What does a blood test show for rheumatic tests?
To determine the level of spread of inflammatory processes in the tissues of the body (joints, organs), their exact location and type, a special study is used - analysis for rheumatic tests. Let’s take a closer look at what it is and when it is prescribed.
Analysis for rheumatic tests is carried out to identify inflammatory processes in body tissues
Why is the analysis prescribed?
To understand the purpose of the analysis, you need to know the answer to the question: “Rheumatic tests - what is it?” Rheumatic tests are a research method performed separately or as part of a comprehensive examination to detect inflammation processes. Inflammation can be acute, chronic, or autoimmune. The analysis is prescribed for the initial determination of the diagnosis, differential diagnosis with similar symptoms, prognosis of the development of the disease, selection and evaluation of an effective method of correct treatment.
Indications for testing
Rheumatoid tests or rheumatic tests are prescribed by a doctor to confirm autoimmune pathologies:
- arthritis;
- thyroiditis;
- polymyositis and autoimmune prostatitis (in men);
- multiple sclerosis;
- scleroderma.
Often, a rheumatoid test is prescribed to determine pathological changes in connective tissue (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, gout).
Indications for such a study are the following symptoms of disorders in soft tissues:
- swelling and pain in the joints;
- changes in body asymmetry;
- impaired mobility of joints and ligaments;
- pain in the lower back, and with weather changes - aches throughout the body;
- frequent headaches that do not respond to analgesics (a symptom of vasculitis);
- prolonged increase in body temperature without a clear reason.
Detection of antibodies to streptococcus
Analysis for rheumatic tests detects antibodies to streptococci that arise at the slightest interaction with the pathogen. If the serological method shows a positive result, this means that there is a tendency to develop diseases such as: glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, acute tonsillitis and many others.
A marker of streptococcal infection is the protein antistreptolysin-O, found in the blood of patients with scarlet fever, myocarditis and meningitis. The microorganism periodically aggravates rheumatoid arthritis, therefore, a rheumatoid test must be tested every six months.
Antistreptolysin-O levels are higher in rheumatism, and in rheumatoid arthritis the values are much lower. Thanks to these antibodies, the two diseases can be distinguished. Various factors will influence the results of future analyses. For example, increased results are influenced by foods, physical activity, skin and liver diseases, and increased cholesterol levels. Antibiotics and corticosteroids are reduced.
Types of rheumatic tests
To confirm autoimmune diseases, a rheumatic complex of several types of markers is used:
- Antistreptolysin-O (ASLO) – identification of the body’s protective cells to streptococcal antigens. This is a kind of test for rheumatism, since ASLO in the blood helps to distinguish a similar disease from rheumatoid arthritis (the concentration of this marker in such pathologies is different).
- Rheumatoid factor (rheumofaktor). With rheumatoid disease, a protein appears in the blood, which the immune system accepts as a foreign body and begins to develop protection against it. The test for rheumatic factor consists of detecting such antibodies to self-antigens. The results allow the identification of connective tissue disease.
- C-reactive protein (CRP) is a type of rheumatic test that indicates an acute inflammatory process in soft tissues. The analysis helps to identify pathology in a timely manner and prescribe antibacterial therapy.
- Total protein. The marker makes it possible to determine the level of protein and its components - albumin and globulin.
- Circulating immune complexes (CICs). Identification of cells that are damaged by the body's protective compounds.
- General blood test (with leukocyte formula) - study of biological material for changes in the number of lymphocytes or neurophils. The test helps identify inflammation caused by infections.
Rheumatological analysis makes it possible to accurately determine the type and location of negative changes in soft tissues. Studying rheumatic tests in a biochemical blood test allows you to prevent the further development of a dangerous disease and select effective treatment.
Is there a possibility of a false result?
Often a decrease in markers occurs due to:
- excess lipids in the blood;
- taking steroid drugs;
- the occurrence of liver cirrhosis;
- destruction of red blood cells, accompanied by the active release of hemoglobin.
An increased result does not at all indicate inflammation if the person being examined:
- suffers from obesity or hyperhidrosis;
- previously had surgery;
- adheres to a low protein diet for a long time;
- smoked immediately before the procedure;
- recently suffered serious injuries;
- takes hormonal contraceptives.
It should be remembered that high rates are diagnosed in pregnant women and newborns for natural reasons.
Diagnostics using rheumatoid tests helps to correctly identify pathology in 90% of cases. At the same time, treatment of the disease achieves positive results under the control of markers much more often.
Let's consider the norms of the most common markers and their decoding.
Total protein
The total protein level refers to all protein components that circulate in the bloodstream. They play an important role in the body:
- Promote natural immune responses;
- Help beneficial substances “reach” the necessary organs and tissues;
- They “monitor” proper blood clotting.
The transcript of the study will normally show the following indicators:
- Children under 12 months – up to 74 g/l;
- Children from one to 4 years old – up to 76 g/l;
- Adolescents from 8 to 15 years old – up to 77 g/l;
- Adults under 60 years of age – up to 86 g/l;
- Patients over 60 years of age – up to 83 g/l.
Excessive levels of this immune marker indicate the presence of the following pathologies:
- Acute inflammation;
- Chronic pathologies;
- Systemic diseases.
Indicators significantly below normal indicate the following problems in the body:
- Insufficient protein absorption;
- Liver pathologies;
- Radiation sickness;
- Extensive swelling;
- Catabolism;
- Long-term plasma loss.
Albumen
The quantitative ratio of albumin and globulin to all other proteins is much higher. Thus, the protein content of albumin makes up more than 50% of all protein compounds. Its task is to transport calcium, potassium ions and hormones. It maintains the desired plasma blood pressure.
Test results that indicate normal albumin levels in the blood:
- In children under 14 years of age – 38-54 g/l;
- In adults under the age of 60 years – 15-60 g/l;
- In elderly patients over 60 years of age – 34-49 g/l.
Elevated albumin levels are caused by the following factors:
- Long-term use of retinol;
- Frequent use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Lack of fluid in the body;
- Prescription of diuretics and hormonal drugs.
Rheumatoid factor
Timely detection of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide means ensuring early diagnosis of a dangerous disease. They reveal the extent of the disease and its presence.
Chronic connective tissue diseases, pathologies caused by severe inflammation in the joint capsule, will cause the level of rheumatoid marker to increase.
In children under the age of 12 years, the presence of 12 IU/ml of the marker is not evidence of a disease; 14 IU/ml in adult patients is a sign of the absence of pathology. The above indications indicate lesions of the connective tissue and the presence of such diseases:
- Pathologies of infectious nature;
- Lupus;
- All types of arthritis;
- Diseases caused by damaged blood vessels;
- Oncological tumors;
- Polymyositis.
Reactive protein
This protein is found in blood plasma. Exceeded natural levels of reactive protein indicate danger: inflammation has taken on threatening forms. Moreover, the indicators will be high in any course of the disease. The marker will respond to the acute and chronic phases. High levels of protein and circulating proteins are a consequence of diseases of the joint tissue.
Such proteins disintegrate in 7 hours. This marker is often used to check the effectiveness of prescribed therapy. If a study during treatment shows the absence of this protein, then we can say with confidence that the patient is on the road to recovery.
Immune complexes and uric acid accumulating in organs and tissues are an indicator of the development of dangerous pathologies. The complexes contain antibodies and enzymes produced by the immune system.
Increased results of immunity complexes and uric acid - disruption of the kidneys, or rather, the structure of their glomeruli. The norm for all age groups should not exceed 90 U/ml.
If the result of immune complexes circulating in the blood is below 30 U/ml, then it is diagnostically useless.
Uric acid
The presence of uric acid in the blood indicates disorders of purine metabolism.
Let's consider the normal level of this acid in the blood of different age groups of people.
- Infants – 80-311 µm/ml;
- Babies from 2 months to 1 year – 90-373 µm/ml;
- From one year to 14 years – 120-363 µm/ml;
- With pathology in an adult woman, the indicator will be above 380 µm/ml;
- In an adult man – above 480 µm/ml.
Inflated study results are associated with the development of the following dysfunctions of the body:
- Kidney diseases;
- Tumors of a malignant nature;
- Gout;
- Severe thinness, exhaustion;
- Kidney and liver stones.
Antistreptolysin O
This is the name for antibodies that block the action of beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Their appearance is due to diseases from which the patient has recently recovered:
- Angina;
- Scarlet fever;
- "Erysipelas."
These markers help distinguish rheumatoid arthritis from rheumatism. This is very important, because the symptomatic manifestations of pathologies are almost the same. During the course of the first disease, the indicators are much lower than during the development of the second.
In conclusion, it should be noted that rheumatoid tests are an important diagnostic indicator. With their help, the presence and stage of the disease is established. However, immune marker “readings” alone are not sufficient to make a diagnosis. Its rationale is a comprehensive diagnosis of the patient. Since there have been cases where increased rates of rheumatic tests were recorded in completely healthy people. And in patients suffering from pathologies, the indicators were normal.
Tags: analysis, enter, rheumatic test
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Norms of blood parameters
There are generally accepted standards for rheumatic complex indicators that help confirm or refute the presence of pathology in the body.
Table “Acceptable values of rheumatic tests”
| Indicators and age group | Meaning |
| ASLO | |
| In adults | From 0 to 203 U/ml |
| In children (up to adolescence) | Up to 151 U/ml |
| Rheumatic factor | |
| In adults | Up to 15 IU/ml |
| In children (up to 12 years old) | Up to 13 IU/ml |
| C-reactive protein (regardless of age) | 0 (an indicator when the rheumatic test is positive, but not more than 5 IU/ml can also be considered a negative value) |
| Albumen | |
| In adults under 60 years of age | |
33–49 g/l
Antistreptolysin-O
The name of the antibody is similar to the name of the pathogenic microbe streptococcus, so it is not difficult to guess what this analysis shows. Hemolytic streptococcus, once in the body, produces the exotoxin streptolysin. In response to this, the body produces specific antibodies called antistreptolysin-O.
Antistreptolysin is a marker of streptococcal infection. The antibody level is an indicator by which the degree of activity of rheumatism is assessed and allows it to be differentiated from rheumatoid arthritis.
The amount of ASLO increases a month and a half after suffering streptococcal tonsillitis and remains for 6-12 months. Laboratory blood tests are carried out at least twice (with an interval of 7-10 days) to assess the dynamics of the process.
Important! If, after suffering from a sore throat, the joints and then the heart become ill in the second month, then first of all they are tested for ASLO.
ASLO norm for a healthy person:
- Ages over 14 years – up to 200 U/ml.
- Under 14 years old – up to 150 U/ml.
How to prepare for analysis
The results of tests for rheumatism and autoimmune pathologies largely depend on the patient’s preparation for the study.
- Venous blood is collected on an empty stomach in the morning.
- It is advisable not to eat anything from the evening until the time of the analysis. You can drink regular water without gas.
- Before donating blood (1-2 days before), do not drink coffee drinks, alcohol, or junk food. Do not smoke on the day of the test.
- At least a day before submitting biological material, reduce physical activity as much as possible, try not to become emotionally overtired, and avoid stress.
Avoid drinking coffee a few days before your test.
How to get tested for rheumatic tests
Blood for rheumatological examination is taken from a vein. To determine the three main markers (rheumatic factor, ASLO and C-reactive protein), it is enough to submit biological material once. The serum is divided into several parts to determine all the necessary parameters. If there are changes in the ASLO marker (suspicion of rheumatism), the test must be taken again after 7 days (the dynamics of the disease are monitored).
Blood and veins are taken for analysis for rheumatic tests
If necessary, a study of additional indicators (albumin, total protein, CEC) may be prescribed. In this case, you will need to donate blood several times - separately for a rheumatic test and for an additional biochemical test.
How long the analysis is done depends on the laboratory. Typically, the results are prepared within 1 working day, and the patient can find out them the next day after the material is collected.
Rheumatic tests: norm, table
It is impossible to retain all the values of the above-mentioned factors in one’s memory, therefore there are reference values of tests that are printed primarily for doctors, and not for patients. For this reason, you should not try to identify any pathology in yourself without the verdict of a medical specialist. When taking an analysis for rheumatic tests, decoding of certain parameters (rheumatic factor, antistreptolysin-O, C-reactive protein, uric acid) is carried out according to established data. For convenience, the values of the norms of the studies carried out were presented in the form of a table.
Revitalization tests: norm, table (main indicators):
Decoding the results
The rheumatic complex allows you to determine the disease with up to 90% accuracy. An increased rheumatic test is true evidence of pathology. But low values of such a result (below the norm) have no diagnostic value.
Table “Increasing markers of rheumatic tests”
| Changes in quantitative indicators | Decoding |
| Strong increase in ASLO in the blood | Rheumatism |
| High ASLO, but not off the charts | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Sore throat, chronic tonsillitis | |
| Osteomyelitis | |
| Scarlet fever | |
| High levels of rheumatoid factor | Scleroderma |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | |
| Injury to the walls of blood vessels | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| Diseases caused by infection - influenza, tuberculosis, rubella, measles, syphilis | |
| Oncological neoplasms | |
| Systemic damage to muscle tissue (polymyositis) | |
| Increased C-reactive protein | Inflammatory processes of an acute (20 times higher than normal) or chronic nature (10 times) that occur against the background of diseases of the joints or bone tissue |
Where can I get it and the price of the procedure?
Rheumatic tests can be done in any medical laboratory.
How much it costs, the analysis depends on the study itself:
- The price of a standard three-component rheumatic complex is on average 1230 rubles. ASLO – 300 rubles, C-reactive protein – 360 rubles, rheumatic factor – 300 rubles. The cost of collecting material is 270 rubles.
- The price of a comprehensive rheumatological examination is 2950 rubles. To the cost of a regular rheumatic test, a general blood test is added - 400 rubles, a study of erythrocyte sedimentation rate, albumin level - 500 rubles, detection of antinuclear antibodies - 550 rubles. Blood sampling for analysis – 270 rub.
Usually the doctor prescribes a standard rheumatic test. If its results do not coincide with the symptoms or the specialist has certain doubts, there is a need for a comprehensive rheumatological examination.
Analysis of rheumatic tests allows you to identify inflammatory processes in soft tissues in the early stages. Thanks to the study, it is possible to detect the cause of pathological changes, determine the dynamics of the disease and select adequate therapy. The main thing is that the results are reliable, and this largely depends on the correct preparation of the patient for the test.
source
Blood test for rheumatoid factor: preparation and interpretation
A blood test for rheumatoid factor is a diagnostic procedure that allows you to confirm or exclude an autoimmune lesion.
Rheumatoid factor is a protein complex that is perceived by the immune system as foreign. It is a combination of autoantibodies A, D, E, G and M.
Mainly, rheumatoid factor is represented by immunoglobulins M (they account for up to 90%). If at the initial stages of the disease they are synthesized in the cells of the synovial lining of the affected joint, then as the process progresses they can form in subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules, spleen, lymph nodes and bone marrow. Once in the bloodstream, antibodies react with normal immunoglobulins (IgG). As a result, a specific immune complex is formed, consisting of normal and pathological antibodies. It has a damaging effect on the vascular walls and joint tissues.
Normally, rheumatoid factor is not detected in the blood during a qualitative analysis. A quantitative test can detect its slight presence, not exceeding 14 IU/ml. In some situations, the analysis is positive when the patient feels completely normal.
Blood test for rheumatoid factor: what is it?
The test involves the detection of specific self-antibodies in the patient’s blood, which, under certain circumstances, change their characteristics and act as an autoantigen, reacting with IgG.
Types of analysis:
- Waaler-Rose reaction;
- latex test;
- nephelometric and turbidimitire determination of the factor;
- ELISA.
The Waaler-Rosev test, which has become a classic test, is now used relatively rarely.
A specific test for the passive agglutination reaction is carried out using sheep erythrocytes treated with anti-erythrocyte serum obtained from the blood of rabbits. The latex test (qualitative analysis) uses a latex surface on which normal human immunoglobulin G is aggregated. In the presence of rheumatic factor, their agglutination reaction begins. The technique is used mainly in screening studies, and in some cases gives false positive results. It is relatively simple and does not require expensive equipment. A positive latex test is not yet the basis for final verification of the diagnosis.
Nephelometric and turbidimitter determination of the factor (quantitative analysis) is more accurate; its results are in fairly good agreement with the latex test. The level of the pathological complex is determined in IU/ml. The result is assessed as positive if the numbers are > 20 IU/ml. In particular, against the background of rheumatoid arthritis, a titer of ≥ 40 IU/ml is determined.
A positive result is detected in 2-3% of completely healthy young people and in almost 15% of elderly people.
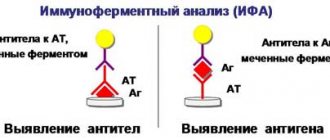
The ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method is considered the most informative. With its help, not only pathological immunoglobulins M are determined, but also Ig A, Ig E and Ig G, which are not possible to detect in other tests. Currently, this technique has been implemented almost everywhere.
Ig A is determined in severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis, and with concomitant vasculitis (inflammatory lesions of blood vessels), the level of Ig G increases.
Data evaluation criteria (in IU/ml):
- slightly elevated level – from 25 to 50;
- elevated – 50-100;
- significantly increased – over 100.
Normal values may vary between laboratories because different equipment and chemicals are used. The form where the data is entered must indicate reference indicators, which should be followed.
One way to determine the norm is to dilute the blood with saline solution 1:20. In a healthy person with such a concentration of biological material, the pathological complex is not detected.
What studies are carried out in parallel with the determination of rheumatoid factor?
In addition to the above studies, laboratories carry out the detection of C-reactive protein, which appears during the acute course of the inflammatory process, and another acute-phase marker - antistreptolysin-O. The presence of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide in the blood is also determined . Additional methods are needed for differential diagnosis with other pathologies with similar clinical manifestations.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will also need data from the following laboratory tests:
- CBC (complete blood count);
- liver tests (determined by a blood test for “biochemistry”);
- general urine analysis;
- analysis of synovial fluid (obtained during joint puncture);
- antinuclear antibody test;
- electrophoresis of plasma proteins.
C-reactive protein
This protein is produced in the liver in response to any inflammation, neoplasm, or injury. Participates in the activation of the immune system, in binding and removing the remains of destroyed cells from the body. Together with ESR, it is a specific marker of inflammatory processes.
The clinical significance of determining C-reactive protein is determined by the direct relationship between its amount and the degree of inflammation. Protein rises rapidly within the first hours after the onset of the inflammatory process, and just as rapidly falls as it subsides.
Important! In newborns, liver function has not yet developed, so inflammatory processes in them may not be accompanied by an increase in C-reactive protein.
The normal level of C-reactive protein is not higher than 0.5 mg/l. A low level or absence of this protein in the blood is not considered a pathology.
Deciphering the analysis for rheumatoid factor
Most often (in 80% of cases) the pathological complex is detected in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis (RA), especially in its most common form - synovitis (inflammation of the synovial membranes of the joints).
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects connective tissue. With this pathology, small peripheral joints are mainly affected.
It has been established that there are two types of RA – seropositive and seronegative. In the first case, the pathological complex is detected in a blood test, but in the second, it is not. A high titer of rheumatoid factor indicates a progressive course of the pathological process. A negative result obtained from a single test is not yet a reason to talk about the absence of RA, especially if there are characteristic symptoms of the disease.
Numerous clinical studies suggest that active production of antibodies is accompanied by many chronic inflammatory diseases.
The results of the study may be affected by certain pharmacological drugs. Against the background of the therapy, the results are often distorted and no longer reflect the real picture.
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, which manifests in children under 10 years of age, leads to an increase in the level of rheumatoid factor in only 5% of cases, even in the presence of an active inflammatory process. The high titer is primarily due to immunoglobulin M. The early onset of the pathology (before 5 years of age) is accompanied by the appearance of RF in an average of 20% of children.
In children who are often sick for a long time, the test may be positive even in the absence of signs of illness at the time of the test. This is due to the fact that IgM is produced against the background of prolonged immunostimulation against the background of past helminthic infestations, viral and bacterial infections. Such specificity of the factor reduces the diagnostic value of the study in pediatric practice.
Rheumatoid factor is always detected in Still's syndrome (a type of juvenile RA) and Felty syndrome, which is similar in symptoms (a type of RA with an acute onset).
With liver cirrhosis and active hepatitis, the RF indicator increases by 2-4 times.
Other diseases for which the RF test gives positive results:
RF is usually elevated against the background of malignant tumor lesions, as well as after surgical operations. As you recover and recover, the indicator returns to normal.
The indicator tends to naturally increase in old age. A positive result may be obtained if the patient is taking anticonvulsants, the antihypertensive drug Methyldopa, or oral contraceptives.
What do test indicators and their norms indicate?
Each of the blood test indicators carries certain information.
Total protein
The amount of total protein can be used to judge a person's overall health. If rheumatic tests reveal an increase or decrease in the amount of protein, this will indicate pathologies in the body. Further examinations are necessary to determine the specific disease that contributed to this.
| The norm of total protein in healthy people | |
| elderly people over 60 years old | 63–84 g/l |
| from 15 to 60 years | 65–85 g/l |
| children 4–15 years old | 58–76 g/l |
| children from 1 year of life to 4 years | 61–75 g/l |
| children of the first year of life | 46–73 g/l |
Factors that can increase protein levels include diseases that lead to loss of body fluids (diarrhea, burns, vomiting), as well as taking hormonal or diuretic medications.
Factors that reduce total protein in the blood: malnutrition, physical stress, diets, drinking large amounts of liquid per day (from 2.5 l).
Albumen
Violation of the ratio of protein fractions of albumin and globulin will indicate problems in the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
| The norm of total protein in healthy people | |
| elderly people over 60 years old | 63–84 g/l |
| from 15 to 60 years | 65–85 g/l |
| children 4–15 years old | 58–76 g/l |
| children from 1 year of life to 4 years | 61–75 g/l |
| children of the first year of life | 46–73 g/l |
Factors that can increase the result: lack of water in the body (dehydration), use of contraceptives (oral) and diuretics.
Factors that reduce albumin in the blood: smoking, dieting, pregnancy and lactation in women.
Rheumatoid factor
This is a large number of antibodies that can be detected in a blood test in patients with specific pathologies. With any acute inflammatory process, hepatitis, collagenosis, rheumatoid arthritis, mononucleosis (infectious), the rheumatoid factor will always be increased.
Eating fatty foods on the eve of the examination may increase rheumatoid factor. In older people, the rheumatoid factor will almost always be elevated due to age-related changes in the body.
The results are reduced by: taking the drug methyldop, as well as excessive fat content in the patient’s blood.
Antistreptolysin
If the indicator is elevated, then it can be assumed that there is a streptococcal infection in the body. Here the body begins to produce specific antibodies to this pathogen. Frequent and prolonged contact with streptococcal infection can lead to autoimmune pathologies. If the rate of antistreptolysin in the analysis for rheumatic tests is increased, then there are prerequisites for the development of chronic tonsillitis, scarlet fever, tonsillitis or erysipelas in the body.
Factors that increase the result: purulent inflammation, high cholesterol in the blood, ARVI, physical activity, kidney and liver diseases.
Factors that reduce the result: taking hormones (corticosteroids and antibiotics).
C-reactive protein
CRP is one of the first to indicate autoimmune diseases and inflammatory diseases in the acute stage. If a blood test shows a sharp increase in the level of C-reactive protein (protein), this may indicate cancer, rheumatic lesions and myocardial infarction.
Increases outcome measures: overweight (obesity), injury, smoking, fresh wounds, recent surgery, use of contraceptives (oral).
Reduce the result: taking steroid drugs and salicylates, damage to red blood cells (hemolysis) and high blood fat content.
Circulating immune complexes
These complexes produce specific antibodies only if immune disorders occur in the body. Rheumatic tests for this complex are prescribed if there is a suspicion that the patient has arthritis, collagenosis, diseases of viral or fungal etiology, glomerulonephritis and allergies.
The main increasing factors: the use of the drug asparaginase (in the treatment of malignant neoplasms), the use of anticonvulsants, narcotic drugs and oral contraceptives.
The results of the analysis are reduced by: radiation and chemotherapy, taking antidepressants and drugs such as phenytoin, methylprednisolone.
The results of a rheumatic test initially help in making a diagnosis, as well as in prescribing an adequate and rational course of further diagnostics to confirm the doctor’s assumptions.
Source: prokrov.ru
Preparing for a blood test for rheumatoid factor
Blood for rheumatoid factor is taken from the patient from a vein. Before collecting material, you should not eat for 8-12 hours ;
It is better if the material is collected in the morning on an empty stomach. Before visiting the laboratory, you can only drink clean water to avoid distorting the results. People with nicotine addiction need to abstain from smoking for 24 hours. You should not drink alcohol or fatty foods for 24 hours. In addition, on the eve of the test, you need to avoid physical activity.
If the patient is taking any medications, the doctor should be informed about this.
Plisov Vladimir, doctor, medical observer
16, total, today
source
Rheumatological examination
Gift for March 8th!
All women by March 8 – 20% DISCOUNT! ONLY 3 DAYS! Dear ladies! We wish you a spring mood, fresh impressions, inexhaustible.
Discounts for friends from social networks!
This promotion is for our friends on Facebook, Twitter, VKontakte and Instagram! If you are a friend or subscriber of the clinic’s page &laqu.
Resident of the microdistricts "Savelovsky", "Begovoy", "Airport", "Khoroshevsky"
This month, residents of the Savelovsky, Begovoy, Airport, and Khoroshevsky districts.
"Men's Health", medical blog (August 2020)
If your joints are swollen and painful at night, your rheumatologist will suggest you check your rheumatology profile. This examination will help make an accurate diagnosis, monitor the dynamics of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
If rheumatic disease is suspected, the following tests are used:
- blood test for uric acid levels;
- blood test for antinuclear antibodies;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor;
- blood test for ACCP (antibodies to cyclic citrulline-containing peptide);
- blood test for C-reactive protein.
Blood test for uric acid levels
Uric acid is the final breakdown product of purines. Every day a person receives purines through food, mainly meat products. Then, with the help of certain enzymes, purines are processed to form uric acid.
In normal physiological quantities, uric acid is needed by the body; it binds free radicals and protects healthy cells from oxidation. In addition, just like caffeine, it stimulates brain cells. However, high levels of uric acid have harmful consequences, in particular, they can lead to gout and some other diseases.
Testing uric acid levels makes it possible to diagnose uric acid metabolism disorders and related diseases.
When to conduct an examination:
- with the first attack of acute arthritis in the joints of the lower extremities, which arose without obvious reasons;
- with recurrent attacks of acute arthritis in the joints of the lower extremities;
- if you have relatives in your family who suffer from gout;
- for diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome;
- with urolithiasis;
- after chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy for malignant tumors (and especially leukemia);
- with renal failure (the kidneys excrete uric acid);
- as part of a general rheumatological examination necessary to determine the cause of joint inflammation;
- with prolonged fasting, fasting;
- with a tendency to excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Uric acid level
The level of uric acid is determined in the blood and urine.
Uric acid in the blood is called urecemia , and in urine - uricosuria . An increased level of uric acid is hyperuricemia , a decreased level of uric acid is hypouricemia . Only hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria are of pathological significance.
The concentration of uric acid in the blood depends on the following factors:
- the amount of purines entering the body with food;
- synthesis of purines by body cells;
- the formation of purines due to the breakdown of body cells due to disease;
- the function of the kidneys, which excrete uric acid in the urine.
Under normal conditions, our body maintains normal uric acid levels. An increase in its concentration is one way or another associated with metabolic disorders.
Normal levels of uric acid in the blood
Men and women may have different concentrations of uric acid in the blood. The norm may depend not only on the gender, but also on the age of the person:
- in newborns and children under 15 years of age – 140-340 µmol/l;
- in men under 65 years old – 220-420 µmol/l;
- in women under 65 years of age – 40-340 µmol/l;
- in women over 65 years of age – up to 500 µmol/l.
If excess of the norm occurs for a long time, then crystals of uric acid salt (urate) are deposited in joints and tissues, causing various diseases.
Hyperuricemia has its own symptoms, but can also be asymptomatic.
Reasons for increased uric acid levels:
- taking certain medications, such as diuretics;
- pregnancy;
- intense loads in athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor;
- prolonged fasting or eating foods containing large amounts of purines;
- some diseases (for example, endocrine), consequences of chemotherapy and radiation;
- impaired metabolism of uric acid in the body due to a deficiency of certain enzymes;
- insufficient excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
How to reduce uric acid levels
Those who suffer from gout know how much trouble an increased concentration of uric acid can cause. Treatment of this disease must be comprehensive and must include taking medications that reduce the concentration of uric acid in the blood (xanthine oxidase inhibitors). It is recommended to drink more fluids and reduce the consumption of foods rich in purines.
It is also important to gradually lose excess weight, since obesity is usually associated with increased uric acid. The diet should be designed so that the amount of foods rich in purines is limited (red meat, liver, seafood, legumes). It is very important to give up alcohol. It is necessary to limit the consumption of grapes, tomatoes, turnips, radishes, eggplants, sorrel - they increase the level of uric acid in the blood. But watermelon, on the contrary, removes uric acid from the body. It is useful to consume foods that alkalize urine (lemon, alkaline mineral waters).
Other tests
Deciphering tests is a complex process, and often the doctor needs to order additional laboratory tests to clarify the relationship between existing results. That is why the doctor immediately prescribes an expanded set of tests in order to increase the likelihood of a quick diagnosis and not waste valuable time performing additional tests.
Circulating immune complexes
Determination of the level of CEC is carried out when, on the basis of other tests and symptoms, it is necessary to differentiate arthritis, rheumatism, viral or bacterial diseases, mycoses, helminth infestations, and allergies.
CEC complexes consist of an antigen associated with an antibody and complement components. The process of CEC formation occurs constantly and is part of the physiological mechanism for removing antigens.
In a normal immune response, immune complexes are immediately captured and destroyed by phagocytes. But when a large number of immune complexes appear, they are found in the bloodstream and settle in the joints, on the walls of blood vessels, and in the glomeruli of the kidneys. This leads to autoimmune tissue damage.
The norm of freely circulating complexes in a rheumatic test of a healthy person is in the range of 30-90 U/ml.
Uric acid
As a result of the liver processing purines, uric acid is formed. It is excreted from the body by the kidneys, which filter the sodium salt of uric acid from the blood.
The accumulation and deposition of uric acid salts in the body in the form of crystals occurs when renal function decreases and leads to chronic organ damage, hyperuricemia (gout), and chronic arthritis.
Normally, in an adult man, the level of uric acid is in the range of 200-400 µmol/liter, in women – 150-300 µmol/liter. The norm in children is 120-300 µmol/liter.
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
Using the ANA test, you can determine the presence of antinuclear antibodies (antibodies to nuclear antigens) in the blood.
ANAs are a group of specific autoantibodies that are produced by our body's immune system in case of autoimmune disorders. Antibodies have a damaging effect on the body's cells. In this case, a person experiences various painful symptoms, such as pain in muscles and joints, general weakness, etc.
Detection of antibodies belonging to the ANA group (for example, antibodies to double-stranded DNA) in blood serum helps to identify an autoimmune disease, monitor the course of the disease and the effectiveness of its treatment.
Blood test for ACCP
Blood test for C-reactive protein
Blood test for ACCP
When is a blood test for antinuclear antibodies necessary?
Detection of antinuclear antibodies may be a sign of the following autoimmune diseases:
How is the antinuclear antibody test performed?
Blood for antinuclear antibodies is taken from a vein in the elbow, on an empty stomach. Before the study, you do not have to adhere to any diet.
In some cases, in order to differentiate various autoimmune diseases, additional clarifying tests for autoantibodies from the group of antinuclear antibodies, the so-called ANA immunoblot, may be required.
What do the test data mean?
Antinuclear antibodies (another name is antinuclear factor ) indicate the presence of some kind of autoimmune disorder, but do not precisely indicate the disease that caused it, since the ANA test is a screening test. The goal of any screening is to identify people at increased risk of a particular disease.
A healthy person with normal immunity should not have antinuclear antibodies in the blood or their level should not exceed the established reference values.
A normal ANA value implies an antibody titer not exceeding 1: 160. Below this value, the test is considered negative.
A positive test for antinuclear antibodies (1:320 or more) indicates an increase in antinuclear antibodies and the presence of a disease of an autoimmune nature in a person.
Currently, two methods are used to detect antinuclear antibodies: indirect immunofluorescence reaction using the so-called Hep2 cell line and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Both tests complement each other, and therefore they are recommended to be performed simultaneously.
The following types of ANA antinuclear bodies can be distinguished in the indirect immunofluorescence reaction:
- homogeneous coloring - can be with any autoimmune disease;
- spotty or speckled coloration may occur with systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, Sjögren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis and mixed connective tissue disease;
- peripheral coloring – characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus;
If the test for antinuclear antibodies is positive, it is necessary to perform an immunoblot of antinuclear antibodies to clarify the type of autoimmune disease and make a diagnosis.
What tests are included in rheumatic tests?
Specific tests for diseases of an autoimmune nature are considered to be the determination of rheumatoid factor and antistreptolysin O. General studies that help determine the degree of inflammation activity include:
- C-reactive protein;
- antinuclear antibodies;
- general clinical analysis - leukocyte count and ESR.
Rheumatoid factor
Represents several abnormal blood proteins (immunoglobulins) that are produced during autoimmune processes.
The higher the level of rheumatoid factor, the more widespread and aggressive the disease is, and the damage covers not only the articular surface, but also the internal organs. In children it is negative in the presence of clinical manifestations, and in elderly patients an increase is detected without symptoms.
Therefore, its independent diagnostic value is low; it is necessary to evaluate the results in conjunction with a medical examination and other tests.
Antistreptolysin O (ASL-O)
Appears when the body comes into contact with streptococcus. It is an antibody to its toxin (streptolysin). Its increase is regarded as a sign of a previous disease, but an increase in concentration (titer) also occurs in healthy people who are carriers of the infection.
A one-time analysis is not informative; it must be repeated several times weekly to assess improvements under the influence of treatment, the need to change the antibiotic or treatment tactics.
C-reactive protein
The most reliable and sensitive indicator of inflammation and tissue destruction. It is produced by liver cells under the influence of bacteria, immune complexes or parts of damaged cells (due to injury or necrosis).
If rheumatoid factor and antistreptolysin O can be present even in the absence of signs of disease, then C-reactive protein always reflects the pathological process. Its level increases in direct proportion to the stage of inflammation and the severity of the disease. It is similar in significance to the ESR of a general blood test, but rises and falls earlier.
Chronic diseases outside the acute stage do not give high values of this protein, but even with this type of course, minimal changes can be monitored using high-precision laboratory methods.
Even patients who appear healthy but have elevated C-reactive protein may be at risk for myocardial and cerebral infarction, advanced atherosclerosis, and thromboembolic complications.
Antinuclear antibodies
These are proteins that begin to form when cells are destroyed. In autoimmune diseases, nucleic acids serve as a simulator for B lymphocytes to produce antibodies. The test for their presence is positive in almost 90 percent of patients with connective tissue diseases - Sjögren's syndrome, combined connective tissue lesions.
An increase also occurs with cancer or any inflammatory reactions in the body, but usually such deviations are less persistent than with collagenosis.
Complete blood count and ESR
The level of leukocytes in the blood is used to determine the degree of inflammation. These cells are responsible for antimicrobial protection. In addition to the total quantity, the percentage of each type is also assessed by determining the leukocyte formula. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) reflects the protein composition of the blood and its viscosity.
These indicators refer to nonspecific indicators of the inflammatory process. Their advantage is the speed and simplicity of analysis, but the disadvantage is many factors that can change the result.
Blood test, ESR interpretation