What is arthrosis of the hip joint?
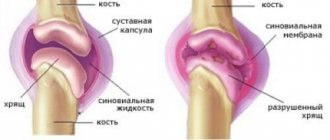
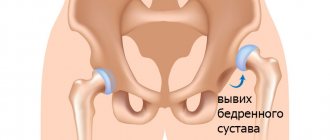
Arthrosis of the hip joint is a very complex disease in which the destruction of the hyaline cartilage that lines the surface of the femoral head (it has a spherical shape) and the acetabulum occurs. Arthrosis is a degenerative disease that most often develops in older people.
Specialized periodicals often publish the results of surveys and medical studies, according to which the female half of the population who have reached the age of 40 are most susceptible to arthrosis of the hip joint. This is primarily due to the anatomical features of the female hip joint, which has a different shape and position than in men. Such differences can be explained by the fact that the hip joint plays an important role in the process of childbirth. The bones of the female pelvis experience heavy stress every day, as a result of which they are more often susceptible to various diseases. Males at a later age (by the age of 60) may experience arthrosis.
According to available statistics, patients who have undergone surgical treatment for arthrosis of the hip joint may develop various complications:
- blood loss during surgery;
- thromboembolism (pulmonary artery) – 0.05% of cases;
- development of infection (after surgery) – 0.5%-2% of cases.
Most often, in this category of patients, infection occurs in the area of the endoprosthesis that performs the functions of the joint. In this case, doctors perform a second operation, during which the endoprosthesis is removed, and after that a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
During thrombolism, the patient experiences a blockage of the pulmonary artery. This type of complication is often fatal, especially for those patients who have a predisposition to blood clots. To prevent such a complication after surgery, patients are given special medications that reduce blood viscosity.
Severe bleeding during surgery is a common complication of surgical treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint. In modern medical centers there is a large supply of blood and its substitutes, thanks to which specialists can easily cope with this complication.
Causes of arthrosis of the hip joint
Modern medicine divides this disease into the following categories:
- Primary arthrosis develops for no apparent reason.
- Secondary arthrosis develops against the background of previous injuries to the hip joint.
To date, the following reasons for the development of arthrosis of the hip joint have been identified:
- depression, as well as prolonged exposure to stress;
- excess weight (even a slight gain of excess weight can cause the development of this disease, since additional stress will be placed on the joints);
- suffered injuries: sprains, bruises, blows, fractures, etc.;
- inflammatory processes;
- damage to cartilage tissue in the joint;
- diseases of the endocrine system (in particular diabetes mellitus) that have a negative impact on the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- poor heredity, against which a joint deformity may develop (a genetic predisposition to arthrosis is the most common cause of this disease);
- displacement or curvature of the femurs;
- hip dysplasia (most often diagnosed in newborns);
- protrusion of the acetabulum;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- changes in the structure of blood vessels;
- necrosis of the femoral head;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- high concentration of uric acid in the patient’s blood (determined by laboratory blood testing);
- gout, osteoradionecrosis, bone tuberculosis, Perthes disease, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in which the hip joint becomes infected with bacteria;
- degeneration of the synovial membrane of the joint into cartilage;
- poor circulation in the hip joint;
- various neoplasms;
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- severe physical stress exerted on the hip joint during sports;
- difficult working conditions;
- advanced age, etc.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint
With arthrosis of the hip joint, patients experience the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the area of the hip and knee joint, as well as in the groin (pain syndrome accompanies this disease constantly, and as arthrosis progresses, it can integrate into the area of the lower extremities);
- impaired motor function (due to excruciating pain, patients cannot move independently, which is why they are forced to use special devices: crutches, canes);
- shortening of the lower (arthrosis-affected) limb;
- crunching in the joint that occurs with any movement;
- lameness and gait disturbance;
- stiffness and limited movements of the limbs;
- When performing X-rays in this category of patients, atrophy of the muscle tissue located in the thigh area is revealed;
- during hardware diagnostics, bone growths may be detected in patients;
- at the 2nd stage of arthrosis, patients experience deformation and upward displacement of the head of the femoral bone (it significantly increases in size and acquires uneven outlines);
- with the 3rd degree of arthrosis in patients, the head of the femoral bone expands, as a result of which the joint space begins to narrow, etc.
Stages of development and course of deforming arthrosis
The first manifestation of the oncoming disease may be mild pain in the area of both joints. As a rule, such signs appear during moderate or heavy physical activity, for example, during long walking. At the same time, when walking a distance of more than two kilometers, lameness often appears in some cases. Symptoms also make themselves felt when climbing stairs. Pain and discomfort in the early stages disappear after rest. The patient may experience a decrease in joint mobility, at the first stage by about 10 degrees.
Later, at the second stage of development of the disease, the pain appears more often and intensifies, and it often radiates to the groin area or knees. The disease causes constant muscle tension, even when the person is not moving, which leads to around-the-clock pain in the hip joint. The distance traveled, after which pain is felt, is significantly reduced, and joint mobility decreases. To relieve symptoms, the patient begins to use a cane.
At the third stage, the pain becomes increasingly stronger and constantly torments the patient. His movement is significantly limited, possible only with the help of crutches for a short distance or a wheelchair. Muscles that are constantly under tension shorten, which leads to a visual decrease in the length of the limb, and disability occurs.
Degrees of arthrosis of the hip joint
Today, medicine knows three degrees of arthrosis of the hip joint. They are accompanied by certain symptoms and directly depend on the stage of the disease.
Signs characterizing arthrosis of the hip joint 1st degree
At the first stage of this disease, patients do not experience pronounced symptoms, as a result of which people rarely go to a medical facility.
With the development of arthrosis of the hip joint of the 1st degree, the following occurs:
- the liquid begins to lose its properties;
- the consistency of the liquid becomes more viscous;
- the fluid is not able to ensure unimpeded movement of the joint.
At the first stage of this disease, the structure of the cartilage tissue begins to deteriorate and microcracks form in it. Over time, as arthrosis progresses, thinning of the cartilage tissue is observed. In many patients, replacement processes begin to occur, against the background of which bone growths form at the location of the cartilage.
At the first stage, arthrosis of the hip joint is very easy to completely cure. The problem is that patients, due to late access to specialists, cannot receive medical care. That is why doctors strongly recommend that people who discover any of the symptoms of arthrosis immediately visit the nearest clinic and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
Signs characterizing arthrosis of the hip joint 2 degrees
Arthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree is accompanied by severe pain, which can be integrated from the hip and pelvis to the knee. At this stage of the disease, patients experience severe damage to cartilage tissue.
All damage can be seen using radiography:
- thinning of cartilage tissue;
- narrowing of the space between parts of the joint;
- changes in the structure of the femoral head;
- the appearance of various neoplasms;
- displacement of the head of the hip joint;
- the number of bone growths (osteophytes) increases.
When carrying out diagnostic measures in this category of patients, inflammation of the periosteum is detected. If this disease is not treated, patients will experience increased pain, motor functions will be impaired, and muscle tissue dystrophy will develop in the lower extremities. Such patients will experience unbearable pain, even while at rest.
Signs characterizing grade 3 arthrosis of the hip joint
During the transition of arthrosis of the hip joint to the third stage, patients experience:
- excruciating pain;
- almost complete destruction of hyaline cartilage tissue;
- impairment of motor functions (patients have limited movements);
- muscle tissue atrophy;
- change in gait;
- shortening of the lower limb;
- joint deformity;
- severe narrowing of the joint space;
- spread of bone formations (spike-shaped), etc.
At the 3rd stage, treatment of this disease is possible only surgically, since no medications can restore cartilage and restore mobility to a person. Currently, this category of patients undergoes sparing operations, during which the damaged hip joint is replaced with an artificial prosthesis. Thanks to endoprosthetics, patients, after undergoing long-term rehabilitation, can return to normal life.
Review of drugs
In most cases, with the first and second degrees of coxarthrosis, conservative treatment is possible. This method of therapy will allow the patient to get rid of the sensation of pain and improve mobility in the affected joint. In addition, medications will help prevent further destruction of joint cartilage, which will stop the progression of the disease.
The main group of drugs prescribed for the treatment of articular diseases of the joints are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), that is, non-hormonal drugs. Nowadays there is a huge selection of such drugs on the market, so your doctor can choose the optimal remedy. This group of drugs has a number of contraindications and restrictions, which is associated with a large number of side effects.
The most popular drugs from the NSAID group:
- Diclofenac, used since the 60s of the last century, is prescribed both in the form of tablets and injections, in addition, it is used in the form of an ointment or gel.
- Nimesulide - used in tablet form and in the form of powders for dilution.
- Ibuprofen is also a proven remedy over the years and is prescribed in the form of ointments, tablets or capsules.
- Meloxicam is a modern NSAID drug, on the basis of which ointments, injection forms and tablets have been developed.
In general, this group of drugs includes several dozen drugs, so your doctor can choose the best one. The effect of drugs from the NSAID group is enhanced by muscle relaxants, which can also be prescribed independently. Among the effective muscle relaxants are drugs such as Baclofen, Sirdalud, Mydocalm.
Sirdalud (505 rubles)
In case of severe pain syndrome, it may be necessary to prescribe hormonal drugs, cytostatics if coxarthrosis (osteoarthrosis) is associated with rheumatism. Vitamins play a significant role in the treatment of osteoarthritis. These include combination agents, chondroprotectors and other drugs.
Ointments
Medicinal ointments are used in the complex treatment of coxarthrosis in order to reduce the process of inflammation, relieve pain and other symptoms and speed up the healing process. The most effective ointments are considered to be those based on the active components of NSAIDs.
These ointments include:
- Butadin, which contains the active component Phenylbutazone from the NSAID group. It is used for most pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, including arthrosis, arthritis, pain syndrome from injuries. Apply 2-3 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
- Bystrum gel (analogues of Fastum-gel, Ketonal). The active ingredient is Ketoprofen. It relieves pain much more strongly than other NSAID drugs, but it cannot be used for a long time.
- Voltaren emulgel with Diclofenac as the active ingredient. The gel acts quickly and is convenient to use. Prescribed 3 to 4 times a day. Analogs are Diklak and Olfen ointments.
- Amelotex gel is considered a drug of the latest generation; it contains Meloxicam. Prescribed 2 times a day for up to 2 weeks.
To relieve symptoms, other ointments that do not contain NSAID components can be used. For example, we can cite Capsicam, the active components of which are turpentine, camphor and dimethyl sulfoxide. The ointment has a local irritant and anti-inflammatory effect. Finalgon has a similar effect.
Kapsikam (321 rubles)
Injections
Tablets for coarthrosis are not indicated for everyone, as they negatively affect the digestive tract. That is why injections with drugs used in therapy are recommended. In first place in terms of effectiveness are drugs from the well-known group of NSAIDs.
- You can note Diclofenac, which is allowed to be injected for up to 3 days, after which you need to switch to medications in the form of tablets. Meloxicam (Movalis) is used using a similar method. In the first three days of injections, pain and inflammation are relieved, after which they switch to a maintenance dosage in the form of tablets.
- For severe pain, it is recommended to prescribe Ketanov or Ketorolac in injections, which can be used for up to 10 days. Dexalgin (Dexketoprofen) is considered a new drug from the NSAID group.
- Since coxarthrosis is accompanied by severe pain, drugs from the group of muscle relaxants can be added to the course of treatment. Their action is aimed at eliminating muscle spasm in the area of inflamed joints, as well as improving blood supply. Mydocalm is considered a popular remedy; Sirdalud is prescribed less frequently.
In the second and third degrees of inflammation, vasodilators are used, which improve the function of delivering nutrients to tissues by dilating the blood vessels around the joints. It is advisable to use Trental, Cynaresin.
Trental (586 rubles)
Severe inflammation is treated with medications from the group of hormonal drugs. This can be either a course of therapy, intra-articular administration of hormones, or a blockade to reduce pain. Diprospan, Kenalog, Hydrocortisone are prescribed.
Vitamins
When treating coxarthrosis, it is necessary not only to relieve pain and inflammation, but also to protect the joint itself from subsequent destruction. It is for this purpose that a group of chondroprotector drugs has been developed. They contain either Glucosamine or Chondroitin, which have a beneficial effect on cartilage tissue.
The following drugs are distinguished:
- Artra.
- Artradol.
- Don.
- Rumalon.
Modern products from the group of chondroprotectors contain both active substances at once. Such drugs include Teraflex, Glucosamine Maximum.
Teraflex (1994 rubles)
To maintain the musculoskeletal system, complexes of vitamins and microelements, such as Vitrum and Complivit, are often prescribed. In addition, taking a course of B vitamins is useful.
Features of treatment for different degrees of coxarthrosis
- In the first degree of coxarthrosis, there is slight pain in the joint area that appears after exercise. During this period, with the help of physiotherapy and taking chondroprotectors, further progression of the disease can be stopped. And also for this, a person will have to reduce the load, periodically undergo a course of physical therapy and massage.
- But in the second degree, the pain syndrome manifests itself clearly. A person experiences pain not only during exercise, but also at rest. Limited joint mobility appears. To relieve an exacerbation, NSAIDs and muscle relaxants are prescribed; in addition, vasodilators may be needed. In case of severe pain, the doctor may prescribe a blockade with hormones or administer drugs based on Hyaluronic acid intra-articularly. Hyaluronic acid stimulates the production of collagen, which is necessary to strengthen cartilage tissue.
- In the third degree, surgical intervention may often be required. In this condition, a person is at risk of disability. To relieve pain, blockades and a combined course of treatment are prescribed.
Deforming arthrosis of the hip joint
Deforming arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis) is a severe form of osteoarthritis. This form of the disease is most often (40% of cases) diagnosed in patients who visited a medical facility for problems with the musculoskeletal system. Both women and men who have reached the age of 40 suffer from deforming coxarthrosis. According to world statistics, deforming arthrosis of the hip joint is more often diagnosed in the female half of the population.
There are a large number of factors that provoke the development of coxarthrosis. The most important reason for the appearance of this disease is poor circulation in the pelvic organs. As a result, harmful enzymes begin to accumulate in the body of patients, which have a negative effect on cartilage, leading to their gradual destruction.
The causes of coxarthrosis include physical and mechanical effects on the hip joint. Most often, this disease manifests itself in people who are professionally involved in sports. Excess weight also puts stress on both the patient's joints and his body as a whole. Deforming arthrosis of the hip joint is usually accompanied by severe pain and limited mobility of the lower extremities. These symptoms should alert the patient and encourage him to contact a specialized medical institution. At the appointment, the patient will be examined and given an x-ray, which will determine the degree of damage and the type of arthrosis.
On the subject: Pain in the hip joint, what to do?
Diagnostics
Many people who develop hip arthrosis may experience pain when moving or doing any other physical activity. Initially, pain occurs only during physical fatigue, but subsequently patients begin to experience pain even during rest. Pain sensations are often integrated from the hip joint to the lower back, knee, hip, etc. Against the background of pain, some people begin to self-medicate, which often leads to irreversible consequences. That is why it is necessary, when such a primary symptom of arthrosis appears, to contact highly qualified specialists who will carry out a diagnosis.
When visiting a medical facility, patients who suspect hip arthritis should seek advice from the following specialists:
- Therapist. This specialist will assess the patient’s general health and determine the cause of the pain syndrome (sometimes pain occurs due to the progression of various chronic diseases).
- Neurologist. Very often, pain in the hip joint is a consequence of the formation of intervertebral hernias, so if such symptoms appear, consultation with a specialist is important.
- Urologist. In the male half of the population, pain in the hip joint occurs as a result of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland. A consultation with a urologist will confirm or refute this suspicion.
- Gynecologist. All women who come to a medical facility with complaints of pain in the hip joint are referred to this specialist. This is due to the fact that during the development of adhesions in the pelvic organs, patients often experience pain, therefore, when diagnosing arthrosis, it is important to obtain the opinion of this highly specialized specialist.
- Rheumatologist or arthrologist. These specialists can diagnose arthrosis of the hip joint in the early stages of its development. With a timely visit to a rheumatologist or arthrologist, the patient will be guaranteed a successful cure for this disease.
- Orthopedist and surgeon. Patients with advanced stage arthrosis of the hip joint are referred to these specialists.
When carrying out diagnostic measures, the specialist will first conduct a personal examination of the patient and collect a history of the disease. During palpation, he will be able to palpate the upper third of the lateral surface of the thigh and identify serious damage to it.
A specialist can carry out a number of simple manipulations, thanks to which it will be possible to make a preliminary diagnosis - arthrosis of the hip joint:
- flexion and extension of the lower extremities;
- turns the lower extremities in and out, etc.
To make an accurate diagnosis, patients are prescribed hardware and laboratory examinations:
- x-ray examination (an x-ray will reveal any damage to the hip joint);
- arthroscopy;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic area;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography (this diagnostic method allows you to identify arthrosis at the very initial stage of development, when it is not yet accompanied by pronounced symptoms);
- laboratory testing of blood and urine (clinical, biochemical) will reveal any inflammatory processes in the patient’s body.
The main task of hardware diagnostics is to identify arthrosis of the hip joint, as well as determine the degree of this disease. It is very important to determine the cause of arthrosis, since the method of treating this disease will depend on this.
There are diseases (for example, bone tuberculosis) that provoke the development of arthrosis, for which traditional treatment cannot be carried out (such diseases can be detected by laboratory tests of urine and blood):
- use ointments and gels that have a warming effect;
- physiotherapeutic procedures performed at high temperatures;
- massage;
- physical therapy, etc.
Diagnosis of coxarthrosis
In the diagnosis of coxarthrosis, the qualifications of the doctor are of great importance. If the orthopedic surgeon begins to treat the spine and forgets to order x-rays of the hip joints, time will be lost. This happens very often.
4 modern methods are recognized as the most truthful and accurate for establishing the diagnosis of coxarthrosis:
- Radiography. The image will help determine the size of the joint space, the presence or absence of osteophytes, and the condition of the femoral head.
- Ultrasonography. It allows you to determine the extent of the disease. View the location, number of growths, and condition of the acetabulum. Presence of changes in the ligamentous apparatus.
- CT (computed tomography). In essence, it differs little from an x-ray, but allows you to obtain more voluminous and detailed images.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). It is considered the most complete and truthful examination method. Allows you to scan the joint layer by layer, recording the slightest changes in the structure of bones and cartilage.
Additional laboratory tests will help determine the degree of inflammation in the joint. At the same time, an examination by an orthopedist remains an integral part of the diagnosis. Only by summing up all the data can one confidently establish a diagnosis, indicating the degree of development of the disease.
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint
At the first stage, arthrosis of the hip joint responds well to conservative treatment. The first task of the attending physician is to relieve pain that prevents the patient from moving.
During drug treatment the following is performed:
- restoration of damaged cartilage;
- restoration of nutrition and blood circulation in muscle and cartilage tissues;
- physical stress on the damaged joint is reduced;
- activation of hidden reserves of the human body, which will promote tissue regeneration at the microcellular level;
- increased joint space;
- restoration of joint mobility, etc.
During drug treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint, the following drugs are prescribed to this category of patients:
- drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect (non-steroidal);
- painkillers;
- muscle relaxants that restore blood circulation in muscle and cartilage tissues;
- chondroprotectors that can restore joint function and stop their destruction;
- steroids are prescribed to patients by injection during an exacerbation of the disease to eliminate pain;
- medications that can dilate blood vessels, etc.
During conservative treatment, patients should adhere to a diet specifically designed for patients with arthrosis of the hip joint. The course of therapeutic therapy includes therapeutic massage, which is indicated for patients with stages 1 and 2 of arthrosis.
At the 3rd stage of arthrosis of the hip joint, patients undergo surgical treatment of this disease.
Before surgery, each patient must undergo mandatory preparation:
- take blood and urine tests;
- undergo a hardware examination (ultrasound, x-ray, fluorography, cardiogram, EEG, etc.);
- get advice from highly specialized specialists who will give permission for the operation (therapist, rheumatologist, arthrologist, orthopedist, etc.).
The day before surgery, the patient must stop eating solid food. It is mandatory to cleanse the intestines (this can be done either with special medications or with an enema). In the evening, the patient will be given a sedative injection to help him fall asleep. Before surgery, the patient should empty his bladder, into which a catheter will be inserted (it will drain urine during the operation). The patient, in the operating room, will have to lie on his side, after which the surgeon will make markings.
Endoprosthesis replacement is performed under general anesthesia (the type of which is chosen by the anesthesiologist based on the state of the patient’s cardiovascular system), after which the patient will come to his senses within a few hours. To prevent the appearance of a gag reflex after anesthesia, you should limit your fluid intake for 5-6 hours. If the patient is extremely thirsty, he should moisten his lips with gauze or a cotton pad.
In order to prevent the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities, each patient's legs (to the knees) are wrapped in elastic bandages. He should wear such a tight bandage for 3-5 days after surgery, especially when moving (if the patient is in bed, in a supine position, he can remove the elastic bandages).
During endoprosthetics, the surgeon performs the following actions:
- cuts off the head of the femur;
- a pin made of a special metal used in the medical industry is inserted into the bone cut;
- the endoprosthesis is tightly fixed on the installed pin (it has an exact copy of the femoral head).
In detail: Endoprosthetics (replacement) of the hip joint
During surgery, the surgeon partially removes the surface of the pelvic bone. Instead, a stock made of polymer materials is installed. This stock is firmly connected to the titanium head, thanks to which the joint can continue to function fully for 20 years. At the final stage of the surgical intervention, the wound is sutured and after that a sterile bandage treated with antiseptic agents is applied to its surface.
Currently, surgeons perform endoprosthesis fixation in two ways:
- using a fragment of spongy bone (the prosthesis is driven in);
- using special medical cement (it is used in surgical treatment of bones).
Many specialists prefer to use bone cement during endoprosthetics, which very firmly fixes the prosthesis and allows patients to move independently after the postoperative scar has healed. This method is ideal for elderly patients. After such endoprosthetics, there is no need for a repeat operation, the purpose of which is to replace the endoprosthesis.
On the subject: Treatment of arthrosis with folk remedies
Recommended exercises for arthrosis of the hip joint
After completing a course of treatment for arthrosis of the hip joint, patients need to gradually return to their usual rhythm of life. Much attention should be paid to restoring motor functions of the joint and lower extremities. For this, experts recommend undergoing rehabilitation, which includes both a special course of physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a very dangerous disease that is difficult to treat. That is why, when choosing the level of physical activity for patients, specialists take into account their age, the severity of the disease, the characteristics of their body, etc. Physical therapy classes should be conducted within the walls of special medical institutions that have premises equipped for these purposes. During daily training, patients are monitored by an orthopedic doctor, who will immediately come to the rescue if necessary.
To prevent physical activity from worsening the patient’s condition, remember the following:
- physical activity must be given gradually;
- each exercise should be performed carefully, without sudden movements;
- before starting classes, you need to warm up all the muscles (this can be done with a regular warm-up);
- If pain occurs in the hip joint during exercise, you should stop training for a while, etc.
Many experts recommend that this category of patients combine therapeutic exercises and other sports:
- swimming;
- skiing, etc.
A healing hip joint will benefit greatly from daily walks in the fresh air, during which strong physical activity is not applied to the site of injury. After completing the rehabilitation carried out in a medical institution, the patient can perform a course of therapeutic exercises at home. During training with an instructor, each patient learns to perform each exercise correctly, as a result of which possible injury during independent physical exercise is almost completely eliminated.
For daily training, it is best to use special mats (orthopedic). During the training process, you should not forget about proper breathing, which should be corrected immediately if necessary. After completing the last exercise from the treatment complex, the patient should perform a short self-massage. For these purposes, you can use special massagers, thanks to which additional stress will be placed on weakened muscles.
If the patient discovers the following symptoms, he needs to stop daily activities for a while and contact a medical facility for consultation:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- increase in temperature;
- increased blood pressure;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- hernias, cysts and other neoplasms, etc.
On the subject: What foods are good for arthrosis?
About medications
For coxarthrosis of the hip joint, drug treatment is aimed at:
- Elimination of pain.
- Restoration of tissue trophism.
- Activation of regeneration processes.
- Improved blood flow.
- Reducing pressure on damaged areas.
- Increase in the size of the joint space.
How should hip joint types be treated to relieve pain? Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint is carried out with medications:
- Non-steroidal drugs that relieve inflammation. They are treated with Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Indomethacin, Brufen, Piroxicam and other medications. They use injections and tablets. They relieve pain.
- Chondroprotective agents. Treatment of coxarthrosis is carried out with Glucosamine, Chondroitin sulfate, Structum, Rumalon, Arteparon. They use injections. These medications provide nutrition to the affected tissue structures, they stop destructive processes, and the joint will function normally.
- Muscle relaxants. Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint is carried out with Sirdalud, Mydocalm. These remedies will relieve muscle spasms and improve microcirculatory processes.
- Medicinal ointments, creams, lotions. Treatment of the hip joint is performed with Gevkamen, Menovazin, Espol, Nicoflex and other drugs. By applying this group of drugs externally, the painful area is stimulated, microcirculatory processes are improved, and spasm is relieved.
- In order to treat the hip joint, steroid injections are used. Treatment with Hydrocortisone, Mitelpred, Kenalog and other medications is used. These injections relieve the aggravated condition and eliminate severe pain.
- Vasodilators are used. They are treated with Trental, Cinnarizine, Teonicol. These medications expand vascular tissues, relax their smooth muscle fibers, improve blood circulation in the joint, and relieve spasms.
What other methods of treating coxarthrosis exist, how to treat it? Kinesio tapes are used. Kinesio taping has long been used in sports medicine. Tape is a special type of cotton, hypoallergenic and elastic plaster. If it is glued to the skin, then:
- Microcirculatory processes intensify, lymph flows out, and a drainage effect is created.
- Muscle function is normalized.
- Painful sensations decrease or disappear completely.
- The articular surface or ligament is carefully fixed.
Kinesio taping has the following advantages:
- The effect lasts as long as the application is applied.
- Efficiency increases with physical activity.
- Does not cause any discomfort.
- There are no drugs in the composition.
For the hip joint, how should it be treated and how to apply it? Hair will interfere with taping, so the skin is cleansed and disinfected. Take 4 tapes, the length of the strips is from 15 to 20 cm. They are applied to the patient in a lateral position so that the articular surface is on the upper side, and the lower limb should be bent at the knee.
The scheme is simple:
- The base of the tape (about 4 cm on both sides) is glued, but not stretched, the main section is stretched as much as possible.
- The first strip is applied in a vertical position so that the central zone of the tape is on the affected joint.
- Another strip is glued in a perpendicular position to the previous one, stretching it as much as possible.
- The next 2 tapes are applied diagonally, stretching as much as possible.
- After application, the tape is rubbed so that it sticks better.
Surgical methods are carried out at the extreme stage of the pathological process, when the joint is not functional.
The joint is usually replaced with prosthetics and the following manipulations are performed:
- The femoral head is cut off and a pin is inserted inside. A titanium analogue of the femoral head is attached to it.
- Sections of the pelvis are removed segmentally and a special polymer stock is attached to connect it to the artificial head.
If the operation was successful and the joint was properly used, then it can serve for about two decades.