Adenoids have long been considered a “disease of childhood.” However, in adults this problem occurs no less often, and its consequences can be extremely serious. A timely visit to a specialist will help you get rid of the troubles associated with adenoids.
Adenoids in adults: symptoms
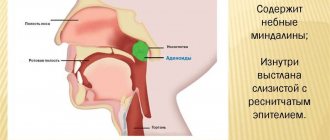
What are adenoids
Adenoids - folds of lymphoid tissue - appear when the nasopharyngeal tonsil begins to grow. Until the child turns 5-7 years old, it works as the main filter on the path of infections to the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract. Then this function is taken over by the palatine tonsils, and the nasopharyngeal tonsil dies off by the age of 14-16.
This is interesting! Adults were thought to lack adenoid tissue. However, the advent of endoscopic equipment refuted this opinion. In every third adult who complains of difficulty breathing, the disease is provoked by the adenoids.
Schematic representation of enlarged adenoids
Doctors consider the reason for the “delay” of the nasopharyngeal tonsil to be a kind of protective reaction of our body to a large amount of dust, allergens and microbes in the air. The growth of lymphoid tissue is provoked by ARVI, sinusitis and tonsillitis - the tonsil, trying to protect the body, grows in volume. The more often a person suffers from ARVI, the greater the possibility of pathology. In some cases, the growth of lymph tissue is provoked by endocrine changes.
Symptoms of adenoids in an adult
The main problem with adenoids is a constantly stuffy nose, impaired nasal breathing, and a lack of air. It's unpleasant and dangerous.
- The patient is forced to breathe through the mouth, which provokes frequent colds and chronic oxygen deficiency.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses - adenoiditis - due to its proximity to the hearing organs can cause otitis, and the respiratory organs receive a whole “bouquet” of diseases - bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis.
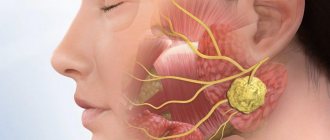
Adenoids
Attention! The consequences of adenoids are memory impairment, decreased thinking abilities, fatigue, headaches, problems with the heart and blood vessels, apnea (sleep apnea) and snoring.
There are 3 degrees of the disease:
- The patient breathes freely during the day, and at night - only through the mouth. A course of conservative treatment (without surgery) may be successful.
- The patient always finds it easier to breathe through his mouth than through his nose, and he snores in his sleep. Both conservative and surgical approaches to treatment are possible, but removal is recommended.
- The patient cannot breathe through his nose at all. At this stage of the disease, unlike previous ones, surgery to remove the nasopharyngeal tonsil is the only means of getting rid of the disease.
Adenoid grades
Adenoids also complicate life from an aesthetic point of view: a runny nose in itself is an unattractive sight, with the added bonus of a nasal voice. A constantly open mouth is a risk of malocclusion and facial deformation. The first step to solving the problem is an examination by an otolaryngologist.
Treatment of adenoids at GUTA CLINIC. Endoscopic adenotomy
To date, there is no more effective way to treat adenoids in adults and children, except adenotomy - surgery to remove the adenoids. However, according to world statistics, “blind” adenotomy gives a fairly large percentage of relapses in the postoperative period (18-62%) - unless it is performed using endoscopic equipment.
Throughout the world, the use of endoscopic equipment has long been the “gold standard” in the surgical treatment of adenoid hypertrophy. At GUTA CLINIC, endoscopic adenotomy has been successfully performed for a long time using the most modern equipment made in Europe and America.
Endoscopic adenotomy is absolutely painless, because It is performed under general anesthesia and is carried out using high-tech medical equipment, which allows the surgeon to perform a low-traumatic operation as accurately and efficiently as possible and avoid incomplete removal of adenoid tissue. The patient's time in hospital is reduced to 1 day, the duration of the rehabilitation period is also reduced, the percentage of relapses is about 1-2%.
Without treatment, adenoids in adults can lead to many unpleasant consequences:
- Mouth breathing is the cause of frequent respiratory tract diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, tracheitis, etc.), diseases of the nasopharynx (chronic rhinitis), and ear diseases (otitis).
- Impaired oxygen supply to the brain leads to decreased mental activity. Lack of oxygen also causes increased blood pressure, general fatigue, and decreased alertness and performance.
- Blocking of the mouth of the auditory tubes by adenoids is the cause of the development of chronic diseases of the middle ear.
At-risk groups
It is especially recommended for the following categories of adult patients to undergo an examination by an otolaryngologist:
- those who had adenoids in childhood, regardless of whether they were removed or not (the disease may return due to genetic predisposition, frequent colds or poor-quality removal);
- those who suffered from a prolonged severe runny nose (the tonsil begins to grow in response to a threat to the body, protecting against infection);
- those who have difficulty breathing through their nose;
- those who suffer from any allergies;
- those who have poor or declining hearing.
An enlarged adenoid closes the Eustachian tube
Are you at risk? Do not put off visiting a doctor in order to improve your quality of life as soon as possible and get rid of a whole range of problems.
Drops and sprays
They are required at any stage of adenoiditis. Vasoconstrictor drops help get rid of hypoxia and lack of oxygen during brain function. Nasal sprays are applied topically. They do not enter the blood and organs, which does not harm the baby’s health.
Iodine-based drops are widely prescribed. They literally burn off excess tissue from enlarged tonsils. They are dripped in courses, strictly as prescribed by the doctor. In addition, be sure to rinse your nose frequently. The child needs to be taught this procedure from an early age.
What examinations will you need to undergo?
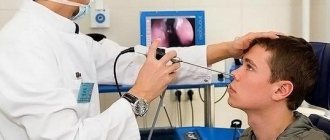
The doctor makes a diagnosis of adenoids based on clinical data supported by the results of computed tomography of the sinuses, biopsy and endoscopy.
- A CT scan takes a few seconds. The radiologist fixes the patient's head in the required position and takes an image. Modern fluoroscopic equipment makes the procedure harmless due to low radiation exposure. Before the procedure, you may be asked to remove hearing aids, glasses, jewelry, and dentures. Pregnant women are not recommended to undergo CT scanning.
- Endoscopy is performed under local anesthesia to eliminate discomfort. An endoscope is inserted into the patient's nasopharynx, through which the doctor looks at the tonsils. However, a simple examination is not enough, because various formations can occur in the nasopharynx.
- A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of overgrown tissue for analysis. Since the patient is under local anesthesia, he will not feel pain. After a histological examination, the specialist can say exactly what problem will have to be dealt with.
Adenoids in adults
If the tissue is truly adenoid, the patient receives a referral to an otolaryngologist for treatment.
Treatment without surgery
A conservative treatment method in adulthood is chosen in cases where surgery is contraindicated for various reasons.
If non-surgical treatment is necessary, the doctor may prescribe:
- physiotherapy (inhalations, magnetic, laser therapy, UHF heating);
- hormonal nasal drops (Nasonex, Flixonase, Avamis);
- homeopathic medicines (Thuja, Agraphis nutans, Calcarea phosphorica, Schussler's salt);
- antibiotics if there is an inflammatory process (Suprax, Cefspan, Amoxiclav).
Suprax drug
To rinse the nasopharynx you can use:
- infusion of horsetail (1 tsp horsetail per glass of boiling water);
- decoction of oak bark, chamomile decoction (5 g of bark per glass of water);
- infusion of St. John's wort (5 g of herb per glass of water);
- sea salt (1/2 tsp per glass of water);
- rotokan or green tea (1 tsp per glass of water).
This type of treatment may relieve symptoms, but will not correct the underlying problem. Therefore, adult patients are usually recommended to undergo surgical removal of the tonsil.
An unusual symptom that should alert you is sticky sweat.
Not always, postoperative consequences appear as described above. Both in normal and pathological status. The condition of the operated children is not similar to one another. A category of severely weakened children who had undergone a long period of potent drug exposure before the operation. In addition, those saturated with drug treatment, strong antibiotics, synthetic hormonal steroids, antihistamines will make it more difficult to endure both the operation and the recovery from the postoperative stage.
In such children, first of all, prolonged bleeding from the operating area and pain in this location are possible. They are prone to aggravated somatic symptoms - the temperature rises above the permissible level (from 37.4 - 38.9).
Parents should carefully monitor the condition and well-being of the baby. Don't be annoying, but don't leave your child unattended for too long. The temperature should be measured, in a calm history, every 4-5 hours.
You will see that the child first begins to sweat on his forehead, although the temperature is low. Then sticky sweat appears, profuse sweating, this is not a very good indicator! Indicates the weakness of the baby, as a painful consequence , typical after unsuccessful removal of adenoids in children.
Related articles The danger of adenoids in children: consequences in adulthood
Adenotomy in the form of cryofreezing, both during laser treatment and when exposed to LED radiation, does not pass without a trace. All the same, children are under pressure. Possible factors include radiation overdose and special sensitivity of the child’s body.
Tip: Important! And remember, dear parents! Physiological weakness after undergoing any type of adenoid removal is a common and acceptable symptom. But, if the child’s weakness manifests itself in extreme forms (incessant dizziness, loss of consciousness, rapid breathing). With the same rapid heartbeat, this is a reason, without a doubt, to call an ambulance!
Adenoid removal surgery
Removal of adenoids using laser
If you want to get rid of adenoids quickly and reliably, you should opt for surgery. Now operations have nothing in common with those that were done before the advent of modern techniques:
- Mandatory anesthesia. Nowadays, during the removal of adenoids, anesthesia is mandatory. This is justified, since during the operation a person may experience fear, scream, and break free. This interferes with the doctor and causes pain for the patient. Therefore, surgical intervention occurs under general anesthesia (in some cases, general anesthesia is contraindicated - under local anesthesia).
- Constant monitoring through an endoscope. A small camera inserted through the patient's mouth or nose allows the doctor to clearly see what his manipulations are doing. This makes it possible to clean out all the adenoid tissue without affecting other organs. “Blind” surgery led to a large number of relapses (up to 62%).
Surgical removal of adenoids
Before the operation, the patient undergoes an examination, which includes blood and urine tests, as well as an ECG.
Attention! Before surgery you should not drink or eat!
Before the operation, it is recommended not to eat anything from 18.00, and in the morning you should not drink anything, including water. There is no need to be afraid of the operation - it is painless and highly effective, the patient does not experience discomfort as it was before.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before you figure out how to treat adenoids in the nose, you should find out the degree of proliferation of lymphoid tissue. To do this, you need to contact an otolaryngologist and undergo an examination.
First, the doctor will simply examine the patient. Rhinoscopy is performed - a small metal funnel is inserted into the nose, allowing you to visually examine the nasopharynx. To obtain a more detailed picture, endoscopic examination, radiography or CT of the nasopharynx is used.
Additionally, a general and biochemical blood test is prescribed to identify a chronic inflammatory process.
The ENT doctor conducts a digital examination of the nasopharynx, assessing the degree of development of adenoiditis. Often, endoscopic examination is prescribed for diagnosis. The nasopharyngeal cavities are viewed using a special device that transmits an image to a monitor. This type of research is the most informative.
Depending on the degree of the disease, treatment of adenoids is prescribed. Very rarely this is a surgical method.
Methods for removing adenoids
The nasopharyngeal tonsil can be removed in several ways; the choice of method is up to the doctor. It determines the optimal method for removing the adenoids (adenotomy).
| Removal method | Tools | By radio waves | Laser | Shaver |
| Equipment | Beckmann's adenotom | Surgitron. Video endoscope | Laser. Video endoscope | Microdebrider. Video endoscope |
| Anesthesia | Local | General, local | General, local | General, local |
| Advantages | Outpatient settings. Self-stopping bleeding | Minimum risk of blood loss. No bleeding after surgery | Bloodless removal | The mucous membrane remains intact. The adenoid is removed promptly and without leaving any residue. Bloodless and scarless removal. Virtually no relapses |
| Flaws | The operation is performed blindly - relapse is possible due to incompletely removed adenoid tissue | — | The operation time is increased. Healthy tissue can be heated by the laser | — |
After the operation, the adult patient remains in the hospital for up to 3 days under medical supervision.