Structure and functions performed by the musculoskeletal system
The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, joints and muscles connected by ligaments and tendons. It is responsible not only for our ability to move.
Functions of the musculoskeletal system
Postural: responsible for the vertical position of the body and balance.
Support function: provides support to internal organs.
Protective: protects vital organs from damage: skull - brain, chest - heart and lungs.
Movement function: provides body movement in space, hand motor skills, facial expressions.
Shock-absorbing: softens the impact force on internal organs when walking and jumping.
Hematopoietic: red bone marrow is found in the ribs, sternum, and pelvic bones.
Metabolic: participates in the metabolism of calcium, phosphorus, iron and other trace elements.
Disorders of the musculoskeletal system limit activity, reduce quality of life, can lead to disability, and affect other processes in the body. Therefore, it is important to diagnose and treat these diseases in a timely manner.
Diseases of the skeleton and muscles in children
The most common diseases are the following:
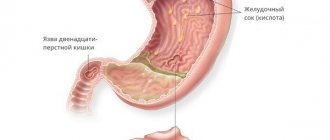
- Hip dysplasia is its underdevelopment or excessive mobility with poor development of connective tissues. May contribute to hip dislocation (subluxation). It is advisable to consult a doctor in the first 3 weeks of the child’s life after diagnosis by a neonatologist.
- Scoliotic disease (scoliosis) is a three-plane acquired, post-traumatic or congenital curvature of the spine. There is a tendency to progress as the child grows.
- Clubfoot (unilateral or bilateral) is an abnormal position of the foot, with the heel deviating inward or outward. Boys are more often affected.
- Flatfoot (initial, transverse, longitudinal) – drooping of the longitudinal or transverse arch of the foot. In advanced cases, pain in the legs and back, gait disturbance, balance problems, protruding big toe bone, and a predisposition to ingrown toenails are found.
- Perthes disease. A defect associated with poor blood supply to the head of the femur, which, if left untreated, can lead to necrosis and hypotrophy of the gluteal muscles.
- Myasthenia gravis (bulbar palsy). An autoimmune disease (genetic mutation) that causes muscles to fatigue quickly. The most susceptible muscles are the eyes, facial muscles, and chewing muscles. May affect the respiratory system. More often it develops in connection with an existing tumor of the thymus gland, as well as with cancer of some internal organs.
- Torticollis. A deformed neck, causing the baby’s head to tilt towards the affected side, the face is partially turned towards the healthy side of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The most common defect is the right side. Causes may include breech presentation, phlegmon, abscesses, and muscle damage in the neck.
- Cerebral palsy. A group of musculoskeletal system disorders associated with abnormalities of the nervous system and various areas of the brain that arose during the prenatal period. Accompanied by disturbances in muscle tone and speech. The gait is unsteady, which leads to frequent falls, and there are often deviations at the mental and physical levels.
- Bursitis. Inflammation of joint (elbow, femoral, and more often shoulder) capsules.
- Dislocation (the joint ends are completely separated) and subluxation (the surfaces of the joints are partially touching) of the joints. At the same time, damage to tendons, blood vessels, and nerves may occur.
Dystrophic changes in the cartilage of the joints may be observed, which will subsequently lead to the development of osteochondrosis (cervical, thoracic or lumbar).
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system occupy third place among all pathologies. In first and second places are diseases of the cardiovascular system and cancer.
Also, the group of diseases of the musculoskeletal system is one of the most numerous. Depending on the area and type of lesion, all diseases can be divided into subgroups:
Degenerative and inflammatory joint diseases - arthropathy
— Infectious arthritis, polyarthritis; — Inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid, deforming, psoriatic, juvenile, etc.); — Arthrosis (deforming, erosive, coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis, etc.); — Other joint diseases (finger deformities, ankylosis, osteophytes, etc.).
Connective tissue diseases
— Polyarteritis nodosa; — Systemic lupus erythematosus; - Dermatomyositis; - Systemic sclerosis.
Dorsopathies
— Deformable (pathological kyphosis and lordosis, scoliosis, osteochondrosis, spondylolisthesis); — Spondylopathies (ankylosing spondylitis, spondylosis); — Other dorsopathies (Schmorl’s hernia, cervical disc disorders, dorsalgia, lumbodynia, sciatica, etc.).
Soft tissue diseases
— Muscle damage (myositis, diastasis, contracture, sprain, tendon rupture); — Damage to the synovial membrane of the joint and tendons (synovitis, tenosynovitis, tendinitis, ruptures of the synovial membrane and tendons); — Other lesions (bursitis, fasciitis, myalgia).
Bone diseases - osteopathy and chondropathy
— Violations of integrity and structure (osteoporosis, osteomalacia, fractures); — Other osteopathies (osteomyelitis, osteonecrosis, osteitis deformans); — Chondropathy (juvenile osteochondrosis, chondromalacia, etc.).
In Russia, the number of people suffering from diseases of the musculoskeletal system increases by 30% every year compared to the previous year. Many patients do not go to doctors because... They consider this pathology incurable and natural for their age.
Types of diseases
Medicine distinguishes between two types of diseases: primary (develop independently) and secondary (as a consequence of injuries). Primary diseases include:
- Osteochondrosis is the most common problem. In places where intervertebral discs are compressed, nerves are compressed, which gradually leads to deformation and displacement of the vertebrae. Most often diagnosed in men 40–60 years old.
- Bechterew's disease is an inflammatory process in the intervertebral joints. The damaged areas are compressed, shrinking in size and causing an unnatural arch in the lower back.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disease. It affects small joints of the limbs, gradually the deformation becomes more pronounced, and movements become difficult.
- Gout is a disease that manifests itself against the background of metabolic disorders. It is most often diagnosed in men who lead an unhealthy lifestyle. Provokes disruption and deformation of joints. Gradually becomes chronic, involving other joints in the process.
Injuries also affect the musculoskeletal system. The overwhelming majority are professional athletes. When there is excessive stress on certain areas, ligaments and muscles, different types of injuries occur. These include:
- Bruises are soft tissue injuries accompanied by swelling, redness and hematomas.
- Sprains – This type of injury is characterized by stretching and tearing of ligaments. Depending on the severity of the damage, they are divided into three types.
- Dislocations are disorders in which the articular surfaces are displaced.
Symptoms of musculoskeletal diseases
Each disease has its own symptoms. The most common of them:
– Pain – in the back, in the joints, in the muscles. It can be sharp, aching or dull, varying in intensity, duration and time of occurrence. – Limitation of mobility - stiffness in the joints, inability to perform normal activities: walking, bending, squatting, working with your hands, etc. – General symptoms are weakness, fatigue, fever.
You can learn more about the causes and treatment of back pain here.
What are the diseases of the musculoskeletal system?
Modern medicine divides diseases characteristic of the musculoskeletal system into primary (developing independently) and secondary (developing against the background of other diseases, being a side effect or symptom).
Let's consider the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system in middle-aged and older people.
Osteochondrosis and spondylosis
Both of these diseases have a similar nature - degenerative-dystrophic processes in the spinal column, causing severe back pain. Also, spondyloarthrosis (spondylosis) and osteochondrosis are the most common ailments caused by the destruction of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs.
In places where the intervertebral discs are deformed, compression or pinching of nerve endings occurs, the formation of osteophytes and the growth of bone tissue, as well as displacement of the vertebrae closer to each other.
Painful sensations occur when standing, sitting or walking for a long time.
The cervical spine and lumbosacral spine are most often susceptible to destruction and dystrophy.
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammation of the intervertebral contents and ligaments of the back, accompanied by pain.
The pain is characterized by its constancy, intensification with changes in external temperature, and is localized along the entire length of the spine or in places of inflammation.
When the nerve endings of the spinal cord are pinched, a person experiences severe pain in an attempt to keep the back in a natural straight position.
It is possible to observe in a patient with spondyloarthritis a constant downward bend or a straight back without a natural arch in the lower back.
Deforming osteoarthritis
As a result of the inability of the joints of the spine to cope with the load placed on them, in the presence of excess weight, heavy training, metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalance, as well as in the presence of neurological and endocrine diseases, a person begins to be bothered by slowly developing back pain.
Deforming osteoarthritis is a chronic disease that provokes a degenerative process in hyaline cartilage, reducing the intervertebral space.
As osteoarthritis progresses, pain increases not only with movement, but also at rest.
The pain increases in the evening, causing a feeling of heaviness and stiffness in the joints, and an audible crunching sound.
Deforming osteoarthritis most often affects the knee, elbow, and hip joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis
The early stage of this disease is characterized by the immune-inflammatory development of human connective tissues and joints. Further, the disease progresses into destructive disorders - polyarthritis.
Most often, symmetrical small joints are affected by dystrophy, less often - temporofrontal, hip, shoulder and others.
The patient is plagued by aching pain in the affected joint, worsening at night or in the morning, as well as during movement. In a quiet position, the pain is less pronounced.
Characteristic signs for rheumatoid arthritis are:
- morning stiffness throughout the body;
- swelling and redness of the affected area;
- severe pain when trying to move the affected joint;
- joint deformity;
- atrophy of the muscles adjacent to the affected area;
- limited movement;
- seasonal exacerbations, accompanied by severe inflammation in the joints and high body temperature.
Over time, rheumatoid arthritis begins to affect other joints of the musculoskeletal system.
Gout or royal disease
This disease often occurs in mature men who abuse protein foods and lead an unhealthy lifestyle.
The causes of gout are considered to be a violation of the metabolism of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of sedimentary structures of urea in the joints.
The formation of monosodium urate crystals leads to joint deformation.
Gout attacks occur as a result of a protein-free diet, alcohol consumption, severe stress or heavy physical activity. Painful sensations increase at night.
The obvious symptoms of gout include the following:
- redness and enlargement of the tissues of the inflamed joint;
- glossy swelling at the site of the lesion;
- burning pain in a joint that feels hot when touched;
- fever.
As gouty arthritis worsens, the patient suffers from constant pain in the deformed joint, which can only be eliminated by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Acquiring a chronic course, gout causes inconvenience to a person in performing simple body movements.
As the disease progresses, other musculoskeletal joints are also involved in the destructive process.
Flat feet
This pathology is hereditary or acquired. With flat feet, the usual structure of the foot changes, the shock-absorbing function of the joint is disrupted, and the muscular corset of the foot weakens.
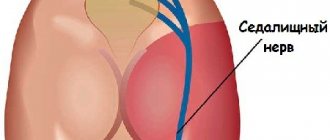
Radiculitis
The disease is typical for older people, manifesting itself with prolonged development of osteochondrosis.
Pain occurs as a result of pinched nerve endings along the spine, protrusion or herniation of intervertebral discs.
Scoliosis kyphosis kyphoscoliosis
Curvature of the spinal column has many stages, classifications and causes.
However, the main ones are: scoliosis, kyphosis, kyphoscoliosis, in which similar processes occur in different areas of the spinal column with different clinical pictures.
The main causes of spinal curvature: trauma, osteoporosis, rickets, prolonged exposure to an incorrect position, infection, tuberculosis and others.
Causes of pathology of the musculoskeletal system
There is a direct relationship between technological progress and the increase in diseases associated with the musculoskeletal system. Transport, communications, mechanization and automation of labor - all this makes the life of a modern person easier and at the same time harms his health. The more his lifestyle changes, the less he moves, the higher his risk of pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
The main factor that provokes the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system is insufficient physical activity. Daily physical activity increases bone density in osteoporosis by almost 4% over 5 months.
In addition to a sedentary lifestyle, diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be caused by:
– past and chronic diseases of internal organs (pneumonia, peptic ulcer, pathology of the pelvic organs, etc.); - birth injury; – dental disorders (bad bite, TMJ dysfunction, etc.); – endocrine disorders; – metabolic pathology; – hard physical labor and excessive stress; – chronic injuries, microdamages; – infections; – harmful environmental factors; – genetic diseases.
Movement is the best prevention of bone and joint diseases. If you jump on one leg every day, then after 2 weeks it will be noticeable on the x-ray that its bones are much denser and stronger than the bones of the other leg.
At-risk groups
There are many diseases of the musculoskeletal system, and every person can fall into the risk zone.
The first risk group includes professional athletes. With an intensive training schedule and loads, it is difficult to avoid injuries to the musculoskeletal system. The very specifics of big sport provoke excessive stress on the body, causing injuries, if not now, then in the foreseeable future.
Other reasons are:
- Congenital anomalies in the development of the thoracic region, spine, limbs, pelvic bones.
- Organ dysfunction due to previous diseases, for example, rickets, hormonal imbalances, infectious and autoimmune diseases.
- Hard physical labor.
- Sedentary work and sedentary lifestyle.
Frequent diseases of the musculoskeletal system include birth injuries. An improper birth process causes damage to ligaments and cartilage in newborn babies. If treatment is not started in time, the problems will get worse.
Prevention of musculoskeletal diseases
Prevention, as well as treatment, comes down to eliminating the causes that cause them. It is impossible to influence genetic disorders, but it is quite possible to influence other factors.
Following simple measures will help avoid expensive treatment and serious complications:
- active lifestyle; - cessation of smoking and alcohol abuse; — weight control; - balanced diet: - timely treatment of the first signs of the disease.
Prevention measures come down to careful attention to health. You cannot ignore or tolerate symptoms, make diagnoses yourself and self-medicate. Any physical exercise without consulting a doctor is dangerous.
At the Quality of Life clinic, we select an individual physical activity program for each patient, taking into account his age, gender, physiological characteristics and the presence of predisposing factors.
Osteopathy and diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Each bone, muscle, and joint has a specific shape, density, temperature, location, and mobility. During illness, these parameters are violated - muscle-ligamentous tension, spasm, dysfunction of bones and joints, and pain appear.
The main principle of osteopathy is the search and treatment of the root cause of the disease, and not its individual symptoms.
Knowledge of anatomy, physiology and hand sensitivity help the osteopath to detect changes in organs and tissues that traditional medicine cannot always detect.
Therefore, with the help of osteopathic treatment, it is possible to prevent the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system in the early stages.
Another advantage of osteopathic treatment is the absence of drugs and instrumental methods, which means its techniques are safe and painless for patients, regardless of their age and general condition.
Osteopathic treatment is effective for pathology of the musculoskeletal system, as well as for its prevention. Here you can learn more about osteopathic treatment of joints in children and adults.
ODA diagnosis groups
There are three groups of diagnoses depending on the cause of the formation of disorders:
- associated with the central nervous system (cerebral palsy of various origins, paralytic syndromes, negative consequences of polio);
- congenital developmental anomalies (hip dislocation, deformed and underdeveloped limbs);
- acquired diseases in which the motor mechanisms of the nervous system remain intact, but there are paresis, defects of the feet or hands, mild scoliosis, polyarthritis (a consequence of injury or intoxication, bone tuberculosis, cancer, rickets, chondrodystrophy).