The essence of the technique
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the ability of ultrasound to penetrate the tissues of the human body. Having reached a dense structure - bones, internal organs - ultrasound is reflected from them and returns back. Sound is not reflected from liquid and air, but is dissipated.
The device's sensor, which emits ultrasonic waves, picks up the reflected sound and transmits it to the computer. There it undergoes processing, which results in an image. Taking into account what the reflected sound shows, the doctor makes a conclusion about the condition of the woman’s pelvis.
Each organ has its own density. The higher it is, the faster the sound is reflected. Such tissues are called hyperechoic and include bones, some types of tumors, and stones. They are shown in white in the picture. Most tissues have a medium echogenicity and appear as a light or dark shade of gray on the scanogram.
What can you see on an ultrasound before ovulation?
An ultrasound examination, which is scheduled for the period from 7 to 17 days of the cycle, involves determining ovarian pathologies. During this period, their active work begins: follicles are formed that are larger or smaller in size.
The largest ones are called “dominant”. They will be the suppliers of eggs in this cycle. It is quite difficult to establish the normal size of the ovaries for this period, since the values change every day.
It is important to know what pathologies can be diagnosed by a specialist during this period:
- polycystic disease (characterized by a large number of follicles in the ovary and small size of the uterus);
- anovulatory cycle (there are no dominant follicles, the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ does not correspond to the day of the cycle);
- follicular cyst (an overgrown follicle that will no longer be able to perform its function, as a result of which it will develop backwards).
In the middle of the cycle, pathologies of hormonal origin are mainly established.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women: what shows how to prepare, how they do it
Examination of the pelvic organs using ultrasound is one of the main instrumental methods for diagnosing diseases of the urinary and reproductive system. Ultrasound helps to see pathologies in the initial stages of their development. The procedure requires proper preparation, on which the reliability of the results depends.
Advantages of the method
Today, ultrasound is one of the most common procedures used in gynecology to diagnose most diseases. This instrumental research method has a number of advantages:
- Absolute painlessness of any type of procedure;
- ease of use;
- no age restrictions;
- high information content;
- no side effects;
- the opportunity to examine the state of internal organs from different angles.
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is done in the following cases:
- conception planning – to assess the condition of the internal genital organs;
- determination of follicle supply;
- ovulation tracking;
- pregnancy - scheduled screenings are carried out three times during gestation;
- preparation for the installation of an IUD;
- monitoring the patient’s condition after an abortion;
- infertility treatment;
- inflammatory diseases of internal organs and the urinary system - endometriosis, adnexitis, cystitis, urolithiasis, etc.;
- menstrual irregularities;
- uterine bleeding;
- nonspecific discharge and pain in the lower abdomen;
- oncological diseases;
- preparation for surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity;
- rehabilitation period after operations;
- monitoring the condition of the genital organs in order to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
A referral for an OMT examination is issued by a gynecologist.
The time of the procedure depends on the indications. For example, if there are complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, problems with conception, menstrual irregularities and changes in the intensity of menstrual flow, an ultrasound scan is prescribed on days 5-7 from the beginning of menstruation.
To determine the functionality of the ovaries and their ability to form a follicle, pelvic ultrasound in women is performed several times during the menstrual cycle:
- on day 8-9;
- on day 14-15;
- on day 22-23.
During pregnancy, subject to its normal course, ultrasound is performed as planned approximately once every 3 months:
- at 11-13 weeks;
- at 20-22 weeks;
- at 32-36 weeks.
The specifics of preparing for the examination directly depend on the method of conducting the examination, so before the procedure it is necessary to clarify with the doctor exactly how the ultrasound will be performed.
It is preferable to carry out any type of diagnosis on an empty stomach. It is advisable not to eat for at least 8-10 hours.
A study in this way is usually prescribed on days 5-7 of the cycle, after the end of menstrual bleeding. It is necessary to prepare for the examination in advance - 2-3 days in advance.
Features of preparation include proper nutrition. It is recommended to avoid consuming the following products:
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- whole milk and fermented milk products;
- meat;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- spicy dishes;
- beans, peas, legumes;
- sweets;
- muffins.
The purpose of preparing for such an examination is also to change your diet. You need to stop eating foods that cause increased gas formation. Before undergoing an ultrasound, it is necessary to give several cleansing enemas. Often the procedure is performed by medical staff directly in the clinic.
Transabdominal ultrasound method
This examination method requires more careful preparation. It is necessary to avoid foods that increase the formation of gases 3-4 days before the ultrasound.
In addition to the dense abdominal wall through which the examination is carried out, it is the gases accumulated in the intestines that can prevent the doctor from examining the exact picture and drawing correct conclusions regarding the condition of the patient’s internal organs. (photo on the right)
The study is performed with a full bladder. A couple of hours before the appointed time, you need to drink 1.5 liters of water or take a diuretic tablet.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is carried out in a special diagnostic room using a device consisting of a sensor and a screen on which the image is displayed.
The patient needs to free the examination area from clothing and lie down on the couch. To relax your abdominal muscles, your doctor may recommend bending your knees.
Methods of conducting ultrasound examination:
- Transabdominal ultrasound. The essence of the method is to study OMT using a special sensor through the abdominal wall. Medical gel is applied to the device and the patient's abdomen. This procedure is used from the second trimester of pregnancy, during menstruation and uterine bleeding. Girls who are not sexually active are also prescribed this ultrasound procedure.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. In the case of such a study, the procedure is carried out by inserting a special sensor into the vagina. The dimensions of such a scanner are significantly smaller than the dimensions of a standard gynecological speculum. A condom must be worn on the device. This method is considered the most reliable and informative. The procedure does not hurt at all.
- Transrectal ultrasound. The study is carried out by inserting a special sensor into the patient’s rectum. This diagnostic method is used quite rarely. The main indication for such a study is a large tumor in the vagina. For girls who are not sexually active, transrectal ultrasound is prescribed if a previously conducted transabdominal examination turned out to be uninformative.
Diagnostics using ultrasound is carried out without punctures, incisions, injections and other surgical procedures, therefore the procedure is absolutely safe. Non-invasive examination has no side effects, contraindications or negative consequences.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women shows the presence of pregnancy at the earliest stage, allows you to determine the condition of the fetus and the degree of its development. Routine screening examinations make it possible to monitor the formation and growth of a child in order to take timely measures if any deviations from the norm are detected.
Ultrasound examination is a reliable method for the timely detection of ectopic pregnancy - a dangerous pathology that threatens a woman’s life. In this case, the fertilized egg is located in one of the fallopian tubes, and not in the uterine cavity.
When interpreting the results, the uzologist must take into account the woman’s age, the structural features of the internal organs, the number of births and abortions performed. Despite all the advantages and informativeness of ultrasound, a specialist cannot make an accurate diagnosis based on examination data alone.
Uterus and cervix
Ultrasound examination of the uterus makes it possible to assess its position, shape and size, and identify the presence of structural changes. Normally, the body’s indicators should be as follows:
- length – about 7cm;
- width – about 6 cm;
- anterior-posterior indicator – 4 cm.
In addition, using ultrasound, the doctor examines the condition and thickness of the endometrium. These indicators of the mucous membrane should correspond to the day of the monthly cycle.
The fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes are hollow in structure, so in a healthy state they are not visualized on the monitor. They are mainly examined to check patency when a woman has problems conceiving.
To do this, a contrast procedure is performed - a special substance is injected into the uterine cavity to assess the condition of the fallopian tubes and the presence of adhesions. Such an examination is prescribed on days 12-14 of the cycle.
Ovaries
Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the position, structure and size of the ovaries. Normally, the indicators should be as follows:
- length – about 3cm;
- width – about 2.5cm;
- thickness – about 1.5cm.
In women of childbearing age, the presence of follicular cysts in the appendages is a normal variant. Examination of the ovaries helps to identify the presence of cysts, polycystic disease, salpingitis and malignant neoplasms.
Bladder
The study allows you to determine the size, shape of the hollow organ and the patency of the ureters. Normally, the bladder should be free of stones, sand and tumor growths. After emptying, the organ should be completely freed from residual urine.
You can undergo OMT diagnostics at a antenatal clinic, a free hospital or an independent diagnostic center. Visiting a specialized clinic has a number of advantages:
- guarantee of obtaining accurate research results;
- carrying out the procedure using the latest medical equipment;
- pre-entry;
- the possibility of a specialist visiting your home with equipment;
- competent customer service;
- no queues.
A network of private medical services is widely popular, in whose diagnostic rooms a comprehensive examination of the abdominal and abdominal organs, the genitourinary system, and mammography is performed. The cost of an ultrasound scan in the clinic is about 900 rubles.
In Russia, ultrasound services are also provided by other private clinics. The price of a pelvic ultrasound for women varies from 1,000 to 6,000 rubles, and interpretation of the results is usually included in the price.
Today, due to poor ecology, carcinogenic foods and unhealthy lifestyles, women are increasingly exposed to various diseases. However, any pathologies in the body must be promptly identified and eliminated in order to prevent the situation from worsening.
Ultrasound examination (US) will come to help diagnose the pelvic organs (PIO). It should be noted that it is necessary to go to a medical center for such a diagnosis not only in cases of any symptoms of the disease.
You should not be afraid of such a procedure; in addition, it is better to put all prejudices aside and carefully monitor your health. In this article we will talk about what a pelvic ultrasound in women is, what this procedure shows and how to prepare for it.
What does it show
What organs does the specialist examine?
Ultrasound diagnostic testing in women is carried out in several ways. Depending on the state of health, the abdominal, vaginal or rectal route of delivery of sound waves is selected.
What can be seen during diagnosis? Using a conductor sensor and a special gel that improves contact, sound waves are sent that are inaudible to the human ear. They are reflected from the surface of organs and formations, after which they are transferred in the appropriate form to the device screen. A sonologist can see echogenic, hyperechoic, anechoic and other shapes. Based on the obtained indicators, a protocol is written.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvis includes examination of the rectum and part of the large intestine, examination of the bladder, ureter, but most often there is a need to examine the condition of the reproductive organs. These include the uterus with the cervical canal and cervix, the fallopian tubes with the ovaries. This is what an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women shows.
During the examination, the condition of the woman’s genital organs, such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tube, etc., is examined.
Norms at the beginning of the cycle
Typically, ultrasound scanning is performed immediately after the end of menstruation. Doctors choose the period from 3 to 7 days of the cycle. Depending on the intensity of bleeding and its duration, a certain period for manipulation is set. What can you see during it?
If you want to find out whether there are pathologies and malfunctions in the reproductive function, then you should do an ultrasound after menstruation. The following indicators are considered normal:
- the height of the reproductive organ is about 5 cm, and the width is 5, the thickness varies from 3 to 4 cm; after menopause (after about 10 years), the height and width are reduced by 1 cm, and the thickness remains the same or decreases slightly;
- the reproductive organ is defined by smooth and clear contours, and its echogenicity is usually uniform;
- the condition of the internal cavity can change every day (in women with a long cycle the endometrium is not yet visualized, whereas with a period lasting 21 days or less it is already noticeable), additional inclusions and neoplasms are not detected;
- the size of the appendages (ovaries) is 3/2/2.5 cm (normally, one organ may be slightly larger than the other);
- the cervical canal is tightly closed, the cervix is without any features or additional inclusions.
An ultrasound can be considered ideal, the conclusion of which indicates “normal” or “no abnormalities.” But this is not always the case. If you are referred for research at the beginning of the cycle, they are expected to see some pathologies. This is the best time to diagnose diseases such as ovarian cysts, fibroids, and uterine polyps. What can you see if they are present?
Contraindications
Vaginal ultrasound examination has a small number of contraindications:
- It is never performed if the patient is a virgin, so as not to violate the integrity of the hymen. In this case, such a patient can undergo a transrectal examination, in which a sensor is inserted into the rectum
- The study is prohibited from being carried out in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, because it may provoke premature contractions or uterine contractions before the expected due date.
- This test is not used if the patient is allergic to latex
- If the patient has epilepsy, since the examination requires that she lie still
Ultrasound of the female pelvis is actively used in gynecology. Using ultrasound, they determine whether a woman is pregnant and monitor its progress. The method is used to diagnose various diseases of the reproductive and urinary system.
Women are prescribed an ultrasound of the pelvic organs with the following symptoms:
- delayed menstruation;
- heavy menstrual bleeding;
- bleeding outside of menstruation;
- chronic pain in the lower abdomen;
- urinary disturbance.
The procedure for ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in women is the only diagnostic method that has almost no contraindications. The examination is safe even for pregnant women. Relative contraindications include inflammation of the abdominal wall or external genitalia.
Indications for transabdominal ultrasound
Ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs in women with a transabdominal sensor is performed for the following indications:
- pain syndrome of unknown etiology;
- suspicion of inflammation of the uterus, tubes, ovaries;
- bladder diseases (tumors, inflammation, stones);
- suspicion of neoplasms of the uterus or appendages (cysts, fibroids, cancer);
- control of the size of uterine fibroids;
- suspicion of genital endometriosis;
- diagnosis of pregnancy, including ectopic;
- monitoring the condition of the fetus and placenta;
- post-abortion and postpartum period (exclusion of remnants of the fertilized egg, parts of the membranes and placenta);
- folliculometry (for infertility);
- monitoring the condition of the ovaries during IVF;
- control of the presence of the IUD in the uterine cavity;
- selection of hormonal contraceptives;
- preventive examination;
- cervicometry during pregnancy.
There are no absolute contraindications to performing a pelvic ultrasound through the anterior abdominal wall. But it is recommended to shift the date of the study to a later time in case of pustular skin lesions, dermatitis, burns and the presence of damage to the skin, so as not to provoke the activation or spread of the inflammatory process.
An ultrasound procedure is usually prescribed when a disease is suspected. Indications for ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs are:
- prolonged pain in the lower abdomen;
- difficulty urinating;
- menstrual irregularities;
- the appearance of intermenstrual bleeding;
- prolonged high temperature without external signs of a cold;
- lower back pain.
A comprehensive ultrasound of the female reproductive organs is prescribed if a woman has problems conceiving or bearing a child. OMT ultrasound is performed on pregnant women in each trimester to assess fetal development. The procedure is recommended for men if they have problems with erection or chronic pain in the lower abdomen.
Ultrasound diagnostics is safe for humans. There are no medical contraindications for it. But there are situations in which it is impossible to perform an OMT ultrasound.
Relative contraindications are:
- pronounced fatty tissue on the abdomen in women, flatulence - for the transabdominal technique;
- early period after surgery on the genitals or rectum.
The absence of a negative effect of ultrasound on the body explains how often ultrasound OMT can be performed without danger to health. The procedure is considered to be extremely safe, so it can be done as many times a year as necessary to control the disease. You should follow the recommendations of doctors - usually the test is prescribed no more than 4 times a year.
How is the procedure done?
The study is organized as follows:
- The patient should remove clothing from the lower part of the body (from the waist down)
- She sits on a special couch in the same way as during a regular gynecological examination.
- The doctor prepares the sensor: puts an individual condom on it, lubricates it with a special gel for the procedure
- The physician then inserts the device shallowly into the patient’s vagina.
- To get a complete picture of the state of the organs, he can move the sensor from side to side
- All data is recorded and processed by a doctor
The gel is necessary to facilitate the penetration of the sensor (and thereby reduce the likelihood of negative sensations) and enhance the ultrasonic effect by increasing conductivity.
This type of examination lasts no more than 10 minutes. It is painless and gives the most complete picture even in cases where an abdominal ultrasound shows nothing or cannot be performed.
How the research is carried out
Ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs lasts 5 - 10 minutes. The patient is asked to undress to the waist or expose the anterior wall of the abdomen and lie down on the couch. The doctor applies a special gel to the abdomen to improve sound transmission and begins to move the sensor over the skin of the abdomen. If necessary, the patient is asked to turn from side to side.
There are several types of ultrasound OMT. They differ in their technique and access to internal organs.
- Transabdominal. The examination is carried out through the anterior abdominal wall. Used in pregnant women and small children if there is no access through the vagina or rectum. The accuracy of the study is low because the organs are located below the level of the pelvic bones.
- Transvaginal. The sensor is passed through the vagina. The effectiveness of the method is the highest, so it is used in most patients.
- Transrectal. The sensor is passed through the rectum. The method is used in men and virgins.
The diagnostic method is determined individually, depending on the characteristics of the female body and the suspected disease. Also, the HTA examination can be simple and expert. The difference between an expert ultrasound of the pelvic organs and a simple one is that the examination is carried out by a highly qualified specialist using modern technology. The procedure is prescribed if there are difficulties in making a diagnosis.
Examination of children
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in little girls is performed transabdominally. The transvaginal method using a special pediatric sensor is very rarely used. Transrectal ultrasound OMT is not performed on a child.
Features of conducting OMT also depend on the chosen technique.
- During a transabdominal OMT examination, it is suggested to lie on your back and expose your abdomen. The doctor lubricates the skin with sound-conducting gel and moves the sensor along the lower abdomen.
- For a transvaginal OMT examination, a woman will need to sit in a gynecological chair. A special attachment is used for the sensor, which is inserted into the vagina.
- When performing TRUS, the patient is positioned on his side with his legs bent. The sensor is inserted into the rectum.
The examination lasts 15-30 minutes, depending on which OMTs need to be examined. After the doctor conducts the examination, he will write down all the results obtained. The patient is given a written report and a printed image. The shelf life of an ultrasound OMT report is usually no more than 6 months.
If bloody discharge from the vagina appears after the vaginal procedure, you should consult a gynecologist. Possible damage to the vaginal mucosa or cervix. You should also consult a doctor if your lower abdomen hurts for a long time after the procedure.
How to properly prepare for a pelvic ultrasound for a woman
Many people are interested in how pelvic ultrasound is performed in women and how to prepare for such a procedure. Ultrasound examination is one of the most harmless and highly accurate diagnostic methods.
Ultrasound examinations of organs in the pelvis can be prescribed by a doctor if there are certain indications. These include:
- pathologies of inflammatory etiology, for example endometritis, cystitis, vulvovaginitis, parametritis;
- presence of suspicion of the development of a tumor disease in the pelvic organs (fibroids, neoplasms of various etiologies);
- pregnancy;
- determining the number of available follicles and identifying the process of ovulation in the ovaries;
- clarification of the condition of the cervix (carried out during pregnancy and after childbirth);
- monitoring the status of the installed intrauterine device;
- monitoring the patient’s condition after surgery (especially after artificial termination of pregnancy).
Women in healthy condition should undergo ultrasound diagnostics for preventive purposes at least once every 2 years. Over the age of 40, this procedure is recommended to be performed every year. This will help identify any diseases that occur in a latent form. Preventive ultrasound should be performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (5-7 days after the start of menstruation).
During a standard examination, a specialist assesses the condition of certain internal organs, taking into account the following characteristics:
- the location of the uterus relative to the pelvis and nearby internal organs;
- the size of the uterus and the types of its contours;
- structural structure of the muscular and mucous tissues of the uterus;
- the dimensions of the inner surface of the uterus, the structure of its walls;
- the size of the cervix, its location and the integrity of the layers;
- the size of the ovaries and the structural structure of the fallopian tubes;
- the condition of nearby tissues and various internal organs.
What does it show
Using an ultrasound machine, you can learn more about the following:
- localization of the uterus;
- general characteristics of the uterus;
- general structure of the myometrium and endometrium;
- internal characteristics of the uterus (wall smoothness);
- characteristics of the cervix (localization, general structural indicators);
- structural and functional characteristics of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Important! 2 days before the ultrasound examination, it is better to refrain from eating raw fruits and vegetables.
An ultrasound examination is often done to identify any pathologies when corresponding symptoms appear.
This research will help with the following:
- identifying the cause of the presence of red blood cells in the urine;
- checking normal bladder function;
- determination of the presence of oncological diseases OMT;
- facilitating the biopsy procedure and pumping out fluid from the formed cyst;
- determination of viral and bacterial diseases OMT, vaginal bleeding;
- searching for an intrauterine device;
- determining the presence of a child in the womb, diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy;
- detection of uterine fibroids, swelling.
As you can see, scientists in the fields of biology and medicine have found a way to use ultrasound for the benefit of society. An ultrasound examination can reveal almost any OMT pathology; moreover, such a procedure is absolutely painless.{amp}lt;p{amp}gt;
Ultrasound examination is not only a safe procedure, but also highly accurate. For example, dangerous X-ray diagnostics may cause errors due to the movements of the patient being examined.
The preparation rules depend on the choice of methodology. During transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women, the view is obstructed by intestinal gases. Therefore, preparation includes following a diet. Before diagnosis, you should not eat foods that cause severe gas formation - milk, brown bread, cabbage.
A diet is prescribed three days before the procedure. You can eat before the examination no later than 10-12 hours. Come for an ultrasound on an empty stomach, you can drink a glass of water.
If you are planning a transvaginal pelvic examination, there is no need to restrict food. It is enough to take normal hygiene measures before the procedure. To examine the bladder, you need to fill it. A woman drinks a liter of water 1-1.5 hours before the procedure; she must not urinate.
They determine in advance on what day of the cycle they will do a pelvic ultrasound. The condition of the reproductive organs directly depends on the phase of the cycle. The diagnostic standard is immediately after menstruation or after 2-3 days. For some diseases, ultrasound is performed several times during the cycle.
What does an ultrasound show?
An OMT ultrasound looks at the condition of the reproductive and urinary organs. Their size, structure, and the presence of pathological changes are determined.
We suggest you read why your hands go numb while sleeping at night: causes, treatment
A comprehensive ultrasound examination involves examination of all of the above organs. It is rarely done. Usually, examination of only those structures that give pathological symptoms is prescribed.
With the help of ultrasound, you can see various OMT diseases:
- cysts;
- tumors;
- inflammation;
- developmental defects;
- stones;
- injuries.
Sometimes OMT ultrasound is prescribed to assess a woman’s condition over time after surgery. An ultrasound scan after childbirth is indicated if there were complications during pregnancy and delivery.
When is a pelvic ultrasound with a sensor necessary?
There are symptoms in which the doctor must refer the patient for a transvaginal examination:
- Pain in the lower abdomen (not related to the menstrual cycle)
- Suspicion of the presence of neoplasms
- Periods of menstrual bleeding that are too short, too long or absent
- Impossibility of pregnancy
- Bloody discharge that is not menstruation
- Presence of fallopian tube obstruction
- Nausea, vomiting and weakness with bloody discharge from the vagina
Doctors recommend using this type of examination for preventive purposes, since not every ailment may have symptoms at an early stage, just as pregnancy in the first trimester may not manifest itself with classic symptoms (nausea, etc.).
In this case, vaginal ultrasound is used for:
- Diagnosis of infertility
- The need to determine the presence of changes in the size of the ovaries and uterus
- Diagnosis of pregnancy
- Pregnancy monitoring (first trimester only)
- General monitoring of the condition of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries
A pelvic ultrasound can be performed simultaneously with two sensors. In this case, an abdominal ultrasound examination is performed first, and then a transvaginal one. The use of two types of analysis at once is necessary to identify disorders in the high-lying pelvic organs.
Preparation for ultrasound diagnostics
Transabdominal ultrasound is performed using an external probe through the abdominal wall with a full bladder. To do this, a woman needs to drink about 1 liter of water an hour before the examination and not urinate.
Transvaginal - for a more detailed study of the condition of the uterus and ovaries, a special sensor is used, which is inserted into the vagina. No preparation is required for this procedure.
The ultrasound examination procedure does not require complex and lengthy preparation. It is better to come to the procedure in loose and comfortable clothes.
If a transabdominal examination is prescribed, the patient should arrive with a full bladder. To do this, you need to drink 3-4 glasses of water two hours before the test. This is necessary so that the doctor can easily visualize the ovaries and uterus.
Typically, diagnosis is prescribed on days 5–7 of the female cycle, that is, when menstruation ends.
All this is done to reduce the formation of gases in the gastrointestinal tract, since gases can reduce the accuracy of the data obtained. In the evening, the day before the examination, you should give an enema.
You should also prepare for this type of examination: a diet that excludes foods that can cause increased gas formation. In the evening before the day of the examination, you need to do a cleansing enema. Before the examination, be sure to go to the toilet and empty your bowels.
If you choose this method, you need to prepare for 3-4 days. This is how long you need to follow a special diet of foods that will not cause increased gas formation. Let us remind you that the gases accumulated inside will prevent the doctor from seeing the exact picture and drawing the right conclusions. When preparing for the examination, you should avoid:
- sweets, buns;
- alcoholic drinks;
- fatty foods;
- beans, peas, legumes;
- spicy dishes;
- carbonated drinks.
A moderate desire to visit the toilet should indicate that the organ is filled to the required level. This condition of the bladder will facilitate diagnosis - it will help the uterus take a place convenient for examination, and will displace the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract from view.
When should women undergo a pelvic ultrasound examination using this method? It is advisable to be examined on days 5–7 of the menstrual cycle.
Normal indicators
Interpretation of ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women begins with measuring the size of the uterus. The length, defined as the distance from the fundus of the uterus to the internal os of the cervix, should be 5–8 cm. The average length in healthy nulliparous women should be in the range of 6.0–7.1 cm. In women who have given birth to one child, there is a slight increase uterine body, more pronounced after several births.
The anterior-posterior size (thickness) of the uterus should normally be within 3–4 cm, and the transverse size (width) should be 4.5–6.0 cm. After several years after the decline of reproductive function, it is permissible to reduce the size of the uterus to 4 –5 cm. An important factor taken into account when assessing the condition of the female reproductive organs is the position of the uterus.
Normally, it is located in the central part of the small pelvis, deviating towards the anterior abdominal wall. This situation in the examination protocol is designated by the term “anteflexio”. The term “retroflexio” refers to a physiological disturbance in the position of the uterine body caused by its deviation back, that is, “bending”, and “lateroflexio” means a displacement of the uterus relative to the central axis of the body.
Important! When assessing the position of the uterus, it should be taken into account that a full bladder causes some deviation from its normal position.
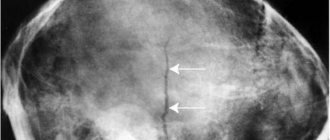
An ultrasound image shows the uterus on the 19th day of the menstrual cycle. The length of the uterine body (number 1) is 57.6 mm, the width (number 2) is 42.9 mm, the width of the uterine cavity (number 3) is 7.1 mm
The cervix on an echogram is defined as a 2–3-centimeter formation, cylindrical in shape, with echogenicity indistinguishable from the uterus. The width of the cervical canal should be between 3–4 mm. When examined by ultrasound, the ovaries appear as oval formations located on both sides of the uterus. The normal length of the ovaries should be 2.7–3.7 cm, width 2.1–2.9 cm, and anterior-posterior dimension – 1.7–2.1 cm.
In general, the size of the ovaries can vary within quite a wide range, since during the growth of the follicles the ovary enlarges. After the isolation of the dominant follicle, which is determined in the first phase of the cycle in the form of a small formation (0.5–1.3 cm), which continues to grow actively until the 12–14th day of the menstrual cycle, the rest decrease again, and the ovary acquires normal size.
By the day of ovulation, the follicle can reach 1.5–2.9 cm in size and can be clearly identified on ultrasound. By visual assessment, the size of one ovary should not exceed half the width of the uterine body. Normally, fallopian tubes are not visible on ultrasound. Immediately after ovulation, the formation of the corpus luteum, a temporary hormone-producing gland, begins, the main purpose of which is to ensure implantation of the embryo and maintain pregnancy.
Preparation for ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women
The corpus luteum appears to be a small formation with heterogeneous thick walls and liquid contents. The entry in the ultrasound examination protocol “corpus luteum cyst” is assessed based on the timing of the diagnosis, since detection of a cyst after ovulation indicates normal functioning of the reproductive system, and before ovulation – a pathological formation.
The endometrial layer in the uterine cavity in the first days of the menstrual cycle is defined as a heterogeneous structure of varying thickness (from 0.3 to 0.8 cm). By the time menstrual bleeding ends (4–5 days of the cycle), the thickness of the endometrial layer is only 0.2–0.4 cm and is practically invisible on the echogram.
At the same time, its layering is clearly determined in the form of the appearance of a thin echo-negative contour 1 mm thick. By day 10, the thickness of the endometrial layer is about 1 cm. In the secretory phase (days 15–27 of the cycle), as well as during menstrual bleeding, a significant thickening of the endometrium occurs (sometimes up to 1.5 cm), which is noted on the echogram in the form of a thickened reflective surface internal cavity of the uterus.
Important! Detection of the corpus luteum and thickened endometrium at the beginning of the menstrual cycle, in the absence of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, can serve as an indirect sign of ectopic pregnancy.
An ultrasound image shows the uterus on the 25th day of the menstrual cycle. The thickness of the endometrial layer is 1.0 cm
A pelvic ultrasound of a healthy woman meets the following criteria:
- pear-shaped uterus, dimensions 7.5x4 cm;
- uterine tubes are long hollow cylinders, 10-12 cm long;
- ovary size 2.5x3.5 cm, oval shape;
- the bladder is oval in shape, wall thickness is 2-4 mm;
- ureters are long, hollow cords.
The uterus and ovaries have medium echogenicity, that is, they are shown in gray in the image. Inside the ovaries there are dark inclusions - maturing follicles.
Research results
Ultrasound examination is also called ECHO diagnostics, since reflected waves are used to obtain an image. Ultrasound reveals diseases of the OMT, or the normal state of the studied systems. The result is presented in black and white. Different colors indicate fabrics with different densities.
The thicker the fabric, the lighter it will look in the photo. For example, bones and cartilage are represented in white. Soft tissues and fluids are marked in dark gray or black. Medium weight fabrics appear grey.
The OMT examination is carried out according to a certain algorithm:
- presence or absence of organs;
- dimensions;
- outlines;
- fabric density;
- the presence of pathological inclusions.
Data for each item is indicated in the conclusion.
Description of the norm
Each OMT has its own range of normal values. If a specialist sees deviations, he indicates them in comparison with the norm.
- The buds are bean-shaped. Their width is 4-5 cm, length - 11-12 cm. They are presented in a uniform gray color with slight darkening at the confluence of the ureters.
- The bladder has a round shape. Wall thickness - 2-4 mm. There are no foreign inclusions in the bladder cavity.
- The ureters are represented by narrow long cylinders up to 5 mm wide.
- The uterus is pear-shaped. Its length is up to 5-7 cm, width no more than 3-5 cm. It is presented in gray with a darkening in the middle. The thickness of the endometrium is from 5 to 17 mm, it depends on the phase of the cycle.
- The fallopian tubes are narrow, long cylinders with a widening at the end. Length 7-12 cm, diameter from 2 to 8 mm.
- The ovaries are oval in shape. Their length is 2.7-3 cm, width up to 2.5 cm. Sizes vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Presented in gray, with multiple darkening at the site of the follicles. If there are a lot of follicles, the term “multifollicular ovaries” is used. This is a variant of the norm.
- The prostate is shaped like a chestnut. Length from 2.5 to 4.5 cm. Width - from 2.3 to 4.1 cm. Shown in gray in the picture.
Ultrasound is used to determine OMT diseases such as tumors, cysts, developmental anomalies, and inflammation. Each pathology has its own characteristics.
- Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. Manifested by an increase in wall thickness of more than 4 mm. Stones may also be found in the cavity of the bladder. They look like rounded white formations up to 2 cm in diameter.
- On an OMT ultrasound, cavitary adhesions are clearly visible. These are growths of connective tissue that appear after inflammatory processes. In the picture they are represented by light stripes between the uterus, ovaries, and tubes.
- Fluid in the pelvis is also easily determined by ultrasound. In the lower part of the pelvic cavity, areas of darkening are visible, which move when the position of the woman’s body changes.
- Myoma is a benign tumor of the uterus. The picture shows the same color as healthy tissue. Fibroids are identified by thickening of the uterine wall in one or more areas. With large fibroids, nodes are visible protruding deep into the uterine cavity or outside it.
- Endometrial hyperplasia is an overgrowth of the mucous membrane. It is determined when the thickness of the endometrium increases by more than 17 mm 1-2 days before menstruation.
- Polyps are limited areas of mucosal growth. They are presented in gray color and have a round or elongated shape. Polyps are considered small if their size does not exceed 1 cm. Larger polyps are subject to removal followed by laboratory testing.
- Endometriosis is the appearance of uterine lining in other OMTs. During menstruation, such areas also bleed. The disease can be identified by dark areas inside the ovaries and bladder. The thickness of such areas changes during different phases of the menstrual cycle.
- Uterine sarcoma is a malignant tumor of muscle tissue. It is represented by a knot of light gray color and irregular shape.
- With endometrial cancer, its compaction is determined, having a lighter color than the rest of the mucous membrane. The tumor has a flattened shape.
- Polycystic ovaries are a hormonal disease characterized by the absence of normal follicles. Instead, cysts form - vesicles containing fluid. In the photo they are represented as dark rounded areas in the middle of the gray main fabric.
- A follicular cyst is the formation of a bubble with fluid instead of a follicle. It looks like a black rounded area. A corpus luteum cyst looks the same - it forms after a ruptured follicle.
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. An OMT ultrasound determines an increase in the size of the prostate, its color becomes darker.
- Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor. Located inside the prostate gland, it is represented by a darker-colored, rounded area.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of sweaty feet at home? Recipes and tips for getting rid of sweaty feet using pharmaceutical and folk remedies
To determine hormonal-dependent diseases of OMT, ultrasound must be done several times during one menstrual cycle.
During a transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs, the following are assessed:
- Uterus. Its size, position (deviation posterior, anterior or lateral), thickness and structure of the myometrium (presence/no space-occupying formations) are assessed.
- Endometrium (M-Echo). Its thickness is measured, its structure and homogeneity (polyps, hyperplasia, synechiae) are assessed.
- Ovaries. Their location, dimensions (width, length, thickness), organ structure, thickness of the tunica albuginea, the presence of follicles, including rupture of the dominant one, whether there are space-occupying formations (cysts, tumors) are described.
- Cervix. The length of the cervix, the condition of the cervical canal and internal os (IO), and the structure of the cervical tissue are assessed.
- Oviducts. Normally, the fallopian tubes are not visualized. In the presence of inflammation, they thicken and expand, and fluid accumulates in the cavity of the oviducts.
- Douglas space. The presence of fluid in the rectouterine cavity (blood or inflammatory exudate) is assessed.
Ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to clarify the gestational age, determine the number of fetuses and their fetometric indicators, the position and presentation of the fetus, the degree of maturity of the placenta, the volume of amniotic fluid, and the condition of the cervical canal.
Diagnosed diseases
Ultrasound can detect pelvic pathologies in the early stages. Each disease has its own echographic signs.
- If endometriosis is suspected, areas of the uterine mucosa are found where they should not be - the cervix, fallopian tubes, pelvic cavity. They look like dark gray stripes on a lighter background.
- With fibroids, benign tumors appear in the wall of the uterus. They are formed by the same muscle tissue, so they do not differ in color in the picture. Fibroids are defined as thickening of the uterine wall.
- Uterine sarcoma is a malignant tumor. It is denser than the surrounding tissue, so in the picture it looks like a light or white thickening in the uterine wall or cavity. There are usually many vessels around it.
- Aplasia of the uterus or fallopian tubes. This is a complete absence of reproductive organs; they are not visible on the scanogram.
- Obstruction of pipes. Caused by adhesions or malformations. The picture shows the absence of a dark stripe inside the pipe - its cavity.
- Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluid. The scanogram shows dark round spots with light rims.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome. Hormone dependent disease. The image reveals enlarged ovaries covered with dark areas - many cysts.
- Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. Its wall thickens by more than 4 mm, and in the picture it looks darker than healthy.
- Bladder tumor. A light or dark formation, usually growing inside the cavity of the bladder.
- Urolithiasis disease. At the bottom of the bladder, light round formations are found - salt stones.
Diseases of the reproductive system rarely occur in isolation; various combinations of them are more often observed.
Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to identify a number of diseases and problems in the reproductive system at an early stage. It allows you to detect:
- Fluid and pus in the uterus and fallopian tubes. The cause of their appearance may be infections, viruses, mechanical damage
- Endomentriosis is an excessive proliferation of cells in the inner layer of uterine tissue into other layers and organs. It can occur due to inflammatory processes, damage (surgery, abortion), the appearance of neoplasms, disruption of the endocrine system, too frequent use of certain medications and substances
- Myoma is a benign neoplasm in the tissues of the uterus or its cervix. May occur due to chronic diseases, frequent abortions, hormonal imbalances, constant stress, pathologies, excess weight, or with hereditary predisposition
- Cysts and polycystic ovaries are tumors filled with fluid. Occurs with endocrine disorders, chronic diseases of the genitourinary system
- Various polyps on the walls of the uterus are benign formations in the endometrium of the organ. They can reach several centimeters in diameter. Their appearance may be associated with polycystic disease, chronic diseases, mastopathy, fibroma
- Inflammation and enlargement of organs can occur due to both infection and injury.
- Hydatidiform mole - appears instead of a full-fledged embryo during the process of conception, filled with fluid. Occurs due to duplication of male chromosomes with the loss of female chromosomes, sometimes due to fertilization of an egg that does not contain a nucleus. This disease is rare
- Fetal development disorders during pregnancy
- Defects and pathologies in the development of the fallopian tubes: obstruction, spiral-shaped or too long tubes, blind passages, duplication of organs
- Ectopic pregnancy occurs when an egg implants outside the uterine tissue after fertilization. Occurs due to blockage of the fallopian tubes, congenital anomalies in them, as well as after an inflammatory process, abortion
- Cancer is a malignant tumor in various organs:
- Chorionepithelioma is a malignant neoplasm that arises during or after pregnancy from chorion cells (the membrane of the embryo attached to the wall of the uterus)
Cost of the procedure
A woman can have a gynecological ultrasound done at a clinic at her place of residence. With a referral from the attending physician, the procedure is free. The cost of examination in private centers depends on which organs will be examined.
| City | Price, rubles |
| Moscow | 300-1500 |
| Saint Petersburg | 350-2000 |
| Ekaterinburg | 300-1200 |
| Novosibirsk | 350-1800 |
| average cost | 325-1625 |
Pelvic ultrasound is prescribed to women to confirm pregnancy and identify diseases. The procedure is carried out in several ways. It has no contraindications and is safe for the female body.
In what phase of the menstrual cycle should a pelvic ultrasound be performed?
On what day of the cycle an ultrasound should be done is indicated by the doctor. The exact date depends on the expected diagnosis and the woman’s general well-being. For example, an emergency examination is carried out in case of bleeding or pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, the day of the menstrual cycle does not matter.
If there is a suspicion of uterine fibroids, then the manipulation is carried out immediately after the end of menstruation. To diagnose endometriosis, an ultrasound is performed before the onset of menstruation. When planning a pregnancy, the patient undergoes research in the first and second phases of the cycle.
During pregnancy, ultrasound diagnostics are performed to confirm the fact of pregnancy and in each trimester. At 11-12 weeks, the doctor conducts the first fetal screening, and at 18-22 weeks - a second screening and 32-34 weeks - an ultrasound of the fetus. Every study is important because... allows you to identify a certain pathology of the fetus at each stage.