Adenoids in the nose in children are a common disease. Manifestations of adenoids are unpleasant and extremely uncomfortable: the child has difficulty breathing, his sleep is disturbed, his sense of smell disappears, and hearing problems arise.
In the article we will look at the features of this disease, and find out how adenoids manifest themselves and what causes they occur. We’ll also figure out how to treat adenoids in the nose in children, and what complications may arise if you give up on therapy.
What are adenoids?
Nowadays, adenoids are a common problem faced by children of different ages. It is noteworthy that the disease is rapidly growing younger, and children aged 2 to 10 years old are faced with it. Only a timely decision on treatment will help prevent dangerous consequences for the child’s body.
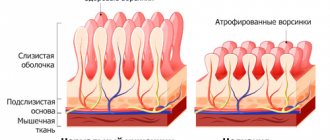
The term adenoids refers to the pharyngeal tonsil located in the nasopharynx. It has the most important function - protecting the child’s body from infections. During the period of illness, the tissues grow, and after recovery they return to their original sizes. However, this does not always happen. In people who often experience various inflammatory processes, the tonsils do not return to their original size. In this case, a diagnosis of adenoid hypertrophy is made, and the patient may also receive a diagnosis of adenoiditis.
Pharyngeal tonsil and its functions
A pathologically overgrown nasopharyngeal tonsil is called “adenoids.”
Adenoids in the nose are not a separate neoplasm, such as polyps, but a consequence of excessive growth of tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. This is an unpaired amygdala, which performs an important protective function. The nasopharyngeal tonsil consists of lymphoid tissue, and it is its proliferation that leads to the formation of adenoids.
In the nasopharyngeal tonsil, immune cells are formed and mature, as well as antibodies to fight viruses and infections. Amygdala hypertrophy is a childhood disease, which is explained by the peculiarity of the functioning of the children's immune system.
Adults almost never encounter this problem, except in rare cases when the disease was not cured in childhood. In general, adenoids are treated with conservative methods, but in severe cases their removal is advisable.
Amygdala hypertrophy is a peculiar response of the body to a weak immune system in children. With age, the size of the tonsil decreases, so most children successfully “outgrow” the adenoids.
The pharyngeal tonsil is a large collection of lymphoid tissue. This organ has a large number of nerve endings and a rich vascular network. When an infectious-inflammatory process occurs, pain appears on the vault of the nasopharynx.
The pharyngeal tonsil takes an active part in the processes of hematopoiesis and ensuring the body's immune defense.
In order to understand how the pharyngeal tonsil works, you need to know where the adenoids are located and what can provoke their pathological growth.
The principle of functioning of the nasopharyngeal tonsils is based on the active capture and destruction of pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate food and inhaled air.
Pathogens, penetrating the body, settle on the surface of the tonsils and are destroyed by immune cells.
In the case of the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the tissues of the tonsils, a decrease in the protective properties occurs, which provokes pathological proliferation of tissues, and instead of protection, they turn into a source of infection for the body.
The pharyngeal tonsil is easy to find; it is located on the roof of the nasopharynx wall.
Symptoms of adenoids in children
The main sign indicating the development of adenoiditis in children is nasal congestion and difficulty breathing, while any discharge from the nasal cavity may be absent. In order to confirm the diagnosis, you should contact an otolaryngologist.
The list of the main symptoms of adenoiditis can be presented as follows:
- sleep disturbances, the child always sleeps with his mouth open, and the sleep is shallow, children can wake up and cry in their sleep;
- attacks of suffocation;
- snoring and snoring;
- holding your breath;
- drying of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- dry cough in the morning;
- nasal speech;
- change in voice timbre;
- headache;
- tendency to rhinitis and pharyngitis;
- lack of appetite;
- addition of otolaryngological disorders;
- irritability;
- moodiness;
- fast fatiguability.
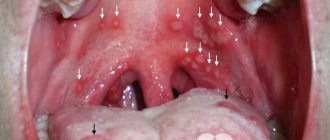
Against the background of enlarged adenoids, adenoiditis often develops, a pathological inflammatory process involving the pharyngeal tonsils. Such a lesion can occur in acute and chronic form. In the acute course, a significant increase in the child’s body temperature is observed, pain is observed, and a burning sensation in the nasopharynx is constantly present. Parents may also notice an increase in the frequency of rhinitis, and nasal discharge can be not only mucous, but also purulent. With adenoiditis, the cervical lymph nodes can also become significantly enlarged.
Manifestations
Symptoms are noticeable even at the very first stage of adenoiditis development. The child sniffles heavily in his sleep, cannot completely blow his nose, and is tormented by frequent runny noses. The most characteristic manifestations indicating an increase in nasopharyngeal tonsils:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Constantly open mouth during sleep.
- Snore.
- Minor hearing loss.
- Brain hypoxia due to improper oxygen metabolism and, as a consequence, anemia, prolonged mental development.
- When speaking, a nasal tone is clearly audible.
Due to the narrowing of the nasal passages, as the baby grows, the face becomes longer, an incorrect bite is formed, and there are delays in the correct development of the jaw. The deformities must be eliminated, otherwise you will have difficulty breathing for the rest of your life.
The above symptoms are characteristic only of advanced stages of the disease. When the degree of adenoids is small, the child will only have difficulty breathing, frequent runny nose, and hearing impairment.
Degrees of adenoids in children
In modern medical practice, three degrees of the disease are distinguished. Classification is made depending on the degree of growth of the adenoids. A pediatric otolaryngologist will be able to determine the stage of pathology in a child during the initial examination.
In some countries, classification involves dividing adenoids into 4 stages. In this case, during the pathological process at stage 4, complete closure of the nasal passage is observed.
Grade 1 adenoids in a child
At the first stage of the disease, overgrown tissue covers 1/3 of the back of the nasal passages. At night, the pathology manifests itself with pronounced symptoms, while during the day the patient does not experience their manifestation. At night, the child may snore and wheeze, and insomnia develops against this background. The child is faced with lack of sleep, as a result of which he becomes more distracted and inattentive.
At this stage of development, the disease is treated exclusively with a conservative method. the prognosis for recovery is high.
Adenoids grade 2 in a child
At the second stage, the adenoids cover about 60% of the lumen. The child cannot breathe normally through the nose not only at night, but also during the day. Speech problems may occur. Timely contacting a doctor at this stage also makes it possible to ensure the treatment process without surgery.
Adenoids grade 3 in children
At the third stage, the existing lumen of the nasopharynx is completely closed by the adenoids. The only possible treatment option is surgery. Drug therapy rarely produces positive results.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the appearance of adenoids in the nose in children is a weak immune system. Hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue is designed to improve the protective function of the tonsil and increase the number of immune cells. However, with an increase in the size of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the process of breathing through the nose worsens, since the organ covers part of the vomer, as a result of which local immunity is further weakened. The result is diseases of the ENT organs associated with impaired nasal breathing.
Causes and predisposing factors to the development of adenoids:
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent ARVI;
- allergic reactions;
- too dry air;
- “childhood” infectious diseases – chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- weakened immunity.
One of the most common reasons is genetic predisposition. It has been proven that children of parents who experienced adenoids in childhood are more susceptible to this disease.
A predisposing factor is a decrease in general immunity. This may be due to various reasons - from long-term use of antibiotics to chronic diseases. Also one of the reasons is the presence of a focus of infection in the body, for example, in the case of chronic tonsillitis.
One of the factors that indirectly affects the development of adenoids is the air that the child breathes is too dry or polluted. This is explained by the fact that the nasopharyngeal tonsil acts as a kind of filter, purifying all the air entering through the nose. If it fails to cope with its functions, the process of proliferation of lymphoid tissue begins and adenoids form.
Adenoids are a childhood disease that in 95% of cases goes away with age. Typically, tonsil volume loss begins during adolescence. However, in some cases the problem remains in adults.
Symptoms of adenoids in the nose in adults and children are as follows:
- difficult breathing through the nose;
- night snoring;
- sleep apnea (with grade 3 adenoids);
- prostration;
- nasal voice;
- frequent otitis and chronic rhinitis;
- hearing loss;
- frequent headaches.
For nasal adenoids in adults, symptoms include difficult nasal breathing and night snoring. All signs and symptoms of adenoids in the nose are generally the same for adults and children, however, in childhood there is a general decrease in immunity and frequent acute respiratory viral infections.
Important! The main problem of adenoids is complications on the nose and ears. Therefore, any cold or acute respiratory viral infection ends in otitis media or sinusitis.
Quite often, the diagnosis of adenoids in the nose in adults is carried out accidentally, for example, if a person complains of snoring at night. This is explained by the fact that the disease is more typical for young children. Adenoids in an adult can be suspected if there is a chronic runny nose and an increased tendency to otitis media, since these two diseases are typical signs of adenoids.
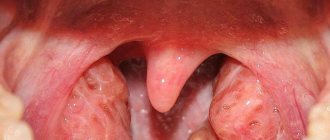
It is impossible to find out on your own what exactly the adenoids in the nose look like, but you can see the proliferation of lymphoid tissue with the help of a special examination. This is due to the fact that the nasopharyngeal tonsil is located deep in the nasopharynx and can only be seen through the nose using a special device.
In general, what exactly the adenoids in a child’s nose look like can be determined using endoscopy. This is an examination during which a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the nasopharynx. With the help of such an examination, the doctor will not only diagnose the extent of the adenoids, but will also show the parents a picture of the growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, because the image during endoscopy is displayed on the monitor. The screen will show pink lymphoid tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil extending beyond the nasopharynx and overlying part of the vomer.
Doctors associate excessive growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsils with an increased level of body defense. However, many researchers are inclined to believe that adenoid disease is hereditary.
If one of the parents suffered from adenoids in childhood, according to geneticists, the possibility of children inheriting the disease is 40-50%. When both parents had enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsils in childhood, the probability of passing the disease gene to their offspring is 60%.
With the development of adenoiditis, any virus or microorganism that enters the nasopharynx cavity “meets” an obstacle in the form of nasopharyngeal tonsils. Due to the activation of immunity, they swell. Often to significant sizes. This prevents infection from getting inside. Due to this protective power, the child’s internal organs are not exposed to the dangers of infection by various inventions. Only the nasopharynx and respiratory organs are affected.
That is why a number of specialists in the field of otolaryngology do not recommend removing even very large adenoids, as well as tonsils for tonsillitis. In the absence of these tonsils, dangerous viruses and microorganisms enter the child’s body that can cause serious harm to the liver, pancreas, stomach, heart, and other vital organs.
Removing the adenoids does not guarantee the disease will return. No doctor will completely eliminate overgrown lymphoid tissue from the nasal cavity. The remnants of the tonsils often grow again and again cause significant inconvenience to the child.
What adenoids look like in children with photos
The most characteristic symptom of adenoids is nasal congestion, which can occur exclusively at night or be present all the time. On
This background often causes dry lips; dry crusts form on them, which are quite painful. Children try to tilt their heads back to ease their own breathing.
Mouth breathing is harmful and uncomfortable, especially if the child is forced to breathe this way constantly. Because of this, perseverance is lost, children become less organized, and school performance often worsens.
Persistent congestion is even more dangerous for newborns. Lack of lumen causes loss of appetite. The baby cannot drink breast milk, nor can he drink food from a bottle. Sensitivity to odors is significantly reduced.
The mucous membranes in the oral cavity constantly dry out. The child develops a cough that disappears after drinking. Characteristic changes in voice timbre, nasality appears. In acute cases of adenoiditis, body temperature rises.
Treatment of adenoids in children
If enlargement of the adenoids occurs against the background of any inflammatory process, then therapeutic measures should be aimed at treating the pathology that is the causative factor. Under such conditions, the size of the child’s adenoids quickly returns to normal. Treatment of such inflammatory processes often requires the use of various antibacterial drugs, especially those of the penicillin group.
The scheme of therapeutic intervention is determined by a specialist individually, depending on the type and nature of the pathology. The treatment regimen may involve the use of medications from the following drug groups:
- Antihistamines. Such drugs are used not only for the allergic form of the disease. Drugs with a similar effect minimize the risk of a patient developing a reaction to sane drugs.
- Nasal rinsing. To rinse the nasal cavity from the accumulation of mucus and pus, you can use preparations based on sea water, sold in the pharmacy chain in the form of a spray and aerosol. The list of the most popular products includes: Humer, Aquamaris, No-sol. You can also make your own saline solution.
- Vasoconstrictors. In the treatment of adenoids, such drugs are used not only in the form of nasal drops, but also in the form of ear drops. Such a recommendation is associated with a high risk of developing various hearing disorders.
- Hormonal drugs. Hormone-based drops can be used to eliminate severe swelling in the nose, but parents should remember that addiction to drugs of this pharmacological group develops quite quickly, and the development of medicinal rhinitis is possible.
- Antiseptics. Antiseptic formulations can be used if the inflammatory process manifests itself against the background of bacterial or viral activity.
Various oils can be used to moisturize the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity. Otolaryngologists recommend using purified sea buckthorn squeeze to lubricate the nasal passage. To speed up the recovery process during the treatment period, it is recommended to take vitamins and immunomodulators orally.
Conservative method
In the most common cases, after diagnosis, the disease is treated using conservative measures. These are various drugs, drops, physiotherapeutic procedures. Thanks to them, the adenoids that filled the cavities in the nose become significantly smaller. By the time they atrophy completely, the child does not experience severe symptoms of the disease.
Doctors prescribe antibiotics. These medications are needed when a serious infection has entered the body that threatens the baby’s life. For viruses, taking antibacterial drugs is strictly prohibited. Only if the disease is clearly bacterial in nature.
Antihistamine tablets can reduce the size of the tonsils if there is tissue swelling of an allergic type.
Adenoid removal
For hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil of the third degree, the only possible treatment method is surgery. It is worth noting that in this case, adenoiditis requires immediate treatment, because it can cause a significant deterioration in the child’s well-being. The absence of normal nasal breathing leads to a significant deterioration in the quality of life.
The operation is carried out as planned, under general anesthesia, within the walls of the otolaryngology department of the children's hospital. The intervention is short in duration, the operation takes a few minutes. If there are no complications, the patient is sent home on the same day.
The list of indications for the operation can be presented as follows:
- lack of effectiveness of sane drug therapy;
- the frequency of relapses of adenoiditis exceeds 4 times a year;
- significant difficulty in nasal breathing;
- recurrent otitis media;
- hearing impairment;
- constant headaches;
- sinusitis;
- stopping breathing during night sleep;
- deformation of the skeleton of the face and chest.
The list of contraindications for the operation can be presented as follows:
- congenital anomalies of the hard and soft palate;
- insufficient blood clotting;
- blood pathologies;
- heart disease and vascular damage;
- inflammation of the adenoids.
The operation is not performed at the time of relapse. The intervention is prohibited during a seasonal outbreak of respiratory viral infections, and within 1-2 months after vaccination.
Currently, there are drugs for general anesthesia that have a short-term effect. When performing adenotomy, it is recommended to use them. Carrying out the operation under local anesthesia is possible, but such an intervention is not recommended, since the child may be left with psychological trauma.
To carry out the intervention, a modern endoscopic technique is used, which is characterized by low trauma. The advantage of this method is the minimal number of complications. The postoperative period is easy and the child does not face strict restrictions.
In order to prevent the risk of complications in the postoperative period, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- taking vasoconstrictor and astringent nasal drops;
- restriction of physical activity for 2 weeks;
- eating food with a soft, uniform consistency;
- Do not eat hot food;
- in the first few days, you should avoid taking a hot bath;
- you should not stay in the open sun;
- It is better to avoid crowded places.
Complications of adenoids
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, adenoids in children can provoke various complications. Most often, such consequences are observed in grades 2 and 3 of the pathological process:
- chronic inflammatory processes affecting the upper respiratory tract;
- high risk of acute respiratory infections, people with adenoiditis can get colds 2 times a month;
- jaw deformation;
- hearing loss, development of otitis media;
- speech dysfunction.
Doctors say that inflamed adenoids are quite dangerous for children. Such inflammatory processes can cause significant developmental delays, which manifest themselves against the background of a lack of oxygen to the brain.
Prevention
Particular attention should be paid to studying the rules of prevention for parents of children who are predisposed to allergic reactions or have a predisposition to adenoiditis. Experts say that the main rule that helps prevent such an inflammatory process is to allocate the necessary time for recovery after an acute respiratory infection. You should not send your child to kindergarten or school immediately after body temperature has stabilized. Contact with new bacteria can cause recurrent disease, namely, frequent colds in some cases cause hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil.
It is equally important to instill in a child a love for the rules of a healthy lifestyle. The child must be aware of the need for proper nutrition and show an interest in physical exercise. Parents should remember that the diet for children of different ages should be varied; the daily menu should include all the necessary vitamins and microelements.