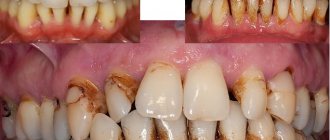
A jaw cyst is a benign formation when a sac of fibrous tissue is filled with fluid (exudate). Often, patients may perceive such a symptom as prolonged inflammation if it has already manifested itself. In most cases, this process is asymptomatic and manifests itself already at the stage of inflammation.
If the problem is ignored, this can lead to what is popularly called “flux” (ondontogenic periostitis), abscess or phlegmon. A jaw cyst is the first symptom of subsequent diseases. The “it will go away on its own” technique does not work in this case, and alternative treatment methods can only remove the symptoms, but not the cause of the tumor.
Causes
The tumor can be located on any part of the jaw. Often the patient considers it to be a short-term inflammation or accidental damage to the gums. In rare cases, this happens, and the small formation disappears after a few days. The problem is that a jaw cyst can form asymptomatically for an indefinite period of time.
Under the influence of internal or external factors, a “bubble” appears on the gum, which may not be painful, but causes stable discomfort. There are several reasons for this:
- Dental diseases of hard tissues. Even “classic” caries without treatment causes infection in the periodontium through the root canals. After this, infection and formation of a tumor occurs (this point can include medical errors, for example, during filling caries canals).
- Inflammation of nearby organs. Sinusitis, stomatitis, periodontitis and other diseases can cause infection to enter the general bloodstream. Next, the bone tissue is affected.
- Traumatic injuries. This type is considered by experts to be the most “unsuccessful”, since the development of a cyst cannot be diagnosed from the very beginning. A bruise, a fracture, a bottle opened with teeth, a chewed nut with weak teeth can provoke the appearance of a cyst.
- Teething. It is worth noting here that this is typical not only for young children who are cutting their milk and permanent teeth, but also for older people - as you know, a wisdom tooth can begin to grow when a person is already quite old.
- A rare factor is congenital anomalies in the development of the jaw and the formation of teeth. Typically, such cases are detected in childhood during preventive examinations by a pediatrician or otolaryngologist.
The proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms is often activated due to poor oral hygiene. In addition, a significantly weakened human immune system is a serious risk factor.
Treatment of follicular cyst of the jaw
The only treatment is surgical - cystectomy and removal of the impacted tooth.
With extensive cysts of the lower jaw, a pathological fracture is possible, so a fixing splint should be applied to the teeth as a preventive measure. Fixation can be carried out either with metal splints made of aluminum or steel wire, or with mouthguards made of quickly hardening plastic using the Frihof method. The article was prepared and edited by: surgeon
Video:
Healthy:
Related articles:
- An omental cyst occurs either as a result of blockage of the lymphatic ducts, or as a result of the proliferation of a detached rudiment of the lymphatic...
- Fibrous dysplasia of the jaw (Braitsev-Lichtenstein disease) occurs mainly in childhood in the form of...
- An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled bubble, ranging in size from a couple of millimeters to ten centimeters (benign…
A large cyst can disrupt the oval of the face, protruding from the side of its location. Particularly dangerous are cysts of the upper jaw, which increase towards the maxillary sinus without showing external signs. The growth of the cyst is always slow, the initial stage is latent without clinical signs. A cystic formation can become an accidental discovery during a routine visit to the dentist, but in 85-90% of cases the cyst is detected during an exacerbation, when it manifests itself as suppuration and severely deforms the jaw. Dentists consider pathological jaw fractures caused by thinning bone tissue to be the most difficult cases. Another serious complication is the growth of a large cyst into the nasal cavity and even into the orbital area.
A jaw cyst can be of two types - odontogenic or non-odontogenic.
An odontogenic cyst is a direct consequence of a chronic advanced inflammatory process in periodontal tissues. An odontogenic cyst can cause symptoms of general intoxication, since for a long time the neoplasm releases decay products of pathogenic microorganisms into the body. Intoxication is manifested by elevated body temperature and transient dull headaches. Suppuration of the cyst is expressed in severe swelling of the jaw tissue, throbbing pain, and asymmetrically swollen face. Odontogenic cysts are divided into the following types:
- Keratocyst.
- Follicular cyst.
- Radicular cyst.
- Root cyst.
Among all types, only radicular and root cysts can be considered purely bone cysts.
- Radicular cyst is diagnosed most often; according to statistics, this type of cyst is detected in 55-60% of patients with characteristic clinical signs of benign tumors of the jaw skeletal system. The cyst develops in the focus of chronic inflammation - periodontitis, often its beginning is a granuloma. The favorite location of a radicular cyst is the maxillary bone. Cysts in this zone can reach 3-4 centimeters, they tend to hyperplasia in the form of processes towards the wall of the cavity, and radical cysts quite often suppurate, while the inflammatory process engulfs the maxillary cavity, provoking odontogenic sinusitis. A large cyst grows slowly, chronically destroying the jaw bone and thinning its cortical layer. In 3-5%, radical odontogenic cysts of the jaw are capable of malignancy.
- A root odontogenic cyst also forms as a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process. It grows very slowly and puts pressure on the tissue of the jawbone, which shifts compensatoryly, thereby disrupting the normal functions of the dentofacial apparatus. Root cysts are characterized by spontaneous pathological fractures of the jaw; osteomyelitis or a malignant tumor of the jaw can become a serious complication of the development of the cyst.
All information presented is for informational purposes only, since only a specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment through a visual examination. Dental medications do not have a significant effect on the functioning of the body, have virtually no contraindications and do not cause adaptability (addiction). The information presented on our website is intended to provide information about medications. Selection and appointment should be carried out by a specialist. Self-medication can be harmful to your health. In our directory you will find all the most common diseases of the oral cavity - caries, pulpitis, gumboil, stomatitis, periodontal disease, fistula, periodontitis, etc. As well as medications: analgesics, antimicrobial agents, antipyretic medications, local anesthetics, astringent gels, means for fixing dentures .
Specialists at the City Dental Center clinic will tell you about the features of such a cyst as a follicular dental cyst. Such a cyst arises from dental tissue, called a tooth germ, that erupts and turns into a tooth.
The causes of follicular dental cysts are pathological processes that appear during the development of molars.
This type of tooth cyst is usually located near the crown of a tooth that has not erupted. A follicular cyst of a tooth wraps around its crown so that it ends up in the cyst cavity. Most often, such a cyst appears in people in childhood, when molars begin to erupt.
This disease is quite insidious and dangerous, as it has a hidden, invisible period of formation and growth. At the very first stages, a follicular dental cyst is not detected in any way, the disease is asymptomatic. Already at later stages of development, when the cyst greatly increases in size, obvious symptoms of the disease appear. Such a cyst is dangerous because its increase in size directly affects the dentition, its shape, and neighboring teeth.
Varieties
A jaw cyst always looks like a small sac filled with fluid. In the cavity of such a cyst, the collected fluid can be cloudy or transparent. But still, there is a certain classification of such formations, dividing odontogenic cysts into types:
- Primodial (keratocysts). In most cases, they form on the gums in places where wisdom teeth erupt. Such a cyst may have one or more chambers. The bag is filled with a mixture of keratin, crystals and dead cells.
- Follicular cyst. This pouch usually forms on the lower jaw, and usually appears when the process of teething is disrupted. Inside such a cyst there is a follicle from which a full-fledged tooth can be formed.
- Radicular. The most common type of cyst. It appears most often after unsuccessful dental treatment, as well as after chronic periodontitis as a complication of the disease. It is localized in the upper jaw and reaches 2 cm in size.
- Residual. It forms in the patient both on the upper and lower jaw, and usually forms in places where teeth have been removed. Inside this new growth is the remaining tooth root that was previously removed.
There are also rarer variants of formation types. For example, aneurysmal. However, in practice they are extremely rare in people, and the reasons for this phenomenon have not yet been studied. There may be blood or hemorrhagic fluid inside an aneurysmal cyst.
Symptoms
The development of a jaw cyst is difficult to miss, since the disease has a number of obvious and pronounced signs. Of course, the disease may have no symptoms for a long time, but eventually the situation will worsen and inflammation will make itself felt. Symptoms will appear primarily due to the following factors:
- severe pain in the area where the pouch forms;
- a significant increase in human body temperature;
- the appearance of varying degrees of deformation changes in the jaw bones;
- purulent discharge from a cystic formation;
- swelling and hypermia of the gums in the patient’s mouth;
- symptoms very similar to sinusitis;
- dizziness and noticeable chills;
- swelling of the lower or upper jaws.
At the first symptoms of inflammation and the formation of any cyst on the gums, the patient must immediately and promptly consult a doctor for emergency medical care. After consultation with a doctor, a program for diagnosing the disease, as well as subsequent treatment, will be determined.
Forecast
The prognosis for jaw cysts is generally favorable - malignancy occurs rarely, and purulent-inflammatory complications are successfully treated with surgical intervention.
The prognosis may worsen under circumstances such as:
- late presentation of the patient to the clinic with signs of inflammation and suppuration;
- self-medication - heat exposure and so on.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
1, total, today
( 63 votes, average: 4.05 out of 5)
Cholisal while breastfeeding: is it possible or not?
Stomatitis in adults - types, symptoms and treatment methods
Related Posts
Maxillary cyst
Cysts of the upper jaw are also called odontogenic, and they form specifically on the upper jaw. A radicular cyst forms near the incisors in the upper jaw, and can sometimes be located in the area of the lateral teeth. In this case, a characteristic pain appears when biting.
Residual cyst. It can form after tooth extraction with difficult healing of the hole. Such a cyst is visible as a darkening in the bone on X-ray images. In this case, after removal of the cyst, curettage of the tooth socket will also be required to cleanse the tissues of the remnants of the contents of the removed formation.
Follicular. This is the flattest cyst, and its peculiarity lies in the likelihood of losing the germ of a permanent tooth. These are usually cysts that are located right next to the bud and lead to obvious problems with eruption.
Clinical picture
A minor radicular cyst most often does not cause the patient any discomfort or manifests itself with mild symptoms, which are often ignored.
During a dental examination, darkening of the molar or advanced caries is detected. When probing the root canals, a person does not feel pain, but a yellowish liquid is released.
As the formation increases, nearby teeth are displaced, the alveolar process is destroyed, and palpation of the affected area causes a “parchment crunch.” A third of patients with root cysts suffer from facial deformity. Large cavities destroy bone tissue and cause jaw fractures.
On this topic
- Oral cavity
Laser removal of dental cyst
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 5, 2020
Suppuration of the capsule develops after mechanical trauma to a molar, unsuccessful dental manipulation, or sinusitis. First of all, the walls of the cavity become inflamed, after which the infection penetrates into the liquid and the contents become purulent.
During this process, the patient suffers from pain in the affected molar, increased body temperature, chills, deterioration of the general condition, hyperemia and swelling of adjacent tissues.
Mandibular cyst
In the lower jaw, a cyst usually does not have pronounced symptoms, and a full examination will be required to detect it. However, in the lower jaw there is a small hole between the fifth and fourth teeth, and with the active development of a jaw cyst, there is a high probability of damage to the nerve that exits in this hole.
If the nerve in the lower jaw is affected by a cyst, the patient will experience very severe pain that spreads to half of the face. This disease is characterized by swelling of the lower part of the jaw and redness, as well as the development of complications in the form of osteomyelitis and fistula. The types of cysts are the same as for the upper jaw.
Hidden and obvious dangers
Even with treatment, there is no guarantee that the cyst will not reappear. But this does not mean that there is no point in dealing with this problem: if the necessary therapeutic measures are not carried out in a timely manner, there is a significant risk of suppuration and subsequent penetration of purulent masses into the blood, which is fraught with the development of sepsis.
In addition, a benign neoplasm can transform into malignant and provoke the development of cancer.
Another consequence of untreated cysts is loosening of teeth and their loss. This can only be corrected in the future with the help of prosthetics.
dentazone.ru
Treatment methods
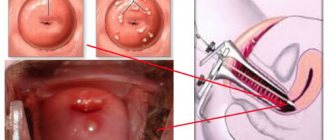
In modern medicine, cyst removal is performed only surgically. Cystotomy and cystectomy are usually used for these purposes. Cystectomy is used more often and consists of complete removal of the formation with closure of the defect after surgery. The indication for this procedure is the small size of the cyst and the location of the cyst in a place where there are no teeth.
Treating the problem with a cystotomy means creating an incision in the cyst, after which it is necessary to remove the flap and trephine the wall. The anterior wall of the cyst and periosteum should be excised using sharp scissors. Treatment involves emptying the cyst, after which the cavity is closed with tampons.
Full recovery is possible in 6-12 months, and in the first 2 months the patient will be forced to regularly undergo dressing changes. In addition, the oral cavity will need to be treated with antiseptic solutions, boiled water, sage and chamomile.
How is a follicular cyst treated?
- To begin with, specialists study the follicular dental cyst, after which they choose the method by which treatment will be performed. There are gradual treatment of the cyst and its immediate removal. Most often, the choice of method depends on the size of the follicular cyst of the tooth.
- If the cyst is large and contains fluid inside it, the dentist will first drain this fluid. He performs an operation: he makes an incision on the cyst, from which the cyst fluid will be removed using a special device. When the inflammation in the follicular dental cyst decreases, the size of the drainage tube is reduced. In order for the fluid to be drained well, it is necessary to visit the dentist as prescribed.
- In another case, the follicular cyst of the tooth is completely removed. This is done if further treatment is prevented by a tooth completely covered by cyst tissue.
Caries
In dentistry, diseases of the oral cavity, gums and teeth are distinguished. Despite the fact that dental diseases are non-fatal, their treatment and prevention should not be delayed, since dental health is an indicator of the health of the entire body. Dentists at the City Dental Center clinic recommend taking preventive measures at least once a year.
Complications and consequences
To understand the need for timely treatment, you need to understand why a jaw cyst is dangerous. The problem, which may not be noticeable at first, ultimately leads to the loss and fall out of healthy teeth. In addition, the formation of purulent foci, as well as sepsis, is possible. Inflammatory processes in the periosteum and bone tissue can also be observed. In some cases, phlegmon of the neck and face can be observed. But the most dangerous fact is that such a cyst can become a malignant formation in the human body.
Methods for diagnosing cystic neoplasms
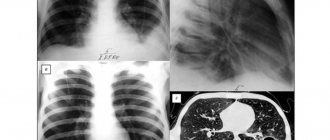
The main method used to detect a jaw cyst is x-ray. Images are taken in the frontal cavity and local ones, aimed at a specific tooth. The most informative is a panoramic photograph of the entire jaw. It helps the doctor more specifically determine the location of the cyst, its degree of growth, and possible impact on nearby teeth. The disadvantage of this study is the high radiation dose, so repeating the panoramic image more than once every 6 months is not recommended.
MRI as a diagnostic method
Without radiation exposure, a scanning method such as magnetic resonance imaging is performed. Thanks to the intrinsic magnetic moment of the nuclei, a high-quality image of the jaw is obtained in any planes and any layers. During scanning, drugs with ionized radiation are not used, however, it is necessary to remove all metal objects, since this study involves a very powerful magnet.
The method has some contraindications: it cannot be used if a person has a pacemaker or if the body contains implants made of metals that interact with a magnet - ferromagnets, such as iron. They also try not to prescribe MRI at any stage of pregnancy, especially in the early stages.
kistaplus.ru