Glucose tolerance test
A glucose tolerance test (GTT) or a glucose tolerance test is a specific examination method that helps identify the body’s attitude towards sugar. With its help, a tendency to diabetes mellitus and suspicion of a hidden disease are determined. Based on the indicators, you can intervene in a timely manner and eliminate threats. There are two types of tests:
- Oral glucose tolerance or oral - sugar loading is carried out a few minutes after the first blood draw, the patient is asked to drink sweetened water.
- Intravenous - if it is impossible to drink water on your own, it is administered intravenously. This method is used for pregnant women with severe toxicosis and patients with gastrointestinal disorders.
Markers of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: what are they?
There are enzymes, the appearance of which in serum indicates the development of the disease. Doctors call such substances markers. To identify them, a blood test is performed.
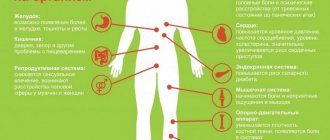
Diabetes mellitus is a serious and incurable disease that can occur in a latent form.
Today in diabetology, there are six stages of development of endocrine disorders associated with insufficient production of pancreatic insulin. A person's genetic predisposition to diabetes is considered to be a combination of genes. Markers of the insulin-dependent form of pathology are divided into genetic, metabolic and immunological.
To identify the disease at an early stage and monitor the course of the pathology, doctors prescribe blood donation to detect antibodies to:
- islets of Langerhans (ICA) . These are prognostic markers for the development of the first form of diabetes; they are detected in the blood 1-8 years before the first signs of illness appear. ICA is detected when insulin synthesis is disrupted under the influence of toxic elements, viruses, and stress. Such antibodies are detected in 40% of patients with type 1 diabetes;
- tyrosine phosphatase (anti-IA-2) . The presence of such a marker indicates the destruction of pancreatic beta cells. Detected in 55% of people with type 1 diabetes;
- insulin (IAA) . These are substances produced by the immune system in response to its own or additionally administered insulin hormone. In people with form 1 diabetes, this marker increases only in 20% of cases;
- glutamic acid decarboxylase (anti-GAD) . Identified 5 years before the first manifestations of insulin-dependent diabetes.
A blood test for C-peptide is also performed. This marker is considered more stable than insulin. With exacerbation of diabetes, the content of C-peptide decreases and indicates a deficiency of endogenous insulin.
HLA typing is also performed. The HLA marker is recognized as the most informative and accurate in terms of diagnosis: it is detected in 77% of diabetic people.
To differentiate diabetes mellitus of the first and second forms, the patient must be given a blood test for anti-GAD and ICA markers.
When planning to donate blood for a biochemical analysis, many are interested in the cost of such an examination. The price of testing plasma for glucose levels and glycated hemoglobin is approximately 900 rubles.
Detection of a complex of autoimmune markers (antibodies to glutamate decarboxylase, insulin, tyrosine phosphatase, islets of Langerhans) will cost up to 4,000 rubles. The cost of determining C-peptide is 350, antibodies to insulin - 450 rubles.
Indications for use
Patients who have the following factors can receive a referral from a general practitioner, gynecologist, or endocrinologist for a glucose tolerance test during pregnancy or suspected diabetes mellitus:
- suspected type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- actual presence of diabetes;
- to select and adjust treatment;
- if you suspect or have gestational diabetes;
- prediabetes;
- metabolic syndrome;
- malfunctions of the pancreas, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, liver;
- impaired glucose tolerance;
- obesity, endocrine diseases;
- self-control in diabetes.
Authorized Products
The diet for impaired glucose tolerance includes the consumption of rye bread, with bran and gray wheat bread up to 300 g per day.
Allowed: lean meat and chicken, which should be boiled or baked, which reduces the calorie content of food. Fish is also selected in dietary varieties: pike perch, hake, pollock, cod, navaga, pike. The cooking methods are the same.
The amount of cereal is limited to the individual norm for each patient (on average - 8 tablespoons per day): barley, buckwheat, pearl barley, oatmeal, millet, legumes are allowed. The amount of cereals and bread should be adjusted. For example, if you have consumed pasta (allowed occasionally and in limited quantities), then on this day you need to reduce the amount of porridge and bread.
The first courses are prepared in secondary meat broth, but it is better to use vegetable broth. Focus on vegetable and mushroom soups, as they are lower in calories compared to cereals. Potatoes in first courses are allowed in minimal quantities.
The diet includes vegetables with a low carbohydrate content (zucchini, eggplant, pumpkin, cucumbers, lettuce, squash, cabbage), which can be used stewed or raw. Potatoes are consumed in a limited manner, taking into account the individual carbohydrate intake - usually up to 200 g per day in all dishes. Beets and carrots contain a lot of carbohydrates, so the question of including them in the diet is decided by a doctor.
Low-fat fermented milk products should be included in the diet every day. Milk and low-fat cottage cheese are consumed in the form of milk porridges and casseroles (cottage cheese is better in its natural form). Sour cream is only used in dishes, and mild low-fat cheese 30% is allowed in small quantities.
Unsweetened berries are allowed (fresh, jellies, mousses, compotes, jam with xylitol). You are allowed to use 1 tsp of honey. twice a day, confectionery products with sugar substitutes (products for diabetics, candy, cookies, waffles). There is also a norm for their consumption - 1 candy twice a week.
Butter and various vegetable oils are added to prepared dishes. Eggs - one per day can be eaten soft-boiled or as an omelet. Coffee with milk and tea with sweeteners, rosehip infusion, and vegetable juices are allowed.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| cherry | 0,8 | 0,5 | 11,3 | 52 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| cowberry | 0,7 | 0,5 | 9,6 | 43 |
| blackberry | 2,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 31 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
| currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 43 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Bakery products | ||||
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| doctor's bread | 8,2 | 2,6 | 46,3 | 242 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| diabetic crackers | 10,5 | 5,7 | 73,1 | 388 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| xylitol | 0,0 | 0,0 | 97,9 | 367 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| fructose | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,8 | 399 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream 15% (low fat) | 2,6 | 15,0 | 3,0 | 158 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.3% | 18,0 | 0,3 | 3,3 | 90 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| beef tongue | 13,6 | 12,1 | 0,0 | 163 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| instant chicory | 0,1 | 0,0 | 2,8 | 11 |
| black tea without sugar | 0,1 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
How to take a glucose tolerance test
If the doctor suspects one of the diseases listed above, he will give a referral for a glucose tolerance test. This examination method is specific, sensitive and capricious. You should carefully prepare for it so as not to get false results, and then, together with your doctor, select a treatment to eliminate the risks and possible threats, complications in the course of diabetes.
Preparation for the procedure
Before taking the test, you need to prepare thoroughly. Preparation measures include:
- a ban on drinking alcohol several days in advance;
- You must not smoke on the day of the test;
- tell your doctor about your level of physical activity;
- do not eat sweet foods during the day, do not drink a lot of water on the day of the test, follow a proper diet;
- take into account stress;
- do not take the test if you have infectious diseases or postoperative conditions;
- Three days in advance, stop taking medications: glucose-lowering, hormonal, metabolism-stimulating, mental depressants.
Causes and symptoms of indicator deviations
IGT is a condition characterized by a slight increase in a substance in the blood. According to the international classification of diseases ICD 10, the condition code is R73.0.
Glucose concentration should be 3.3-5.5 mmol/l. When conducting a glucose tolerance test, normal values after consuming a sweet solution should be up to 7.8 mmol/l. We can talk about IGT at figures of 7.8-11 mmol/l.
The absorption of carbohydrates can deteriorate for various reasons:
- hereditary predisposition;
- overweight;
- physical inactivity;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- disruption of insulin synthesis by the pancreas;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- thyroiditis;
- atherosclerosis;
- liver diseases;
- hypothyroidism;
- gout;
- taking certain medications;
- age from 50 years.
IGT can occur in pregnant women. This is due to the fact that the placenta performs the function of synthesizing hormonal substances that reduce tissue resistance to insulin. About 3% of pregnant women experience gestational diabetes. As a rule, this phenomenon is temporary, and after childbirth the amount of glucose stabilizes.
How can you lower blood sugar at home without medications? We have the answer!
Read about the causes of low progesterone during pregnancy and methods for correcting indicators at this address.
Follow the link https://vse-o-gormonah.com/zabolevaniya/diabet/insulinorezistentnost.html and learn about how to prepare for an insulin resistance test and what the test results show.
At the initial stage, increased glucose tolerance may not manifest itself in any way. The disorder can be detected through a laboratory blood test. Gradually, the pathology progresses and manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- dry skin;
- itching in the genital area;
- long healing wounds;
- frequent urination;
- strong thirst;
- decreased sex drive;
- loss of appetite;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle in women;
- vascular damage;
- blurred vision.
READ ALSO: Rules and nutritional features for type 2 diabetes mellitus with overweight, recommendations for creating a daily menu
Even in the absence of symptoms of the disorder, with a high risk of developing diabetes, it is necessary to donate blood from time to time to test glucose tolerance.
In what cases is GTT necessary?
The main purpose of the test is to prevent metabolic disorders and prevent the onset of diabetes mellitus. Therefore, all people from risk groups, as well as patients with diseases that can be caused by long-term, but slightly elevated sugar, should take a glucose tolerance test:
- overweight, BMI;
- persistent hypertension, in which the pressure is above 140/90 most of the day;
- joint diseases caused by metabolic disorders, for example, gout;
- diagnosed narrowing of blood vessels due to the formation of plaque and plaque on their inner walls;
- suspected metabolic syndrome;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- in women - polycystic ovary syndrome, after cases of miscarriage, developmental defects, the birth of an oversized child, gestational diabetes mellitus;
- previously identified glucose tolerance to determine the dynamics of the disease;
- frequent inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and on the surface of the skin;
- nerve damage, the cause of which is not clear;
- taking diuretics, estrogen, glucocorticoids for more than a year;
- diabetes mellitus or metabolic syndrome in close relatives - parents and siblings;
- hyperglycemia, recorded once during stress or acute illness.
A general practitioner, a family doctor, an endocrinologist, and even a neurologist and a dermatologist can issue a referral for a glucose tolerance test - it all depends on which specialist suspects a disorder of glucose metabolism in the patient.
Test procedure
Although the glucose tolerance test is very simple, you will have to spend about 2 hours in the laboratory, during which changes in sugar levels will be analyzed. It will not be possible to go for a walk at this time, as staff supervision is required. Typically, patients are asked to wait on a bench in the laboratory hallway. Playing exciting games on your phone is also not worth it - emotional changes can affect the absorption of glucose. The best choice is an educational book.
Stages of identifying glucose tolerance:
- The first blood donation must be done in the morning, on an empty stomach. The period since the last meal is strictly regulated. It should not be less than 8 hours, so that the consumed carbohydrates have time to be utilized, and no more than 14, so that the body does not begin to starve and absorb glucose in non-standard quantities.
- A glucose load is a glass of sweet water that you drink within 5 minutes. The amount of glucose in it is determined strictly individually. Typically, 85 grams of glucose monohydrate is dissolved in water, which equates to 75 grams pure. For persons 14-18 years old, the required load is calculated based on their weight - 1.75 g of pure glucose per kilogram of weight. If you weigh more than 43 kg, the usual adult dose is allowed. For obese people, the load is increased to 100 g. With intravenous administration, the portion of glucose is greatly reduced, which makes it possible to take into account its losses during digestion.
- Blood is donated again 4 more times - every half hour after exercise. Based on the dynamics of sugar reduction, one can judge about disturbances in its metabolism. Some laboratories take blood twice - on an empty stomach and after 2 hours. The result of such an analysis may be unreliable. If your blood glucose peak occurs at an earlier time, it will not be recorded.
An interesting detail is that citric acid is added to the sweet syrup or simply given a slice of lemon. Why lemon and how does it affect the measurement of glucose tolerance? It does not have the slightest effect on sugar levels, but it allows you to eliminate nausea after a one-time intake of a large amount of carbohydrates.
Laboratory determination of glucose levels
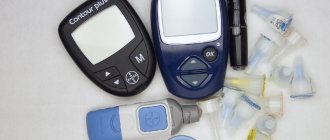
Currently, blood is almost never taken from a finger. In modern laboratories, the standard is to work with venous blood. When analyzing it, the results are more accurate, since it is not mixed with intercellular fluid and lymph, like capillary blood from a finger. Nowadays, sampling from a vein is no less traumatic than the procedure - laser-sharpened needles make the puncture almost painless.
When blood is collected for a glucose tolerance test, it is placed in special tubes treated with preservatives. The best option is to use vacuum systems, into which blood flows evenly due to the difference in pressure. This avoids the destruction of red blood cells and the formation of clots, which can distort the test results or make it impossible to perform it altogether.
The laboratory assistant’s task at this stage is to avoid blood damage - oxidation, glycolysis and coagulation. To prevent the oxidation of glucose, sodium fluoride is contained in the test tubes. Fluorine ions in it prevent the breakdown of the glucose molecule. Changes in glycated hemoglobin are avoided by using cool tubes and subsequent refrigeration of samples. EDTA or sodium citrate are used as anticoagulants.
Normal indicators
Satisfactory indicators when conducting a glucose tolerance test are normal.
Shown in the table:
| Values | Test with sugar “load” |
| Normal values mmol\L | First sample – 3.5 – 5.5; |
| After drinking sweet water, less than 7.8 | |
| Indicators for diabetes, mmol/l | The first sample is more than 6.1; |
| After taking sweet water more than 11.1 | |
| Value for prediabetes, mmol/l | First sample 5.6 – 6.1; |
| After drinking sweet water 7.8 – 11.1 | |
| Values for hypoglycemia, mmol/l | Less than 3.5 |
Important! It is worth remembering that the norm is almost the same for children and adults, but for older people it is higher.
If poor results are detected after a tolerance test, the doctor should order a repeat test to rule out a false result.
Tolerance test
If a person is already affected by diabetes, subsequent blood draws for GTT are not carried out. If the diagnosis is confirmed, a laboratory blood test for glucose or a rapid test (glucometer) is used for further monitoring.
This is done in order to control sugar levels and not prevent complications, as well as for the correct selection of maintenance therapy and proper nutrition. Those affected by diabetes need to radically reconsider their lifestyle and diet, and the best way to do this is to see a qualified doctor.
What are the norms during pregnancy?
When carrying a child, a feature of the expectant mother’s body is that it undergoes serious changes, during which a large amount of vitamins and nutrients are consumed in the mother’s body.
Pregnant women need careful care, a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, which is prepared by a qualified doctor. In some cases, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed for greater effect.
During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to constantly be monitored by a doctor and regularly take blood tests. Violation of the mother’s body parameters can lead to serious deviations in the future development of the child’s body.
With prolonged hyperglycemia, gestational diabetes is diagnosed, during which the level of glycated hemoglobin increases.
Normal indicators for pregnancy are:
| Blood sampling time | Glucose level (mmol/l) |
| On empty stomach | From 5.1 to 7.0 |
| An hour after taking the sugar load | More than 10 |
| Two hours later, after taking the sugar load | More than 8.5 |
During pregnancy, it is better to take the test between the twenty-fourth and twenty-sixth weeks. In this way, consequences for both the child and the expectant mother can be prevented.
The higher your blood sugar level, the higher your risk of complications during childbirth. Since with elevated levels of glucose in the blood, wounds heal slowly. As a result, heavy bleeding during childbirth can lead to death.
Glucose tolerance test during pregnancy
If someone says that pregnant women do not need to undergo GTT, this is completely wrong!
Pregnancy is a time of radical restructuring of the body to ensure good nutrition of the fetus and provide it with oxygen. Changes also occur in glucose metabolism. In the first half of the pregnancy, GTT gives lower values than usual. Then a special mechanism is activated - some muscle cells stop recognizing insulin, more sugar remains in the blood, and the child receives more energy through the bloodstream for growth.
If this mechanism fails, it is referred to as gestational diabetes. This is a separate type of diabetes that occurs exclusively during pregnancy and goes away immediately after birth.
It poses a danger to the fetus due to impaired blood flow through the vessels of the placenta, an increased risk of infections, and also leads to high weight of the child, which complicates the course of labor.
Diabetes and blood pressure surges will be a thing of the past
Diabetes is the cause of almost 80% of all strokes and amputations. 7 out of 10 people die due to blockages in the arteries of the heart or brain. In almost all cases, the reason for such a terrible end is the same - high blood sugar.
You can and should beat sugar, there is no other way. But this in no way cures the disease itself, but only helps fight the consequence, not the cause of the disease.
The only medicine that is officially recommended for the treatment of diabetes and is also used by endocrinologists in their work is the Dzhi Dao Diabetes Patch.
The effectiveness of the drug, calculated according to the standard method (the number of recovered patients to the total number of patients in a group of 100 people undergoing treatment) was:
- Normalization of sugar – 95%
- Elimination of vein thrombosis – 70%
- Eliminate palpitations – 90%
- Relief from high blood pressure - 92%
- Increased vigor during the day, improved sleep at night - 97%
Manufacturers of Zhi Dao are not a commercial organization and are funded by the government. Therefore, now every resident has the opportunity to receive the drug at a 50% discount.
Most often, for GTT, glucose is taken orally, that is, simply drinking its solution. This path is the most natural and fully reflects the transformation of sugars in the patient’s body after, for example, a rich dessert. You can also inject glucose directly into a vein using an injection. Intravenous administration is used in cases where an oral glucose tolerance test cannot be done - in case of poisoning and concomitant vomiting, during toxicosis during pregnancy, as well as in diseases of the stomach and intestines that distort absorption processes into the blood.