A pinched nerve in the cervical spine develops when the nerve roots originating in the spinal cord are pinched by other structures - various pathological neoplasms or muscle fibers, vertebrae and discs. Doctors call this process cervical radiculopathy. This pathology is considered very common, and the intensity of pain is many times stronger than with a similar problem in the lower parts of the spinal column.
Features of the structure of the cervical spine
The canal of the cervical spine contains a large number of blood vessels, including the vertebral arteries, through which the brain is nourished. The structure of the cervical spine is quite complex - this section is very mobile, and the muscular-ligamentous apparatus is relatively weak, which makes this section highly vulnerable. The cervical vertebrae have layers of intervertebral discs and are located in close proximity to each other. When the shock-absorbing ability of the cervical intervertebral discs is impaired, the cervical nerve is pinched, which causes unbearable pain and the possibility of motor activity in the pinched area is sharply reduced.
Possible causes of pinching
There are many reasons that can provoke radiculopathy. The main disease that leads to this phenomenon is considered to be cervical osteochondrosis; in addition, the disease can occur when there is a spasm of the back muscles in the cervical region.
Pathology can also be caused by:
- the presence of hernial formations or protrusions,
- injuries,
- long-term loads,
- development of malignant tumors,
- displacement of the vertebrae,
- a sharp and incorrect turn of the head,
- diseases of the myendocrine system,
- a sedentary lifestyle, which results in the development of pathological muscle weakness,
- frequent hypothermia,
- heredity.
Reference! A predisposition to radiculopathy can begin to develop in utero - in cases where the formation of the skeleton occurs incorrectly, or during pathological childbirth.
Causes
The main causative factor during which a pinched nerve in the spine manifests itself is a high level of load with progressive osteochondrosis. But there are also several other reasons.
- Excessive physical work, represented by a complex of repetitive movements performed primarily by the arms and torso.
- Poor posture is a common cause of pinched nerves.
- Inflammation of the joints.
- Carrying a child (weight gain, which leads to changes in the skeleton).
- The presence of growths on the vertebrae due to underlying diseases.
- Genetic predisposition to nerve entrapment.
- Excess body weight, which creates a high load on the vertebrae.
Note that pinching of the spinal nerve is the result of the influence of numerous factors. To avoid complications, it is important to determine the nature of the disease and undergo a course of therapy.
Symptoms and manifestations of the disease
Symptoms of pathology are directly related to which particular area is affected. In this case, the pain symptom can be observed not only in the neck, but also in the arm.
Signs of the disease may be as follows:
- When you move your neck suddenly and stand up, you feel dizzy,
- headache with throbbing, which originates in the occipital region,
- hands, and especially fingertips, feel numb or tingling,
- severe cutting pain in the cervical region, which radiates to the shoulders and shoulder blades,
- attention and memory become worse,
- decreased hand functionality,
- minor paralysis of the neck and arms,
- with significant pathology, facial paralysis may be observed, as well as impaired speech function, and swelling of the oral mucosa is possible.
If the nerve is pinched very strongly and the arteries are involved in the process, the clinical picture will be very clear. The patient may feel nauseous and in some cases cannot even get out of bed.
Important! Pinching of the trigeminal nerve and artery can cause a serious illness - ischemic stroke.
Occipital neuralgia of the cervical region is characterized by pain in the back of the head, which is often observed on one side. The pain resembles an electric shock or lumbago; such attacks can last from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, and can be repeated several times a day. In addition, occipital neuralgia of the neck is characterized by the presence of pain points, the touch of which causes severe pain.
Inflammation of the cervical nerve also manifests itself as severe pain, numbness, muscle atrophy and movement disorders. Neuritis has similar symptoms to tumor processes, cerebrovascular accidents and other ailments, so differential diagnosis is required.
How does the treatment work?
Through various types of diagnostics, from manual to hardware, the doctor determines the main symptoms, after which treatment begins. It must be systematic and largely conservative. In exceptional cases, a pinched nerve by the piriformis muscle is a consequence of some disease, the treatment of which is impossible without surgery.
Main directions:
- medications - analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants to relax muscle tissue; those. drugs that improve blood circulation, restore innervation and reduce pain and inflammation; in some cases, it is possible to block the affected area with an anesthetic;
- manual therapy (individual approach required);
- physiotherapy - magnetic laser therapy, electrophoresis;
- reflex methods - acupuncture, pharmacopuncture, etc.;
- massotherapy;
- exercises.
Most often, the techniques are used only in combination, and a certain combination of them will give the best effect. To achieve success in therapy, it is necessary that the doctor decides to use certain methods.
As for the exercises, it is important to strictly perform exactly those prescribed by the specialist, taking into account individual characteristics - this will help to quickly relieve pain and tension, and restore motor activity.
If left untreated, a pinched sciatic nerve can lead to complications. Ligaments and joints degrade, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs and limbs occurs. It is important to be attentive to your health: this will save time and money.
At the first signs resembling those described, you need to hurry up and visit a doctor. In addition, we recommend avoiding hypothermia, leading an active lifestyle, but at the same time not giving yourself too much or especially unusual stress.
Additional useful information:
- My free books, videos and master classes
- My exercise programs and video courses
- My printed books (available in major online stores)
- Free online marathon “How to save your face from old age”
See more useful materials on my social networks:
YouTube | VKontakte | Yandex.Zen | Instagram | Telegram | Facebook
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
I will be very grateful if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends 
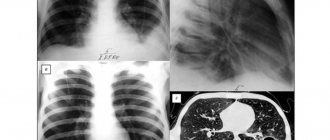
Diagnostic methods
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must question the patient in detail about all disturbing symptoms, examine the affected area and assess neurological functions. Then assign the following research methods:
- x-ray of the spinal column,
- MRI, CT,
- electromyography,
- clinical blood and urine tests.
How to treat pinching
How to treat pinching should be determined by a competent specialist; therapeutic tactics directly depend on the form of the disease, the presence of concomitant diseases, the patient’s age and other factors.
Medicines
The basis of medication treatment is tablets or injections, which have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Most often prescribed:
- Diclofenac,
- Ketanov,
- Baralgin,
- Indomethacin ointment,
- Piroxicam.
In addition, the doctor prescribes vitamins, local painkillers (Fastum gel), and drugs with a sedative effect (motherwort, Novo-Passit) are prescribed to improve the quality of sleep.
After the acute course of the disease has been stopped, chondroprotectors (Chondroxit, Theraflex) are prescribed, which are necessary for the regeneration of cartilage tissue. The disease is usually treated at home; hospitalization is indicated in especially severe cases.
Manual therapy
This treatment is aimed at eliminating increased pressure on the pinched nerve, releasing it and restoring motor activity in the affected area of the spine. Manual therapy also helps eliminate muscle spasms. In some cases, such therapy is prescribed until the patient has fully recovered, and the goal is to manually release the nerve. Spinal traction is performed very rarely; soft techniques are most often used. Manual therapy is not recommended if the cause of the disease is disc destruction or in the presence of an intervertebral hernia.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures help to cope with different types of pathological process, they strengthen the muscle frame and the pressure on the nerve is reduced. Such procedures are prescribed for the following purposes:
- elimination of puffiness,
- relief of pain syndrome,
- warming up,
- improve blood circulation.
Acupuncture
Using this technique you can achieve:
- anti-inflammatory effect,
- improving blood movement through blood vessels,
- eliminating muscle spasm,
- calming effect
- regeneration of cartilage tissue.
The advantage of this technique is a significant reduction in the amount of medications used.
Massage and exercise therapy
Massage is prescribed in almost all cases; it significantly reduces muscle spasms, improves metabolic processes, and restores blood circulation. Once muscle pressure on the nerve is relieved, the level of nerve entrapment is reduced.
It is very effective to combine massage with physical therapy. Exercises that strengthen the muscle frame are shown. A properly selected set of exercises for the neck, sternum and lumbar region significantly improves the condition of the spine, and, therefore, the load is distributed correctly and the nerve is released.
Operating method
If all the treatment described above does not produce a positive effect, doctors may suggest surgery. However, this is an extreme measure, and the decision on the advisability of the operation depends on the following circumstances:
- general condition of the patient,
- the presence of concomitant ailments,
- patient's age,
- the cause that led to the pinched nerve.
The postoperative period most often takes about 2 months.
Self-treatment
It is advisable that all therapeutic measures are prescribed and carried out by competent specialists; to relieve pain, the patient can independently do gymnastic exercises, carry out warm wax applications, and make a classic mass using anesthetic ointments. The use of traditional medicine is allowed.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine in its arsenal has a large number of different remedies that are used in the presence of pinching. For example, the following:
- To eliminate pain and reduce muscle tension, you can prepare and use an ointment. You need to take 1 part juniper and 6 parts bay leaf. Grind the ingredients into powder and mix with butter.
- To reduce pain, you can combine 15 grams of cream or any other fat with conifer cones, and rub the resulting product into the affected area every 4 hours.
- To prepare an anesthetic, you can pour a handful of lilac (flowers) into half a liter of vodka and leave for 7 days. The resulting product is used to wipe the painful points.
- If there are no contraindications, you can take a medicinal bath - take 250 grams of calamus per 3 liters of water and boil for half an hour. Then pour the broth into the bath and add water. In addition to calamus, you can use oak bark, chestnut, sage, chamomile and other medicinal plants.
How to determine?
A medical examination is necessary so that proper treatment of a pinched nerve can be carried out subsequently. The doctor prescribes an examination to determine the nature of the disease, causes and characteristics. It includes a set of activities:
- UAC;
- CT;
- MRI;
- manual type research;
- electrical conductivity test;
- performing x-rays.
The resulting images will help determine the current state of the spine and whether other diseases are present in the skeleton and muscle structures. After the results of the pathology are summed up, treatment for a pinched nerve is prescribed.
Prevention
Instead of treating a pinched nerve, it is much easier to carry out preventive measures that will prevent the development of this pathology:
- when working at a computer for a long time or when sitting for a long time, you need to periodically stretch your neck,
- It is recommended to sleep on special pillows and an orthopedic mattress,
- regularly do exercises that will strengthen the neck muscles,
- monitor your gait and body position,
- do not lift heavy objects and do not overload the body,
- engage in swimming or yoga - these activities will not only help prevent the pathology discussed, but will also help protect against many other diseases.
Radiculopathy of the cervical spine is not only very painful, but also quite dangerous. The canal of the cervical spine contains large blood arteries that supply the brain with oxygen; as a result of pinching, brain starvation can develop, entailing quite serious and sometimes irreversible consequences. Therefore, a pinched nerve should be taken seriously and this pathology should be carefully treated.
Signs and symptoms of a pinched nerve
- tingling;
- burning;
- lack of sensitivity;
- pain;
- muscle weakness.
Symptoms may be worse when the person lies down or immediately after waking up. A pinched nerve can cause other problems. Symptoms of conditions such as sciatica, tennis elbow, and carpal tunnel syndrome may occur in people with a pinched nerve. Pinching can occur anywhere on the body, most commonly in the neck, back, elbows, and wrists.
There are several symptoms that require attention and consultation with a doctor:
if a pinched nerve affects the bladder;
inability to lift objects.