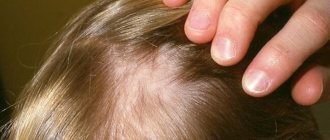
general description
This pathology is often a benign neoplasm on the skin, which mainly rises above its surface. In some cases, it may take on a lumpy shape, and sometimes remains a small spot of different color.
Intradermal nevus has a painless surface and soft structure. The color of the neoplasm can be different: pink, red, brown and even black.
An intradermal nevus can be located on the neck, scalp, or face. Very rarely, the formation occurs on the body or limbs. It should be borne in mind that if the tumor is benign, then it practically does not cause pain. It degenerates into a malignant form, melanoma, in only 20% of cases.
If there is some discomfort in the area of the skin lesion, or the intradermal nevus begins to grow rapidly, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Intradermal nevus (intradermal melanocytic)
The main features of intradermal nevus; Similar tumors; Nevi formed on its basis; Delete.
Intradermal melanocytic nevus. Main features
Intradermal nevus (intradermal) is a subtype of the common acquired melanocytic or pigmented nevus. More precisely, this is the last stage of its development before disappearance. Most of the pigment cells - melanocytes - pass into the underlying layer of skin called the dermis, some of the pigment cells die and are replaced by fat and connective tissue.
This is where all the characteristic changes occur, such as loss of color, proliferation of dense tissue that makes up the dermis and a large convexity of the nevus. Intradermal nevus is very common after 30-40 years, especially among women. On the face, this type of nevus can be found in the area of the lips, nose, mouth, in the hair growth area, and less often in the area of the ears and eyes.
It is extremely rare that an intradermal nevus appears in the area of the feet and hands. The usual size of these moles is from 0.5 to 1 cm. The color of the formation is most often flesh-colored or light brown; darker formations are rare. They have the shape of smooth bumps or nodes with a wide base. It may appear as a soft, loose, wrinkled pouch of skin.
Nevi with a narrow stalk are often located on the trunk, neck, armpit and groin. Raised, protruding nevi are more prone to injury. The dome shape is the most common. The surface may be shiny. The top of the nevus may be covered with single hairs, brown crusts, scales, and dilated vessels.
Some intradermal nevi may have a stalk - a more narrowed base. The pigment cells of the intradermal nevus are located too deep - in the dermis, and almost do not synthesize melanin, which is the reason for the lighter color compared to borderline nevi. However, some such growths remain brown in color.
Intradermal nevus does not change for many years and causes mainly only cosmetic problems. Ulcers on an intradermal nevus or bleeding appear only as a result of injury and heal on their own within a few days. The addition of a secondary infection or expansion of sebaceous gland cysts can cause acute inflammation and swelling of the nevus.
At first, such changes in the nevus may be concerning due to suspicion of melanoma, however, these changes quickly disappear with treatment. On the other hand, if no improvement is observed, a biopsy may be performed.
Many intradermal nevi on the face and nose. This picture is not uncommon.
A pigmented intradermal nevus of such a dark color is rare.
Skin tumors similar to intradermal nevus
There may be dilated blood vessels on the surface of the mole. Due to this, an intradermal nevus can sometimes strongly resemble an incipient basal cell carcinoma without ulceration, but is much softer to the touch than a basal cell carcinoma. In addition, basal cell carcinoma may have retraction in the center and uneven edges.
Trichoepithelioma, neurofibroma, dermatophyroma and fibrous papule are benign tumors very similar in appearance to intrademal nevus. Dermatofibroma can be identified by its characteristic depression, retraction in the center with pressure on the edges.
Fibroepithelial polyp and neurofibroma may be impossible to distinguish from intradermal nevus by appearance. It is extremely rare that apigmented melanoma appears, similar in appearance to an intradermal nevus, or the nevus itself eventually turns into melanoma.
An experienced dermatologist or oncologist will be able to rule out melanoma. In difficult situations, a biopsy may be performed.
Melanocytic nevi formed on the basis of intradermal
- Papillomatous nevus is another type of intradermal or complex nevus. This mole has a characteristic papillary surface, which, together with its pink color, makes it very similar to a mulberry. Papillomatous intradermal nevus is more often found on the skin of the torso, the surface of the arms, and the neck. The mole is soft to the touch and has a pink or brown color. Under the microscope, only a small part of papillomatous nevi are classified as intradermal melanocytic nevi. Most of them have part of melanocytes between the epidermis and dermis, part of melanocytes in the dermis, and belong to complex pigmented nevi. Intradermal papillomatous nevus differs in appearance from the complex one in that it is lighter in color, is more elevated and does not have a dark flat rim along the edges. This variety is most often confused with seborrheic keratosis (age warts). Especially if there are crusts or scales on the surface of the nevus. However, the opposite usually happens; all lesions of seborrheic keratosis are considered nevi. Since the papillomatous nevus has an uneven surface, injuries occur even more often than usual for intradermal nevi. It is better to see a doctor for an injured mole, because it is difficult to distinguish them from melanoma. Typically, injured moles heal within one to two weeks. If healing does not occur, you should consult an oncologist.
- Dysplastic nevus can rarely form from intradermal nevus. In order to call an intradermal nevus dysplastic, a violation of the uniformity of color, irregular shape, symmetry, or suspicious growth is sufficient. As always, the first thing to rule out in this case is melanoma.
- Nevus Setton or halonevus , also, sometimes, is formed from intradermal pigment. More precisely, a light circle or rim appears around an initially ordinary mole. The light rim contains leukocytes that attack pigment cells. As in the case of a dysplastic nevus, you first need to remove suspicion of melanoma by contacting an oncologist.
The photo shows an intradermal nevus with a shiny surface and dilated vessels. Very similar to basal cell carcinoma.
Papillomatous intradermal nevus with many small papillae, soft, clear contours.
Intradermal nevus most often needs to be removed for cosmetic reasons. Especially when a mole grows on the face. Slightly less often, the reason for removal is persistent injury due to its location in inconvenient places and the towering nature or narrow stem.
Infrequently, an intradermal nevus is removed due to suspected melanoma or basal cell carcinoma, and tissue samples are sent for histological examination. The set of methods for removal is standard for all melanocytic nevi (laser, radio wave, surgical).
It is better not to use cryodestruction and electrocoagulation, especially on the face.
Source: https://skinoncology.ru/nevus-kozhi/vnutridermalnyj-nevus
Reasons for appearance
Until now they have not been clarified for sure. But in any case, this pathology is a consequence of abnormal functionality of the skin. There are factors that can trigger the development of the disease:
- Allergic skin pathologies.
- Intrauterine developmental disorders of the fetus.
- Heredity.
- Hormonal disorders, for example, changes in the body's functioning during pregnancy or menopause in women.
- Dermatological infectious pathologies.
Intradermal papillomatous nevus can also develop as a result of severe toxic poisoning of the body, and the substance due to which it appeared is not important.
What signs indicate the development of melanoma?
An intradermal nevus is considered a benign formation, but sometimes malignant processes begin to develop in it. The following signs indicate this:
- A benign mole is symmetrical and has smooth edges. Melanoma is more asymmetrical, with a ragged outline .
- Malignant formation is characterized by uneven color.
- The diameter of melanoma is more than 5 mm. However, the nevus rarely exceeds these sizes.
- An ordinary birthmark does not change its shape, but melanoma grows over time.
Types of pathology
There are quite a lot of them:
- Galonevus.
- Blue. It has a relatively small size and a special blue color.
- Borderline. This formation is characterized by the fact that it rises above the surface of the skin only partially.
- Intradermal papillomatous nevus. Its size can exceed 1.5 cm, and over time it can grow even larger. Most often it appears as a brown lump, similar to a wart. Stiff black hairs can be seen inside the growth. With careful handling of this neoplasm, it rarely degenerates into malignant.
- Non-cellular. It often occurs on the face rather than causing serious physical discomfort. Its shape is usually convex. Due to its location, the tumor must be removed.
- Intradermal melanocytic nevus. It has a rich color and a regular, clear shape. It can be found on the chest and even on the genitals. The size of the neoplasm rarely exceeds 0.5 cm. It may be at the same level with the skin or rise slightly above it.
Some of these formations can develop into melanoma. However, with careful treatment and timely treatment, intradermal skin nevus is not dangerous.
Intradermal nevus, what is it, photos, symptoms, stages of development
The moles we all know can be dangerous to health, or they may not cause any harm. However, experts caution that there are hidden risks of transition from benign to malignant.
Suspicious moles in the language of doctors, scientists and laboratory researchers sound like a skin nevus, which appears as a result of the displacement of migrating melanoblasts within the epidermis. Many people define papillomatous intradermal nevus as a phenomenon that forms in the womb.
It is necessary not only to understand intradermal melanocytic nevus, what it is and what its nature is, but also to study all its varieties, stages of development and take into account all the recommendations of doctors that are given in such cases.
Intradermal nevus - what is it?
Answering the question of how a melanocytic intradermal nevus manifests itself (in English – “melanocytic nevus intradermal”), what it is, it should immediately be noted that the nature of such a phenomenon does not necessarily have to be pathogenic.
Moles or birthmarks may well be benign and appear either at birth or during puberty, in adolescence.
Doctors say that only in 15-16% of cases a pigmented nevus can degenerate into a real melanoma, which should be removed immediately.
Externally, the intradermal nevus, the photo of which is presented in this material, resembles a rounded wart, but only colored in one shade or another, or flesh-colored, but with a denser texture. The surface is usually not painful either when pressed or without applying pressure to the bulge.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n_5C4DqzpFU
FOR REFERENCE: In the most common cases, nevi are located on the neck, face, décolleté, and on the body - the torso, arms and legs; their occurrence is less common.
Varieties
If a person has such a skin formation in large quantities, a strange color, in the form of spots, moles, warty growths, or it changes shade, size, shape or texture, then we can talk about different types. Based on structure, quality and uniformity, round growths on the skin can be divided into the following types:
- Warty or papillomatous.
- Pigmented or melanocytic.
- Noncellular.
- Rare dysplastic.
- Halonevus or Setton nevus.
If on the skin you see an overly convex round phenomenon of a flesh-colored or darkish (sometimes even black) color, then it’s time to talk about the warty variety. The size of such papillomas can sometimes even exceed 1-1.5 cm, and also increase over time. The surface is lumpy, and in the middle of the papilloma you can even see a small number of hairs.
If a diagnostician determines that a person has a pigmented intradermal nevus, then, firstly, the tests will show an excessive accumulation of melanin in that place, secondly, the growth itself will have a distinct outline, and thirdly, the size of such formations, as a rule, is not exceed 0.5 cm. In structure, such varieties are both lumpy and smooth, and in location they are found not only in the chest area, but also on the genitals.
Noncellular nevi include moles that have an extremely unpleasant appearance and are often located on the face and neck, thereby creating a cosmetic, aesthetic defect.
Very often, such a deficiency can be found at the age of hormonal surges - in teenagers, women facing menopause and in other cases.
All experts are confident that such growths should be removed.
However, in addition to such a phenomenon on the human body as intradermal melanocytic nevus or another, it is also necessary to distinguish such varieties that show the localization of the accumulation. These are the following non-cellular types:
- Borderline.
- Difficult.
- Intradermal.
Intradermal is formed due to the migration of a large accumulation of melanoblasts, which first form between the dermis and the basal membrane, and then move into the dermal layer of the papillary level. It turns out that papillomas or moles of the intradermal type are located simultaneously in two layers - in the dermis and epidermis
NOTE! It is the intradermal nevus that is the final stage of development of moles. The deeper the mole goes into the dermis, the darker it will become.
How and for what reasons does it appear?
Diagnostics and therapy have not yet determined the unambiguous reasons for the appearance of such skin abnormalities as pigmented nevus or some other one. According to generally accepted opinions, which have indeed been practically confirmed, the prerequisite for the appearance of such moles is hereditary and develops in utero.
Immature cells that carry melanin to the skin during the formation of its color may appear in the form of spots in some depressions of the skin. Therefore, papillomatous intradermal, melanocytic pigmented nevus of the skin is formed mainly for genetic reasons.
Birthmarks or moles can form as the child grows, or they can remain the same size.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Papillomatous intradermal melanocytic nevus of the skin does not necessarily appear visually in infancy. They can appear at 12 years old, at 30 and at 40.
Intradermal nevus: 7 stages of development
Like any formation, a nevus, photos of which can be viewed here, has its own stages of development.
They can be divided into 7 most basic stages:
- Visually, moles may not immediately appear due to the fact that they are still forming under the layer of the epidermis.
- Once between the layers of the dermis and the upper outer layer of the skin, moles can change their color or texture.
- Once the moles or birthmarks move further towards the outer layer of the skin, reddish-brown spots will be visible on the skin.
- As the child grows, so do the moles, gradually acquiring clear boundaries and shapes.
- The mole is already completely noticeable, which indicates the final stage of its formation.
- But there is also a stage of transformation, when after some time the mole will take on a more convex shape, its size or color may change, depending on the variety.
- The last transformation is the discoloration of the mole and the covering of it with small amounts of hair, which indicates that melanin stops being produced.
There are moles that seem to be “spread” over the skin, covering the entire area occupied by them. There are moles like warts in the form of a growth. What if there is an intradermal pigmented nevus, a photo of which is in this article, which is formed on a stalk. This means that first a rod appears on the surface of the epidermis, on which the mole is already “sitting.”
IMPORTANT! If the mole is on a leg, then it should not be allowed to break or come off, so such a person has to watch it often, carefully put on or take off clothes and try not to cut it with hair or anything else.
Doctors' recommendations
In cases where doctors are contacted to remove this growth, mole, spot, removal is not always immediately prescribed. It is often suggested to first observe the formation on the skin, and this may take more than one year.
When a papillomatous intradermal melanocytic nevus is removed, the nearby healthy skin is also covered by 2-3 mm. This is done in order to prevent as much as possible the new formation of moles in the same place.
When for some reason a mole cannot be surgically removed, doctors recommend applying special applications of 5% Fluorouracil or Tretinoin.
IMPORTANT! Typically, the following methods are used to eliminate moles: cryodestruction, laser surgery, radiosurgery and electrocoagulation. In this case, much attention is paid to the hormonal background (its dynamics) throughout the entire course of treatment, as well as before and after its administration. In order to protect yourself as much as possible from various complications that moles, nevi, and papilloma can cause in the body, you need to follow several important preventive rules and measures.
First of all, such formations on the skin should always be hidden from direct sunlight, and should not go to a solarium to sunbathe under ultraviolet light if there are a lot of moles on the body. If a person develops more and more nevi over time, he needs to go to the doctor.
And when this or that operation is performed, you should never neglect the doctors’ recommendations on how to care for the place where the mole was, and what kind of lifestyle you should continue to lead.
about intradermal nevus
Source: https://MedoDerm.ru/rodinki/vnutridermalnyj-nevus.html
Diagnostic features
The presented pathology must be detected in a timely manner. Diagnostics involves the implementation of a set of measures that will help determine the type and degree of complexity of the disease, as well as the predisposition of the neoplasm to degeneration. So, the doctor must perform the following actions:
- External examination of the affected area and determination of its morphological features: location, size, shape, color.
- Dermatoscopy of the tumor, which will make it possible to distinguish it from other diseases.
- Siascopy. This is a new digital diagnostic method that allows you to more accurately determine the characteristics of the development of pathology.
- Ultrasound of the skin.
- Biopsy of a tumor element to confirm or refute the oncological prognosis.
THE MAIN DIFFERENCES OF BENIGN MOLES FROM MALIGNANT MOLES
A number of characteristics allow you to accurately determine which moles are dangerous. The benign formation is not asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle, then both sides will correspond to each other.
A cancerous lump does not meet these requirements.
Unlike melanoma, a common pigmented spot has smooth, rather than jagged, borders.
We suggest you read Rash on the stomach, face, chest, arms during pregnancy: how to treat
The presence of colors and brightness is another exciting symptom.
The formation changes size over time and becomes larger than 6 mm. Noncancerous nevi look the same. You need to be alert if a mole begins to grow or gives other unusual signals regarding its general condition.
The only way to accurately establish a diagnosis and confirm or refute suspicions of cancer is to conduct a histological examination of cells using a biopsy.
How does the disease develop?
An intradermal papillomatous nevus can appear from birth, although it is very difficult to notice immediately. Education develops in several stages:
- The neoplasm is still under the epithelium, so it often goes unnoticed.
- Gradual movement of nevus cells into the upper layers of the dermis.
- Acquiring a convex shape. As the child grows, the intradermal melanocytic nevus of the skin increases in size.
- Stunting of growth and discoloration of nevus cells. At this stage, the inflammatory process and degeneration of the tumor may begin.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
In principle, if you have an intradermal melanocytic nevus, you should consult a doctor, even if it does not bother you. However, there are direct indications for contacting a specialist:
- The tumor is located in places where it can be constantly injured: on the scalp, soles of the feet, genitals.
- The formation begins to bleed, and a feeling of itching and burning appears.
- The tumor has an unnatural color, is large in size, or is growing rapidly.
- The patient feels pain in the affected area.
- The patient has close relatives who have had melanoma.
Treatment of pathology
It must be said that papillomatous intradermal melanocytic nevus is not amenable to drug therapy. In most cases it must be removed. You can do this in several ways:
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen. This procedure may be used if the nevus is located in areas hidden under clothing. After the operation, very noticeable marks remain. This operation may cause severe burns. It completely destroys the neoplasm, so there is simply no material left for further analysis.
- Surgery using a scalpel. This procedure allows you to get rid of even a very large nevus. However, such an operation is traumatic, it requires a long recovery period, and it leaves noticeable scars. But as a result, the material can be examined for the presence of malignant cells.
- Electric cauterization. This is a practically painless method of removal, but it is impossible to obtain a nevus for research, since it is completely destroyed.
- Laser treatment. It is quite effective and can be used on any part of the body. The wound heals quickly after surgery, and the risk of infection is very low. But even in this case there is no material left for further research.
- Radio knife. This is the most progressive method of combating the disease. It contains the advantages of all previous methods, and the only disadvantages that can be highlighted are the high cost of the procedure.
Treatment tactics
Most intradermal pigmented nevi are safe and do not require treatment, only dynamic observation. Moles have to be removed if their integrity is damaged, especially repeatedly. This is usually due to their localization, which does not allow avoiding periodic mechanical trauma: on the palms, soles, neck, waist. Often pigment spots are removed for aesthetic reasons.
There are several ways to remove intradermal pigmented neoplasms.
| Method | Description |
| Surgical removal | A traditional technique in which mole resection is performed with a scalpel under local or general anesthesia. The disadvantages of the method include the appearance of scars formed after excision. However, the nature of the postoperative scar depends largely on the suture material and the qualifications of the operating doctor: it is possible to apply an almost invisible cosmetic suture. |
| Radio wave excision | A non-contact technique based on the use of high frequency radio waves. The required effect is achieved due to the thermal energy generated in the tissue when it is exposed to high-frequency radio waves emitted by a special Surgitron apparatus. Sterility, bloodlessness, low trauma, absence of noticeable scars after healing of a postoperative wound are the undeniable advantages of the method. |
| Electrocoagulation | The conversion of high-frequency current into thermal energy is the basic principle of operation of an electrosurgical high-frequency device used in dermatology for excision of intradermal tumors. The technique makes it possible to coagulate vessels damaged during surgery, which reduces operation time and blood loss. |
| Cryodestruction | The method is based on the effect of low temperature on fabric. To achieve the desired effect, liquid nitrogen supplied through a special cryoprobe is most often used as a cooling solution. During cryodestruction, the surrounding tissues are practically not damaged, no bleeding occurs, and rough scars are not formed during the healing process. |
| Laser removal | The technique involves the use of a carbon dioxide or neodymium laser. The advantages of laser removal include the ability to accurately dose the radius and depth of exposure, and the ability to maintain the integrity of surrounding tissues. After removing small formations, there are practically no traces left. |
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to properly remove a mole on the body at home
Electrocoagulation is one of the effective methods for removing benign skin lesions
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mNX2Elt6ofU
You can choose different methods for removing moles only if you are absolutely sure of their benign nature. If the formation is traumatized or there is the slightest suspicion of its malignancy, one should resort only to surgical excision, which should be carried out by an oncologist. It must be removed radically, and subsequent histological examination is required.
Electrocoagulation is one of the effective methods for removing benign skin lesions
Features of laser surgery
Papillomatous intradermal melanocytic nevus should be completely removed. Otherwise, it will begin to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Laser surgery is performed under local anesthesia and lasts only 5 minutes. After it is completed, you will go home the same day, and the recovery period will be reduced significantly.
For work, the specialist uses a special device capable of producing laser radiation. He gradually cuts off the thin plates of the tumor until it is completely removed. The depth and intensity of radiation are adjusted in each individual case. It all depends on the size of the education and its features.
Preventive measures
Intradermal pigmented nevus is a rather unpleasant disease that can develop into a malignant tumor. However, if you follow some preventive measures, then such an outcome of events can be avoided. So, don't forget these rules:
- You should not overuse visits to the solarium or stay there for too long.
- In summer, avoid being exposed to direct sunlight for long periods of time, especially between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- You should not visit saunas or steam baths too often.
- People with fair skin should be especially careful with the sun, as they are more susceptible to the appearance of moles and melanomas.
- The neoplasm must not be injured.
If you discover a mole that has suddenly changed color, shape or size, consult a doctor immediately. Be healthy!
Prevention and reviews
A person cannot influence the appearance of moles. It is necessary to monitor their condition and take certain measures to avoid the development of oncology.
Measures:
- It is necessary to reduce the time spent in the sun, and do not overuse the solarium.
- You should not frequent baths and saunas.
- You should be careful and try not to damage the nevi.
- If there are suspicious changes or damage to an intradermal mole, you should go to the hospital.
Intradermal nevi do not cause much trouble to a person. It is necessary to note every change, take timely measures, and begin the necessary treatment.