Prostatic hyperplasia is a very common pathological condition in men after forty years of age. Statistics indicate that more than thirty percent of men at this age have problems associated with prostate enlargement. Due to its widespread prevalence and high number of life-threatening complications, this problem is of serious interest to researchers in this field. This article describes the causes that can lead to the occurrence of benign prostatic hyperplasia, modern methods of diagnosis, treatment and prognosis for such patients.
general description
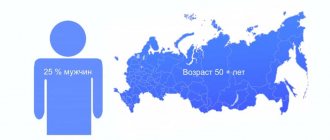
Adenoma is found in 30-40% of men after 50 years, in 75-90% after 65 years. These statistics are explained by the fact that the prostate develops before puberty, and then its functions begin to slowly decline. The gland tissues gradually atrophy, and cystic formations appear in them - the first precursors of the disease.
The development of adenoma begins with the formation of one or several small nodules in the periurethral glands (figure below), located in the submucosal layer of the bladder neck (at the border of the neck and seminal tubercle). They are separated from the prostate by a layer of smooth muscle. Gradually, the nodules enlarge, form spherical masses and invade new tissue - nodular prostatic hyperplasia develops. The process always begins in the cranial (front) part of the prostate.
Longitudinal section of the prostate: a – prostate tissue (stroma); b – layer of smooth muscle; c – periurethral glands.
As the nodes increase in size, they push the prostate tissue to the outer borders. As a result, the tissues are compressed, compacted, pressed against the membrane and form a surgical capsule. If the adenoma is removed in time, the pressure on the prostate tissue will disappear and after about 6-7 months they can restore their structure.
Photodynamic therapy
Prostate adenoma in men, the symptoms of which were mentioned earlier, can be treated with photodynamic therapy. The essence of the method is that non-toxic substances are administered intravenously. Afterwards, the affected organ is exposed to special light. This effect is detrimental to pathologically altered cells.
Photodynamic therapy consists of several main stages:
- At the first stage, as mentioned earlier, photosensitizers are introduced within a few minutes.
- The second stage lasts several days. During this time, photosensitizers accumulate in the organ.
- At the third stage, self-irradiation occurs. The therapy acts exclusively on damaged organ tissue. This is achieved through three-dimensional modeling. It allows you to place laser LEDs as accurately as possible.
Types of adenoma
Adenoma can develop from three groups of periurethral glands: two on the sides of the posterior urethra and one slightly higher - in the area of the bladder triangle (subcervical group). In the first case, a subvesical adenoma (bilobar) is formed, which elevates the bladder on one (unilobar) or on both sides (bilobar). An intravesical adenoma (middle lobe) develops from the glands of the subcervical group, which can protrude into the bladder in the form of a tongue (cervical). It is possible for all three groups of glands to grow at once.
Mixed adenoma: 1 – intravesical adenoma; 2 – subvesical adenoma.
The adenoma can be asymmetrical, grape-shaped or unilateral. The surface of the formations is always smooth, the consistency of the contents is elastic and homogeneous to the touch.
Depending on what tissues are involved in the adenomatous process, the following types of tumor are distinguished:
- Adenomatous prostatic hyperplasia (composed predominantly of glandular tissue);
- Fibrous (from fibrous connective tissue);
- Myomatous (stromal, composed of muscle tissue).
Glandular hypertrophy of the prostate is considered a true adenoma. Mostly mixed forms are diagnosed. Glandular-stromal hyperplasia of the prostate gland is considered the most dangerous from the point of view of prerequisites for malignant degeneration.
There are three types of tumors based on their mass:
- Up to 30 g – small.
- Up to 70 g – average.
- Up to 250 g – large.
Depending on the direction of growth, adenoma can be of three types:
- Intravesical (directed to the bladder);
- Rectal (growth is directed towards the rectum);
- Mixed.
Urologist-andrologist Alexey Viktorovich Zhivov about the symptoms of prostate adenoma
The rectal form is considered the safest because it does not cause problems with urination, bladder and kidneys. There are no symptoms, and the growth is detected only during preventive examinations.
The bladder form is manifested by urinary disorder (pain, leakage and urinary retention). The urethra is compressed, its tissues are swollen and react sharply to external irritating factors: alcohol intake (even in small quantities), hypothermia, sexual overstimulation.
A detailed article about the symptoms of prostate adenoma at different stages.
Based on the nature of tumor spread, focal and diffuse prostatic hyperplasia are distinguished. In the first case, the tumor is localized, in the second, the entire gland is affected.
Stages of adenoma development
Each stage of adenoma development has its own group of symptoms associated with structural changes in the tissues of the bladder, its neck and urethra. Main stages:
- Compensatory (preclinical). The obstructed outflow of urine is compensated by tension in the releasing muscles of the bladder (detrusor). It can still be completely emptied with a certain degree of straining. In men over 50 years of age, an early sign of adenoma may be premature ejaculation and the appearance of blood in the semen (due to rupture of blood vessels). For some, constant straining causes hernias and hemorrhoids. At this stage, libido may increase.
- Stage of dysuria. The detrusor fibers are partially replaced by connective fibers, urination becomes difficult, the bladder stretches, its walls become thinner and deformed. An uncontrollable (imperative) urge to urinate appears. At first the symptom bothers you only at night, then at any time of the day. The stream of urine falls vertically, there is almost no pressure. Due to stagnation of urine, stones form in the bladder and cystitis develops. Increased pressure leads to dilation of the ureters and damage to kidney tissue, leading to kidney failure. Additional symptoms: dry mouth, thirst, irritability.
- Paradoxical ischuria – urine leakage due to retention. Due to stretching and partial atrophy of the walls of the bladder, the man no longer feels its constant overcrowding, urine leaks drop by drop. Kidney failure worsens, and the resulting intoxication leads to gastrointestinal disorders, the skin becomes dry and jaundiced.
The process of adenoma development is illustrated below:
Normal prostate Growth of adenoma Stagnation of urine Formation of stones Formation of hernias (diverticula) Closure of the urethra
Symptoms of the disease
You can recognize a developing disease by the following manifestations:
- during the process of urination and its initiation, it is necessary to strongly strain the abdominal press;
- the process of emptying the bladder itself can take a long time;
- the stream of urine is weak and constantly interrupted;
- the urge to urinate gradually becomes more frequent, especially at night, which is associated with incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- inability to hold urine when the urge to go to the toilet arises;
- constant incontinence and the need to use urological pads and diapers;
- the end of sexual intercourse is very painful, which gradually reduces sexual desire;
- urine may begin to come out drop by drop, causing acute urine retention.
With the complication of prostate adenoma and its transition to a severe stage, all symptoms will intensify, which will negatively affect the patient’s life. In severe cases, only surgery can help, which is why it is so important to pay attention to the symptoms. Even if they are repeated 1-2 times, you need to undergo a full examination.
Video - Prostate adenoma: causes, symptoms, treatment
Causes of adenoma
After 45 years, men begin to experience a persistent shift in hormonal balance towards female estrogens. This is due to the natural decline of the endocrine function of the testicles. Testosterone production decreases, the pituitary gland of the brain tries to compensate for this by stimulating the production of gonadotropins. In parallel, in the prostate tissue, under the influence of 5-alpha reductase, the active form of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, accumulates. It is what stimulates cell proliferation.
The prostate reacts even more actively to excess female hormones. The aromatase enzyme converts testosterone into estradiol, which also promotes the growth of adenoma.
Provoking factors:
- Passive lifestyle;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Excess weight;
- Stress.
Causes of prostate hyperplasia
Some researchers associate the development of adenoma with irregular sex life, but the disease is often diagnosed in sexually active men.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Doctors have not yet established the exact reasons for the development of prostate adenoma in men; more precisely, they exist, but have not been fully studied. Most often, the main provoking factor is considered to be hormonal changes that occur with age. For this reason, the risk of developing the disease increases significantly over time. The essence of such hormonal changes is to reduce the level of testosterone, that is, the male sex hormone, and to increase the amount of estrogens, that is, female hormones.
The risk of developing prostate adenoma is also influenced by predisposing factors, the main ones being:
- heredity. It has been proven that prostate adenoma develops more often in those men whose fathers suffered from the same problem;
- age. As mentioned earlier, nodular hyperplasia practically does not occur in people under 30 years of age, and after 40, every third person has it;
- wrong lifestyle. If you lead a sedentary lifestyle, suffer from obesity, or have a sedentary job, then the risk of developing prostate adenoma is extremely high. If you play sports, you can significantly reduce it;
- various diseases. According to qualified professionals, many medical conditions (such as diabetes or heart failure) may be considered a risk factor when considering prostate adenoma. It is also worth understanding that the medications that are prescribed when available are no less dangerous (mainly beta blockers are dangerous).
Diagnostics
At the first signs of urinary retention, you should consult a urologist. After collecting anamnesis, the doctor performs a rectal palpation examination of the prostate. The adenoma is palpable as a smooth elastic formation. The gland is evenly enlarged; the presence of hard nodes may be a sign of cancer.
Ultrasound provides a more accurate assessment of the size and structure of the prostate. Using this type of study, the condition of the ureters, bladder, and its fullness are also determined.
To check the functioning of the kidneys, a biochemical blood test is prescribed. Important indicators are residual nitrogen, urea, and creatinine. Urine is also examined for the presence of blood, infections, and glucose.
Urologist Kamaletdinov Rinaz Enesovich clearly talks about the diagnosis and treatment of prostate adenoma
For adenoma, a mandatory diagnostic procedure is to fill out the IPSS questionnaire and a urination diary. The questionnaire contains only 7 questions, to which you need to choose one of 6 answer options. The total score determines the severity of symptoms.
Example IPSS questionnaire and example voiding diary. Fill them out and show them to your doctor.
Men over 50 years of age may have a blood test for PSA (prostate-specific antigen). Exceeding the value, in addition to adenoma, may also indicate the development of a malignant process. A biopsy will help rule it out. Using a thin needle under local anesthesia, the doctor removes a piece of prostate tissue and sends it for histological (cellular) analysis.
Urine flow rate is measured by flowmetry. To do this, a man just needs to urinate into a vessel connected to a special device.
The condition of the walls of the bladder and urethra can be assessed from the inside using urethrocystoscopy. The procedure involves the urethral insertion of a thin device with a video camera. A more accurate picture is provided by CT urography (a series of X-rays taken after the administration of a contrast agent).
Treatment
Conservative and surgical methods are used to treat adenoma. The choice depends not so much on the stage and size of the tumor, but on the severity of symptoms. For example, with an intravesical adenoma, the size of the tumor may be minimal, but due to its overhanging the urethra in the form of a valve, urinary retention occurs.
Medicines
To relieve the symptoms of adenoma, alpha-blockers (terazosin, doxazosin) are actively used. The drugs act on the alpha receptors located in the muscles of the prostate, as a result of which it relaxes and urination becomes freer. The downside is that there are the same receptors in the vascular walls, the relaxation of which provokes a decrease in pressure. For men with hypotension, this can be dangerous. These drugs do not prevent the growth of adenoma, but significantly alleviate the symptoms.
To reduce the effect of dihydrotestosterone on the prostate, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Proscar, Avodart) are used. In the treatment of early stages of adenoma, herbal preparations that have an antiandrogenic and anti-inflammatory effect are also used. Saw palmetto extract (Permixon, Prostaseren) has the property of suppressing the action of 5-alpha reductase. African plum extract (Tadenan) inhibits the proliferation of adenoma cells. The effectiveness of these drugs has been clinically proven.
At the initial stage of adenoma, you can also use peptide-based products (Prostatilen, Robaveron). Significant relief of symptoms is provided by a course of Cialis (a PDE-5 inhibitor based on tadalafil).
The most effective medications for the treatment of prostate adenoma.
Drug therapy is supplemented with physiotherapy:
- UHF therapy.
- Ultraphonophoresis of oxyprogesterone.
- Electrical stimulation.
- Prostate massage.
Magnetic therapy, laser therapy, and thermotherapy have an anti-inflammatory effect. Thalasso and aerotherapy are used to stimulate local immunity.
Surgical methods
Many men suffering from adenoma complain that some medications make them dizzy, others cause impotence, and often ask the doctor to take radical measures. Indeed, the effect of conservative therapy is short-lived, and there are quite a lot of side effects.
Indications for surgical treatment of adenoma:
- Preservation of residual urine in a volume of more than 200 ml;
- Formation of stones in the bladder;
- Chronic urinary tract infection;
- Recurrent acute urinary retention.
The essence of surgical treatment of adenoma is the removal of tumor tissue from the prostate lining (adenomectomy). There are three types of surgical access to the gland:
- Open method - through an incision in the skin and muscles.
- Endoscopic - the instrument is inserted through the urethra.
- Laparoscopy - instruments are inserted through several small punctures in the lower abdomen. Recommended for large volumes of growth.
Basic endoscopic methods:
- TUR (mechanical excision of adenoma tissue).
- Laser ablation. The adenoma tissue wrinkles from the heating waves and releases the urethra. There may be urinary tract irritation and the need to repeat the procedure.
- Laser vaporization. Vaporization of adenomatous tissue with a laser beam.
- Laser enucleation (Holep). The affected tissue is excised as a whole block, then piece by piece is removed through the inserted instrumentation.
Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Therapy for BPH is individual and depends on many parameters, such as the age and condition of the patient, the degree of hyperplasia (there are three degrees), and histological data. There are two methods that are most often used in this case: drug therapy aimed at eliminating clinical manifestations, as well as reducing the size of the organ, and surgical intervention, with appropriate correction of conservative treatment.
At the first symptoms of prostate adenoma, drug treatment is used
The choice depends on the size of the tumor; at the first stage, only conservative treatment is indicated; at the second stage, a combination of medication and surgery is used, which is used if there is no effect of drug treatment; and at the third stage, removal of the pancreas is indicated, followed by a study of the structure of parenchyma cells.
Treatment with pharmaceutical drugs involves the prescription of A-blockers, which relieve spasm of smooth muscles and improve the outflow of urine, as well as drugs that inhibit 5a-reductase. Surgical treatment is possible both through open access and transurethral route.
How to live with adenoma
If prostate adenoma does not cause significant discomfort, then if certain conditions are met, it is quite possible to live with it. First of all, it is necessary to avoid provoking factors:
- Hypothermia.
- Abuse of alcohol and sex (masturbation).
- Avoid smoked foods, marinades, spicy foods and caffeine (read about the diet for prostate adenoma).
- Do not overheat (it is better not to go to the bathhouse).
As for cycling, rowing machines and similar loads on the groin area, they are not contraindicated. The only condition is that the seat must be either soft or with a cutout. Movement and light physical activity will only alleviate the condition: improve blood and lymph flow, strengthen the pelvic diaphragm. What you should not do is squat with a heavy weight.
Myths about adenoma:
- “Every second man over 50 gets sick.” An adenoma is considered a disease only when symptoms and urination problems appear.
- “Adenoma occurs due to lack of sex.” Sex doesn't have much of an impact.
- “Adenoma is a precursor to prostate cancer.” These are different diseases that actually have nothing in common with each other.
- "The adenoma is resolving." This is impossible. It cannot be completely cured conservatively, only temporarily reduce the size by 20-30% and alleviate the symptoms.
- “After surgery, you can give up on your intimate life.” This is wrong. Gentle methods in 90% of cases allow you to maintain and improve erectile function.
The earlier treatment is started, the fewer the consequences.
How to cure prostate adenoma?
First of all, it is worth noting that this disease can be cured both medically and surgically. Moreover, drug treatment will be effective only in the early stages of the disease. So you shouldn’t delay your visit to the doctor, otherwise the protracted illness will not go away.
Drug treatment is a painless and simpler option, but this does not mean that you can just buy the first medicine you come across at the pharmacy and start taking it right away. Only an experienced urologist can select a set of necessary medications, calculate the dosage, and select drugs that are compatible with each other. Self-treatment will not only not help cope with the disease, but may even cause harm.
In the drug treatment of prostate adenoma, oral (tablets and mixtures) and rectal medications (suppositories) are used. Each medicine has its own effect on a man’s body. When treating prostate adenoma, the doctor may prescribe several drugs at the same time. It is worth taking a closer look at the most popular oral medications.
- Vitaprost - the medicine relieves swelling and improves bladder tone.
- Alpha - in addition to combating swelling of the prostate gland, it also eliminates pain when urinating.
- Gentos – relieves inflammation of the prostate and increases the tone of the bladder.
- Speman and Tadenan - restore male reproductive function.
- Herbion Urtica - helps reduce the volume of the prostate.
Often, for prostate adenoma, the doctor prescribes rectal medications. These can be Vitaprast , Bioprost , Vitaprinol . These drugs have similar effects - they help the prostate gland decrease in volume, improve blood circulation and reproductive function.
Do these medications help? If the disease is diagnosed early, such treatment will give a positive result. Recovery depends on how accurately the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations. Taking medications should not be skipped under any circumstances.
In addition to traditional medicinal methods, there are also more modern methods of treating prostate adenoma. These methods are not so widespread, but in some cases they help cope with the disease. The most popular of them are photodynamic therapy, ozone therapy, physiotherapy, diet therapy and herbal medicine.
During photodynamic therapy, special substances are introduced into the patient's body - photosensitizers , which fight pathologies in tissues, tumors of various types and inflammation. The procedure is simple and does not require surgery. Most often, one procedure will be enough, positive changes can be seen after 2-3 months.
Ozone therapy is a new direction in the treatment of prostate adenoma. Ozone contains active oxygen, which has a positive effect on the body's cells, improves metabolism and microcirculation of vitamins and minerals. This is a safe and painless treatment method - the patient is simply injected into a vein with nitrogen solution. This procedure must be repeated 3 to 5 times, and you can take any medications prescribed by your doctor and not be afraid of complications.
Physiotherapy is not an independent method of treatment. This method is used in the earliest stages of prostate adenoma development or after the main treatment to maintain the result. There are many different types of physical therapy, the essence of which is to directly influence the prostate gland in order to destroy overgrown tissue. This effect can be carried out using high or low temperatures, electric or magnetic microwaves. The doctor will select the necessary procedure.
Diet therapy is more likely not a treatment, but a prevention of the disease. The doctor prescribes a special diet that must be followed during treatment.
Herbal medicine is treatment with medicinal plants. The method can be called “folk”. The patient needs to take an infusion of onions, eat walnuts, pumpkin and sunflower seeds more often.
In severe forms of the disease, drug treatment may be ineffective, in which case the doctor may suggest surgery. Most often, prostate adenoma is operated on using endoscopy . This method is more gentle, since during the operation a small incision is made, which is necessary to insert the endoscope inside. The entire operation is carried out “in-house”. After such surgery, there are no large scars left, the patient does not lose much blood and recovers much faster.
Most often, doctors resort to this type of surgical intervention. However, there are situations in which an “open” operation is necessary.
Complications
Adenoma itself does not pose a threat to life. The consequences of its neglected condition are dangerous. The most severe complication is acute renal failure, filling of the kidneys with urine, and intoxication. It usually occurs due to acute urinary retention. Urgent help is needed - diversion from the bladder through a cystostomy tube, which will take from several weeks to several months.
Drainage tube for acute urinary retention
Other complications of adenoma:
- Cystitis and urethritis;
- Inflammation of the testicles, appendages, prostate;
- Chronic pyelonephritis.
Blood in urine and semen against the background of adenoma appears due to ruptures of blood vessels and their inflammatory melting.
Prevention
Measures to prevent adenoma:
- Avoid overcooling your feet.
- Avoid frequent and prolonged constipation.
- Periodically activate blood flow in the pelvic area: perform special exercises, jog, and have regular sex life.
Researcher at the Research Institute of Urology Dmitry Alekseevich Voitko will give 10 tips that will help maintain and strengthen the health of the prostate gland
- Adjust the diet: minimize the amount of mustard, smoked meats, canned food, alcohol, caffeine.
- Stop smoking.
- Do not hold back urination (do not tolerate it).
- Do not drink a lot of fluids at night.
A healthy lifestyle will maintain a normal hormone balance and prevent the early development of adenoma.