Photophobia is a special manifestation in which a person’s eyes react painfully to light. The symptom is characterized by increased sensitivity of the visual system. If a person has this condition, then whenever light enters his eyes he will experience discomfort and squint. In medical terminology, photophobia is called photophobia or heliophobia (fear of the sun).
For the human eye, there is an optimal light intensity, exceeding which causes discomfort. When exposed to a bright source of light, the patient's vision deteriorates and blindness occurs. However, this is a normal reaction of the body to changes in light. Photophobia is that a person is overcome by unpleasant sensations even at a normal level of light.
It is also worth considering that photophobia is not an independent disease - it is a manifestation of the disease.
Etiology
The causes of photophobia vary widely. Since this is a symptom of a disease, the factors that provoke the development of the symptom are the illnesses themselves. In addition to diseases, there are other reasons for this phenomenon:
- structure of the eye;
- negative impact of the environment;
- diseases of viral or bacterial origin.
Photophobia of the eyes also develops due to the use of medications - quinine, tetracycline, doxycycline, belladonna, furosemide.
It has been revealed that the symptoms of photophobia appear in the following eye pathologies:
- ulcers and disruption of the structure of the cornea;
- tumors;
- – damage to the cornea;
- Iritis is a disorder of the iris.
Quite often, this symptom appears in pathologies of the central nervous system or during an acute attack. Prolonged wearing of lenses can also worsen vision and contribute to the appearance of photophobia.
Photophobia in a child appears under the influence of such pathologies:
- melanin deficiency;
- acrodynia;
- pathology of the oculomotor nerve;
- conjunctivitis.
Prognosis for the development of photophobia
You will have to seek treatment for the vision abnormality in question in any case, because constant sharp pain in the eye area will lead to constant discomfort and the patient will not be able to withstand this condition.
Pronounced signs of visual impairment signal an exacerbation of chronic diseases and the development of ophthalmological pathologies.
In certain cases, photophobia
is a normal reaction and occurs in every person. For example, when the light is turned on suddenly in a dark room. Therefore, in the case of photophobia in adults or children, it is important to be able to distinguish normality from pathology and know in which diseases visual disturbances are observed.
Treatment of photophobia is closely related to preventive measures and depends on the cause that caused the unpleasant symptoms.
Diagnostics
If there is photophobia of the eyes, the patient must consult a doctor and get examined. To determine an accurate diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo the following studies:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- examination of the fundus vessels;
- corneal analysis.
If the etiology of a symptom is unclear, additional instrumental examination methods may be prescribed.
To cure photophobia in children, you must first seek the help of a pediatrician. The doctor will refer you to a specialist and prescribe the above-mentioned examination methods. The child needs to undergo a blood test to determine the level of thyroid hormones, as well as an ultrasound of the gland and Dopplerography of the great vessels.
Diagnosis of photophobia
Photophobia is diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints and the presence of additional symptoms, as well as additional examinations and tests.
The examination includes:
- eye examination,
- corneal scraping (ophthalmoscopic examination),
- examination of the eyeball using a slit lamp,
- lumbar puncture,
- ultrasound examination of the eyes,
- computed tomogram of the brain,
- electroencephalography.
Treatment
Symptom therapy is prescribed after determining the causes of the pathology. Doctors advise patients to follow simple rules:
- on sunny days do not leave the house without sunglasses;
- use eye drops;
- During migraine attacks, it is advisable for the patient to go to a dark place.
Timely treatment of photophobia and the causes of its occurrence contributes to the rapid relief of this symptom.
However, quite often the symptom is not formed against the background of any disease, but is congenital. In this case, doctors recommend adhering to the above rules.
Contents of the article: classList.toggle()»>expand
Photophobia or photophobia is increased sensitivity to light, which causes lacrimation, painful sensations in the eyes, and closing of the eyelids.
It is important to distinguish photophobia from a pathological fear of exposure to the sun - “heliophobia”. Pathology is a consequence of mental illness.
Diagnostic methods
To detect photophobia, the doctor must first examine all the symptoms that bother the patient, and then understand the cause of their occurrence.
Fear of light can be determined by the following symptoms:
- when pressing on the eyeballs, pain occurs;
- , which becomes permanent;
- the patient squints and twitches his eyelids all the time;
- There are frequent and regular pains in the head.
There are situations when a person begins to have difficulty oriented in space and experiences temporary short-term loss of vision.
To detect the cause of the pathological process and draw up an effective treatment regimen, the patient may be prescribed the following diagnostic methods:
- Brain CT and electroencephalogram – can detect serious chronic disorders;
- diagnostics using a slit lamp;
- collection of cerebrospinal fluid.
Only after undergoing a thorough examination and diagnosis will the doctor be able to create a correct and effective treatment regimen.
Treatment
Treatment depends entirely on the cause of photophobia. If the phobia is not associated with another disease, then it is recommended to make some adjustments to your daily life: wear sunglasses with a UV filter (or), reduce the amount of time spent at the PC and TV, and apply eye drops.
Minor inflammatory processes can be treated with eye drops
, which contain antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, moisturizing components and enzymes.
Photophobia is a symptom of many ophthalmological diseases, so treatment will be based on identifying and eliminating the cause that led to the appearance of this negative sign.
Diagnosis and treatment
What is photophobia of the eyes? We have already found out the causes of this disease. Now let's talk about its diagnosis and treatment. People who complain of photophobia should go to the hospital for further evaluation and treatment. As a rule, diagnosis of this disease is carried out by two specialists: an ophthalmologist and a neurologist. They will prescribe the necessary studies, which include fundus examination, ophthalmoscopy, corneal scraping, cerebrospinal fluid studies, MRI or CT of the brain, EEG, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and chest radiography. After all the necessary examinations, you will be prescribed medical treatment. It is very important to exclude self-medication and entrust your health to professionals.
How to eliminate a disease such as photophobia of the eyes? The causes and treatment are presented to your attention in the article. The essence of treatment for photophobia is to eliminate the underlying disease that led to the development of photophobia. As soon as you manage to get rid of this cause, the unpleasant reaction to light will go away on its own. If photophobia is caused by taking certain medications, then the doctor will select an analogue for you that will not provoke such a reaction to light. If photophobia is congenital or related to environmental factors, you may be advised to wear contact lenses that minimize negative reactions to light. For photophobia provoked by viral or infectious diseases, the doctor will most likely prescribe antibacterial therapy. We can include both medicines in the form of eye drops, tablets and injections. During treatment, wearing glasses with tinted lenses can significantly alleviate the symptoms of photophobia.
Now we know how to eliminate photophobia of the eyes. The causes that need to be treated first must be diagnosed in time. Do not put off going to the doctor, as this is fraught with consequences.
Photophobia in children
The first cause of pathology is congenital. Some children lack (or have small amounts of) the pigment melanin.
Often children's photophobia develops against the background of febrile conditions.
, viral diseases: corneal damage, tumor, tuberculosis-allergic.
Conjunctivitis
The disease provokes inflammation of the mucous membrane. There are also conjunctivitis. A characteristic symptom is fear of bright light.
"Acrodynia" or "pink disease"
Characteristic symptoms: pink and clammy hands and feet, high blood pressure, profuse sweating, loss of appetite, fear of light. Late treatment may result in death.
Motor nerve palsy
Signs: the upper eyelid droops, the pupil dilates and does not adapt to changes in lighting, so the child develops photophobia. The causes of the disease are varied.
Endocrine ophthalmopathy
An autoimmune process associated with thyroid diseases. The child may complain of photophobia in the eye.
Tuberculous-allergic keratoconjunctivitis
An infectious-allergic disease that manifests itself in children with tuberculosis of the lungs or lymph nodes.
The disease begins suddenly, with obvious signs of photophobia, lacrimation, and inflammation of the cornea. One eye is affected. Despite the fact that in some cases photophobia does not cause concern, at the first signs of pathology you should consult a doctor. Photophobia can be a signal of serious disorders in the body
.
An effective remedy for restoring vision without surgery or doctors, recommended by our readers!
Often, when leaving a dark room on a sunny day, tears begin to flow from your eyes. I really want to close them with my hands. This is the weakest manifestation of photophobia. In more severe pathologies, pain, pain, and lacrimation occur at the slightest ray of light. Photophobia is one of the most common ophthalmological diseases.
Photophobia is a symptom of the disease
Heliophobia is a fear of sunlight, a mental illness that has nothing to do with eye function. Fear of sunlight is usually associated with fear of other diseases. For example, such as skin cancer, sunburn, eye diseases that cause photophobia. Another similar disease is Gunther's disease. In this case, photophobia is just a symptom in which there is a fear of getting sunburn.
A child may develop photophobia due to an insufficient amount of melanin in the body or congenital defects. Children often stare at welding for a long time, which contributes to the occurrence of a disease such as snow ophthalmia. Insomnia, stressful situations, loss of appetite, fatigue, tachycardia, increased sweating - all this affects the quality of a child's vision.
Another cause of photophobia can be paralysis of the oculomotor nerve. With this disease, the child’s health is not impaired in any way, but the eyelid is drooping and the pupil is greatly dilated. Because of this, the development of photophobia begins.
Thyroid dysfunction is one of the causes of photophobia. At the first suspicion, consult an ophthalmologist. He will prescribe a number of procedures with the help of which he will establish an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
List of procedures to determine the source of the symptom:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
- Ophthalmic procedure.
- EEG (electroencephalography) is a procedure that examines brain activity.
- Test showing thyroid hormone levels.
Symptoms of pathology
Photophobia of the eyes is one of the signs of a serious illness. It may cause:
- headache;
- profuse lacrimation;
- redness of the eyeball;
- feeling of the eye being clogged with dust or sand;
- pain and stinging in low light;
- decreased level of vision;
- blurred objects and unclear vision of the surrounding world.
Purulent discharge, swelling of the eyelid, severe redness of the eye and a significant deterioration in visual acuity are symptoms of more severe pathologies, in which it is necessary to urgently consult an ophthalmologist. If all symptoms are absent, but discomfort persists, it is necessary to undergo examination by a neurologist. Very often, photophobia can be caused by disorders of the nervous system.
Symptoms
With photophobia, additional symptoms almost always occur; certain signs indicate the development of a certain disease.
What diseases can lacrimation indicate:
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- rabies.
Headache along with photosensitivity occurs with the following diseases:
- migraine;
- hemiplegic migraine;
- meningitis;
- cervicogenic headaches;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- encephalitis.
Photophobia, accompanied by elevated temperature and fever, occurs with the following diseases:
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- purulent accumulations;
- stroke with hemorrhage;
- accumulation of pus in the visual organs;
- hemorrhagic fever;
- trigeminal neuralgia.
The development of attacks of nausea and vomiting occurs with the following ailments:
- meningitis;
- meningoencephalitis;
- brain abscess;
- migraine.
If you experience photophobia with or without additional symptoms, consult your doctor immediately. Do not use ophthalmic drugs, nootropics, antipsychotics, antibiotics without prior consultation with a specialist. It is also prohibited to use analgesics and other painkillers for a long time.
Causes of photophobia
The causes and treatment of the pathology may vary, but often photophobia occurs as a symptom of a more serious illness.
- Cutting pain and lacrimation occur with conjunctivitis of the eyes.
- Inflammatory process on the iris of the organ of vision during iritis. Causes lacrimation, pain in the eyes, photophobia.
- Microtraumas. The appearance of ulcers on the cornea, tumors and ulcerative formations.
- Cases with albinism when light hits the pupil and iris of the eye.
- Exposure to harmful radiation during certain industrial activities.
- With a lack of melanin pigment associated with congenital pathologies.
- For allergic reactions to medications.
- Harmful radiation from a monitor or TV screen in a child.
- With prolonged exposure to bright light (light music in clubs, laser shows).
- The occurrence of photophobia during attacks of glaucoma.
- Photophobia - with retinal detachment, after an unsuccessful operation or burn.
For some pathologies, a full cycle of examination will be required using instrumental diagnostic methods - ultrasound, MRI. For less complex diseases, an examination by an ophthalmologist is sufficient.
Causes of the disease
The occurrence of photophobia of the eyes in humans can be caused by various sources. The main factors influencing the development of the disease are:
- ophthalmological diseases
of an inflammatory nature (conjunctivitis, iritis, keratitis); But how herpetic keratitis is treated will help you understand this - congenital anomalies
of the structure of the organs of vision, in which the pupils are deprived of the coloring pigment melanin. But this will help you understand what retinal pigmentary dystrophy looks like; - complications
after infections and viruses; - prolonged presence near a computer monitor
, leading to dryness of the mucous membranes; - poor environmental conditions;
- use of certain medications;
- manifestations of depression;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- mechanical damage to the cornea of the eye. But how corneal erosion is treated is described in great detail in the article
- oncology of the visual organs.
But what diseases cause photophobia can be found out from this
The course of the disease is accompanied by various symptoms. Among them are the following manifestations:
- lacrimation;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the eye area, headache. But why it appears, you can find out in the article at the link.
- blurred vision;
- burning sensation and itching, swelling;
- redness of the eyes. But you can see how to use eyelid ointment for inflammation and redness
- dizziness up to loss of consciousness;
- ringing in the ears, hearing loss;
- increased anxiety.
The video shows a description of the disease:
Identification of the actual cause of the manifestation of photophobia of the eyes must be carried out in a medical institution with a mandatory examination of the visual organs, so that the doctor can prescribe the correct treatment for the disease.
It is necessary to reduce the amount of time spent behind a computer screen or watching TV.
You should not rub in the eye area, so as not to provoke further development of the inflammatory pathological process.
To relieve unpleasant sensations, special ophthalmic drops ““, “Oxial”, “Katinorm” are used, which have a moisturizing effect, protect the mucous membrane of the eye, causing the effect of an artificial tear.
When purulent discharge appears in the eye area, they resort to the use of eye antibiotics or antiseptics:
If the cause of photophobia in a person is mechanical damage to the organs of vision in the form of a bruise, burn or wound, then an urgent visit to a specialist is required to provide emergency assistance. Before seeing a doctor, you can treat your eyes with antiseptic drops, followed by applying a clean, sterile gauze bandage.
A fairly effective method in the treatment of photophobia of the eyes is the use of various natural herbal remedies. The most common ones are:
Treatment of the disease
The prescription of the treatment method and the use of medications depends on the severity of the disease. For therapeutic drug treatment, the following is prescribed:
- Eye drops with Interferon.
- Antibiotics and antiseptic drugs for inflammatory processes, purulent formations - in the form of drops.
- Injections and tablets with antibiotics.
- Infusions and solutions for rinsing.
- Some healing ointments applied to eye patches.
- Medicines for pain relief and stopping inflammatory processes.
Advice! Patients with photophobia must wear sunglasses until complete recovery.
For some pathologies and at the very beginning of the disease, you can use traditional medicine recipes using medicinal plants:
- Pour a teaspoon of eyebright into a glass of boiling water. Let it sit for several hours and strain. We wash the affected eye with this infusion before going to bed. It's good to make lotions. Soak a napkin and place a cotton pad on the eye. You can instill three drops of this infusion into your eyes. After 10 days of taking it, you need to take a break.
- Pour 50 g of sweet clover inflorescences with a glass of water, boil for 20 minutes over low heat, let cool, strain. Use as lotions.
- Wash your eyes with a solution of 4 tablespoons of flax seeds and a glass of water every morning to relieve redness and itching of the eyes in children and adults.
- Sea buckthorn oil can be used to treat photophobia. 2 drops in each eye. This procedure relieves the symptoms of the pathology.
Neurological photophobia is treated by a neurologist. For it they use:
- physiotherapy procedures;
- therapeutic exercises;
- drug treatment;
- For particularly complex forms of pathology, surgical treatment is prescribed.
Photophobia with meningitis and encephalitis must be treated in a hospital.
In order to prevent eye pain, photophobia, burning, tearing, and redness, you need to follow simple recommendations from specialists. Observe personal hygiene rules. To prevent damage from ultraviolet radiation, it is necessary to use protective equipment (safety glasses, welding masks). For dry eye syndrome, it is necessary to use drops. Constantly do light exercises for your eyes. Be sure to wear quality sunglasses when in the sun.
You should not delay a visit to a specialist at the first symptoms of photophobia.
Eyes hurt from the light
Problems with the appearance of increased photosensitivity of the eyes can occur in both adults and children. At a young age, sunphobia can be a reaction to childhood diseases such as measles or rubella.
To understand why photophobia began, you need to pay attention to the following signs: if fear of light is noted in one eye, then this is most likely the result of injury or pathology of the organ of vision; if in both - infection or manifestation of an anomaly developing in the brain.
What to do if you have increased photosensitivity
A person experiencing pain in the eyes even in low light, with redness of the sclera, accompanied by dizziness, or with weakened visual function, should urgently consult a doctor.
The doctor will determine what disease caused these signs and prescribe treatment.
At the first signs of deterioration in visual function due to developed photophobia, it is necessary to carry out supportive and preventive measures. These include homeopathic treatment.
By secret
- Incredible... You can cure your eyes without surgery!
- This time.
- No trips to the doctors!
- That's two.
- In less than a month!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how our subscribers do it!
Photophobia is an abnormal intolerance by the visual organs of artificial or natural light, under the influence of which discomfort occurs. The causes of photophobia of the eyes can be different and may be accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms.
Photophobia or photophobia
The concept of photophobia is a fairly common concept and can occur in people of all ages. This is intolerance to bright light with the eyes, otherwise called photophobia or heliophobia.
When light gets into the eyes, a person begins to feel a sting, and even pain, and he wants to immediately close his eyes and hide. Here it is necessary to note the fact that for the human eye organs there is a certain level at which we perceive even bright light quite adequately.
But in cases where bright light cannot be tolerated and is perceived as aggression, we can talk about the presence of such a negative manifestation in a person as photophobia. The causes of photophobia lie in the symptoms of another eye disease; this is not a separate type of disease at all, but a consequence of a pathology occurring in the human eye organs.
Why do the eyes react painfully to light?
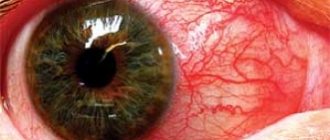
Another name for this phenomenon is photophobia. Hypersensitivity to light, its fear is especially acute under the influence of bright light sources, and in twilight or dark conditions, discomfort in the eyes is often less. The main manifestation of the pathological condition in question is a reflexive closing of the eyelids and the desire to cover the eyes with hands from the light. Often there is also pain in the eyes, increased formation of tear fluid, a feeling of “sand” in the eyes, which may indicate ophthalmological pathologies.
When asking questions about why photophobia occurs and what disease it may be a symptom of, one should consider not only eye diseases among the possible causes. Thus, photophobia develops against the background of certain diseases of the central nervous system, is present in infectious lesions of the body that occur with severe intoxication, and appears as a side effect when taking certain medications (for example, furosemide, tetracycline). These reasons may be indicated by additional manifestations: headache, nausea, elevated body temperature, etc.
A short-term increased sensitivity of the visual organs, which occurs as a result of prolonged stay in a room with low lighting, is considered a normal physiological phenomenon. This is explained by the fact that the pupil does not have time to quickly adapt to new conditions. This occurs after sleep, with prolonged reading, or working at a computer monitor. If a symptom occurs frequently and does not go away for a long time, this should alert you.
Psychosomatics of photophobia
Sometimes fear of light is a neuropsychological disorder in which a person has a panicky fear of sunlight. This deviation is called heliophobia and is accompanied by the appearance of the following symptoms while exposed to open sunlight:
- increasing anxiety;
- the desire to hide in a safe place, to escape;
- trembling throughout the body;
- weakness;
- increased heart rate;
- loss of consciousness.
Heliophobia forces a person to limit his time outdoors, narrow his social circle, and make it difficult to learn and find employment. Due to isolation, not only the psychological state suffers, but also physical health, because... without sunlight, the body does not produce vitamin D. People with this phobia have pale skin, low body weight, problems with teeth and the skeletal system.
Fear of light during a cold
With viral and bacterial diseases of the respiratory system, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, photophobia of the eyes is often observed, especially when looking directly towards light rays. The symptom is caused by intoxication of the body, associated with the proliferation of pathogenic microbes and the penetration of their waste products into the blood, and from there into the muscle tissue, including the eye. In addition, the patient experiences redness of the eyeballs, burning sensation in the eyes, and pain when moving the eyes.
Sometimes pathogens infect the structures of the eye apparatus, causing a concomitant inflammatory process in the membrane surrounding the eyeball. In this case, depending on the signs of what disease, fear of light is accompanied by mucous or purulent discharge from the eyes, pain, and swelling of the eyelids. Less commonly, optic neuritis, which has similar symptoms, occurs against the background of cold infections.
Photophobia with meningitis
With such a serious illness as, infectious inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord occurs. Photophobia and headache, intolerance to loud sounds, a sharp rise in body temperature, vomiting, and a rash on the body are the main symptoms of the disease. In patients, intracranial pressure increases, and brain nerves and ocular vessels may be affected. Due to its rapid progression and dangerous complications, patients with meningitis require immediate hospitalization.
Photophobia with measles
Adults rarely get sick, but once infected, the disease is severe, often with complications. This viral pathology is certainly accompanied by symptoms such as photophobia and lacrimation. Along with them, there are other characteristic manifestations: sudden deterioration of the condition, severe weakness, increased body temperature, headache, runny nose, rash. The appearance of light intolerance in measles is primarily associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organs of vision.
Photophobia – cataracts
The disease, which occurs in many older women, is characterized by a decrease in the transparency of the eye lens, partial or complete clouding. The main manifestation of this pathology is the appearance of blurred vision, in which objects are seen with blurred contours and look as if placed behind foggy glass. Often objects appear double before the eyes and color perception changes.
In many cases, this disease causes increased sensitivity to light, with photophobia increasing in the evening, and vision in the dark is significantly reduced. In addition, it is typical to see rainbow halos around light sources - lanterns, lamps. This is due to the fact that light rays, reaching the clouded lens, are scattered and do not reach the retina.
Photophobia in glaucoma
Among the causes of photophobia of the eyes, glaucoma stands out - a number of pathologies of the visual organs, accompanied by increased intraocular pressure due to impaired fluid outflow. As a result, pathological changes develop in the ocular structures, visual acuity decreases, and the optic nerve and retina are damaged. In adult patients, photophobia, the causes of which are associated with a type of this pathology - angle-closure glaucoma, is accompanied by symptoms such as eye pain, headache, and nausea.
Symptoms
A person suffering from photophobia, when exposed to an illuminated space, squints, closes his eyes, and tries to protect his eyes from the light with his hands. When wearing sunglasses the situation improves slightly. Increased photosensitivity may be accompanied by additional symptoms, such as:
- Headache;
- Pupil dilation;
- Redness of the eyes;
- Feeling of “sand” or “stinging” in the eyes;
- Impaired visual acuity;
- Unclear outlines of objects.
Photophobia is a disorder in which a person experiences increased sensitivity to bright light. Another name is photophobia. The cause can be many diseases of the organs of vision. Scientists have found that people with light eye color are more likely to be affected by photophobia. In advanced cases, complete intolerance to light is observed. What diseases cause photophobia?
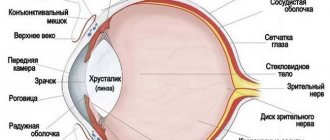
Photophobia - symptoms. With photophobia, a person reacts painfully to bright light sources: there is acute pain in the eyes, redness, irritation of the mucous membrane, a desire to squint, to turn away from the light source. Headache is a symptom accompanying photophobia. The thing is that the nerve endings of the retina are excessively sensitive, so at the slightest disturbance in the functions of the retina, photophobia of the eyes may occur.
Photophobia of the eyes - causes:
- Inflammatory diseases - conjunctivitis, keratitis. In this case, the eye tries to protect itself and maintain clarity of vision.
- Various eye injuries - sunburn, incorrectly selected lenses or glasses, curvature and ulcers of the cornea, retinal detachment.
- Heredity.
- Congenital differences in the structure of the eyes and body (albinos).
- Light eye color (the amount of pigment that protects the retina from light is very small).
- Various nervous diseases (meningitis, frequent migraines).
- Infectious diseases (measles, rabies, rubella).
- Poisoning with various toxic substances (mercury).
Causes also include adverse reactions to medications (Belladonna, furosemide, tetracycline, doxycycline, quinine). Under the influence of drugs that constrict the pupil, the retina is exposed to direct sunlight. Entry of a foreign body into the retina of the eye. In this case, photophobia is observed only in one eye. Environmental factors - excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eyes (looking at the sun or welding). Spending a long time in front of the monitor, fatigue and overwork, frequent depression and stress.
How to get rid of photophobia?
Depending on the diseases in which photophobia is observed, methods of getting rid of this symptom will vary. To establish a diagnosis, consultation is often required not only with an ophthalmologist, but also with specialists in other fields of medicine. Having found the provoking factors, it is necessary to begin treatment, which can consist of conservative methods or surgical interventions. While treatment is being carried out, photophobia of the eyes can be minimized by following the recommendations:
- wearing sunglasses, preferably with brown filters;
- limiting watching TV, staying at the computer;
- if the symptom occurs in paroxysms, you should be in a darkened room at this time.
Drops for photophobia of eyes
Photophobia of the eyes, the causes of which are explained by ophthalmological diseases, is eliminated through the use of eye drops, often the following:
- antibacterial (antiseptic) – Levomycetin, Tobradex;
- anti-inflammatory (hormonal and non-hormonal) – Dexamethasone, Indocollir;
- moisturizing – Oxial, Cationorm;
- vasoconstrictors – Okumetil, Vizin.
In some cases, along with treatment with eye medications, it is recommended to perform gymnastics and eye massage. If, after using the drops prescribed by the doctor, photophobia does not disappear or decrease within 3-5 days, the treatment requires adjustment. Repeated and additional diagnostic measures may be required.
Treatment of photophobia of the eyes with folk remedies
With your doctor's permission, you can try to reduce your fear of bright light through folk remedies. Many plants have proven themselves to be effective in treating ophthalmic symptoms, and photophobia of the eyes, the causes of which are associated with eye pathologies, is no exception.
Drops recipe
What does photophobia mean? What are the causes and symptoms of this disease? And, most importantly, what means of eliminating the problem are most effective?
In medicine, the term photophobia (photophobia)
indicates a state of hypersensitivity and intolerance by the eyes to light, both natural and artificial. Of course, photophobia is especially noticeable when exposed to bright light sources.
Photophobia cannot be considered as a real pathology. As a rule, it is only a consequence of other pathological processes occurring in the body.
How to avoid photophobia?
Before trying to get rid of photophobia on your own, consult your doctor. Photophobia is not a separate disease, but only a symptom. This is why it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist. He will conduct a thorough examination, find out the cause of the symptom, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Further treatment will depend on the cause of photophobia. For example, if any viral disease occurs, antiviral and antibacterial therapy will be prescribed. After final recovery, vision will return to normal.
However, there are small methods of self-prevention. It will help you reduce the unpleasant sensations from bright light, avoid redness and irritation of the mucous membrane of the eye. In some cases, photophobia has nothing to do with the appearance of diseases and disorders of the visual organs. In this case, you should buy dark sunglasses. Be sure to wear them on a bright sunny day. Glasses must have protective properties against ultraviolet rays.
If photophobia is caused by taking any medications, you should consult your doctor about changing medications.
Using antiseptic eye drops. The drops should have anti-inflammatory properties and soothe the mucous membrane of the eye. Wear special contact lenses or glasses that block sunlight. Avoid bright light sources. These small tips will help make life easier for people with photophobia.
Photophobia is not a disease, but just a symptom. Occurs due to the effects of various diseases, disorders in the function of the organs of vision. Symptoms of photophobia are redness of the eyes, dilated pupils, tearfulness, irritation of the mucous membrane, frequent blinking, avoidance of bright light sources. To alleviate the symptoms of photophobia, you need to purchase sunglasses with protection from direct ultraviolet rays, and use antiseptic eye medications aimed at relieving pain and removing inflammation and redness.
Photophobia of the eyes is a manifestation of a painful reaction of the visual organs to daylight. In medicine, this concept is called photophobia (fear of sunlight). The disease is characterized by unpleasant sensations and squinting of the eyes when natural or artificial light penetrates them.
When you are in the dark, the feeling of discomfort disappears. All this has its own causes and is also accompanied by certain symptoms.
Causes of photophobia
The main causes of photophobia can be grouped into four broad categories, namely: non-pathological conditions, diseases of the eyes, nervous system and other causes.
Non-pathological causes
Photophobia is a condition that almost everyone has encountered when moving from a dark environment to bright sunlight, this increased sensitivity of the eyes can be caused by:
- Too intense light. What matters here is the personal threshold of tolerance, which is variable and even depends on mood (for example, a state of anxiety can increase sensitivity to light).
- Light eyes . In particular, green eyes are more sensitive to light. Their pigment contains low amounts of melanin, which is known to protect against UV rays. Therefore, the threshold for sensitivity to light is higher in people with dark eyes.
- Albinism. This is a hereditary anomaly of character, which consists in a deficiency of pigmentation of the skin, choroid (the middle layer located between the sclera and the iris), as a result of which the eye acquires increased sensitivity to light.
- Pupil dilation. Can be caused by medications or drugs: atropine, cocaine, amphetamine, scopolamine, anticholinergic drugs, etc., as well as a state of excitement.
- Injuries and improper behavior - for example, prolonged use of contact lenses, exposure to bright light sources, prolonged gaze on a computer monitor or projector, etc.
Eye diseases and associated symptoms
Sometimes increased sensitivity to light
may be a consequence of eye pathology, then it is accompanied by other clinical manifestations:
| Pathology | Associated symptoms |
| Damage to the surface of the cornea, for example due to improper use of contact lenses. | Manifested by burning and lacrimation. |
| Congenital achromatopsia. The disease is characterized by the inability of some retinal cells to perceive colors and adapt to light. | Grayscale vision, photophobia, nystagmus (involuntary eye movement). |
| Aphakia. Absence of the lens of the eye. May be congenital, but more often results from surgery | Accompanied by farsightedness. The absence of a lens causes much more light than normal to reach the retina of the eye, causing photophobia. |
| Aniridia. The absence of the iris, which reduces the intensity of light reaching the retina. | Decreased vision. |
| Cataract. Loss of transparency of the lens, which reduces visual perception. | A decrease in visual perception is accompanied by intolerance to high-intensity light, blurred vision, the appearance of light halos, eye fatigue, and burning. |
| Conjunctivitis. Inflammation of the conjunctiva or membrane that surrounds the eyeball. | Symptoms include photophobia, redness of the eyes, watery eyes and discharge, pain and swelling of the eyelids. |
| Retinal detachment . The photoreceptors that form the retina are separated from the pigment epithelium. | Symptoms of the disease include photophobia, pain, and photopsia (seeing rays of light or black particles). |
| Endophthalmitis. Severe eyeball infections almost always lead to eye surgery. | Accompanied by photophobia, severe pain and blurred vision. |
| Congenital glaucoma. An eye disease typical of newborns or the first year of life. | One of the most unpleasant symptoms is severe photophobia, so strong that the child constantly hides his face. It is also accompanied by corneal edema, an increase in corneal diameter and blepharospasms. |
| Uveitis. Inflammation of the choroid, usually of an autoimmune nature. Often combined with Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, colitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. | Symptoms include photophobia and blurred vision, vitreous detachment, i.e. "flies" in the field of view. |
| Optic neuritis. An inflammatory process of the optic nerve, which can have several causes: multiple sclerosis, viral infection, autoimmune disease, tuberculosis, Devic's disease. | Symptoms of photophobia, in some cases loss of vision, pain and involuntary eye movements. |
| Rabies. Dangerous viral infection. | It has very severe symptoms and among the first symptoms are headache and photophobia. |
| Richner-Hanhart syndrome. A genetic disease characterized by the body's inability to synthesize the enzyme tyrosine aminotransferase, which is produced in the liver. | Causes serious problems with eye function, including pain, redness, photophobia and decreased vision. |
Nervous system disorders and light sensitivity
Some nervous system diseases that affect the brain and nerves have light intolerance among their symptoms.
In particular, these include:
- Cystine accumulation. Cystine is an amino acid, but with a certain genetic defect it accumulates in the form of insoluble crystals in various organs. The accumulation of cystine crystals in the eyes leads to increased sensitivity to light.
- Botulism. Food poisoning caused by foods contaminated with a toxin from the Clostridium bacterium. Causes dilated pupils (and therefore photophobia) and muscle paralysis.
- Vitamin B2 deficiency. Riboflavin deficiency is usually associated with nutritional problems or liver dysfunction. Among the problems that accompany vitamin B2 deficiency is sensitivity to light caused by pupil dilation.
- Magnesium deficiency. Magnesium is a very important microelement for the body. Its deficiency causes numerous disorders, including migraines and light intolerance.
- Headache and migraines. Headaches are often accompanied by intolerance to light and intense sounds.
- Consequences of alcohol abuse. The so-called hangover leads to a set of unpleasant symptoms, among which the most common are headaches and intolerance to intense light sources.
Causes
Brain diseases that provoke the development of photophobia:
- Migraine
is a disease that occurs when the vessels that supply blood to the trigeminal nerve are activated. The patient experiences severe headaches, which are accompanied by photophobia and nausea. - Meningitis
is an inflammation of the meninges due to an infectious lesion; as a result of damage to neurons, a fear of light occurs. - Encephalitis
is an inflammatory process of the brain substance of various etiologies. With severe headaches and impaired consciousness, increased sensitivity to light also occurs due to irritation of the meninges. - Stroke
– during a stroke, the blood supply to an area of brain tissue is disrupted, and when it is damaged, neurological symptoms occur, one of which is photophobia. - Brain abscess
is a localized accumulation of pus in the brain. When intoxication damages organ tissue, swelling of the brain and irritation of its membranes occurs, which provokes the development of photophobia. - Acromegaly
is a tumor of the pituitary gland in which the secretion of growth hormone increases. Growth hormone is a mediator that affects brain activity; when in excess, it provokes neurological disorders, including photophobia. - Tension headache
- photophobia occurs against the background of severe overexertion and accompanies cephalalgia. - Rabies
- when infected saliva gets on the skin or in the blood, the virus is activated, which provokes a disruption of the autonomic system.
Other causes of photophobia:
- eye injuries;
- burns of the visual organ;
- entry of a foreign body;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- keratitis;
- uveitis;
- iritis;
- glaucoma;
- iridocyclitis;
- corneal ulcer;
- retinal disinsertion;
- complete or partial absence of the iris.
What to do if you have photophobia
Due to the complex and varied etiology of the disorder, it is difficult to give an unambiguous treatment protocol, and often completely impossible.
The first step is, of course, a correct diagnosis, that is, establishing the exact cause causing sensitivity to light.
If the cause is non-pathological, it is necessary to determine the source of the problem: taking medications or drugs that cause pupil dilation.
If the cause is pathological, then we can try to keep the symptoms under control through a range of remedies, which we list below:
- Supplements. Most suitable are those based on lutein and zeaxanthin. Due to their antioxidant properties, such supplements have a protective function for vision.
- Natural remedies. Include the use of drops and compresses obtained from certain herbal products, namely chamomile, artichoke, mallow and butterbur.
- Sunglasses . The easiest way to keep photophobia under control. Note that brown filters are the most effective.
What treatment is prescribed?
Effective drugs
If a person develops photophobia after a severe bruise, injury or burn to the eyes, the mucous membrane must be treated with antiseptic agents, a sterile bandage applied and the victim urgently taken to the hospital.
To relieve discomfort, the doctor will select the necessary drug.
It is important to treat increased eye sensitivity to light in a comprehensive manner, so first of all, medications are prescribed that eliminate the root cause of the pathology. To prevent it from being painful to look at on the street or in a bright room, the doctor will prescribe special eye drops. If a person reacts inadequately to light due to damage to the organs of vision by a bacterial infection, bactericidal ophthalmic drugs are prescribed, for example, such as: Traditional medicine will help reduce pain.
You can try to treat photosensitivity of the eyes using alternative medicine methods, after consulting with your doctor. Medicines prepared at home are not able to get rid of the main cause of photophobia, but with their help they will be able to remove unpleasant symptoms, inflammation, redness, burning and itching. The following home remedies have worked well:
- Anti-inflammatory herbal infusion. Pour 1 tsp into the teapot. calendula and chamomile flowers, pour 300 ml of boiling water over everything. Leave the product for 40 minutes, pour a little into a clean container, moisten gauze or cotton wool in it and wipe your eyes 3-4 times a day. You can put the infusion in your eyes, this will help cure the disease faster.
- Drops on silver water. Boil 500 ml of water, cool and lower the silver item into it. Cover the container with the liquid with a napkin and set aside for 5-7 days. When the product is ready, use it in the form of eye drops daily in the morning, afternoon and evening before bed. To enhance the effect, it is recommended to add honey and aloe juice in a ratio of 5:1:1.
Compresses based on sea buckthorn oil, which are recommended to be applied to the eyelids for half an hour before bedtime, help strengthen visual function and improve vision.
The phenomenon of photophobia, or intolerance to light radiation, can manifest itself in different ways. Sunlight and artificial light can cause discomfort or increased tearing, rapid eye fatigue, or a feeling of sand in the eyes after several minutes of working at the computer. The causes of light intolerance can also be different, from relatively harmless to serious pathologies. Let's figure out what to do if you have eye intolerance and what remedies can help.
Treatment of photophobia
If photophobia occurs, you should consult an ophthalmologist. It is possible that in the future the person will need consultations and examinations from other doctors, depending on what disease he or she has been diagnosed with. With photophobia, it is not the symptom itself that is treated, but the disease that caused the fear of light.
To relieve symptoms, your doctor may recommend temporarily wearing dark sunglasses and taking some anti-inflammatory eye drops. The patient will also have to temporarily give up certain types of cosmetics and sunbathing.
It should be remembered that photophobia is only a symptom of a possible serious illness, so the main thing is to detect a possible pathology. With proper treatment, photophobia will go away on its own.
Possible complications
If you ignore the symptom of photophobia, the causes of the problem will only get worse and can lead to dangerous consequences. These could be neuralgic or eye diseases, loss of vision, etc.
Photophobia not only reduces the patient’s quality of life, but can also cause a pathology such as heliophobia. This is a psychological pathology that manifests itself as a strong, panicky fear of the rays of the sun. Thus, even having gotten rid of photophobia, a person always risks experiencing the fear that bright lighting will again provoke discomfort and pain. Manifestations of heliophobia are as follows:
- Increased heart rate and breathing;
- Trembling in hands;
- Leg tremors;
- Cardiac arrhythmia;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Dizziness, fainting;
- Panic attack, hysteria.
Prevention
To avoid diseases of the visual analyzer, accompanied by photophobia, you should lead a healthy lifestyle. Avoid eye injuries or excessive eye strain, and do not forget to take unloading breaks when working at the computer or watching TV. Another good habit is to undergo regular examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Photophobia is the increased sensitivity of the visual organs to bright light. The cause of photophobia of the eyes can be both illness and prolonged exposure of a person in a room with no lighting. Damage may also occur due to the use of certain medications.
. Most often, a noticeable dilation of the pupils is observed, which refers to the reason for the sun's rays hitting the retina.
What symptoms accompany photophobia?
Sunlight or bright artificial lighting can cause great discomfort in a patient with photophobia, and even real agony. At the same time, he will squint or try to close his eyes completely. The patient may experience lacrimation and such symptoms of photophobia are most often observed with conjunctivitis and ophthalmic herpes. Photophobia can also be accompanied by headaches, fever, and even vomiting. The development of these symptoms may be preceded by meningitis, migraine or stroke.
People with dark eyes have less light sensitivity because they have more pigment that protects them from bright light.
Different patients may have partial or complete intolerance to high light levels.