Testicular torsion is a fairly common problem among men. Half of all cases of this pathology occur between the ages of 10 and the time of puberty. In all other cases, this disease affects young children and adult men. Testicular torsion is a mechanical injury in which the connective tissue between the testicle and epididymis rotates in any direction. In this case, not only the testicles and spermatic cord are twisted, but also pinching occurs, and sometimes necrosis of testicular tissue occurs.
Causes of torsion
The prerequisite for the occurrence of such a pathological condition is excessive mobility of the testicle due to the lack of its normal attachment to the bottom of the scrotum. This increased displacement of the organ is due to a number of anatomical and topographical features that can occur in children and adult men:
- congenital elongation of the spermatic cord;
- inguinoscrotal hernia;
- testicular inversion;
- hypoplasia or aplasia of the testicular guide ligament;
- separation of the vas deferens and the neurovascular bundle, etc.
A testicle that has not descended into the scrotum . In a child, this pathology is often associated with prematurity and disproportionate growth of the genital organs.
The immediate causes of organ torsion are:
- scrotal injuries;
- outdoor games;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- active movements;
- physical exercise;
- wearing tight clothes and underwear;
- sexual intercourse and other moments that contribute to the contraction of the muscles that lift the testicle.
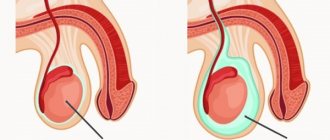
With this pathology, the testicle rotates around its vertical axis. a sharp disruption of blood circulation occurs in the gonad , thrombosis of the veins of the spermatic cord develops, and serous-hemorrhagic transudate begins to accumulate in the cavity of the testicular membrane.
What is testicular torsion?
This is a phenomenon that accompanies twisting of the spermatic cord. The spermatic cord holds the testicles in the scrotum, and when it gets twisted or pinched, blood flow to the testicles stops. Without surgical treatment, they may die and require removal. In other cases, their functionality will be impaired, leading to infertility.
The cause of testicular torsion is usually unknown. Some men undergo anatomical changes that increase the likelihood of torsion. In general, it can happen to a man of any age, but is most often diagnosed in newborn children and adolescents.
Classification and symptoms of pathology
Typically, torsion is unilateral, and bilateral development is very rare. According to the mechanism of development, pathology can be intravaginal or extravaginal.
Extravaginal torsion is characterized by twisting of the spermatic cord along with its membranes. This form of pathology is most often observed in children under one year of age and is associated with increased tone of the cremaster muscle, looseness of the fusion of the membranes, a wide and short inguinal canal, etc.
Intravaginal testicular torsion occurs due to the twisting of the spermatic cord inside its own membrane. This condition usually occurs in children over three years of age and in adults. At the same time, the cremaster muscle reflexively contracts, the testicle begins to be pulled up, making a rotational movement.
There are many symptoms of this disease. The main ones are:
- sharp pain in the testicles;
- vomit;
- nausea.
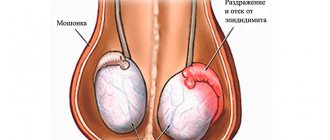
When twisting, the testis can be felt at the top; sometimes the appendages can be located in front. The spermatic cords are thickened. After some time, swelling and hyperemia occurs .
In addition, the symptoms of the pathology may vary depending on age. If testicular torsion is diagnosed in a newborn child, then in this case half of the scrotum is enlarged, its contours are changed due to the torsion of the testis, and the skin has a reddish or bluish tint. After birth, a few hours later, the baby begins to worry, develops a fever and vomits.
Symptoms of torsion in older children and adult men are as follows:
- severe pain in the groin;
- elevated testis;
- temperature increase;
- blue discoloration of the skin;
- nausea and vomiting.
In addition, when you try to lift the testicle upward, the pain begins to intensify.
Diagnostics
Before sending the patient to undergo various examinations, the doctor must determine what factors could contribute to the occurrence of such a pathology: has the scrotum been recently injured, is there discharge from the urethra , etc. After this, he examines the genitals, paying attention to the color of the scrotum, the position of the painful testicle, the density and size of the spermatic cord zone and finds out whether there is induration and hydrocele.
The pathological testicle is most often felt in the upper part of the scrotum, since shortening of the spermatic cord occurs as a result of such pathology. In addition, the spermatic cord thickens. After some time, swelling of the entire scrotum occurs.
If the doctor doubts the correctness of the diagnosis, he will prescribe additional examinations:
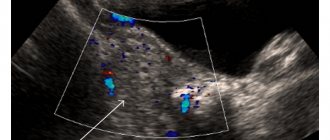
- Ultrasound;
- radionuclide scanning;
- dopplerography;
- general urine analysis.
In some cases, a puncture is taken from the membranes of the testicle.
Treatment
In a small number of men, torsion can be eliminated using a special manual detorsion technique. To do this, the patient lies on his back, and the doctor turns the testicle in the opposite direction of torsion. It should be remembered that the left testicle rotates counterclockwise, and the right one in the opposite direction. For convenience, you need to focus on the seam of the scrotum .
The doctor takes the pathological testicle with his fingers along with the skin of the scrotum and turns it in the opposite direction from the suture, then releasing it. If necessary, this action is repeated several times until the tissue becomes more mobile and the pain decreases. If there is no positive result, the treatment is interrupted, and the patient undergoes urgent surgery.
Due to the fact that the testicles are very sensitive to blood supply, at the slightest sign of swelling of the scrotum, urgent surgery is required. The testicle left without blood supply dies irrevocably after 6 hours.
Surgery is performed based on the patient’s age. In infants it is carried out through the groin, and in older children and adult men - through the scrotum. To determine the shape of the entropion, during the operation all tissues are opened and the testicular membrane is reached. The exposed testicle is straightened and placed in the correct position, while assessing the degree of damage.
To find out whether there is blood supply to this organ, special medications are injected into the spermatic cord to accelerate blood circulation. If the situation does not improve, then the testicle is removed. If the blood supply has been restored a little, then heat compresses based on sodium chloride are used. If everything went well, then after some time the testicle acquires a healthy color.
The testicle is removed only in case of necrosis. To exclude errors, additional studies are carried out, for example, by X-raying it. If there is a lumen, we can say that it is alive. In addition, to check viability, the tunica albuginea of the testicle is cut in the lower part. If blood starts flowing, then this important organ is alive. But if the color does not improve, the blood vessels do not pulsate, and blood does not flow from the cut in the membrane, then such a testicle should be removed, since it is pointless to treat it.
If it is possible to maintain the blood supply to the testicle, then it is sutured to the scrotal septum without tension on the spermatic cord. A thin drainage tube is inserted into the incision, through which antibiotics are supplied, washing the pathological organ for 2 to 3 days. After this, the living testicle is lowered into the scrotum and fixed there.
After surgery, the doctor prescribes medication to the patient to help improve local blood circulation and restore testicular function. This could be a novocaine blockade , taking sodium heparin, acetylsalicylic acid, etc. If such a need arises in the future, an operation is performed to more securely secure the testicle on the other side. This prevents recurrence of torsion in the future.
Symptoms
Testicular torsion in a boy is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Sharp and sudden pain in the scrotum area.
- The pain may cause nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
- The testicle swells, increases in size, and is located above the healthy one.
- Due to poor circulation, the scrotum becomes pale and cyanotic.
- Urinary problems may occur.
It is important to note that in newborn babies, symptoms of testicular torsion may not appear, that is, the baby does not cry in pain. A sign of pathology may be swelling of the scrotum on one side, visible asymmetry. If the baby has different testicles, it is better to consult a surgeon.
Torsion develops quickly. In the acute stage of the disease, which lasts the first day, it is necessary to consult a doctor to avoid complications of the disease. Then the pathology passes into the subacute stage, the pain subsides slightly, and then into the chronic stage. According to statistics, if the testicle is not straightened in the first day, it dies due to poor circulation. As a result, the testicle must be amputated.
Consequences
We can talk about the consequences after the operation, taking into account the timeliness of the person seeking help and the treatment started. If the patient consults a doctor 6 hours after the first symptoms appeared, then in this case the doctor guarantees the safety of the testicle and its functions in 100% of cases. After 12 hours to a day from the onset of the pathology, in 80% of cases this organ dies . And it is almost impossible to save him if he goes to the hospital a day or more after the initial symptoms appear.
Testicular torsion often threatens infertility in men. In addition, a link has been established between cancer and testicular torsion. More than half of the patients who have ever suffered from this pathology are susceptible to developing cancer.
Thus, testicular torsion in both a child and an adult is a very dangerous condition . It is impossible to prevent twisting of the testes and their appendages. The only recommendation in this case is to treat your genitals with care and try to avoid injury to this area. At the first symptoms you should consult a specialist.
Diagnostics
Testicular torsion requires emergency medical care, so if you have the slightest suspicion, you should immediately see a doctor. He will conduct an examination, prescribe a urine test and an ultrasound examination of the scrotum.
Testicular torsion should be treated within 4-8 hours from the onset of symptoms. If this can be done, as a rule, the testicle can be “saved.” If you seek help later, especially after more than 24 hours, the testicle may be permanently damaged. Sometimes the only option is surgical removal.
General rules and methods of treatment
The safety of the testicle and future reproductive function will depend on how quickly measures are taken to eliminate torsion. If no more than 6-12 hours have passed since the onset of the pathology, the chances of saving the organ are very high (80-90% of cases). After a day, the testicles completely cease to be vital.
In order to prevent the development of organ dystrophy and the death of its tissues, the spermatic cord must be untwisted. This is done in two ways:
- external manual detorsion;
- surgery.
View a selection of effective treatments for prostate hyperplasia in men.
What is thyroid myxedema and how to treat the disease? Find out the answer from this article.
On the page, read about how and how to treat hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes.
Manual unwinding
The method is conservative and its effectiveness is about 2-3%. This method is used for infants.
Procedure steps:
- the child is placed on his back;
- the doctor rotates in the opposite direction to the torsion. The left testicle unwinds counterclockwise, the right one - clockwise;
- when rotated, the testicle is slightly pulled downwards.
READ ALSO: What is the corpus luteum in the ovary: symptoms and causes of disorders, methods of treating abnormalities
The manipulation is considered successful if pain has been eliminated and the testicle has returned to its physiological position.
Surgery
Surgery for testicular torsion in boys has to be resorted to more often. The condition does not tolerate delay and threatens serious complications, including organ loss. It is important for the doctor to determine the degree and shape of the torsion and the viability of the testicles.
For children, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. The incision is made through the groin or scrotum. The surgeon exposes the testicle, removes it from the protein membrane and determines the degree of tissue damage using transillumination. The undestroyed testicle is sutured to the scrotum without strongly pulling the spermatic cord.
To increase blood circulation in the organ, a solution of Novocaine with Heparin is administered. Install drainage. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection.
If tissue necrosis is detected, removal of the testicle (orchiectomy) is indicated. When the child reaches adulthood, this defect can be corrected by installing an artificial implant.