Modern medicine is developing rapidly. Diseases that were previously considered incurable can now be cured quite successfully. For example, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, or as the disease is also called, erythema malignant exudative. This is a rather complex disease, during which delayed systemic allergic reactions disrupt the full functioning of the entire body. The skin is affected by ulcers of varying sizes, the mucous membranes swell, and in some cases the membranes of the internal organs of a person are also affected.
According to statistics, Stevens-Johnson syndrome in children most often occurs in the age group from 3 to 14 years. The source of development is a variety of diseases. Cases of the development of the disease before the age of 3 years have also been recorded. The pathology of the syndrome is especially severe in them.
Causes
The causes of Steven Johnson syndrome can be divided into subgroups:
- medications.
An acute allergic reaction occurs when a medication enters the body. The main groups causing Steven Johnson syndrome: penicillin antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, sulfonamides, vitamins, barbiturates, heroin; - infections.
In this case, the infectious-allergic form of Steven Johnson syndrome is recorded. Allergens are: viruses, mycoplasmas, bacteria; - oncological diseases
; - idiopathic form
of Stevens Johnson syndrome. In such a situation, clear reasons cannot be determined.
general information
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a severe bullous lesion of the skin and mucous membranes of an allergic nature. Stevens-Johnson syndrome occurs against the background of an acute condition of the patient with the involvement of the genitourinary system, visual organs and oral mucosa.
Causes:
Toxic-allergic reaction to certain medications:
- penicillin antibiotics up to 55%;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs up to 25%;
- antiepileptic drugs, vaccines, narcotics and the like up to 18%
- sulfonamides up to 10%;
- vitamin complexes and other medications that affect metabolic processes in the body by up to 8%.
These are the most commonly used causally significant medications.
Infectious detonators. The allergic form is distinguished in association with pathogenic microbes, rickettsia, mycoplasmas, various enterobacterial carriers, protozoal and fungal infections.
Oncology.
Primary Stevens-Johnson syndrome is recorded in almost 25-50 percent of cases.
Clinical picture
Steven Johnson syndrome appears at a young age from 20 to 40 years, but there are times when this disease is diagnosed in newborn children. Men are more often affected than women.
The first symptoms affect the upper respiratory tract system by infection. The initial prodromal period extends to two weeks and is characterized by fever, severe weakness, cough, and headaches. In rare cases, vomiting and diarrhea are caused.
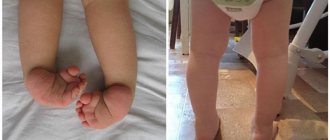
The skin and mucous membranes of the mouth in children and adults are affected instantly within five days; the location can be anywhere, but most often a rash occurs on the elbows, knees, face, reproductive organs and all mucous membranes.
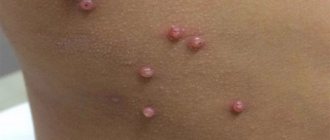
With Steven Johnson syndrome, swollen, compacted papules of a dark pink color appear, round in shape, the diameter of which is from one to six centimeters. There are two zones: internal and external. The internal ones are characterized by a grayish-blue color, in the middle a bubble appears inside which contains serous fluid. The outer one appears in red.
In the oral cavity, on the lips, cheeks in children and adults, Stevens John syndrome is manifested by broken erythema, blisters, and erosive areas of a yellowish-gray color. When the blisters open, bleeding wounds form; lips and gums swell, hurt, and become covered with hemorrhagic crusts. The rash on all areas of the skin feels burning and itching.
In the urine excretory system, the mucous membranes are affected and is manifested by bleeding from the urine excretory tract, a complication of the urethra in men, and vulvovaginitis in girls. The eyes are also affected, in which case blephoroconjunctivitis progresses, which often leads to complete blindness. Rarely, but the development of colitis and proctitis is possible.
There are also general symptoms: fever, headaches and joint pain. Malignant exudative erythema develops in people over forty years of age, acute and very rapid, heart contractions become frequent, hyperglycemia. Symptoms of damage to internal organs, namely their mucous membranes, manifest themselves in the form of stenosis of the esophagus.
The final fatality rate for Steven Johnson syndrome is ten percent. Complete loss of vision after severe keratitis caused by Stephen John syndrome is observed in five to ten patients.
Exudative erythema multiforme is diagnosed together with Lyell's syndrome. It is held between them. In both of these diseases the primary lesions are similar. They may also be similar to systemic vasculitis.
Characteristics of the disease
This syndrome was first mentioned in 1922. It received its name from the author, who described the main symptoms of the disease. It can appear at any age, but is more common in people over 20 years of age.
In general, it is a disease of the skin and mucous membranes of the human body caused by allergies. It represents the form when epidermal cells begin to die, resulting in separation from the dermis.
Johnson syndrome is a malignant exudative erythema that can lead to death. The condition caused by the syndrome threatens not only health, but also life. It is dangerous because all the symptoms appear in a matter of hours. We can say that this is a toxic form of the disease.
This syndrome does not occur like a normal allergic reaction. Bubbles form on the mucous membranes, which literally stick to the throat, genitals, and skin. Because of this, a person may choke, refuse to eat, because... it is very painful, the eyes can stick together, turn sour, and then the blisters fill with pus. And it must be said that such a condition is very dangerous for a person.
The patient with Stevens Johnson Symptom is in a state of fever, the disease itself progresses at lightning speed - increased body temperature, sore throat. These are all just initial symptoms. This is very similar to a cold or ARVI, so many simply do not pay attention and do not suspect that it is time to treat the patient.
However, the person’s condition only worsens further. The rash all over the body and on the mucous membranes develops into non-healing erosions, from which blood constantly oozes. Plus, all this provokes fibrous plaque.
Often, skin damage occurs in more than one area of the body, and later all the rashes merge together. As the disease progresses, it causes skin detachment.
However, doctors state that this pathological condition is very rare and only 5 people out of a million people are prone to the pathology. To this day, science is studying the mechanism of development, prevention and treatment of the Syndrome. This is important because people with this disease require emergency assistance from qualified specialists and special care.
Video: The Scary Reality About Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a very severe skin disease, a malignant type of erythema exudative, in which severe redness appears on the skin. At the same time, large blisters appear on the mucous membranes and skin. Inflammation of the oral mucosa makes it difficult to close the mouth, eat, and drink. Severe pain provokes increased salivation and difficulty breathing.
Inflammation and the appearance of blisters on the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system complicate natural bowel movements. Urination and sexual intercourse become very painful.
Most often, Stevens-Jones syndrome occurs as an allergic response to antibiotics or drugs intended to treat bacterial infections. Representatives of medicine are inclined to believe that the tendency to the disease is inherited.
Scientists believe that the exacerbation may be caused by several factors.
Most often, Stevens-Jones syndrome occurs as an allergic response to antibiotics or drugs intended to treat bacterial infections. The reaction can be caused by drugs for epilepsy, sulfonamides, and non-steroidal painkillers. Many drugs, especially synthetic ones, also affect the symptoms that characterize Stevenson Johnson syndrome.
Infectious diseases (influenza, AIDS, herpes, hepatitis) can also provoke a malignant form of exudative erythema. Fungi, mycoplasmas, bacteria that enter the body can provoke an allergic reaction
Finally, symptoms are very often recorded in the presence of cancer.
More often than others, Stevens Johnson syndrome occurs in men between twenty and forty years of age, although the disease has been reported in women and children up to six months old.
Since the disease is an immediate type of allergy, it develops very quickly. It begins with severe malaise, the appearance of unbearable pain in the joints, muscles, and a sharp increase in temperature.
After a few hours (less often, days), the skin becomes covered with silvery films, deep cracks, and blood clots.
At this time, blisters appear on the lips and eyes. If initially the allergic reaction in the eyes is reduced to severe redness, then later ulcers and purulent blisters may appear. The cornea and the back parts of the eye become inflamed.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome can affect the genitals, causing cystitis or urethritis.
To make a diagnosis, a general blood test is required. Usually, in the presence of the disease, it shows a very high level of leukocytes, rapid erythrocyte sedimentation.
In addition to the general analysis, it is necessary to take into account all the drugs, substances, and food that the patient took.
Treatment of the syndrome usually involves intravenous transfusion of blood plasma, drugs that cleanse the body of accumulated toxins, and the introduction of hormones. To prevent the development of infection in ulcers, a complex of antifungal and antibacterial drugs and antiseptic solutions are prescribed.
It is very important to follow a strict diet prescribed by your doctor and drink plenty of fluids.
It has been statistically established that if you contact a specialist in a timely manner, treatment ends quite successfully, although it takes a lot of time. Therapy usually lasts 3-4 months.
If the patient does not begin to receive drug treatment in the first days of the disease, Stevens-Johnson syndrome can be fatal. 10% of patients die due to late treatment.
Sometimes after treatment, especially if the disease is severe, scars or spots may remain on the skin. It is possible that complications may occur in the form of colitis, respiratory failure, dysfunction of the genitourinary system, and blindness.
This disease absolutely excludes self-medication, as it is potentially fatal.
Diseases of the skin and integument can be extremely dangerous and accompanied by unpleasant consequences in the form of others and death. To prevent this from happening, timely diagnosis of each ailment and prompt qualified assistance are important. One of these phenomena is Stevens-Johnson syndrome, photo
which is presented in the article. This disease is striking and difficult to treat, especially in the later stages. Let's consider the features of its clinical course and methods of therapeutic intervention to eliminate problems and improve the health of the body.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome - what is it?
The disease Stevens-Johnson syndrome (ICD code 10) is a dangerous toxic form of the disease, characterized by the death of epidermal cells and their subsequent separation from the dermis. The course of these processes entails the formation of vesicles in the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, genitals and some other areas of the skin - the main symptoms of the disease
. If this happens in the mouth, it becomes difficult for the sick person to eat and it hurts to close the mouth. If the disease affects the eyes, they become excessively sore, covered with swelling and pus, which causes the eyelids to stick together.
When the genital organs are affected by the disease, difficulty urinating is observed.
The picture is accompanied by a sudden start of disease progression, when a person’s temperature rises, a sore throat begins, and a feverish state may occur. Due to the similarity of the disease to the common cold, diagnosis at the initial stage is difficult. most often occurs on the lips, tongue, palate, pharynx, arch, larynx, and genitals. If you open the formations, there will be non-healing erosions from which blood oozes. When they merge, they turn into a bleeding area, and some of the erosions provoke fibrous plaque, which worsens the patient’s appearance and worsens their well-being.
Treatment errors
- In no case should you start treatment with small doses of corticosteroids, and you should not use them for a long time after the end of treatment.
- If an infectious disease has not developed, you should not use antibiotics at all. The treatment algorithm should not contain penicillin antibiotics or vitamin preparations. They are considered strong allergens.
- Treatment for Stevens Johnson syndrome is similar to standard treatment for allergies, but since this is a more severe disease, you must immediately consult a doctor and he will prescribe individual treatment for each patient.
Lyell's syndrome and Stevens Johnson syndrome difference
Both phenomena are characterized by the fact that the skin and mucous membranes are noticeably damaged, as well as soreness, erythema, and detachment. Since the disease causes noticeable lesions in the internal organs, the patient can “finish” fatally. Both syndromes are classified according to the most severe forms of illnesses, but can be provoked by various factors and causes.
- In terms of the frequency of the disease, Lyell's syndrome accounts for up to 1.2 situations per 1,000,000 people per year, and for the disease in question - up to 6 cases per 1,000,000 people over the same period.
- There are also differences in the causes of the lesion. SSD occurs in half of the situations due to medication, but there are situations in which identifying the cause is impossible. LS manifests itself in 80% of cases due to medications, and in 5% of cases there are no treatment measures. Other causes include chemical compounds, pneumonia and viral infectious processes.
- The location of the lesion also suggests several differences between the two types of syndromes. Erythema forms in the area of the face and limbs; after a few days, the formation becomes confluent. In SSc, lesions predominantly appear on the trunk and face, and in the second disease, a general type of lesion is observed.
- The general symptoms of ailments converge and are accompanied by fever, increased temperature, and the occurrence of painful sensations. But with SL this indicator always increases after the mark of 38 degrees. There is also an increase in the patient’s anxiety and a feeling of severe pain. Kidney failure is the background for all these ailments.
There are still no clear definitions of these diseases; many classify Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a photo of which is presented in the article, as a severe form of erythema multiforme, while the second disease is preferred to be considered the most complicated form of SSc. Both ailments in development can start with the formation of erythema in the iris area, but with LS the phenomenon spreads much faster, resulting in necrosis and exfoliation of the epidermis. In SSD, peeling of layers occurs on less than 10% of the body, in the second case – on 30%. In general, both diseases are similar, but also different, it all depends on the characteristics of their manifestation and the general indicators of symptoms.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome causes
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a photo of which can be seen in the article, is represented by an acute bullous lesion in the area of the skin and mucous membranes, and the phenomenon is of allergic origin and of a special nature. The disease occurs as part of the deterioration of the sick person’s condition, while the oral mucosa, along with the genitals and urinary system, are gradually involved in this process.
Common causes of the disease
The development of SSc usually has a precursor in the form of an immediate allergy. There are 4 types of factors that influence the onset of disease development.
- Infectious agents that affect organs and aggravate the general course of the disease;
- Taking certain groups of medications that provoke the presence of this disease in children;
- Malignant phenomena are tumors and neoplasms of a benign type that have a special nature;
- Causes that cannot be determined due to insufficient medical information.
In children, the phenomenon occurs as a consequence of viral diseases, while it has a different nature and is clearly determined by the use of medications or the presence of malignant tumors and phenomena. As for small children, a large number of phenomena act as provoking factors.
- Herpes;
- hepatitis;
- measles;
- flu;
- chickenpox;
- bacteria;
- fungi.
If we consider the effect of medications on the child’s body, we can assign a role to antibiotics and non-steroidal drugs aimed against the inflammatory process. If we consider the influence exerted by malignant tumors, we can highlight the leadership of carcinoma. If none of the above factors is related to the course of the disease, we are talking about SSD.
Details of information
The first information about the syndromes was highlighted in 1992; over time, the disease became described in more detail and was given a name in honor of the names of the authors who deeply studied and understood its nature. The disease is extremely severe and has another name - malignant exudative erythema
. The disease is related to bullous type dermatitis - along with SLE,. The main clinical course is that blisters appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
If we consider the prevalence of the disease, it can be noted that it can be encountered at any age; usually the disease clearly manifests itself at the age of 5-6 years. But it is extremely rare to encounter the disease in the first three years of a baby’s life.
. Many research authors have found that the highest incidence is present among the male population, which includes them at risk. which can be seen in the article, is also accompanied by a number of other symptoms.
Causes
The main cause of Stevens-Johnson syndrome is the development of an allergic reaction in response to taking antibiotics and other antibacterial drugs.
Currently, a hereditary mechanism for the development of pathology is considered very likely. As a result of genetic disorders in the body, its natural defenses are suppressed. The disease is based on intoxication of the patient’s body and the development of allergic reactions in it. Some researchers tend to consider pathology as a malignant type of multimorphic exudative erythema.
This pathology always develops in the patient very quickly, rapidly, since in essence it is an immediate allergic reaction. Initially, severe fever and pain in the joints and muscles appear. Subsequently, after just a few hours or a day, damage to the oral mucosa is detected.
Defects also appear in the area of the red border of the lips. Eye damage occurs as conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes), but the inflammatory process here is purely allergic in nature. In the future, bacterial damage may also occur, as a result of which the disease begins to progress more severely, and the patient’s condition sharply worsens.
Lesions can often also involve the genitals, which manifests itself in the form of urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), balanitis, vulvovaginitis (inflammation of the female external genitalia). Sometimes mucous membranes in other places are involved. As a result of skin damage, a large number of red spots are formed on it with raised areas above the skin level, like blisters.
After opening the blisters, bright red skin defects remain in their place, which are then covered with crusts. Mostly, the lesions are located on the patient’s torso and in the perineal area. There is a very pronounced disturbance in the general condition of the patient, which manifests itself in the form of severe fever, malaise, weakness, fatigue, headache, and dizziness.
When conducting a general blood test, an increased content of leukocytes, the appearance of their young forms and specific cells responsible for the development of allergic reactions, and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are detected. These manifestations are very nonspecific and occur in almost all inflammatory diseases. A biochemical blood test may detect an increase in the content of bilirubin, urea, and aminotransferase enzymes.
The clotting ability of blood plasma is impaired. This is due to a decrease in the content of the protein responsible for coagulation - fibrin, which, in turn, is a consequence of an increase in the content of enzymes that carry out its breakdown. The total protein content in the blood also becomes significantly reduced.
To make a correct diagnosis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, it is necessary to interview the patient as fully as possible about his living conditions, diet, medications taken, working conditions, diseases, especially allergic ones, of his parents and other relatives. The time of onset of the disease, the effect on the body of various factors that preceded it, especially the use of medications, are clarified in detail.
Preparations of adrenal hormones in medium dosages are mainly used. They are administered to the patient until there is a lasting significant improvement in the condition. Then the dosage of the drug begins to be gradually reduced, and after 3-4 weeks it is completely discontinued. In some patients, the condition is so severe that they are unable to take medications by mouth on their own.
In these cases, hormones are administered in liquid forms intravenously. Very important are procedures that are aimed at removing immune complexes, which are antibodies associated with antigens, from the body circulating in the blood. For this purpose, special drugs for intravenous administration and blood purification methods in the form of hemosorption and plasmapheresis are used.
Drugs taken orally are also used to help remove toxic substances from the body through the intestines. In order to combat intoxication, at least 2-3 liters of liquid should be introduced into the patient’s body daily through various routes. At the same time, make sure that this entire volume is removed from the body in a timely manner, since when fluid is retained, toxins are not washed out and quite severe complications can develop. It is clear that the full implementation of these measures is only possible in an intensive care unit.
A fairly effective measure is intravenous transfusion of solutions of proteins and human plasma to the patient. Additionally, medications containing calcium, potassium, and antiallergic drugs are prescribed. If the lesions are very large and the patient’s condition is quite severe, then there is always a risk of developing infectious complications, which can be prevented by prescribing antibacterial agents in combination with antifungal drugs.
As already mentioned, 10% of all patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome die as a result of severe complications. In other cases, the prognosis of the disease is quite favorable. Everything is determined by the severity of the disease itself, the presence of certain complications.
- Symptoms similar to upper respiratory tract infections, such as fever {amp}gt; 39°C, sore throat, chills, cough, headache, whole body pain
- Target lesions. These lesions, which are darker in the middle surrounded by lighter areas, are considered diagnostic
- Painful red or purple rash, blisters on the skin, mouth, eyes, ears, nose, genitals. As the disease progresses, the flaccid blisters may coalesce and rupture, causing painful sores. Eventually the top layer of skin forms a crust.
- Facial swelling, swollen lips covered with ulcers, mouth ulcers. Throat ulcers cause difficulty swallowing, and diarrhea may occur, causing dehydration
- Swelling, swelling of the eyelids, inflammation of the conjunctiva, photosensitivity when the eyes are sensitive to light
It is interesting that from the time of exposure to the trigger cause to the full development of all signs of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, it can take either 1 day or several weeks. Everything will depend directly on the level of reactivity of the human immune system: the more “stimulated” it is in, the faster Stevens-Johnson syndrome will appear.
Symptoms of Stevens-Johnson syndrome have their own signature, main manifestations and additional signs.
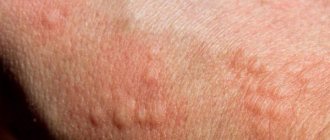
The main manifestations, of course, will be skin lesions. Certain localized lesions called bullae or blisters appear on the skin. Their main symptom is that if you touch them with any object, the skin will immediately begin to peel off. But these bubbles do not appear immediately. First, itching and a rash will appear in certain areas of the skin, which will contain both spots and raised papules. This rash is also called measles-like, because it is similar to that of measles.
Then this rash gradually turns into blisters with a flaccid, collapsing lid. The skin nearby and from these blisters can come off in whole layers, as if from a severe burn. Beneath the peeled skin, a red surface is revealed that may become wet.
The first elements of skin lesions in Stevens-Johnson syndrome appear on the face and limbs. After a few days they spread and merge. But, and this is an important diagnostic sign, the scalp and palms with soles are practically not affected. The most severe manifestations of Stevens-Johnson syndrome will be on the limbs and torso.
Skin lesions in Stevens-Johnson syndrome are extremely large. They can imitate the picture as if the skin is affected by a burn of at least 2nd degree. Those areas of the skin that are exposed to pressure and friction from clothing are most affected.
But if treatment is prescribed in time and correctly, the affected areas are restored. Their complete healing will take about 3 weeks. And here again it should be remembered that areas exposed to pressure and areas of natural openings will take longer to heal.
- It is recommended to immediately stop taking the drug that provoked the development of the disease; it increases survival with a short half-life.
- Mechanical destruction of early synechiae if they form is recommended.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome symptoms photo
SSD is a disease characterized by an acute onset and rapid development in terms of symptoms.
- Initially, you can notice malaise and an increase in body temperature.
- Then acute pain in the head area appears, accompanied by arthralgia, tachycardia and muscle ailments.
- Most patients complain of sore throat, vomiting and diarrhea.
- The patient may suffer from bouts of coughing, vomiting and blistering.
- After opening the formations, you can find extensive defects that are covered with white or yellow films or crusts.
- The pathological process involves redness of the labial border.
- Due to severe pain, patients find it difficult to drink and eat.
- Serious allergic conjunctivitis, complicated by purulent inflammatory processes, is observed.
- Some diseases, including SSc, are characterized by the occurrence of erosions and ulcers in the conjunctival area. Keratitis and blepharitis may occur.
- The organs of the genitourinary system, namely their mucous membranes, are noticeably affected. This phenomenon affects 50% of situations; symptoms take the form of urethritis and vaginitis.
- The skin lesion appears as an impressively large group of raised blistering-like lesions. All of them have a purple color and can reach a size of 3-5 cm.
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
can affect many organs and systems. Often leading to tragic consequences and death.
The period during which new rashes form lasts several weeks, and complete healing of the ulcers requires 1-1.5 months. The disease can be complicated by blood oozing from the bladder, as well as colitis, pneumonia, and kidney failure. As a result of these complications, about 10% of sick people die, the rest manage to cure the disease and begin to lead a full-fledged normal rhythm of life.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome treatment in children scheme
Clinical recommendations suggest rapid elimination of the disease through a preliminary study of its nature. Before treatment is prescribed, a certain diagnostic complex is carried out. It involves conducting a detailed examination of the patient, conducting an immunological examination of the blood, and a skin biopsy. If there are certain indications, the doctor will definitely prescribe a full X-ray of the lungs and an ultrasound of the genitourinary system, kidneys and biochemistry.
Therapeutic measures
The disease Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a photo of which can be assessed in the article, is a serious illness that requires appropriate intervention from a specialist. Systematic procedures involve carrying out measures aimed at reducing or eliminating intoxication, relieving the inflammatory process and improving the condition of the affected skin. If there are chronic missed situations, special action drugs may be prescribed.
- Corticosteroids – to prevent relapses;
- desensitizing agents;
- drugs to eliminate toxicosis.
Many people believe that it is necessary to prescribe vitamin treatment - in particular, the use of ascorbic acid and group B drugs, but this is a misconception, since the use of these drugs can provoke a deterioration in general health. overcome
The name DDS (Lyell and Johnson syndrome) refers to severe inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes - erythema multiforme. The disease was discovered in the USA in 1922. It was described by two pediatricians, Lyell and Johnson, after whom the syndrome got its name. The disease is characterized by an acute course, with damage to the mucous membranes and skin of at least two organs. Currently, Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome occurs throughout the world in people mainly over the age of forty. Recently, the disease has begun to be diagnosed in children and even infants.
Prerequisites for the disease:
1. Taking certain medications; Often, signs of Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome occur with an overdose of drugs. There are cases of the disease due to taking just one and the correct dose of medicine. Most cases of the disease were provoked by taking antibiotics, more often when taking antibiotics from the penicillin series. There is a lower likelihood of the disease when taking local anesthetics, sulfa drugs, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. 2. Infectious diseases; Increased risk factors are bacterial and fungal infections. An acute allergic reaction to SSD can develop after contact with herpes, HIV, influenza and hepatitis viruses. 3. Oncological diseases; 4. Idiopathic form. This is a disease whose causes experts have not been able to identify. Lyell-Stevens Johnson syndrome may occur for an unknown reason.
Main symptoms of SSD
In most cases, the syndrome begins to manifest as severe pain in the joints. SSD is an acute or rapid form of allergy and therefore begins unexpectedly. The patient may initially think that he is suffering from a respiratory disease. At this stage, severe persistent weakness, joint pain, and fever are felt. An ill person may suffer from nausea and vomiting. The initial state of the syndrome lasts several hours or several days. Then severe rashes appear on the mucous membranes and skin. The rash appears in different places. A feature of the syndrome is symmetrical rashes. An allergic reaction makes itself felt with severe itching and a burning sensation. The rash is localized in different ways. Most patients experience rashes on the face, back of the hands and feet, and on the bends of the knees and elbows. The mucous membranes in the mouth are most often affected, and a little less often - the eyes. Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome is characterized by a papule-shaped rash with a diameter of two to five millimeters. Each papule is visually divided into two parts. In the center of the vesicle, a small cavity with blood (hemorrhagic contents) and protein fluid (serous substance) is clearly visible. The outer part of the bubble is bright red. Papules that form on the mucous membranes are more painful. They quickly burst, leaving painful erosions with an unhealthy yellow coating in place. Damage to the mucous membranes in intimate places can lead to urethral stricture in men and to the development of vaginitis in women. When the eyes are damaged, blepharoconjunctivitis and other eye diseases that impair vision develop. With any form of Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome, patients experience pain and an increasing feeling of anxiety. Pain from a rash on the mucous membranes leads to refusal of food.
Diagnosis of SSc syndrome
A detailed and correct anamnesis must be compiled.
SSD is one of the severe forms of an allergic reaction, so it is possible to identify some patterns in the early allergic manifestations of a sick person. The patient must provide the attending physician with the most complete information possible - tell whether allergic reactions have occurred before. Also, the doctor must know which substances and how severe the allergy was. The attending physician prescribes a general blood test and biochemical study for the patient. The test results will reveal aminotransferase enzymes, bilirubin and urea in the blood. Through a thorough external examination, the strength and nature of the allergic lesion is revealed. Often, a correct diagnosis is impossible without an immunogram. This study is aimed at searching for antibodies of a specific class in the blood. Diagnosing Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome itself is not an extremely difficult task. Almost all prescribed studies are aimed at excluding diseases such as pemphigus or other diseases with similar clinical manifestations. How is SSD treated? Detection of Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome requires urgent medical assistance. What urgent needs does the patient need before being admitted to the inpatient department? The following emergency measures are carried out: Vein catheterization; Infusion therapy (saline or colloid solutions are administered to reduce the concentration of allergens in the blood); Intravenous administration of prednisolone in a single dose of 60-150 mg; Due to severe swelling of the laryngeal mucosa, the patient is transferred to a mechanical ventilation device. After the patient is admitted and his condition is stabilized in the hospital department, he is prescribed basic treatment. The attending physician will prescribe analgesics for pain relief and glucocorticosteroid drugs against inflammation. If the skin or mucous membranes are infected, strong antibiotics are prescribed, except for drugs based on penicillin and vitamins. Complications accompanying Lyell and Stevens Johnson syndrome require additional therapy. Lesions of the skin and mucous membranes are treated with antiseptic solutions and anti-inflammatory ointments. The patient should receive a hypoallergenic diet, excluding the consumption of all types of fish, coffee, citrus fruits, honey and chocolate. Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a bullous acute lesion of the mucous membranes and skin of an allergic nature. Usually the disease occurs against the background of severe conditions involving the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitourinary organs and eyes. Stevens-Johnson syndrome can be diagnosed by a thorough examination of the patient, blood tests using the immunological method, skin biopsy and coagulogram. Taking into account the varying degrees of severity of the disease, X-rays of the lungs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, biochemical urine analysis are performed, and of course, consultation with other specialists. Treatment is carried out using the method of extracorporeal hemocorrection, through infusion therapy and glucocorticoid therapy. Antibacterial drugs are also prescribed.
The first data on Stevens-Johnson syndrome were published only in 1922. Over time, Stevens-Johnson syndrome got its name in honor of its discoverers, after whom the disease was later named. This disease is a variant of exudative erythema multiforme, which occurs in a severe form. The disease also has a second name - malignant exudative erythema. Stevens-Johnson syndrome belongs to bullous dermatitis, just like Lyell's syndrome, allergic contact dermatitis, pemphigus, Haley-Hailey disease, bullous variant of SLE and others. Interestingly, a common symptom of all of the above diseases, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, is the appearance of blisters on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is detected at very different ages. However, it most often occurs in people between 20 and 40 years of age, but is very rare in the first three years of a child’s life. The prevalence of Stevens-Johnson syndrome ranges from 0.5 to 5-6 cases per 1 million people per year. Many researchers note that the disease is more common in men.
Causes
Medicines
This is the most common reason. A reaction occurs within a week of starting the drug, although it can happen even after a month or two, for example, when taking anticonvulsants. The following drugs are particularly implicated in the syndrome:
- Antibiotics: Sulfonamides or sulfa drugs such as cotrimoxazole;
- Penicillins: amoxicillin, bacampicillin;
- Cephalosporins: cefaclor, cephalexin;
- Macrolides, which are broad-spectrum antibiotics; actions: azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin;
- Quinolones: ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin;
- Tetracyclines: doxycycline, minocycline;
- Anticonvulsants are used to treat epilepsy to prevent seizures.
Medicines such as lamotrigine, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbitone, in particular the combination of lamotrigine with sodium valproate, increase the risk of Stevens Johnson syndrome.
- Allopurinol, which is used to treat gout
- Acetaminophen, considered a safe medicine for all age groups
- Nevirapine, a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, is used to treat HIV infection
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are pain relievers: diclofenac, naproxen, indomethacin, ketorolac
Infections
Infections that may predispose include:
- Viral infections. With viruses: swine flu, influenza, herpes simplex, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis A, HIV are associated with SJS.
Most often, Stevens-Johnson syndrome is caused by drugs. The number of such cases is equal to 85% of the total incidence of this syndrome.
The main drugs that cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome are, of course, antibiotics: sulfonamide antibiotics and antibiotics of a number of cephalosporins. Stevens-Johnson syndrome is also caused by excessive use of ointments containing diclofenac sodium. In addition, drugs of a number of carbamazepines and antibiotics - ampicillins have the same effect.
Therefore, it is extremely important when prescribing therapy with the above drugs to take into account the body’s possible sensitivity to them and prescribe clearly defined doses, without overusing their quantities.
In addition to antibiotics, Stevens-Johnson syndrome can also be caused by special series of antiepileptic drugs. Some sedatives can also be included in a number of medications that provoke Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Interestingly, in some patients Stevens-Johnson syndrome can occur without taking the medications described above. In a very small percentage of patients, this syndrome occurs due to the invasion of bacteria, food allergens, and the ingestion of pathogenic chemical compounds into the body. Stevens-Johnson syndrome can even develop after vaccination, as a result of the body's enhanced allergic response to new and foreign substances - antibodies.
The allergic cause plays one of the key roles due to which Stevens-Johnson syndrome occurs in children. Like most serious illnesses, this syndrome is extremely painful for a small child. Babies with Stevens-Johnson syndrome have the appearance of being “scalded with boiling water” - the skin necrosis in this syndrome in children is so terrible and widespread.
The main pathogenetic causes of Stevens-Johnson syndrome are still unknown. It is only known that allergic activity in the body increases sharply. T-lymphocytes with cytotoxic abilities are activated: these cells are literally loaded with active substances that can destroy foreign cells.
But the thing is that with Stevens-Johnson syndrome, all aggressive activity is aimed at the body’s own structures, namely the skin. These toxic lymphocytes attack the constituent parts of the skin, the cells called keratocytes. Keratocytes, under the influence of toxic substances for them, are destroyed, and the crown phenomenon of Stevens-Johnson syndrome occurs: the skin settles and literally moves away from its base.
It should be noted that Stevens-Johnson syndrome develops extremely quickly. The speed of its manifestation is ensured by certain hypersensitivity reactions of the body, which trigger the appearance of this anomaly.
By the way, in addition to variants of Stevens-Johnson syndrome with established trigger factors, there are also those where the cause of the syndrome cannot be established at all. Such forms are usually characterized by a higher rate of appearance and more severe lesions.
Modern medical science does not yet have answers to all questions about the causes of the development of this disease.
There are four groups of factors believed to provoke the onset of the disease:
- Medicines
- Pathogens of infections
- Oncological diseases
- Unidentified reasons
According to the observations of specialists, in most cases (up to 85%), the development of the syndrome is observed as a result of taking medications - antibiotics of a number of sulfonamides, ampicillins and cephalosporins. The causative agent can also be an ointment containing diclofenac sodium.
When using these drugs, one should take into account the body's sensitivity to the active substances they contain. It is recommended to avoid violating the dosage and frequency of administration. Food allergens, pathogenic bacteria, and pathogenic chemicals can also provoke the development of the syndrome.
Read: Heel spur
In some cases, the disease occurred as a result of vaccination as a result of an allergic reaction of the body to the presence of foreign substances - antibodies.
In children, Stevens-Jones syndrome develops against the background of bacterial and fungal infections, as well as viral diseases (chicken pox, herpes simplex, influenza, measles).
The pathogenetic causes of the development of the disease have not yet been fully studied. However, experts were able to establish that when there is a threat of the manifestation of the syndrome in the body, increased allergic excitability is observed.
The active substances of T-lymphocytes, which normally destroy foreign cells, in Stevens-Jones syndrome direct an aggressive effect on the body's tissues, in particular on the mucous membranes and skin. The disease develops rapidly.
The reasons for the development of the pathological condition require further study.
Most authors believe that the basis of the disease is the body’s hypersensitivity to the action of drugs and toxins, and associates the development of the disease with the use of various medications - sulfonamides, antibiotics, pyrazolone derivatives, etc. Preliminary exposure to a viral or bacterial infection on the body is also important, for for which medications were used.
The disease develops as a result of preliminary polyvalent sensitization of the body by viral, bacterial or drug allergens, followed by resolving exposure to drug allergens.
Before the age of 3, Stephen-Jones syndrome appears after acute viral infectious diseases: herpes, measles, influenza, chicken pox. It has been established that the provoking factor for the onset of the disease can be a bacterial infection in the form of tuberculosis, gonorrhea or mycoplasmosis. The formation of the disease as a result of fungal infection - trichophytosis and histoplasmosis cannot be ruled out.
If you have symptoms of Stephen-Jones syndrome, you need to remember what medications you have taken recently. If these are various types of antibiotics, nervous system stimulants and some sulfonamides, then it is possible that they provoked an allergic reaction.
- Weakening of the body due to infectious diseases. This leads to a sharp decrease in the effectiveness of the immune system. The following diseases can provoke the development of pathology:
- Ingestion of certain medications: drugs for the treatment of gout (allopurinol);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen);
- antibacterial drugs (penicillin, sulfonamides: biseptol, sinersul, etc.);
- anticonvulsants and antipsychotics;
- radiation therapy.
A separate reason, or a combination of them, can provoke the development of this syndrome, and in adults this condition is more often caused by taking medications, and in children - by infectious diseases.
It should be noted that the presence of a drug on the list of medications that can cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome is not a reason to refuse a doctor’s prescription.
These drugs are used to treat serious diseases; without proper medical care, the risk of complications of these diseases is higher than the risk of developing Stevens-Johnson syndrome; not everyone has an allergic reaction to these drugs.
Therefore, the appropriateness of prescribing such drugs should be assessed by a doctor, taking into account all factors and the patient’s medical history.
Causes of Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Stevens-Johnson syndrome develops under the influence of rapid allergic reactions. There are only four groups of factors that can provoke the occurrence of the disease:
- medicines;
- infections;
- malignant diseases;
- reasons of unknown nature.
In childhood, Stevens-Johnson syndrome very often occurs against the background of viral diseases, such as viral hepatitis, measles, influenza, herpes simplex, chickenpox, and mumps. The main provocateur may be a bacterial factor (tuberculosis, mycoplasmosis, salmonellosis, tularemia, yersiniosis, brucellosis), as well as a fungal cause (trichopytosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis).
In adulthood, Stevens-Johnson syndrome is explained by the administration of medications, as well as a possible ongoing malignant process. Among medications, the main cause may be antibiotics, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, sulfonamides and a central nervous system regulator.
Interestingly, carcinomas and lymphomas play a leading role in cancer and the development of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. If it is impossible to establish the etiological factor, we are talking about idiopathic Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Diagnosis and treatment of the syndrome
Stevens-Johnson disease is a serious illness that requires appropriate treatment and examination by a treating specialist. Systematic procedures include activities that are aimed at reducing or eliminating toxins from the body, relieving inflammation and improving the overall condition of the skin. If the patient experiences chronically missed situations, then special means may be prescribed.
- corticosteroids - to protect against possible relapse;
- desensitizing drugs;
- means to eliminate toxicosis.
Many people believe that a special course of vitamin treatment is important in this case - including the use of ascorbic acid and group B products, but this is not true, since the use of such drugs can develop a deterioration in the patient’s general health. You can overcome blisters on the body with the help of local therapy, which is needed to eliminate the inflammatory process and remove swelling.
The most commonly used are painkillers, antiseptic ointments and gels, specialized enzymes and creams, as well as keratoplasty. If remission of the disease occurs, then a comprehensive examination of the oral cavity and sanitation is necessary. Timely provision of correct assistance will help improve the overall picture of the disease and several times increase the patient’s chance of a quick recovery.
Before starting to treat Stevens-Johnson syndrome in children, a certain set of diagnostic procedures is carried out. If there are special indications, a professional doctor prescribes the patient to undergo an X-ray of the lungs and an ultrasound of the genitourinary system, kidneys and biochemistry.
If there is a special need, the child undergoes examinations by other specialists. Most often, such a disease is identified by a dermatologist or relevant specialized doctors, relying primarily on complaints, tests and main symptoms. A clinical blood test must be performed to identify signs of inflammation. Differential diagnosis is also important, since the disease can be confused with dermatitis, which is accompanied by the development of rashes and blisters on the face.
Symptoms of Stevens-Johnson syndrome
The onset of Stevens-Johnson syndrome is characterized by rapidly developing symptoms. At the very beginning it is usually noted:
- general malaise with body temperature rising to 40°C;
- characteristic headache;
- arthralgia;
- tachycardia;
- muscle aches;
- your throat may hurt;
- a cough may appear;
- vomit;
- diarrhea.
After a couple of hours (maximum - after a day), large blisters appear on the oral mucosa. After the opening of such blisters, extensive defects appear on the mucous surfaces, which are covered with a white-gray or yellow film. Crusts formed from dried blood also appear. The border of the lips may be involved in this pathological process. Due to severe damage to the mucous membranes in Stevens-Johnson syndrome, patients are not even able to drink or eat.
Effect on the eyes
Eye damage in its characteristics is very similar to allergic conjunctivitis, however, it is often complicated by secondary infection with the further development of inflammation with purulent content. Stevens-Johnson syndrome is also characterized by the formation of erosive and ulcerative elements on the cornea and conjunctivitis. Such elements are usually small in size. Damage to the irises and the development of iridocyclitis, blepharitis and keratitis are also possible.
Damage to mucous membranes
Infection of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system occurs in 50% of cases of this syndrome. The lesion is expressed by urethritis, vulvitis, balanoposthitis, vaginitis. Usually, scarring of erosions and ulcers of the mucous membranes leads to the formation of urethral stricture.
How is the skin affected?
The affected skin is represented by a significant number of rounded elements with elevation. Such elevations resemble blisters and are purple in color, reaching 5 cm. A peculiarity of the elements of such a skin rash in the case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome is the appearance of blood and serous blisters in the center. If such blisters are opened, bright red defects covered with crusts form. The main place of rashes is the skin of the perineum and torso.
The time for new rashes to appear in Stevens-Johnson syndrome lasts approximately 3 weeks, and healing lasts 1.5-2 months. It should be said that the disease is complicated by pneumonia, bleeding from the bladder, colitis, bronchiolitis, secondary bacterial infection, acute renal failure and even loss of vision. Due to developing diseases, about 10-12% of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome die.
Diagnosis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome
A doctor can identify Stevens-Johnson syndrome based on the presence of specific symptoms that can be detected during an experienced dermatological examination. By interviewing the patient himself, you can determine the cause that caused the development of this disease. A skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis. Histological examination may reveal necrosis of epidermal cells, as well as possible perivascular infiltration by lymphocytes and subepidermal appearance of blistering-like elements.
Clinical analysis will help identify nonspecific signs of inflammation, and a procedure such as a coagulogram will help detect clotting disorders. Using a biochemical blood test, a reduced level of proteins is determined. The most valuable thing in diagnosing Stevens-Johnson syndrome is considered to be a blood test using an immunological method. With the help of such a study, it is possible to detect an increased level of T-lymphocytes, as well as specific antibodies.
To diagnose Stevens-Johnson syndrome you will need:
- carrying out bacterial sowing of separated elements;
- coprogram;
- urine analysis (biochemical);
- taking a Zimnitsky sample;
- Kidney CT;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- X-rays of light.
If necessary, the patient can seek advice from a urologist, pulmonologist, ophthalmologist and nephrologist.
Differential diagnostics are also carried out in order to distinguish Stevens-Johnson syndrome from dermatitis, which is known to be characterized by the presence of blisters (simple contact dermatitis, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, allergic dermatitis, various forms of pemphigus, including vulgar, true, foliate and vegetative, as well as Lyell's syndrome).
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell's syndrome is important, since both pathological conditions are characterized by severe lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, accompanied by pain, erythema and exfoliation.
The first difference is that with Stevens-Johnson syndrome the rash is initially localized in the torso and perineum, while with Lyell's syndrome it is generalized.
The second difference that helps differentiate one disease from another is the rate of development of epidermal detachment and the extent of skin necrosis. In Stevens-Johnson syndrome, these phenomena form more slowly and cover about 10% of the patient's total skin area; in the case of Lyell's syndrome, necrosis covers about 30%.
Treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome is carried out using significant doses of glucocorticoid hormones. Due to damage to the oral mucosa, drugs must be administered by injection. The doctor begins to gradually reduce the administered doses only after the symptoms become less pronounced and when the patient’s condition improves.
In order to cleanse the blood of immune complexes formed in Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the method of extracorporeal hemocorrection is usually used, including membrane plasmapheresis, immunosorption, cascade filtration and hemosorption. Specialists perform transfusions of plasma and protein solution. Great importance is given to the amount of fluid introduced into the human body, as well as maintaining daily diuresis. For the purpose of additional therapy, drugs containing calcium and potassium are used. If we talk about the treatment and prevention of secondary infection, it is carried out using local or systemic antibacterial drugs.
Treatment
Treatment and assistance with the development of Stevens-Johnson syndrome should be carried out as quickly as possible to prevent a significant worsening of the pathological process, which allows saving the patient’s life.
First aid consists of replenishing the victim’s body with fluid, which he constantly loses in the process of activating pathological processes in the skin.
The video below will tell you about the diagnosis and treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome:
In a therapeutic way
Since this condition is characterized by a rapid worsening of pathological processes in the skin, providing assistance in a therapeutic way is not clearly effective. The most effective is the use of certain medications to relieve pain and eliminate the main symptoms of the disease.
Bed rest and a diet based on liquid and puree foods can be considered an important therapeutic agent for this condition.
By medication
The most important thing at the stage of activation of Stevens-Johnson syndrome is the use of glucocorticosteroids. Also, medications with a pronounced effect include:
- discontinuation of previously taken medications to eliminate the possibility of exacerbation of the current condition;
- administering infusions to prevent severe dehydration;
- disinfection of the skin using products that dry the affected areas;
- taking antibacterial drugs;
- antihistamines that relieve skin burning and itching;
- disinfection of mucous membranes using Solcoseryl ointment or hydrogen peroxide.
The promptness of providing medical care determines its effectiveness and the achievement of significant results in treatment.
Other methods
- Surgery is not recommended for Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Traditional methods also turn out to be powerless when the process of skin damage is active.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (photo of a child)