Bacteria belonging to the Mycoplasma class are intracellular parasites. Mycoplasma in children manifests itself as an infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract, urogenital tract, and is the causative agent of atypical pneumonia. Microbes, having firmly established themselves inside the epithelial cells of organs, remain inaccessible to the elements of the body's immune defense. In complex cases, long-term antibiotic therapy is necessary.
What is mycoplasmosis in men
Mycoplasmosis is an inflammation of the genitourinary, respiratory or central nervous system caused by microorganisms of the Mycoplasmataceae family. They occupy an intermediate position between bacteria and viruses. Their size is so small that it is impossible to see with a light microscope. They do not have their own cell walls, for which they are classified as soft-skinned animals - Mollikutes. Mycoplasmas parasitize on the walls of host cells, attaching to them with a sliding process - an organelle. Why is it dangerous:
- Depletion of energy and nutritional resources of the donor cell;
- Violation of protein and amino acid synthesis;
- Distortion of the structure of the donor cell membrane, which leads to a failure of metabolic processes and information transfer between other cells.
In total, the mycoplasma family includes more than 100 species. According to various sources, from 9 to 16 of them are found in the human body, but not all are pathogenic. The causes of mycoplasmosis have not yet been established.
Pathogen
Depending on the type of pathogen, several types of mycoplasmosis are distinguished. Urogenital can be provoked by the following: genitalium, hominis, urealyticum. The last two are considered opportunistic, since they rarely cause pronounced inflammatory reactions on their own. Usually found against the background of chlamydia, gardnerellosis, and trichomoniasis.
Mycoplasma genitalium is transmitted sexually and through the placenta from mother to child - it is an acquired and congenital form. The microorganism parasitizes primarily on the cells of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract. Areas of colonization:
- Inner lining of the testicles;
- Epididymis;
- Urethra;
- Prostate tissue;
- Vas deferens.
How mycoplasma genitalium is transmitted, where it arises and how it manifests itself in men is explained by urologist, dermatovenereologist Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin.
Parasites can attach to sperm, disrupting their motor activity and often causing death. Mycoplasmas can also interfere with the process of sperm formation, causing infertility.
In men, mycoplasma infection accounts for 10 to 25% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis. In addition, it provokes balanoposthitis, prostatitis, vesiculitis, epididymitis. The incubation period after infection is from 1 to 3 weeks, but can last up to 2 months - it all depends on the state of health and the presence of other infections. The development period of mycoplasma from the moment of attachment to the cell wall is 6 days. Mycoplasma arthritis can begin 2 weeks after sexual intercourse.
Mycoplasma genitalium
Mycoplasma urealyticum, also known as ureaplasma, unlike genitalium, is not an absolute pathogen. Like hominis, it does not manifest itself for a long time. Under certain conditions, it begins to actively multiply, which provokes cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, and can concentrate on sperm.
Mycoplasma hominis is usually found in sexually active individuals. In men it can cause prostatitis and urethritis, and in cases of weakened immunity it sometimes provokes respiratory diseases. It remains in the body for a long time asymptomatically, until reproduction begins under the influence of provoking factors. The incubation period averages 3-5 weeks. There are no specific signs.
Mycoplasma urealyticum and hominis are found in the rectum and genitourinary organs of 20-75% of healthy people. Transmitted primarily through sexual contact. Theoretically, infection is possible through close household contacts, but there is no evidence of this.
Video about symptoms, modes of transmission and treatment of mycoplasma hominis
Respiratory mycoplasmosis is caused by mycoplasma pneumoniae. It is the cause of atypical types of pneumonia, an infection of the upper respiratory tract. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is transmitted by airborne droplets. This pathogen accounts for 6% of all cases of acute respiratory infections and 22% of acute pneumonia. According to WHO, every year from 8 to 16 million people fall ill with respiratory mycoplasmosis. The disease usually progresses without complications and responds well to antibiotic treatment.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Mycoplasma fermentans can parasitize both the genitourinary tract and the respiratory tract. It is characterized by an active form of inflammation, which is difficult to respond to antibiotic therapy and often recurs. The infection can cause rheumatoid arthritis, weakens the immune system, and disrupts the structure of the kidney tubules.
There is also Mycoplasma salivarum, which parasitizes the oral cavity. Can provoke stomatitis, gingivitis, pulpitis, chronic osteomyelitis.
What are IgG antibodies to mycoplasma hominis
Antibodies are protein compounds found in human blood plasma.
They are responsible for humoral immunity.
They are synthesized by plasma cells that develop from B lymphocytes.
Immunoglobulins G have two functions:
- bind to mycoplasma hominis antigens, preventing them from causing harm to the body;
- trigger the complement activation system (this is required to destroy the bacterial cell).
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of pathogen and its location. Men most often suffer from urethritis caused by Mycoplasma genitalia. Signs:
- Scanty clear discharge from the urethra, appearing mainly in the morning.
- Pain and burning when urinating, increased urge.
- Redness of the urethra.
- Dull diffuse pain in the pelvis or nagging pain in the groin.
Discharge from urogenital mycoplasmosis in the photo – https://prntscr.com/truzl2.
In some cases, mycoplasmas cause Reiter's syndrome, which is characterized by a combination of conjunctivitis, fever, fever and joint inflammation.
If mycoplasmas have penetrated the epididymis, a nagging pain occurs in the scrotum, groin and perineum. The skin over the site of inflammation sometimes turns red. When the prostate is damaged, symptoms characteristic of chronic prostatitis appear. Pyelonephritis is manifested by lower back pain and fever.
Read more about the symptoms of mycoplasmosis in men
Mycoplasma hominis IgG positive - what does this mean?
Immunoglobulins are specific immunity factors.
That is, they only fit certain antigens, like a key only fits a certain lock.
Antibodies to mycoplasma hominis are formed only if this particular bacterium enters the body.
Accordingly, based on the presence of immunoglobulins, we can conclude: the body has already encountered mycoplasma.
This caused the process of antibody formation to start.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should you contact: if you experience discomfort from the genitourinary system, you should contact a urologist. If the only symptoms are pain during urination and discharge, then a venereologist or andrologist will help.
The diagnosis of mycoplasmosis has its own characteristics:
- Smear microscopy is not used because the infection has no clear structural signs.
- Serological and immunofluorescent techniques are also not always informative.
- Due to the difficulties of cultivating the pathogen, bacterial culture is rarely used.
The optimal diagnostic method is PCR in REAL TIME mode. Mycoplasma DNA is detected in blood or other material even at minimal concentrations of the pathogen. Depending on the location of the inflammation, a smear from the urethra, pharynx or nose, prostate secretion, or joint fluid can be used as a biomaterial. Disadvantage of the method: not all laboratories can identify the type of mycoplasma.
Dermatovenerologist Vyacheslav Vasilyevich Makarchuk tells what tests should be taken if mycoplasmosis is suspected
Additional diagnostic methods for various types of mycoplasmosis:
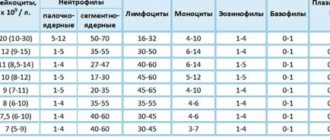
- General blood analysis. During inflammation, the number of leukocytes increases.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. With mycoplasmosis, the indicator is increased.
- General urine analysis.
- Determination of the titer of IgA antibodies to a specific type of mycoplasma infection in the blood. IgA protects mucous membranes, so its presence can signal the presence of mycoplasma.
- Determining the IgM titer will help identify an acute inflammatory process, and IgG - a chronic one.
Imaging methods include ultrasound and x-ray.
Indications for the study
In addition to the fact that the main indications for laboratory testing include the above-mentioned symptomatic signs, one should also include unprotected sexual intercourse, preparation for subsequent conception, miscarriage, inability to conceive a child, routine examination in the initial weeks of pregnancy. It is also possible to undergo a mycoplasma test for preventive purposes.
Also, indications for the analysis procedure are:
- when diagnosing diseases of the pelvic organs;
- when vaginosis is detected;
- upon detection of tubal infertility.
At the same time, a test for mycoplasma in women can be prescribed if there is a suspicion of the presence of mycoplasmosis, before IVF, before surgery, as well as to clarify the results obtained from the therapy.
Treatment
Should Mycoplasma hominis be treated: in most cases, no. The exception is inflammatory processes, the only source of which is this type of microorganism. If the amount of DNA according to the analysis results exceeds 104 copies, then the likelihood of inflammation is high, and it is recommended to undergo a course of treatment.
Most doctors believe that mycoplasma genitalium and pneumoniae are subject to mandatory treatment. Even their asymptomatic presence can cause harm to the body, but according to WHO recommendations, treatment should begin only in the presence of severe inflammation.
Video about methods of treating mycoplasma in men
Drugs
The following groups of drugs are used to treat Mycoplasma genitalium:
- Tetracyclines;
- Fluoroquinolones;
- Macrolides;
- Aminoglycosides.
Mycoplasmas are not sensitive to other types of antibiotics.
For acute infectious inflammation, Doxycycline is prescribed. Classic treatment regimen: 100 mg once a day for 5 days. Therapy can be extended up to 3 weeks. Alternative: Clarithromycin 250 mg per day for 5-7 days. As an additional line of therapy, Levofloxacin is prescribed 250 mg per day for 3 days. For conjunctivitis, Levofloxacin drops are prescribed 4-8 times a day.
Ampicillin has a bacteriostatic effect - it does not destroy, but slows down the growth and development of mycoplasma. It is eliminated quickly, so you will have to take several tablets a day to achieve the desired concentration. Standard regimen: 250 mg 2 times a day for a week. For the treatment of hominis and genitalium, it is usually prescribed as an adjuvant drug.
Azithromycin is prescribed 1 g once or 0.5 g once a day for 3 days. Take one hour before meals or 2 hours after.
Urogenital mycoplasmosis rarely develops independently, therefore, depending on the type of concomitant infection, antifungal drugs or metronidazole are prescribed.
Treatment regimen for chronic mycoplasmosis:
- Metronidazole 2 g once or 500 mg 2 times a day for a week;
- Tinidazole 2 g once;
- Doxycycline 0.1 g 2 times a day for 10 days.
Summary table with various treatment regimens for mycoplasma in accordance with clinical guidelines:
In parallel with antibiotics, probiotics are prescribed: Hilak Forte, Linex.
Folk remedies for the treatment of mycoplasma are useless. You can drink tinctures of echinacea, ginseng or eleutherococcus to strengthen the immune system.
A control test is taken one month after the end of the course of treatment.
Preparatory stage
Many analyzes require preliminary preparation. In this case, there are also certain rules on how to take the test:
- on the female side, the test for mycoplasmosis can be carried out on any day of the cycle, but it will be better if the smear is taken a few days before the start of menstruation or immediately after its completion;
- When taking an analysis using the PRC method, it is not recommended to empty the bladder several hours before taking the material.
Compliance with the above rules makes it possible to identify the most reliable results and subsequently, based on the data obtained, to formulate an effective method of therapy.
Where to get an IgG test for Mycoplasma hominis
To be tested for mycoplasmosis, you can contact our clinic.
We have venereologists who have extensive experience in identifying and treating this disease.
Here you can donate blood for antibodies.
Additionally, the doctor may take smears for PCR or bacteriological culture.
These tests confirm the diagnosis.
If mycoplasmosis is detected, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy.
How to treat IgG to mycoplasma hominis
In one of the previous sections, we talked about the fact that IgG is not pathogenicity factors or fragments of bacteria.
These are our own antibodies.
They do not harm the body.
On the contrary, they allow him to fight the infection.
Accordingly, it is not immunoglobulins that need to be treated, but mycoplasmosis.
As long as the bacterium remains in the body, it provides antigenic stimulation.
The immune system continues to synthesize antibodies.
But they are not able to lead to the complete extermination of Mycoplasma hominis.
Therefore, this infectious disease can last for years in a chronic form.
Over a long period of time, an STD can cause complications.
Infertility appears and perinatal risks increase.
The likelihood of other infections, both sexual and nonspecific, increases.
To get rid of mycoplasma, you need antibiotics.
Eradication of this bacterium allows a person to:
- get rid of the symptoms of inflammation of the genitourinary tract;
- remove IgG from the body;
- eliminate the risks of complications;
- calmly become pregnant without fear of perinatal losses or the formation of congenital deformities;
- be sexually active without worrying about possible infection of your partner.
Treatment is often prescribed before surgery or invasive manipulation of the reproductive organs.
Because the presence of Mycoplasma hominis increases the risk of postoperative infectious complications.
Antibiotics are used to treat mycoplasmosis.
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- tetracyclines;
- macrolides.
- Fluoroquinolones are used less frequently.
They are used as reserve drugs if antibiotics from other pharmacological groups are contraindicated or have not worked.
Treatment usually lasts for 2 weeks.
After its completion, control of cure is necessary.
During treatment, a blood test for IgG may be performed.
But it makes sense to conduct this study only in dynamics.
Quantitative diagnostic tests are needed.
By the dynamics of the titer you can judge whether the treatment is working or not.
If the titer decreases by 4 times or more within a week, this indicates the success of therapy.
If the titer remains unchanged or increases over time, one has to admit that the prescribed antibiotic is not working.
Perhaps Mycoplasma hominis is not sensitive to it.
The action in such cases is as follows:
- the antibiotic is replaced with another (the pharmacological group is changed);
- A culture for Mycoplasma hominis is performed to determine the sensitivity of this bacterium to antibacterial drugs.
An antibioticogram significantly increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Failures are rare if antibiotics are prescribed, to which Mycoplasma hominis is highly sensitive.
Complications
Discomfort is not at all the worst consequence of the proliferation of mycoplasmas. Unfortunately, mycoplasmosis is dangerous not in itself, but because of the consequences that it can cause.
Long-term infection with Mycoplasma hominis and Mycoplasma genitalium in women leads to the development of the following diseases:
- Salpingoophoritis is an inflammatory process in the uterine appendages (fallopian tubes, as well as ovaries). Due to damage by bacteria to the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube, swelling occurs, which can cause obstruction and, as a result, infertility. The disease develops against the background of the spread of Mycoplasma hominis.
- Cystitis, an inflammation of the bladder, and pyelonephritis, an infection of the kidneys, can also be caused by Mycoplasma hominis.
- Infertility. Due to the appearance of endometritis and salpingoophoritis, which are a complication of mycoplasma infection, a woman is unable to become pregnant. Since the endometrium of the uterus is damaged, during fertilization the egg is rejected by the inflamed tissue and cannot be implanted. The inflammatory process causes the walls of the fallopian tubes to swell, which leads to blockage and blockage of the path for sperm to reach the egg. As a result, the likelihood of conception is low.
- Urethritis is the appearance of an inflammatory process in the urethra (urethra). Characteristic signs: burning, itching, pain in the urethra. The pain that is present intensifies when the bladder is emptied. Most often, such a complication as urethritis develops with the participation of Mycoplasma genitalium.
- Gardnerellosis or otherwise vaginal dysbiosis. Observed when infected with mycoplasma species hominis.
- Vaginitis is a disease of the genital organs (vagina), in which the inflammatory process causes damage to the area. At the site of destruction of the epithelium by mycoplasmas, itching and burning are felt, these symptoms are accompanied by discharge mixed with pus and mucus, which has an unpleasant odor. During moments of intimacy, a woman experiences increasing pain.
- Endometritis is an inflammatory disease in which mycoplasmosis spreads higher and causes the development of infection on the inner mucous membrane of the uterus and cervix. Clinical picture: the appearance of discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen, discharge with blood during and before ovulation. Often women suffering from endometritis cannot become pregnant, and if this happens, there is a risk of spontaneous abortion in the early stages. The development of endometritis is promoted by Mycoplasma hominis.
- Pathological processes during pregnancy. Early birth and miscarriages at the beginning of pregnancy are caused by damage to the endometrium of the uterus, which is unable to ensure the normal functioning of the fetus.
- Autoimmune diseases are a disruption of the human immune system, which is forced for a long time to fight infectious and inflammatory processes occurring in the body.
Recent studies have shown that people suffering from arthritis are often affected by mycoplasmas, which provoke inflammatory joint diseases. In severe cases, if the body's defenses are completely depleted, sepsis may develop.
Mycoplasmosis is especially dangerous for pregnant women. It can cause various pathologies of fetal development or pregnancy complications, including miscarriage. Subsequently, secondary infertility may develop.
Mycoplasmosis during pregnancy
Mycoplasmosis during pregnancy is detected 2-2.5 times more often than without it. And in women suffering from “habitual” abortions, mycoplasma is detected in 25% of cases. This is a serious reason to think about the problem. There is an opinion that mycoplasmosis in pregnant women is so common due to changes in hormonal levels, as well as other physiological processes that occur with a woman (for example, the state of the immune system). The presence of urogenital mycoplasmosis causes a huge risk of premature birth and the birth of a child with extremely low body weight. It is believed that mycoplasmosis during pregnancy is more often caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum than by other species.
Urogenital mycoplasmosis quite often causes postpartum or post-abortion complications, which are severe, accompanied by high fever and can lead to undesirable consequences. Also, mycoplasmosis in pregnant women can penetrate through the amniotic sac, causing inflammatory changes in the membranes and the inner lining of the uterus. These conditions are what cause premature births and early abortions.
It is generally accepted that asymptomatic and low-symptomatic variants of the course are more dangerous for a pregnant woman and more often contribute to the development of complications. A child can become infected from the mother both during pregnancy and during childbirth. The more premature the child was born, the more severe the manifestations of mycoplasmosis will be in him. Mycoplasma is found in the spinal cord and respiratory system. To prevent such severe consequences for the mother and unborn child, it is necessary to screen pregnant women for genital mycoplasmosis. It is advisable to do this while planning a child.
If a woman comes to the gynecologist with complaints of slight vaginal discharge, and the doctor detects yellowish discharge and symptoms of inflammation of the cervix and vagina in the speculum, then she must be referred for laboratory diagnostics.
To detect mycoplasmosis, PCR is mainly used (polymerase chain reaction - detection of parasite DNA fragments in a sick woman) and culture on special media (mycoplasma colonies grow in 4-7 days). The material for the study is vaginal discharge. If the test results are positive, then the diagnosis of urogenital mycoplasmosis is considered confirmed. Next, the doctor must explain to the woman all the possible consequences of the disease and explain measures to combat them.
How does mycoplasmosis become infected?
How is mycoplasmosis transmitted?
Several routes of transmission of the pathogen of this infection have been established:
- sexual;
- intrauterine (the fetus becomes infected during intrauterine development);
- oral-genital;
- perinatal (in this case, the newborn becomes infected with mycoplasmas while passing through the infected birth canal of the mother).
In addition, the possibility of infection through common household items should not be excluded, although this route of infection is very rare. The incubation period of the mycoplasmosis pathogen usually ranges from 15-16 to 20 days.
How can you get infected?
The source of infection is a sick person or a bacteria carrier. There are 2 ways of transmission of mycoplasmosis:
- Sexual transmission: this microorganism lives on the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system, infection occurs during sexual contact,
- The vertical route of transmission of infection is infection of the child during childbirth; such cases are rare, since during pregnancy the woman undergoes a medical examination and, if a carrier of mycoplasma is detected, receives the necessary treatment.
The cause of mycoplasmosis is the reproduction of mycoplasma in a woman’s body. Unprotected sexual intercourse increases the risk of developing such a disease (only barrier methods of contraception will help prevent infection). Since the Mollicutes class of bacteria lives on the mucous membranes of healthy people, exposure to certain factors can provoke its proliferation:
- long-term use of antibiotics suppresses the microflora of the genital organs, which allows mycoplasma to multiply uncontrollably,
- diseases leading to immunodeficiency,
- frequent stress activates pathological processes throughout the body, reduces resistance to infections,
- taking glucorticosteroids,
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases,
- hormonal disorders,
- dysbacteriosis,
- carrying out invasive (requiring penetration into the body) measures for diagnosis or treatment (in the absence of proper care for the postoperative wound),
- pregnancy (during this period, hormonal levels change, resistance to infections decreases, diseases that were previously chronic worsen),
- unhealthy diet
- alcohol abuse (alcohol-containing liquids cause changes in the male gonads, provoking changes in the microflora),
- promiscuous, unprotected sexual intercourse.
What diseases does mycoplasma cause in women?
With mycoplasmosis, the female sex begins to suffer from the following diseases:
- Urethritis. This is an inflammation of the urethra. The pain increases during urination. It is characterized as burning, stinging and itching,
- Vaginitis. This is a mycoplasma infection of the vaginal mucosa. A woman feels an unpleasant odor from intimate places, feels burning and itching, and sees mucopurulent discharge in copious amounts. If you have sexual intercourse during vaginitis, the process will be very painful,
- Endometritis. The disease occurs when the infection reaches the mucous membrane of the cervix and the uterus itself. The woman feels severe discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen. Light bleeding may occur between natural periods. Endometritis often causes infertility and early miscarriages,
- Adnexitis. This is a lesion by inflammatory processes of the uterine appendages. With adnexitis, the fallopian tubes swell. As a result, women are often diagnosed with tubal infertility.
ELISA for IgG antibodies to Mycoplasma hominis
An enzyme immunoassay is a test that helps determine the level of antibodies in the blood.
It can be qualitative or quantitative.
The use of qualitative methods for the determination of IgG alone is impractical.
Because this immunoglobulin can be in the blood both during active and past infection.
IgG is only relevant if:
- its titers are determined;
- the study is carried out dynamically, with a break of 1-2 weeks;
- Other classes of antibodies are additionally determined: IgM and IgA.
The most common diseases caused by mycoplasmosis infection
- Urethritis - in most cases, the symptoms of this disease manifest themselves in the form of inflammation of the urinary tract and occur as a result of human infection with microorganisms of the type mycoplasma genitalium. Most often, such problems arise in the male half of the population.
- Bacterial vaginitis (gardnerellosis) - also manifests itself under the influence of mycoplasmas; the main role in this case is played by infection of the species mycoplasma hominis. Approximately 15-20% of the fair sex are susceptible to gardnerellosis.
- Inflammatory lesions of the female reproductive organs - namely the uterus and its appendages - quite often develop under the influence of mycoplasmas; mycoplasma hominis usually also plays a major role in such a situation.
- Pyelonephritis - inflammatory diseases of the kidneys can also be caused by microorganisms such as mycoplasma hominis.
- Prostatitis - often with the development of signs of this pathology in the urinary tract, men determine the presence of mycoplasmas. And although the role of this infection in the occurrence of prostatitis has not been scientifically proven to date, it should be considered one of the possible causes of the symptoms of this disease.
When do IgG to mycoplasma hominis disappear after treatment?
Immediately after the end of therapy, IgG may remain in the blood.
And in fairly high titers.
But after a few weeks the titers decrease significantly.
This is due to the cessation of antigenic stimulation.
Antibodies are no longer produced.
And those immunoglobulins that were synthesized earlier gradually leave the blood.
Within several months, IgG is detected in very low titers.
Then they cease to be defined at all.