occurs in the case of an incorrectly selected dose of the drug, or simply when taking the drug on your own.
If a side effect develops, the dose of the drug should be adjusted, but if this does not help, the drug should be discontinued or replaced with another.
The most common side effects include:
- decreased sexual desire;
- unregulated surges in blood pressure;
- if you use progesterone every month, you may accumulate excess body weight;
- liver disorders;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- skin pigmentation;
- discomfort in the mammary glands;
- frequent headaches, migraines;
- unformed vaginal discharge.
Also, a possible side effect may include the fact that menstrual bleeding does not occur during several cycles of using the drug; in such a situation, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the woman’s reproductive organs. If one of the above effects develops, you should definitely consult with your doctor about further treatment strategies.
Side effects and drug overdose
When progesterone injections are prescribed, the following undesirable consequences occur:
- Thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism (including vessels of the brain, retina, lungs).
- Hypertension.
- Peripheral edema.
- Impaired liver and kidney function.
- Headache.
- Decreased mood, depression.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Lack of appetite.
- Increased body weight.
- Galactorrhea is the leakage of milk from the mammary glands unrelated to lactation.
- Soreness of the mammary glands.
- Decreased libido.
- Intermenstrual bleeding.
- Pain at the injection site.
- Allergic reaction.
The dosage of the drug should be determined by a doctor
. Exceeding the recommended dose increases the risk of side effects. Long-term use of medications in high doses also leads to the cessation of menstruation.
While using the drug, concentration decreases. Until completion of the course of therapy, it is not recommended to engage in activities that require rapid psychomotor reactions (including driving a car).
The problem of delaying menstrual periods can affect any woman. Stressful situations, a change of city, gynecological pathologies or changes in diet can cause this condition. In such cases, doctors often prescribe Progesterone injections to induce menstruation.
This hormone has a direct effect on the duration of the menstrual period; it is able to regulate the process. How does this happen? After the introduction of synthetic Progesterone during a delay, the injections sharply increase the level of the hormone in the body, which after some time drops sharply, and as a result, critical days begin.
Many women decide to start self-treatment if they have not had their periods for a long time. They use folk remedies and buy medications without consulting their doctor. This cannot be done; any treatment should begin after examination and testing. Self-therapy with Progesterone during delay or other means further aggravates the imbalance of female hormones.
A delay usually indicates pregnancy. A woman buys a test, but it shows 1 line. Of course, the question immediately arises: “Why are there no periods?”
The main reasons for the absence of critical days (CD):
- MC without ovulation and development of the corpus luteum;
- absence of ovulation with the presence of a dominant follicle in the epididymis;
- the presence of a cyst on the appendage or in the corpus luteum;
- hypofunction of the corpus luteum.
Such conditions are formed due to an excess of estrogen, which leads to a lack of progesterone. The result is pathological changes in the inner mucous layer of the uterus; it does not go through all stages of development in order for full monthly uterine bleeding to begin. For CD to occur, it is necessary to increase the concentration of progesterone. Therefore, Progesterone injections or pills are prescribed for delay.
How to induce menstruation with injections
If menstruation is absent for no more than 3 - 5 days, this is not a reason to inject progesterone. The drug is hormonal, so it requires careful use. And with frequent, long-term use, it requires examination. At a minimum, you need to conduct a pregnancy test, because the absence of menstruation on time can be caused by pregnancy.
If it is determined that the cause of the delay is a deficiency of gestagen, the treatment regimen may vary depending on the cause that provoked the problem:
- with minimal hormonal imbalance, 4 - 5 injections of a 1% drug, given once a day, are sufficient;
- a more serious disorder requires 6 to 10 injections daily.
The one-time volume of the drug is determined by the doctor. It can be 0.5 - 2.5 ml, no more. The concentration of the solution is also recommended to be different. Maximum – 2.5%. But with it, you should not administer more than 1 ml at a time.
If the treatment regimen was chosen correctly, the intake was not disrupted, after completing the progesterone injections, menstruation began 3 to 5 days later - this is an excellent result.
Mode of application
Average cost: Progesterone 1% (10 amp.) – 375 rub., Progesterone 2.5% (10 amp.) – 675 rub.
Progesterone is administered in injections intramuscularly or subcutaneously, depending on the purpose and condition of the patient. The dosage and duration of the course are also determined individually in each specific case.
- Dysfunctional bleeding from the uterus
Depending on the severity of the condition, the doctor may prescribe a 6-8-day course, during which it is recommended to administer ½-1.5 ml daily. If bleeding develops after surgical curettage, then therapy can begin 18-20 days after surgery. When the patient is contraindicated for cleaning the uterus or for some reason it cannot be performed, then administration of drugs during bleeding is allowed. In this case, after 3-5 days, the body may respond in the form of increased blood loss. If therapy is carried out on a woman suffering from moderate or severe anemia, then in order to avoid complications, it is recommended to administer 200-250 ml of blood before starting the Progesterone course.
After stopping bleeding, therapy should be continued for at least 6 days. If it continues, doctors may decide to stop it.
- Progesterone injections to induce menstruation
If the MC disorder is caused by a hormonal imbalance in the body, then before starting treatment it is necessary to take tests to determine the level of hormones. This will allow you to more accurately determine the course and dosage of the drug. If hypogonadism or amenorrhea is diagnosed, therapy begins with the administration of estrogen drugs to improve the condition of the endometrium. After endometrial restoration is completed, hormone injections begin. If there are no special prescriptions from the gynecologist, then progesterone injections to induce menstruation should be administered according to the instructions for use. The developers of the drug advise injecting ½ ml or 1 ml. In the first case, the drug is administered daily for 6-8 days, in the second - every other day in the same course.
- Therapy of algodismenorrhea
To relieve a woman from painful menstruation, it is recommended to inject ½-1 ml of the drug before it begins (6-8 days before). If necessary, repeat courses are carried out.
- If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy (miscarriage)
- How to inject the drug
The injection solution should be used immediately after opening the ampoule, and the remaining medicine should be disposed of.
- Choose a site for injection: it is better to inject into the upper outer part of the left or right buttock.
- Disinfect the injection site by wiping it with a cotton swab and alcohol, and let it dry.
- Insert the needle at right angles to the surface.
- Release the medicine slowly, pressing the plunger evenly.
- Determine the injection site (anterior thigh, lower abdomen) and disinfect it.
- Gather the skin into a fold, insert a needle into its base at a right angle or 45.
- Release the medicine slowly to avoid damaging local tissue.
After completing the procedure, carefully remove the needle and press the puncture site with a cotton swab and alcohol for several minutes.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
It is undesirable to use progesterone preparations for therapy during pregnancy and pregnancy. But in case of emergency, the doctor may prescribe progesterone tablets or injections if there is a lack of corpus luteum hormones in the body and this can provoke an interruption of pregnancy.
Women who want to get pregnant in the near future should also abstain from drugs.
Contraindications
Despite the effectiveness of the drug and the fact that the active substance that provides the effect is similar to what is produced by the body, it also has contraindications. They cannot be ignored. Progesterone is a powerful drug that, if used incorrectly, can cause problems for a healthy woman. It is prohibited to use it if there are the following diagnoses:
- malignant neoplasms in the mammary gland or reproductive organs;
- serious liver dysfunction, hepatitis;
- venous thrombosis or pre-existing conditions;
- problems with the heart and blood vessels;
- diabetes;
- allergies, manifested by breathing problems, and bronchial asthma;
- high blood pressure;
- frequent migraines;
- epilepsy;
- depressive states.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy in the near future, the use of progesterone should be limited. It is unacceptable to use alcohol at the same time.
After how many progesterone injections do menstruation begin?
Many people are interested in how long after progesterone injections menstruation begins. The number of injections that will be required to stimulate menstruation for each woman is determined based on the test data obtained. That is, first of all, doctors determine the current concentration of progesterone in the blood at the end of the luteal phase and after that they indicate how many injections will be needed to normalize hormonal levels.
The maximum allowed quantity is 7 injections. In most cases, 3-4 are enough, which are administered every other day, intramuscularly. Intravenous progesterone is prescribed only in extreme cases.
After injections there is a high probability of side effects. Among them:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- lethargy;
- general malaise;
- exacerbation of current allergic reactions.
If after the first injection you experience at least one of the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor. If progesterone withdrawal is prescribed, stimulating therapy will be used in the future.
Drug interactions
The drug Progesterone is used strictly under the supervision of a gynecologist or reproductive specialist. You need to know how the active component interacts with the components of other drugs.
READ ALSO: Hormonal drug Oxytocin: instructions for use, indications for injections, possible side effects
Important details:
- the lactogenic effect of oxytocin is reduced by progesterone injections;
- the influence of indirect anticoagulants is reduced;
- the effect of antidepressants, diuretics, drugs for hypertension, Bromocriptine increases;
- the activity of synthetic analogues of gonadotropins increases;
- taking barbiturates reduces the effect of using the “pregnancy hormone” in the form of injections and vaginal suppositories.
Alcohol and hormonal drugs, including Progesterone, are incompatible.
When is treatment needed?
Injections are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor. Using them yourself without prior consultation is strictly prohibited! You need to understand that any attempts to regulate hormonal levels in the future will lead to negative consequences, and maybe even worsening the imbalance.
As a rule, in case of rare disruption of the menstrual cycle, conservative therapy is used, which consists of taking medications and vitamin complexes (increased amounts of vitamins A, E and C), which stimulate the production of sex hormones.
But even if this does not help, then progesterone injections are prescribed. Too long a delay can lead to partial atrophy of the organs of the reproductive system, followed by chronic infertility. This must be avoided at all costs.
Does it happen that taking a course of injections does not bring a positive result and your period never comes?
This happens quite often. In this situation, the doctor conducts an additional examination of the patient and sends her for repeated tests. If no contraindications are identified, progesterone injections are administered again. And so on until the required concentration of hormones is achieved. The only case where this will not happen is that the woman will be pregnant at the time of the prescribed course, but such cases are excluded, because the first step is to examine the pelvic organs.
Also, menstruation will not occur if there are physiological disorders in the reproductive system. That is, the organs of the genitourinary system simply do not perform their functions. Such cases are considered separately. A sexually transmitted infection may be detected, or perhaps a congenital pathology in the development of the ovaries (menstruation occurs randomly or is completely absent from birth).
Are there any contraindications to progesterone injections?
They are not prescribed for people under 20 years of age or for single cases of delay.
Their use is also prohibited during the period of infectious infection (even if it is a common sore throat).
There will be no point in taking injections even if a woman has been using hormonal birth control pills for the past few months. This is due to the pathological reaction of the immune system to a sharp artificial increase in hormone concentrations.
No injections
Not only injections can achieve hormonal balance. Injections that induce menstruation are a special case. Initially, the patient may be prescribed progesterone tablets, which act similarly, but the concentration of the hormone in them is lower.
The most popular drug based on this hormone is Norkalut. It is taken daily, 1 or 2 tablets, for 5 or 10 days. In this case, menstruation may begin while taking the pills or a few days after stopping them.
Every woman may experience a delay in her period, even if menstruation is delayed by 10 days - this is not yet a reason to sound the alarm. By the way, worrying is even harmful, since emotional stress interferes with the onset of menstruation. If you don’t have your period for a month, and the pregnancy test shows a negative result, then you need to see a doctor and take the pills he prescribed. If the tablets turn out to be ineffective, only then does it come to injections.
Progesterone is a steroid hormone that is produced in both women and men. The ovaries are responsible for the production of this hormone in women, and the testes in men. The substance is secreted in small quantities by the adrenal glands in women and men. The functions of progesterone in the human body are directly related to the functioning of the reproductive system.
Progesterone injections can be prescribed for various indications, the most common of which are:
The need to use progesterone injections for certain purposes is determined by taking a special blood test.
Only the attending physician can prescribe progesterone injections - self-medication in this case is strictly prohibited (especially during pregnancy), because only a specialist can determine the very need for treatment with progesterone, as well as the exact dosage of the drug.
If your doctor has prescribed progesterone injections to induce menstruation or during pregnancy, then you must complete the entire course of treatment without interrupting it or ending it prematurely at your own request.
Analogues of the drug
You can find out about similar drugs that cause the onset of menstrual periods from the pharmacist at the pharmacy. There are a number of drugs that are similar in their effect to Progesterone. They differ in names, composition and list of contraindications.
Medicines that can replace Progesterone to induce menstruation include Utrozhestan, Duphaston, Dydrogesterone, Norkolut, etc. However, before choosing one of the listed medications instead of Progesterone if there is a delay, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist, because the result of taking them can be unpredictable.
Method of congestion and dosage
Progesterone should be administered internally or subcutaneously.
It is important to treat it with extreme caution in case of illness of the cardiovascular system, epilepsy, migraine, diabetes, arterial hypertension, chronic neurological insufficiency, bronchial ї asthma, depression, hyperlipoproteinemia. It is also important to pay special attention to the use of progesterone in patients with mental disorders in the history of illness.
During the period of ingestion of Progesterone, it is important to carefully control the level of glucose in patients with diabetes. In addition, it is necessary to be aware of the first signs and symptoms of thromboembolism. If the stench grows loudly, it is necessary to rejoice.
It is not necessary to supplement this hormone for the treatment of patients with impaired liver function or in cases of bleeding from the urinary tract, if the cause has not been established.
Early pregnancy: it is possible to delay menstruation if you are taking high doses of Progesterone.
If dysfunctional uterine bleeding is detected, 0.5-1.5 ml of 1% dose is prescribed daily, the treatment period is 6-8 days. If the mucous membrane of the uterus was removed in advance, then injections of Progesterone begin to work after 18-20 days.
For hypogonadism and amenorrhea, estrogen drugs are administered to the kidney. Once their congestion is completed, then they begin to congeal Progesterone 0.5 ml 1% dose daily or 1 ml 1% dose every other day for 6-8 days.
In case of algodysmenorrhea, the hormone must be taken 6-8 days before the onset of menstruation. Administer injections of Progesterone daily, 0.5-1.0 ml of 1% solution, the treatment period lasts for about 6-8 days.
To stop the weekend threat, inject 0.5-2.5 ml of 1% progesterone solution every day or every other day until the symptoms of the weekend threat disappear.
In addition, it is important to note that the maximum single dose for adults when administered internally is 25 mg.
Children
Progesterone is not prescribed for children.
Showing
Women should take progesterone if they have:
- amenorrhea;
- anovulatory uterine bleeding;
- endometriosis;
- endocrine infertility, including caused by insufficiency of the endocrine body;
- non-existent vaginosis (severe or fleeting weekend due to insufficiency of the function of the abdominal body);
- oligomenorrhea;
- PMS;
- uterine fibroids;
- algodismenorrhea (through hypogonadism).
In addition, Progesterone is used to suppress lactation in Chiari-Frommel syndrome, reduce proliferative processes, as well as their liquidation in the mucous and meatballs of the uterus.
Contraindicated
Progesterone should not be prescribed if:
- increased sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- impaired liver function, hepatitis, benign hyperbilirubinemia, hepatic and nitric deficiency;
- cholestatic swelling during pregnancy (indicated in the history of illness);
- new creation of the mammary ovary or state organs;
- tachycardia, weakness of the body to thrombosis, active venous or arterial thromboembolism, severe thrombophlebitis;
- porphyria;
- nervous disorders with symptoms of depression;
- Vagity after the 36th year, post-natal vaginity or frozen vaginess in the anamnesis;
- Vaginal bleeding due to uninstalled gait, as well as after an abortion.