general information
Sometimes it is necessary to treat pyoderma as an independent disease; in other cases, the pathology is provoked by other health problems. It is known that the risk of pyoderma is increased in those suffering from diabetes, since the functioning of the circulatory system is disrupted, and the skin cells do not receive the nutritional components necessary for normal functioning.
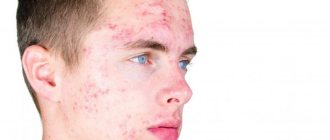
You can understand that treatment for pyoderma is required by a wide list of symptoms. Most cases are characterized by a change in the shade of diseased areas of the skin: the skin becomes reddish, then rashes and purulent blisters appear on them. If left untreated, the blisters open and ulcers form in their place. Without adequate therapy, such lesions take a very long time to heal.
Chronic pyoderma, provoked by staphylococci, causes a high degree of scar formation on the skin.
One of the types of pyoderma is folliculitis. Carbuncles also have similar manifestations. These diagnoses are made if pathological processes affect the skin areas where hair follicles accumulate. More often, treatment of this type of pyoderma in the perineum and armpits is required.
Types and symptoms
Damage to the epidermal layer in pyoderma can be either superficial or deep, and the nature of the disease can be acute or chronic. Depending on the presence of a particular pathogen, three types of disease are distinguished:
- staphylococcal - staphyloderma;
- streptococcal - streptoderma;
- mixed - streptostaphyloderma.
In the photo below you can see what the main signs of the streptococcal form look like in adults.
Staphylococcal pyoderma is usually accompanied by infection of the superficial layers of the skin. Its varieties are the following diseases:
- Ostiofolliculitis is damage to the hair follicle with the formation of purulent pustules. Most often it appears on the face in the area of the beard and mustache, as well as on other parts of the body where hair growth is possible. After the ulcers disappear, there are no scars left.
- Folliculitis is the appearance of red papules in place of the hair follicles, transforming into nodules with gray-green pus. After the inflammatory process subsides, a scaly spot forms, and then a scar.
- Vesiculopustulosis is an infection of the sweat glands. Mostly occurs in newborns and children under three years of age. At the site of the lesion (armpits, groin or under the hair on the head), prickly heat begins, and then pustules form.
- Sycosis is a chronic inflammation of the hair follicles with periodic relapses. Affects the scalp, skin of the mustache, eyebrows and beard, and groin area.
- Furunculosis is the formation of inflamed, painful nodules with purulent contents - boils. Possible fever and headaches. It affects individual parts of the body (neck, buttocks, forearms), but can also be generalized.
- Carbuncle is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of several hair follicles simultaneously with the formation of an extensive infiltrate filled with pus. The disease is accompanied by high fever, nausea, vomiting, and neuralgic pain.
- Hidradenitis is the formation of an infiltrate on the sweat glands with a channel for the secretion of pus. There is redness of the skin, swelling, increased body temperature, and general malaise. The disease is chronic with periodic relapses.
Streptococci affect the upper layers of the skin, forming phlyctenas - blisters filled with exudate . The most common types of streptoderma include:
- Fox's impetigo is a highly contagious disease that affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, eyes and bronchi.
- Zaeda is a slit-shaped erosion located in the corners of the mouth. Accompanied by redness, swelling, and is often chronic.
- Lichen simplex is the appearance of pink spots covered with small scales on the face, arms and legs. Usually occurs in children in the spring.
- Paronychia is an infection of the nail fold with the formation of blisters. The skin takes on a bluish tint, and the nail plate becomes dull and deformed.
- Erysipelas is a lesion of the subcutaneous fat layer and lymphatic vessels. The skin is scarlet in color, hot to the touch, reminiscent of the peel of an orange.
- Cellulite - affects the legs and face, causing swelling, redness, and blistering. It occurs with fever, chills, and severe pain.
- Ecthyma - single or multiple blisters concentrated on the legs and buttocks. When phlyctena dries out, ulcers form and then scars.
People with particularly weakened immune systems may experience simultaneous exposure to streptococcal and staphylococcal infections. In these cases, the deep layers of the skin are affected with a tendency to peripheral growth. There may even be ulceration of the epidermis.
The most common sign of the disease in children is a rash in the form of yellow purulent dots, in place of which purulent blisters form, drying out to form crusts.
If left untreated, an ulcer may appear at the site of the bladder, and then a scar. Other symptoms of the disease in a child include:
- itching and burning;
- skin redness;
- soreness;
- swelling.
Symptoms of pyoderma in young children can be seen in the photo below.
Diagnosis of the disease
To select the optimal treatment program for pyoderma of the face, body, groin area and other areas, you must first do a series of specific tests to confirm the diagnosis. At the appointment, the doctor takes scrapings from diseased areas of the skin and sends them to the laboratory for thorough examination. If bubbles are present, samples of their contents are obtained. By identifying the pathogen, you can finally understand whether pyoderma occurs or the patient suffers from another disease.
In addition to scraping, the doctor collects complaints, finds out the peculiarities of the patient’s life to compile an anamnesis. As a rule, patients do not carefully observe the rules of hygiene, and this contributes to the active development of pathological microflora. The clinical picture of pyoderma differs significantly from other skin diseases, so diagnosis is rarely a difficult task.
Development mechanism
Pyoderma is a contagious disease, that is, it can be transmitted through direct contact from a sick person to a healthy person.
Depending on the type of pathogen, this occurs as follows:
- staphylococcal infection spreads by contact - through hands, clothing, dishes, household items;
- Streptococcal infection in 95% of cases is transmitted by airborne droplets, since the pathogen is located mainly on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract.
The incubation period can last from 3 to 10 days. The mechanism of development of pyoderma has two main forms:
- Primary - occurs on intact healthy skin.
- Secondary - is a complication of other diseases (heat rash, eczema, scabies).
Infection of newborn children is possible in utero if the expectant mother has suffered an infectious disease, or after childbirth through contact with sick people and infected objects.
Where did the trouble come from?
Before delving into the essence of the symptoms and treatment of pyoderma, it is necessary to understand what leads to the development of the disease. Three bacterial species from the coccus family can provoke pathological processes: pio-, staphylo-, and streptococci. In extremely rare cases, the disease is provoked by other pathogens. Scientists have found that microorganisms that can cause pyoderma normally live on the skin of any healthy person. When immunity decreases and skin nutrition deteriorates, colonies begin to multiply, which leads to pathological processes. Due to the symptoms of pyoderma, treatment is more often required for people suffering from:
- diabetes;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruptions in the functioning of the hematopoietic organs;
- hormonal imbalance.
Causes and risk factors
Pyogenic bacteria - staphylococci and streptococci, which in the vast majority of cases are the causative agents of pyoderma, are present on the skin and mucous membrane of every person and do not cause much harm . Limiting factors include:
- high density of the surface layer of the skin;
- mechanical removal of microorganisms during natural desquamation and water procedures;
- preventing sweat and sebaceous gland secretions from the penetration of bacteria into the depths of the skin epidermis.
When immunity decreases, pathogenic microorganisms become active and infect the skin.
Negative conditions that contribute to the development of pyoderma include:
- microtraumas, abrasions, scratches and other lesions;
- long-term treatment with hormonal drugs or antibiotics;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body;
- unbalanced diet;
- diseases of the endocrine system, including diabetes;
- nervous exhaustion;
- hereditary predisposition;
- underweight or overweight;
- presence of chronic diseases.
The activation of pathogenic microflora can be caused by professional conditions - work in damp and hot rooms, prolonged exposure to the cold.
Workers in agriculture and some industries are at risk. Failure to comply with basic hygiene requirements can provoke the development of the disease.
Most cases of pyoderma in children occur between birth and 12 months. Infection occurs through contact through toys, personal hygiene items, bedding, and dirty hands.
Very often the cause of the disease is insufficient adherence to hygiene rules. If a child is in wet diapers for a long time, and his delicate skin comes into contact with urine or feces, irritation appears, which will be a “gate” for tiny pathogenic microflora to enter the body.
Tender age
Quite often it is necessary to select drugs for the treatment of pyoderma in children. The incidence rate is higher among infants. Most cases are explained by insufficient hygiene, which leads to suppuration in the umbilical area. The natural protection of the skin in infancy is quite weak, so the risk of developing the disease is significantly higher than in older people. From statistics it is known that up to 40% of all cases of childhood skin diseases are pyoderma.
In older children, pyoderma is explained by frequent injuries received during games. All these cases are particularly difficult due to the limited applicability of various drugs for the treatment of young patients. The practice of treating pyoderma with folk remedies is widespread - it is believed that home recipes are effective but safe. True, even their use should be practiced only under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of pyoderma in adults
If you suspect pyoderma, you should consult a dermatologist. Only a specialist, after examination and questioning, can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment! However, even before visiting a doctor, the patient must adhere to the following rules:
- You should not shave the hair in the area affected by ulcers, so as not to provoke the spread of pathogenic flora. Hairs that interfere with skin care should be carefully cut off with scissors.
- It is not advisable to wet the affected areas of the skin. In severe forms of the lesion, covering the face and body, any water procedures are prohibited, but areas of healthy skin can be wiped with a damp sponge.
- Pyoderma is not a contagious disease , but precautions must be taken. The sick family member should have their own dishes, bedding and towels.
- The abscess itself cannot be touched , but the skin adjacent to it should be treated with salicylic acid, a solution of potassium permanganate or any other antiseptic. Pay special attention to the cleanliness of your hands, which should be washed frequently to prevent infection of healthy skin.
- Pay attention to nutrition - reduce the amount of salt and easily digestible carbohydrates consumed in your diet, eat more fermented milk products, vegetables and fruits. It has been noticed that alcohol and dishes rich in extractive substances - broths, smoked meat and fish, as well as sausages.
Attention! In cases where pyoderma becomes protracted, the patient has chronic diseases or his immunity is currently weakened, the dermatologist can prescribe treatment with antibacterial drugs, having previously determined the type of pathogen.
For the treatment of pyoderma the following is used:
Antibiotics. Tetracyclines and macrolides have proven themselves to be effective. You should know that Tetracycline and Erythromycin are not recommended for the treatment of pyoderma in children, as well as in pregnant women. You should not self-medicate (not all antibiotics are equally effective, for example, penicillin is useless in the treatment of most pyoderma) - only a doctor can choose the right antibiotic!
Combined antibacterial drugs . These may be Claforan, Cephorin and other cephalosporins, which are prescribed if the disease is caused by mixed pathogenic microflora, since combined drugs have a detrimental effect on many types of microorganisms.
Sulfonamide drugs. Not as effective as antibiotics, however, in the required dosages, the use of Biseptol and Sulfomonomethoxin is quite justified, especially if antibiotics are contraindicated or cannot be used for some other reason.
Specific immune therapy. Used to activate the body's defenses, often in combination with antibiotics; consists of subcutaneous administration of antigens, staphyloprotectins and toxoids; used for chronic and sluggish, but lingering pyoderma.
To stimulate the immune system, physiotherapy is also used , for example, autohemotransfusion and ultraviolet irradiation of blood. In addition, most patients are advised to take Schisandra tincture or Eleutherococcus extract, as well as take vitamin-mineral complexes (as prescribed by a doctor) containing B vitamins (B6 and B12).
Attention! Boils and carbuncles cannot be opened independently. Ichthyol ointment, which is applied to the skin formation, will help reduce the discomfort that occurs when the abscess matures.
The right start is the key to success
The first thing you need to do is visit a doctor as soon as symptoms of pyoderma appear. Treatment for adults and children is chosen by a qualified doctor, focusing on the characteristics of the case, individual intolerances, the course and severity of the pathology. The course will be taught by a dermatologist, although if you have signs of illness, you can also come to an appointment with a therapist - the doctor will write a referral to a highly specialized specialist.
At the appointment, the doctor will tell you: first you need to cut the hair short in the affected area. Treatment of pyoderma of the head, armpits, groin area and other areas with hair involves strictly cutting them; shaving is not allowed. Eliminating long hair prevents the transfer of bacteria to healthy skin areas.
An important rule of the therapeutic course is the exclusion of water procedures, except for the most necessary ones. It is especially important to follow this rule if large areas are affected and the disease is severe.
To maintain the strength of the body, the doctor will recommend following a special diet during treatment. You will have to give up:
- acute;
- fried;
- alcohol;
- salty.
Treatment of pyoderma in adults and children involves treating the affected areas with aniline compounds and a pink solution of potassium permanganate. If your hands are not infected, you will need to wash them thoroughly every day using antibacterial soap. During treatment, it is important to constantly cut your nails and treat them with iodine solution every day. This will prevent the spread of pathological microorganisms over the entire surface of the body.
Prevention of pyoderma
Primary measures to avoid infection with pyogenic bacteria:
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Perform antiseptic treatment of wound surfaces, cuts and scratches.
- Conduct timely treatment of chronic diseases that provoke pathology (diabetes mellitus, gastritis, hormonal disorders and others).
- Avoid contact with people affected by infection.
Streptococcal and staphylococcal pyoderma tend to recur, so it is important to perform secondary prevention of the disease:
- Periodically visit a dermatologist for a routine examination.
- Provide antiseptic skin care.
- On the recommendation of a doctor, perform preventive treatment (sanitation of focal infections, ultraviolet radiation and other measures).
Options and approaches
If the disease is chronic, treatment of pyoderma with antibiotics is practiced. The choice of remedy is strictly at the discretion of the doctor. The doctor takes samples from the affected areas, identifies what pathological microflora is present, and what substances it is sensitive to. Based on the information received, a comprehensive course is developed. Bacteriological analysis is carried out by inoculation using nutrient media.
You can take drugs to stimulate the immune system in order to increase the effectiveness of the course of treatment for pyoderma. The photo below shows aloe vera in particular. This plant grows in almost every home, and its anti-inflammatory qualities are known to everyone.
However, sometimes more serious methods are needed to maintain the body’s defenses. The doctor may prescribe a blood transfusion or ultraviolet baths. Such procedures will disinfect the fluid in the circulatory system. The choice of methods to maintain immunity depends on the severity and form of the disease.
Basic principles of therapy
After a thorough diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment that pursues the following goals:
- elimination of provoking factors;
- impact on the site of the disease;
- preventing the spread of infection.
Depending on the clinical form and severity, medications from various pharmaceutical groups are used in treatment for both external and internal use.
Drugs for local therapy
In cases of shallow damage to the skin, the areas must be cleaned of necrotic tissue, and the abscesses must be washed with antiseptics:
- brilliant green;
- methylene blue;
- Fukortsin;
- 1% salicylic acid solution;
- 2% boric acid solution;
- Gentian violet.
After opening, the ulcers and phlyctenas are treated with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide and lubricated with a disinfectant.
Bathing and washing during the treatment period are limited, and healthy skin around the site of the disease is treated daily with a 0.1% aqueous solution of potassium permanganate.
For local treatment of pyoderma, bactericidal external ointments are used:
- Levomekol;
- Zinc ointment;
- Thymogen;
- Triderm;
- Geoxyzone;
- Fucicort.
The course of treatment with these drugs is 1-2 weeks. In the absence of the expected effect, as well as in cases of lesions such as boils, carbuncles, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections. The duration of antibiotic therapy depends on the severity of the disease, but no more than 7 days.
Carrying out immunotherapy
In the case of a chronic form of pyoderma with relapses occurring more often than after 3 months, special therapy aimed at stimulating weakened immunity is indicated. The following drugs are indicated for patients with skin diseases:
- dry staphylococcal vaccine;
- human antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin;
- streptococcal bacteriophage;
- Leukinferon.
Before prescribing one of these drugs, the body’s sensitivity to them is determined, for which a special study is performed - an immunogram.
Features of treatment for children
Pyoderma in a child should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor, using prescribed medications in strict dosages.
To wash the skin, use lotions based on a 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate. To prevent infection, ointments are applied (Lincomycin, Erythromycin). In case of severe suppuration, bandages with ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky liniment are applied.
In difficult cases, antibiotic therapy, administration of immunostimulating medications, and antihistamines are indicated. The duration of treatment depends on the course of the disease and is determined by the doctor individually for each patient.
Folk remedies
Alternative therapy drugs that can be used at home will help to quickly and effectively cure pyoderma. The most popular recipes are given below:
- Pour 1 cup of boiling water over 2 tablespoons of yarrow herb and leave in a water bath for 25-30 minutes. Use as a lotion for purulent rashes several times a day.
- Grind raw beets, put the pulp in gauze and apply to the ulcers 2 times a day.
- Cut a 3-year-old aloe leaf lengthwise and turn the flesh out. Wipe affected areas morning and evening.
- Pour a tablespoon of dry dill seeds into 1 glass of water and bring to a boil. Leave for 2 hours. Strain and use to wipe the affected areas.
Before using folk remedies to treat pyoderma, you should consult your doctor. Many medicinal herbs are allergens and can aggravate the course of the disease.
Treatment at home
Mild pyoderma can be treated at home. Of course, you first need to go to the doctor to clarify the diagnosis and coordinate therapy with him, but there is a high probability that the doctor will approve the use of simple traditional medicine recipes if the pathology is mild. The advantage of this approach is the minimal risk of an allergic reaction, the absence of systemic effects on the body, and stimulation of skin regeneration. With the correct use of traditional recipes, the risk of relapse is minimized.
So, where to start treating pyoderma? The photo below shows a dandelion. This plant, familiar to many, is often considered a weed, but healers can tell about its powerful healing properties.
For pyoderma, dried rhizomes and leaves of the plant are used. Take a couple of teaspoons per glass of boiling water, boil the mixture for at least five minutes, then let it brew for eight hours. Before taking the medicine, warm it up. Single dosage – half a glass. The medicine is used before meals.
There are many herbs that can help if treatment for pyoderma is necessary due to symptoms. In the photo, for example, nettles. It is used as tea leaves and eaten daily as soon as you feel thirsty. The effect of nettle tea is especially pronounced for boils and suppuration.
You can use a decoction of rye grains for food. This medicine is recommended for the chronic form of the disease. The decoction is consumed several times a day.
Classical therapy
Antibacterial drugs are used in the treatment of any form of pyoderma. Most of them are used externally. For complicated staphylococcal pyoderma, oral use of broad-spectrum antibiotics is prescribed.
In the acute period, antibiotics are prescribed for a week. When pyoderma becomes chronic, antibiotic therapy lasts up to 15 days. Broad-spectrum antibiotics come to the rescue. Typically these are penicillin drugs and cephalosporins.
Common drugs from the penicillin group include Ampiox and Amoxicillin. These antibiotics are effective against coccal infections. They are capable of destroying the cellular structure of microorganisms and preventing the proliferation of bacteria. Both products are used 3 times a day for the period recommended by the doctor. Of the cephalosporins, the most popular are Cefazolin, Cefotaxime, and Cephalexin. These agents destroy the cell wall of bacteria and help cope with a mixed type infection.
From the tetracycline series, drugs such as Doxycycline and tetracycline hydrochloride are recommended. These drugs block the production of protein by bacteria. Among aminoglycosides, antibacterial agents such as Gentamicin and Amikacin are often used. They destroy bacterial cells and interfere with protein synthesis. Macrolides have a similar effect. Thus, Clarithromycin reduces the activity of intracellular microorganisms and inhibits protein synthesis.
External treatment of the skin for staphylococcal pyoderma is a prerequisite for effective treatment. For this purpose, drugs such as:
- brilliant green – suppresses the activity of gram-positive bacteria;
- salicylic acid - used in the form of an ointment, has an anti-inflammatory effect and softens the upper layer of the epidermis;
- solution of potassium permanganate – disinfects, neutralizes the negative effects of certain toxins;
- chlorhexidine - used in the form of a solution or gel for external use. It has increased activity in various environments, including human blood and purulent contents. Suppresses the activity of pyogenic bacteria, which is especially important for staphylococcal pyoderma;
- "Triamcinolone" is a drug in the form of a cream for treating affected areas. Has an antiallergic effect and blocks inflammation;
- “Fukortsin” - a solution is used to treat the skin in order to reduce the activity of coccal infection and block the action of fungi.
Lots of options
Treatment of pyoderma with folk remedies involves the use of yarrow. Take a glass of boiling water for a couple of tablespoons, infuse the mixture for an hour, then drain the water and use it for compresses. Gauze swabs soaked in the infusion are applied to the affected areas of the skin.
There are several options for using a smoker. You can squeeze juice from a fresh plant, which is also used for lotions. A piece of cotton wool is soaked in the liquid and applied to the damaged areas. Another option is an ointment to treat pyoderma. There will be 50 g of Vaseline per tablespoon of dried leaves, mix thoroughly. The medicine is applied to diseased skin.
Calamus roots are mixed with sunflower oil (ten times more liquid than plants), boiled for a third of an hour, allowed to cool, drained and eaten a tablespoon at a time. The optimal program is twice before meals until complete recovery. Another option for using oil is to mix it with celandine in the same proportions as indicated above, and use the medicine to lubricate diseased areas of the skin.
How beautiful birch trees are always in photos! For symptoms of pyoderma, treatment of adults and children can be practiced using the buds, leaves, and sap of this wonderful tree, which is not for nothing considered one of the symbols of our country. The simplest option, which is also the most effective, is a medicine made from birch buds. Take a glass of water per tablespoon of the product, boil it for a third of an hour, let it cool, then drain the water and use it to treat the affected areas.
Simple and effective remedies can be made from other available products. For example, beets are peeled, crushed, and the pulp is applied to purulent inflammations. It is no more difficult to use potatoes: the root vegetable is also peeled and crushed, applied to gauze, secured with a bandage on the affected area and left for two hours, after which the mass is replaced with a new one.
Prevention measures
To prevent the appearance of pyoderma, doctors recommend the following protective and preventive measures:
- compliance with general hygiene regime and personal hygiene rules;
- sports and physical activity;
- nutritious, regular meals high in vegetables and fruits;
- mandatory treatment of even minor injuries to the skin surface with antibacterial solutions;
- timely contact with a specialist and professional treatment;
- isolation from the group of persons affected by pyoderma until their complete recovery;
- sanitization of foci of chronic infection of the pharynx and nasopharynx;
- vitamin therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation.
Get well!
Effective and simple
Above you can see aloe (there is a photo in the material). For symptoms of pyoderma, treatment using this plant is possible in the form of a tincture. Every day, the affected areas are wiped with the medicine. Aloe shows the greatest effectiveness in the presence of suppuration.
Viburnum juice is mixed with water (a couple of tablespoons per glass), and the prepared mixture is wiped over the affected areas. Another option for external use is an infusion of dill seeds (pre-crushed). For a glass of water - a tablespoon of the product. Dill is poured with boiling water and left for 10 minutes.
It is believed that a mixture of strawberry, walnut, and violet leaves will be beneficial. A sequence is added to the composition. An infusion is prepared taking into account the following proportions: per liter of water - 50 g of a mixture of herbs. Pour boiling water over the dry product, leave for half an hour, strain off the liquid and use it as food. Single dose – half a glass, frequency – up to six times a day.
For a glass of boiling water, take a tablespoon of a mixture of equal amounts of burdock, elecampane, and walnut (leaf). Boil everything together for 10 minutes, then drain the liquid and use it for food. Dosage – glass. Three-hour intervals should be maintained between doses.
For a couple of glasses of carefully ground poplar buds, take half a glass of vegetable oil, let it brew for a day, boil over low heat, wait for it to cool. The finished product is used on the affected areas, lubricating the skin with it.
A good local treatment option is a mixture of wax, spruce resin, and butter. The components are taken in equal volumes and the mixture is applied to the affected area.
Finally, traditional healers may recommend alcohol with garlic. The products are taken in equal quantities, the root crop is crushed into a pulp. The medicine is used for local treatment of festering areas; three layers of gauze are applied on top and secured with a bandage. The drug will dry out the skin, open pores, and prevent the proliferation of pathological microorganisms. The dressing is changed three times daily. The medicine is used until complete recovery is achieved.
Treatment of deep pyoderma
In surgery there is a rule: “If there is pus, it should be removed.” Therefore, if signs of accumulation of even a small amount of pus appear, this is an indication for its evacuation by surgical method. Previously made attempts to puncture ulcers and suction the pus turned out to be ineffective - the purulent cavity must be wide open for adequate outflow of pathological contents.
Strictly prohibited:
- open areas of pus yourself - such manipulation should be carried out by a surgeon in a clinic or surgical hospital;
- warming the foci of suppuration - this can be fraught with a wider spread of the pathological process.
Surgical intervention can be of different volumes depending on the size of the purulent focus, but the following manipulations are often performed:
- opening of a purulent focus. At the same time, one should always remember about the presence of possible “pockets” and purulent leaks, so the opening should be wide if necessary;
- sanitation (cleaning) of a purulent focus by washing with antiseptic solutions;
- drainage with rubber drains (narrow long strips), and when opening large purulent foci - with thin polyvinyl chloride tubes. The end of the outlets or tubes is inserted into the cavity of the abscess, the other is brought out to remove the residual purulent contents and rinsing waters;
- applying a bandage with a hypertonic solution.
The postoperative wound is not sutured.
At the same time, conservative therapy is used. It is based on the following purposes:
antibacterial drugs. First, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used, then, when the results of bacteriological culture are ready, antibacterial drugs are prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to them;
- painkillers;
- dressings. Until the postoperative wound is completely cleansed, local antiseptic drugs are used, followed by regenerating agents that accelerate the overgrowth of the cavity of the former abscess with granulation tissue:
- staphylococcal toxoid, antistaphylococcal hyperimmune plasma - in difficult cases.
An integrated approach is the key to success
Unfortunately, there is no such unique recipe that would describe what is suitable for everyone (and even demonstrate it in the photo!) for the treatment of pyoderma. In adults and children, the disease is more often provoked by insufficiently responsible adherence to hygiene rules, but this factor is far from the only one. After analyzing the patient’s condition, the doctor will be able to understand what points need to be included in therapy. It can be:
- treatment of the underlying disease;
- exclusion of aggressive factors that depress the health of the skin;
- prescribing a specific diet;
- ban on certain procedures;
- taking medications;
- hygienic and sanitary measures for treating inflammation.
Quite often, pyoderma is observed due to hormonal imbalance, endocrine disorders and improper metabolism, low immunity. In these cases, it is indicated to begin treatment of the main disease, while simultaneously using drugs to alleviate the symptoms of pyoderma. By eliminating or smoothing out the effect on the body of the main problem, you can get rid of skin rashes.
Sometimes pyoderma is provoked by:
- overheat;
- hypothermia;
- dirt;
- chemical substances;
- wounds.
Treatment of the disease involves eliminating all these factors, otherwise no course, even the most powerful drugs, will produce results.
During therapy, it is necessary to eat protein foods, avoiding carbohydrates. Fermented milk products and fiber-rich vegetables and fruits are shown. To relieve local manifestations of pyoderma, the affected areas are washed twice daily with salicylic alcohol.
Symptoms
The symptoms and treatment of pyoderma are described in detail on numerous online portals dedicated to skin diseases. To recognize the diagnosis, you need to know how the disease manifests itself in the affected body.
Pyoderma may be accompanied by itching and rashes.
Symptoms are represented by the following conditions:
- the appearance of a skin rash;
- feeling of itching and discomfort;
- purulent discharge from the center of neoplasms;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- increased swelling;
- boils, folliculitis, carbuncles, sycosis.
Pyoderma itches, so the symptoms negatively affect the state of the nervous system, provoke increased nervousness, aggression, emotional decline, and depression. If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic, where periodic attacks alternate with periods of remission.
Treatment nuances
If pyoderma is accompanied by inflammation of the follicles, phlyctenas, ostiofolliculitis, the patient is indicated for the procedure of opening purulent formations. It is carried out strictly under sterile conditions using a special needle, after which the surfaces are carefully treated with brilliant green. If pyoderma develops in the form of sycosis, the mustache and beard can only be removed strictly by hand.
Staphyloderma requires the use of ichthyol. The drug is applied to ripening ulcers, and after opening them, bandages with a special medicinal solution are used (at the doctor’s choice). When the pus has gone, you can use antibiotics in the form of an ointment. For impetigo, the resulting crusts are treated with fucorcin and the course is supplemented with antimicrobial drugs. Syntomycin emulsion and:
- "Levosin".
- "Levomekol".
Sometimes patients are prescribed antimicrobial drugs with systemic effects. Indications for such therapy will be:
- heat;
- intoxication;
- large areas of infection;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- lymphangitis;
- purulent inflammation on the face.
The most widely used drugs are from the penicillin series - Amoxiclav and its analogues, as well as drugs containing erythromycin and chloramphenicol. To increase effectiveness, the patient is prescribed multivitamin complexes and immunostimulants. If pyoderma is very severe, staphylococcal toxoid is taken.
Complications
With P., allergic rashes (syn. pyoallergides) occur, more often after irritating local therapy of primary foci of P. (impetigo, boil, hidradenitis, chronic, deep P., etc.) or after the administration of immune drugs (vaccines, staphylococcal toxoid, etc. ). Pyoallergides can manifest as lichenoid, pustular, erythematous, erythematosquamous, eczematous, polymorphic rashes. They appear suddenly, sometimes accompanied by malaise, headache, fever and other general symptoms. Specific allergic skin reactions (see Skin tests) in the presence of pyoallergides are sharply positive.
Pyococci are not cultured from the blood and for the most part are not found in pyoallergides. In immunobiological terms, pyoallergides are the opposite of the so-called. pyemids, or pyemic dermatoses, which are rashes that occur hematogenously with staphylococcal or streptococcal sepsis, usually accompanied by anergy. Pyemids, especially staphylococcal ones, are characterized by true polymorphic rashes with a pustular component (spots, nodules, blisters, superficial and deep pustules, flat infiltrates, etc.); Pyococci are cultured from the blood. Piemida indicate a severe course of the pyococcal process.
Factors and methods
The optimal course of treatment is chosen taking into account not only the form of the disease, but also the age of the patient. It's hardest for little kids. The localized form is usually eliminated at home, but strictly following the doctor’s recommendations. To monitor your recovery, you will definitely need to visit a doctor.
When pyoderma occurs in a newborn, foci of inflammation are treated with antiseptics and antibiotics. They use alcohol, aniline preparations, calendula in the form of a tincture (sold in any pharmacy), and salicylic acid. If the areas are itchy and swollen, the child is given antihistamines. A specific option is chosen based on the acceptability of its use by young children. Precise instructions on age restrictions are in the instructions for use.
If the baby has several foci of inflammation at the same time, use ointments with antimicrobial components (tetracycline, metronidazole, erythromycin). For boils that appear in small numbers, at a distance from each other, Vishnevsky ointment and other drugs that are effective for foci of suppuration are indicated.
It is unacceptable to squeeze out the contents of the abscess yourself. This is especially dangerous if pyoderma appears on the face. There is a high probability of blood poisoning, meningitis, in which the membranes of the brain become inflamed. If you start a therapeutic course, the boil will gradually go away on its own.
Causes of pyoderma
Provoking factors for the development of pyoderma are overheating or cooling, high air humidity, contamination of the skin surface, overwork, stressful conditions, damage to the skin of varying severity, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and metabolism.
With pyoderma, the sweat and sebaceous glands and hair follicles are most often affected, but deeper penetration of the infection also occurs, in which boils with one purulent rod or carbuncles with two or more rods develop.
Pyoderma can be acute or chronic; the nature of the disease and its severity depend on the general condition of the body, the depth of the inflammation, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases.
Hard case
If the patient's condition is poor, infusions (intravenous fluids) are indicated. Solutions with salts and glucose are used, including polygyukin, reopoligyukin. The specific choice remains with the doctor.
You can choose the most successful antibiotic if you first check the sensitivity of the microflora to different substances. Based on this, a decision is made in favor of cephalosporin, penicillin, macrolides, fluoroquinolones or other groups. There are known cases where pyoderma was provoked by pathological microscopic life forms that are resistant to most known modern drugs.
In this case, the doctor prescribes combined drugs and regularly checks the effectiveness of the course.
Most often, pyoderma is caused by staphylococci, which means that it is the drugs developed against these pathogenic microorganisms that will show the best effect. Modern patients have access to:
- antistaphylococcal plasma;
- gamma globulin.
With the help of such substances, artificial resistance of the body to the pathogen is formed.
To increase the body's defenses, the patient is prescribed:
- phototherapy;
- autohemotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
There may be situations when surgery to remove a purulent formation is indicated. This is more typical in cases where a doctor diagnoses hidradenitis, furunculosis, and carbuncles.
Diagnosis of pyoderma
Laboratory tests involve conducting general blood and urine tests, and studying reactions to syphilis. To identify the causative agent of pyoderma and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics, the purulent contents of the pustules are examined.
Histological and immunological studies are recommended. If necessary, a consultation with an endocrinologist and neurologist is scheduled. Doctors of narrow specializations can send for hormonal testing and identify a hidden form of diabetes. The help of an immunologist is required if staphylococcal pyoderma is not treatable and the level of immunity needs to be established.
For a more accurate diagnosis, differential diagnosis is often necessary. The symptoms of furunculosis are similar to the symptoms of hidradenitis and carbuncle. Folliculitis can be confused with acne, lichen planus, hidradenitis, or ingrown hairs.
Chronic ulcerative pyoderma should be distinguished from iodo- and bromoderma. Sycosis is similar in appearance to trichophytosis, but with the latter the symptoms are more pronounced. There is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, and scarring of the skin appears.
Pyoderma on the face
The peculiarity of this localization is the difficulty of combating it, the increased risk of infection by pathological microflora of internal systems and vital organs. Medical statistics show that pyoderma more often appears on the face in young women. The disease comes unpredictably and progresses rapidly. Most often the rashes are localized to:
- temples;
- forehead;
- chin.
Rarely, other parts may be affected.
The affected areas of the skin first become red and swollen, and after a couple of days numerous pustules appear here. Skin pathology brings a lot of unpleasant sensations and impressions, your health worsens, and sleep is disturbed. Patients are apathetic and have no appetite. In some cases, pyoderma can be cured within a month, but there are also difficult situations when the course lasts for a year. For therapy, hormonal ointments and creams that control inflammatory processes are usually used.
Diagnostics
It is not difficult to diagnose different forms of deep pyoderma - this is done on the basis of the patient’s complaints, medical history, and examination data. But it is also important to clarify the details - in particular, to determine the type of pathogen that provoked the development of the purulent process.
Physical examination reveals:
- upon examination - swelling of the tissues, redness of the skin over the purulent focus;
- on palpation (palpation) – pain, swelling, increased local temperature.
Of the instrumental research methods in the diagnosis of deep pyoderma, the following are used:
- puncture - puncture of a purulent focus with suction of purulent contents, which are then examined under a microscope;
- biopsy - collection of fragments of the wound surface with subsequent examination under a microscope. It will be required to assess the condition of tissues in suspicious cases - for example, if they have an atypical appearance, the walls of an ulcer are too dense, healing after cleansing of pus, and so on;
- revision using a surgical probe - if a deep “crater” has formed due to pus formation, then its characteristics are studied using a surgical probe. Also, using a probe, you can feel the bottom of the ulcer.
If there is a suspicion of the formation of metastatic purulent foci, then the following can be used:
- ultrasound examination of soft tissues;
- X-ray examination of the chest organs;
- X-ray examination of the abdominal organs;
- computed tomography (CT) is the most informative for the analysis of hard tissues, therefore it is used when bone damage is suspected (in particular, osteomyelitis - purulent melting of bone tissue with the formation of fistulas);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most informative when studying soft tissues.
Laboratory research methods that are used are:
general blood test - an increase in ESR and the number of leukocytes (leukocytosis) is detected with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, which indicates an inflammatory process;
- blood culture for sterility - performed with the progression of any form of deep pyoderma, when there is a suspicion of the development of sepsis. Normally, human blood is sterile;
- bacterioscopic examination - the punctate is examined under a microscope, the pathogen is identified in it. A large number of leukocytes are also detected, sometimes erythrocytes;
- bacteriological examination - the punctate is inoculated on nutrient media, the colonies are expected to grow for several days, and the type of pathogen is determined based on their characteristics. Most often, staphylococci or streptococci are detected, often mixed microflora. This diagnostic method is also used to determine the sensitivity of an infectious agent to antibiotics, which is important for subsequent medical prescriptions;
- histological examination - the histological (tissue) structure of the biopsy is studied under a microscope. This, first of all, is important for confirming or denying the diagnosis of malignant pathology - a number of such neoplasms can manifest themselves in the form of an ulcer, which can also fester when a secondary infection is attached.
Forecast
The prognosis for deep pyoderma is generally favorable - modern surgery has learned to treat it well.
The prognosis worsens in weakened patients with a reduced level of immunity, since in a fairly short period of time severe complications may develop that can lead to death.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
5, total, today
( 56 votes, average: 4.27 out of 5)
Rectal bleeding: causes, symptoms, treatment
Retropharyngeal abscess: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment