A few words about diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by elevated fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels.
In addition to hyperglycemia - elevated sugar levels, an integral sign of uncompensated diabetes mellitus is glycosuria - the release of glucose in the urine. Diabetes mellitus translated from Greek means “to pass through,” that is, water does not stay in the body at all, but all comes out.
Diabetes mellitus is not a modern disease, as many believe, but has its roots deep in history. Diabetes mellitus was first mentioned in Ancient Roman documents dating back to the third millennium BC.
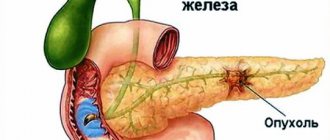
And for many hundreds of years, scientists and doctors have been trying to find out the reasons for the development of diabetes mellitus in order to prevent the development of this disease in subsequent generations and to find a cure to help those already sick, but so far all those who were sick were doomed. At the very beginning of the 20th century, scientist Paul Langerhans discovered special cells of the pancreas - beta cells, responsible for the synthesis of insulin. These cells are located in groups that are named after the scientist who discovered them; they are called the islets of Langerhans. After the discovery of these cells, a series of experiments followed, which in 1921 made it possible to isolate a substance from beta cells, which was called insulin (the name is derived from the word “islet”).
The discovery of insulin marked the beginning of a new era in endocrinology and patients with diabetes had the chance to live a fuller life than they had before the discovery of insulin.
Subsequently, scientists were able to provide patients with a wide range of insulins of different action (short or long-acting) and origin (beef, pork, human).
The task of modern endocrinology is to select the type of insulin that is suitable for the patient and give him the opportunity to live a full life.
Women get sick: their own specifics
On average, symptoms of diabetes are more common in women than in men. There are many reasons for this. In addition, many representatives of the fair sex trigger the disease: the first manifestations are quite weak, so women put off going to the doctor until the very last moment, when it becomes clear that treatment needs to be started urgently. Therapy will be much more effective if you consult a specialist at the first manifestations. Despite their relative harmlessness, the danger of the condition should not be underestimated. And the first thing that many people pay attention to is excessive hair loss. Normally, a person should lose about a hundred hairs per day, but this is due to metabolism. In diabetes, metabolism is disrupted, so growth slows down and hair loss increases. The hair becomes brittle, loses its shine and beauty, the hair becomes thinner and grows slowly.
One of the symptoms of diabetes in women is drowsiness. Many people do not attach much importance to it, but this sign is more than alarming, reflecting that the body does not have an adequate supply of energy for everyday tasks. This is explained by the inability to form energy from glucose due to metabolic disorders. If during the night's rest the cells do not store the necessary energy volumes, during the working day the woman feels tired and weak. Monitoring your condition in this way is an important reason to visit a doctor and get tested.
What happens in the body during diabetes
In diabetes mellitus, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in the body is disrupted, that is, compensation for the absorption of carbohydrates and fats is disrupted. To compensate for diabetes mellitus, the absorption of carbohydrates is of greater importance.
Carbohydrates, fats and proteins contained in foods entering the body are absorbed under the influence of digestive enzymes. Carbohydrates, turning into glucose molecules, are the main source of energy, which is necessary for all processes occurring in cells.
Glucose accumulates in the blood; in order for it to be used by cells, it must enter the cell itself. This is precisely why insulin is needed; it acts as a so-called key that opens the door to the inside of the cell for glucose molecules. Insulin is also necessary to create an energy reserve, which is formed in the following way - some of the glucose molecules are not used immediately, but are processed into glycogen, which is stored in the liver and used by the body as needed (during fasting, hypoglycemia).
A healthy body immediately reacts to the influx of carbohydrates into it by producing the amount of insulin necessary to absorb the incoming amount of carbohydrates.
But in diabetes mellitus, insulin synthesis is disrupted (it is produced in insufficient quantities or not produced at all, or its action is impaired). In this case, glucose cannot pass into the cells; it accumulates in the blood, due to which the blood glucose level increases above normal, while the cells and the entire body lack energy. For the normal functioning of the body, it is necessary to allow glucose molecules to pass into cells and be absorbed there, and this is possible by administering insulin injections (with type 1 diabetes) or taking drugs that normalize the effect or structure of insulin (with type 2 diabetes).
How is diabetes diagnosed?
There are standards for normal sugar levels. Sugar measurements are taken on an empty stomach and after meals. It is possible to analyze glucose levels in whole blood and plasma. Note that whole blood readings are 12% lower than plasma readings. To facilitate the translation, there is the following rule - the value in whole blood is multiplied by 1.12 - this is how the value in blood plasma is obtained. Conversely, divide the plasma value by 1.12 to obtain the whole blood value.
Glucose is measured in several units - mol/l and mg/dl.
The normal fasting whole blood sugar level is considered to be 3.3 – 5.5 mmol/L (59.4-99 mg/dL). 1.5-2 hours after eating, sugar should not exceed 7.8 mmol/l. More detailed data is given in the table. There should be no traces of sugar in the urine.
If glucose values are higher than normal, then we can talk about impaired glucose tolerance.
To make a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, you need to take a number of blood tests, such as:
- GG (glycated/glycolyzed hemoglobin);
- Antibodies to insulin
- C-peptide
And based on the results of these tests, we can talk about the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus.
Nowadays, many different laboratories perform these tests, and the technique of performing them may vary, so when you receive the result, you need to have the norm next to the result so that you can compare whether your results exceed the established norm.
If the result of a blood glucose test is higher than normal, the doctor will prescribe further examination, including a “sugar curve” or “stress test.” In this type of examination, blood is donated for sugar on an empty stomach, then the patient drinks 75 g of glucose and donates blood again after a while. In a healthy person, sugar will not rise above 7-8 mmol/l, and when sugar rises to 11 mmol/l and above, they speak of diabetes mellitus.
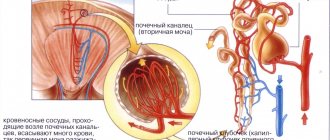
When blood sugar exceeds 7-9 mmol/l, it begins to be excreted in the urine. Therefore, during the examination, a urine test for sugar is prescribed. The higher the sugar in the blood, the correspondingly more of it is in the urine. The appearance of sugar in the urine may be a sign of newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus or decompensated diabetes mellitus with a poorly selected treatment regimen.
Treatment
The main treatment is insulin therapy, which is administered subcutaneously (in form 1) and orally. Injected insulin binds to blood sugar and reduces its activity. The dosage is determined individually. Hypoglycemic drugs help normalize metabolic processes and reduce blood sugar levels.
Secondary diseases are treated in a specific way: for nephropathy with diuretics, for hypertension - with adrenergic blockers.
Treatment is accompanied by nutritional correction with strict calorie counting. Throughout therapy, it is necessary to monitor sugar levels using a handy glucometer and monitor urine acetone.
Signs of diabetes
The main signs of diabetes are severe thirst, constant feeling of hunger, frequent urination, excretion of sugar in the urine, and the smell of acetone.
Often the development of diabetes is accompanied by severe dryness and flaking of the skin, itching of the skin and mucous membranes. In women, diabetes can be detected after visiting a gynecologist with complaints of itching in the vagina, persistent thrush. Since decompensated or not yet established diabetes mellitus provides fertile ground for the development of fungal infections.
The patient may also experience severe weakness, cramps and pain in the calf muscles, severe weight loss (with type 1 diabetes) and weight gain (with type 2 diabetes).
Increased sugar can cause nausea and vomiting, poor healing of wounds and scratches.
If you notice some signs that may suggest the development of diabetes, it is better to immediately consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examination.
Insulin-dependent type: what to look for?
Treatment of symptoms of this type of diabetes mellitus is more relevant for patients twenty-five years of age and younger. The disease progresses brightly, its symptoms are clearly expressed, and the course is predominantly labile. Patients are characterized by the accumulation of ketone bodies and hypoglycemia. The onset is usually acute and coma is possible. In a blood test, insulin and C-peptide are either not detected at all or are present in significantly smaller quantities. You can suspect the disease by constantly tormenting thirst. The mouth is dry and there is a frequent urge to urinate. Patients often lose weight unpredictably, feel weak, performance decreases, and appetite increases. In diabetes, the skin and perineum may itch, and boils may form. Pyoderma is often observed.
For this type, symptoms of diabetes in children and adults include sleep problems, sudden mood swings and a tendency to be irritable. Many people complain of a sore head, soreness in the heart and leg muscle fibers in the calves. For patients with diabetes of this type, there is a higher risk of contracting tuberculosis; there is a danger of inflammatory processes affecting the kidneys, the system of urine excretion pathways from the body. A considerable percentage of diabetics suffer from pyelonephritis and pyelitis. Blood tests show elevated glucose levels. The severity of symptoms is directly determined by the stage of the disease, the duration of its course, and the specific individual qualities of the patient.
If you notice these types of diabetes symptoms, you should make an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible. The first form of the disease develops quickly and soon provokes a deterioration in health. The consequences of the disease can be quite severe, including coma and death.
Types of diabetes
There are several types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes or diabetes mellitus in pregnant women is also distinguished.
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the fact that pancreatic cells stop producing insulin. At first, insulin may be produced, but in insufficient quantities. Over time, the beta cells die and insulin stops being produced altogether.
This type requires external administration of insulin.
Type 1 diabetes is also called, although not entirely correctly, diabetes of the young, since it most often develops in children, adolescents and people under 30-35 years of age. But there are exceptions everywhere, so it can also be detected in older people. This type is not as common as type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is incurable! Neither pills nor any other means will help restore dead beta cells that produce insulin. But the main thing to remember is that with properly selected therapy, people with diabetes live long, fulfilling lives without denying themselves anything. You just have to spend some effort and time to achieve compensation.
Type 2 diabetes is more common than type 1 diabetes. It is also called diabetes of the obese, as it develops in people suffering from excess body weight and diabetes in the elderly. Although the latter is not entirely true, although it mainly affects people after 40 years of age and older, recently it has been diagnosed in children and young people.
In type 2 diabetes, insulin is produced in sufficient, and sometimes in excess, quantities. But there is a violation of its structure or the mechanism of its effect on cells. That is, insulin is produced, but it cannot transport glucose into the cells, so glucose molecules accumulate in the blood, which explains the increased blood sugar.
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by gradual development. Often a person finds out that he has diabetes only after being tested for a completely different reason.
Diabetes of the second type requires drug treatment (special sugar-lowering drugs); treatment with insulin therapy is possible (according to test indications, if it is impossible to achieve normoglycemia through diet and sugar-lowering drugs). In some cases, it is possible to maintain normal sugar levels by following a strict diet and exercise. Since diet and exercise contribute to weight loss, and achieving normal body weight reduces tissue insulin resistance, which leads to the normal effect of insulin on cells and the return of normal blood sugar levels.
It is incorrect to call type 1 diabetes “insulin-dependent” and type 2 diabetes “insulin-independent.” Since not only type 1 diabetes can be insulin-dependent, but also type 2 diabetes; just as type 2 diabetes can be not only insulin-independent, but also insulin-dependent.
Another form of diabetes is gestational diabetes, or, as it is also called, diabetes during pregnancy. It occurs in some women at different stages of pregnancy. Its manifestations are the same - increased blood sugar levels.
Often, to achieve normal compensation for gestational diabetes, it is necessary to follow a diet and exclude fast carbohydrates. But sometimes this is not enough, then insulin therapy is started during pregnancy. It is possible to use only long-acting insulin or a combination of short and long-term insulin.
This diabetes may completely go away after childbirth and no longer remind you of itself. But often after some time (sometimes after several years) it turns into type 2 diabetes, somewhat less often it manifests itself in the form of type 1 diabetes.
Childhood diabetes: features
As with diabetes in women, symptoms in children suggest liver damage. Changes in internal organ systems are possible, and not always predictable. But rubeosis and xanthosis, characteristic of many adult patients, are practically not observed in children. If adequate treatment is not started, the skin will soon begin to peel off and become dry. Swelling is possible if the disease is accompanied by severe exhaustion. Pathology can be suspected by the tongue - the color changes to bright red, the surface is dry, the papillae are smoothed. Many people develop gingivitis and pyorrhea due to diabetes. The latter is much more difficult to tolerate in childhood than in older patients. Caries progresses. Heart sounds are muffled when auscultated, a systole murmur is possible, from which it is concluded that vascular tone is reduced. The pressure is usually below normal, the pulse is small. Capillaroscopy gives a red background, shows a wide bend of the artery, and pathological changes in the myocardium can be seen on the ECG.
One of the symptoms of diabetes in women, men, and children is dyspepsia. It is known that at a young age with such a diagnosis there is a higher likelihood of an increase in liver volume. The longer the disease lasts, the more pronounced the symptom. When examined, the organ is denser than normal and provokes pain. If diabetes is severe, red blood cells, proteins, and cylindrical cells are found in the patient’s urine. The filtration functions of the kidneys may be inhibited. If the child is old enough to describe his sensations, he complains of dizziness and headaches, while the condition is weak. Against the background of diabetes, memory suffers, limbs hurt, the sensitivity of the skin is impaired, tendon reflexes weaken and fade away. Problems of visual accommodation are observed - these are recorded much more often than in the case of adult patients. There is a risk of retinopathy and cataracts. Retinitis and ocular muscular paralysis are rare, but such a course is possible.
Causes of diabetes mellitus
To date, scientists and doctors cannot identify the causes that contribute to the development of diabetes. There are several theories. One of which says that a person is already born with a predisposition to diabetes, and external conditions only contribute to its development.
The conditions that provoke the development of diabetes mellitus are:
- stressful situations
- severe infections
- taking certain medications
- severe injuries
- surgical interventions
- pregnancy
Little things worth noting
Symptoms of diabetes in men and women include itching of the feet and palms. Up to 80% of patients noted that the initial stages of the disease were accompanied by such sensations. Symptoms may occur infrequently, but even rare manifestations deserve attention. In addition, many people notice that wounds heal slowly. Itching in the perineal area is possible, however, it cannot be regarded as the main symptom of the disease - perhaps the reason is gynecological pathology. If itching accompanies other diabetic symptoms, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Over time, a new symptom of diabetes mellitus in women appears - appetite is activated, craving for sweets. True, glucose is still not absorbed by the cellular structures, the tissues starve, the brain sends new impulses, stimulating the person to eat. The cravings sometimes become frighteningly strong. This will cause weight gain, tissues become even less sensitive to insulin, instead sugars accumulate in the circulatory system, blood vessels and the heart suffer. It makes sense to pay attention to where deposits of excess kilograms are localized. If the area of accumulation is the waist, there is a high probability of chronic high blood pressure, cardiac dysfunction, and metabolic disorders.
Groups at risk of developing diabetes
Although the causes of diabetes are not precisely known, doctors identify several risk groups in which diabetes is most likely to develop.
The risk groups for developing diabetes include people who may note the following points:
- overweight and obesity (typical of type 2 diabetes);
- presence of relatives with diabetes;
- suffered severe infections;
- previous surgical interventions;
- age over 40 years
The strong half of humanity: the danger is great!
Although the disease is more common in women, the incidence of diabetes symptoms in men increases. In general, the manifestations are similar to those described above. When the disease occurs, even the smallest wounds begin to heal slowly and poorly; over time, trophic ulcers can form. Advanced diabetes can cause gangrene. Among the primary symptoms, it is worth noting increased frequency of urination, dry mouth, constant thirst, and hunger. Many patients note that they do not have the strength to cope with ordinary activities that previously were not difficult.
With diabetes, especially in middle and old age, intimate life almost completely disappears, a person loses the desire for such activity. Symptoms of diabetes mellitus in men include potency disorders.