Home » Asthma » Allergic asthma »
- Antihistamines
One form of asthma in which a person has a high degree of sensitivity to various types of allergens is called allergic asthma. As soon as the allergen hits the mucous membrane, the body begins to react to the irritant.
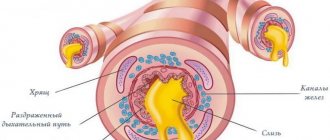
The immune system is activated, resulting in sharp contractions of the muscles located in the respiratory tract. Bromchospasm occurs, which causes inflammatory processes in the muscles. The body, reacting to this, secretes thick and viscous mucus.
Allergic asthma affects about 45% of adults and up to 85% of children. This is almost 7% of the entire world population.
Causes leading to allergic bronchial asthma
People of any gender and age are prone to asthma, and the disease is characterized by an attack of lack of air to breathe, as well as the release of mucous sputum when coughing in small quantities. The situation is aggravated under the influence of allergic irritants.
The reasons that can give rise to the development of asthma are the following:
- Accumulations of dust.
- Feather pillows.
- The hair of domestic dogs, cats and other pets, as well as bird feathers.
- Mold fungi.
The true cause of the disease is difficult to establish. It may appear and disappear without any specific reason.
Symptoms characteristic of the disease manifest themselves under the influence of a strong pathogen - “tiger”, or a complex of other factors. The course of the disease is different for each patient, since tiggers are individual for each patient.
Usually, a person suffering from asthma can identify for himself the cause of worsening symptoms. To more accurately determine the factor causing the disease, doctors recommend keeping a diary in which they record observations of the course of the disease. Pathogens that cause inflammation in the respiratory tract:
- Allergens. They provoke the body to react to a foreign stimulus. Allergies have many unpleasant symptoms, which are often a precursor to asthma, both in children and adults. Popular allergens in human everyday life are: pollen, mold, animal hair allergies, house dust mites. The appearance of bronchial asthma against the background of allergies often happens if the symptoms of the root cause are not eliminated and the disease is allowed to take its course.
Cases of signs of bronchial asthma appearing after ingesting allergenic foods or undergoing long-term therapy (with medications) have been recorded.
- Tiggers are the results of the vital activity of viruses and fungi, which leads to the appearance of cold symptoms and a weakening of the body’s barrier functions. At the next stage, the symptoms worsen, which leads to the appearance of signs of bronchial asthma. In this case, the reason is most likely not in an allergic reaction of the body, but in the infectious course of the disease. Frequent respiratory diseases caused by colds disrupt the integrity of the mucous tissues in the respiratory organs, which leads to a worsening of asthma.
- The causes of asthma symptoms are: allergies to cold, excessive gas pollution, concentrated odors, cigarette smoke. Asthmatics react sharply to smoke, as it is too aggressive an irritant. Forced stay in smoky rooms complicates the course of the disease. Children and adults - passive smokers - suffer from particular sensitivity to tobacco smoke. It is being in such a room that will cause the attack for the first time.
- Living conditions and places of professional activity can stimulate the appearance of signs of bronchial asthma. Having contact with paints, varnishes, sprays, detergents, chemicals, asthmatic symptoms are easily explained.
- Asthma is a consequence of experienced tragic events, emotional shocks, and depressive symptoms.
- Genetic predisposition. A 50% chance of acquiring a disease by inheritance is allowed if one close relative had such a disease. The percentage increases if two parents have this diagnosis.
Causes of the disease
Provocateurs that are the source of the disease are divided into the following categories:
Indoor allergens. The culprits for their appearance may be: pets (wool, feathers); cockroaches (scales and excrement); mycelium (fungus and mold); dust mites (their droppings that float in the air with dust). Open space allergens. Such provocateurs are caused by pollen from trees and grasses. Accordingly, the disease develops during flowering. This is usually spring and early summer. Food allergens. Most often they are found in products containing antigens similar to plant pollen. These can be eggs, milk, peanuts, shellfish, strawberries, and some types of fruit.
The rarest type of allergic asthma is a reaction to food irritants. But at the same time, this form of the disease is accompanied by very strong manifestations, which are impossible to cope with on an outpatient basis. Therefore, to eliminate respiratory failure, the patient is hospitalized. Sometimes allergic asthma triggered by food can be life-threatening.
The causes of pathology in individual individuals have not been established. It is believed that this is the influence of the genetic predisposition of the organism and ecology.
Symptoms characteristic of two diseases
The result of treatment depends on timely identification of the cause of the disease and a correct diagnosis. To prescribe adequate therapy, the doctor must evaluate the signs of asthma in an adult against the background of allergies. What does the attending physician pay attention to:
- Allergic asthma is characterized by sudden onset of symptoms. The first symptoms that appear during activity or inactivity, at any time of the day, are shortness of breath and lack of air for full breathing. Attacks also occur when inhaling toxic compounds in the air: smoke, burning, soot, temperature changes, and the aggressive influence of plant pollen.
- Cough is a typical sign of an asthma attack. It is usually dry and accompanied by difficulty breathing. The patient has difficulty clearing his throat. In this case, sputum is released in small quantities.
- Breathing is frequent and shallow. As you exhale, you notice a prolongation of the process. People with this pathology report difficulty exhaling air, as it requires additional effort.
- When performing the respiratory function, characteristic wheezing and whistling sounds are felt, which can be heard without the additional use of a phonendoscope. With auscultation it is difficult to make a mistake in making a diagnosis.
- During an attack, the patient assumes an orthopneic position.
It is important to identify the disease in the initial stages, since if symptoms worsen, there is a high risk of serious complications.
Any degree of severity of bronchial asthma began its development without global disturbances in the body. The further course of the disease leads to more serious pathologies:
- There is a loss of strength, poor health, the patient is unable to continue to perform motor actions, shortness of breath appears and the asthmatic can only assume the position of orthopnea. Between attacks, the patient leads a normal lifestyle.
- Blueness of the skin, acrocyanosis. Symptoms lead to asphyxia and respiratory failure.
- Tachycardia. During an attack, the myocardium contracts significantly. In the middle stage of the disease, the contraction of the heart muscle noticeably decreases.
- Dystrophic changes occur in the nails. The plates bulge, the phalanges of the fingers thicken.
- Allergic bronchial asthma is characterized by the manifestation of signs of pulmonary emphysema. As a result of this flow, the chest becomes more voluminous, bulges, and the pulmonary boundaries (percussion) expand. Auscultation shows decreased breathing.
- Symptoms of cor pulmonale. Pulmonary hypertension in the pulmonary circulation appears as a result of severe disease. Pathological changes occur in the heart muscle.
- With bronchial asthma, due to the lack of normal respiratory function, the head hurts and feels dizzy.
- Having been diagnosed with bronchial asthma, the body is more susceptible to allergic reactions and diseases (rhinitis, eczema, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis).
Characteristics of the disease and symptoms
Allergic asthma is the most common form of bronchial asthma, which is a chronic heterogeneous disease that causes constant inflammation of the bronchi.
The most common cause of asthma is allergies. An allergy is an overreaction of the immune system against harmless substances such as pollen. And the most common form of allergy is hay fever: plant pollen causes nasal congestion, sneezing and often itchy eyes.
The mucous membranes of the bronchi have a similar structure to the nasal mucosa and therefore can react to allergens in a comparable way. This can lead to the development of allergic asthma. The mucous membrane of the bronchi swells, mucus is intensively formed, and the airways narrow. Cough, shortness of breath and chest tightness are typical symptoms.
Bronchial asthma has allergic and non-allergic triggers, although mixed forms are possible. The most common trigger is allergies and especially all-season allergens such as pets, mites and dust. Other common allergens:
- alder and birch pollen (one family of allergens);
- grass and rye pollen;
- animal hair (for example, dog, guinea pig, cat);
- mold spores.
The classic causes of bronchial asthma are physical stimuli:
- induced physical activity;
- hormonal influences;
- irritating stimuli such as cigarette smoke;
- viral infections.
In allergic asthma, symptoms in adults are mixed. This means that both allergic and non-allergic stimuli can trigger an asthma attack. Different stimuli can reinforce each other. For example, physical stress or smoking can increase the sensitivity of the bronchial mucosa to allergens. Both allergic and non-allergic rhinitis have a significant impact on the course of bronchial asthma.
The manifestations of the disease are varied. Symptoms can vary greatly from patient to patient. Episodes of coughing and wheezing , possibly with sputum and a night cough, are typical This can sometimes be followed by a long period without symptoms. Shortness of breath due to allergies in adults is a constant symptom.
Disease severity - classification
The disease is characterized by a progressive course that appears from time to time. There are several forms of the disease, and depending on a number of factors, the severity of the disease varies among patients. If you do not allow bronchial asthma to progress, this will prevent concomitant illnesses.
Clinical forms:
- Non-infectious-allergic (atopic) - it is characterized by the appearance of signs of suffocation without foci with inflammation in the respiratory tract. Over time, the situation becomes more complicated and leads to an asthmatic state of lack of air (up to several days).
- Infectious-allergic - bronchopulmonary infection can become the primary ailment for allergic bronchial asthma. Inflammatory foci in the nasopharynx also begin.
- Mixed - it tends to develop without the influence of a virus; pathogenic microflora joins during the disease process.
- The disease progresses atypically: signs of acute emphysema appear, and there is a lack of air in the lungs—oxygen starvation.
There are three degrees of severity of allergic bronchial asthma:
- Mild course with rare attacks, short duration. In the interval between attacks, the person leads a normal lifestyle.
- The course is of moderate severity. Attacks occur more frequently and affect certain systems and organs. Work activity should be moderate.
- Heavy current. Constant attacks of oxygen starvation, feeling of suffocation.
Degrees of the disease
Allergic bronchial asthma comes in 4 forms of severity, the division depends on the severity of general symptoms and the severity of the person’s condition:
- Intermittent degree. Attacks of suffocation during the day occur very rarely, no more than once a week. At night, attacks occur no more than 2 times a month. Relapses of the disease pass quickly enough and have virtually no effect on the general health of the patient .
- Mild persistent degree. Signs of the disease appear more often than once a week, but no more than once a day. More than 2 night attacks may occur in a month. During a relapse, the patient's sleep is disturbed and his general health deteriorates.
- Persistent asthma of moderate severity. The disease occurs almost every day, and attacks during sleep occur more than once a week. The patient's sleep quality deteriorates and performance decreases.
- Severe persistent asthma. The disease manifests itself very often, both during the day and at night. The patient's performance and physical activity are greatly reduced.
Symptoms and further treatment differ at different stages of the disease. In the mildest cases, it is enough to eliminate the allergen and the patient’s condition improves, but in severe cases of allergic asthma, various medications are prescribed to stabilize the condition .
There are many different allergens in nature. It is not possible to completely protect a person from them.
Diagnosis of the disease
Allergic bronchial asthma in children is a common disease often diagnosed in children. In the first stages, signs indicate obstructive bronchitis. In this case, it is important to differentiate the disease in a timely manner, and for this purpose an integrated approach is used. Bronchial asthma of allergic etiology is manifested by frequent monthly attacks.
The disease has symptoms of many pathologies. You should not try to diagnose yourself. How to distinguish asthma from allergies, and which treatment methods are more effective, should be determined by the attending physician. For effective treatment, you should not postpone a visit to a therapist, and subsequently to an allergist. The list of examinations indicated for such clinical manifestations includes:
- Standard blood and urine tests to rule out respiratory illnesses.
- Examination of mucous secretions and sputum.
- Chest X-ray.
- To exclude cardiac asthma, an ECG is justified.
- Carry out thorough auscultation.
About 10% of people are diagnosed at work; asthma makes itself felt when in contact with allergens and irritants. The disease can be caused by:
- Animals - from veterinary and agricultural workers.
- Woodworking industry, plant components - carpenters, printers, confectioners.
- Contact with enzymes - healthcare workers, bakers, pharmacists.
- People working with anhydrites (electronics, siols, paints - chemical production).
- Diisocyanates (foams, varnishes, polyurethane - rubber manufacturers and foundry employees are susceptible).
- Latex.
- Metal salts.
- Amines.
The signs of the diseases are similar because they are concomitant.
Allergic asthma in children
Allergic asthma in children can manifest itself at absolutely any age , but more often it happens after one year. Increased risk of developing diseases in children who have a predisposition to allergic diseases, as well as in patients with previously noted allergic diseases in the past.
Often allergic asthma in children can be hidden under the guise of obstructive bronchitis. For this reason, if a child has already had 4 or more episodes of obstructive bronchitis (bronchial obstruction) in one year, an urgent need to go to an allergist and begin effective treatment.
Treatment of allergic asthma in children begins with identifying the allergen that triggered the allergic reaction. It is recommended to administer medications by inhalation using an ultra-fine dispersed spray of the drug, carried out under the supervision of the attending allergist (immunologist). This procedure significantly increases the effectiveness of treatment and helps improve immunity.
Treatment methods
Therapy for allergic asthma is prescribed after an accurate diagnosis has been established. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the qualifications of the attending physician and timely treatment.
With such a disease, it is important to identify the cause that causes dangerous symptoms and limit the patient’s interaction with allergens and attack triggers as much as possible. Only people suffering from this disease can identify the triggers that provoke the appearance of symptoms of allergic asthma.
Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT therapy) is used for treatment. To ensure the effectiveness of immunotherapy, solutions of allergens are introduced with increasing dosages.
Inhalations are also used to relieve symptoms and methods of alternative medicine, which are allowed only after consultation with the attending physician. It is also recommended to review your diet so as not to provoke a reaction caused by a food allergy.
How to cure the disease
Every person is interested, if he has been diagnosed with allergic asthma, how to treat such an ailment.
To successfully fight the disease or at least reduce the number of attacks, it is necessary, if possible, to eliminate from the environment all objects that are provocateurs.
The following measures are usually taken:
All things in which dust can accumulate are removed - carpets, thick curtains. Frequent thorough cleaning of the house is simply necessary. Use of dust-proof coverings for mattresses and pillows. Windows are kept closed to prevent dust from entering the house from outside. Air conditioners are used with replaceable filters. Humidity in the house should be no more than 50%. When this indicator is exceeded, a comfortable environment for the development of ticks is created.
If the measures taken do not help to completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease, then medications are used. But it is important to remember that allergic asthma cannot be treated on its own. Treatment medications should only be recommended by a doctor.
Medicines for the treatment of allergic asthma
The following medications are used to treat allergic bronchial asthma:
For the main regimen, beta2-agonists are used:
- Salbutamol;
- Ventolin;
- Formoterol.
Inhalations with glucocorticosteroids (fluticasone) have worked well. The doctor also prescribes monoclonal antibodies, antileukotriene medications, cromones, methylxanthines (Theophylline). Often, the doctor considers it appropriate to prescribe combination drugs that contain active components from different groups of treatment agents (Seredit).
Additionally, antihistamines (Loratadine) and mucolytics (Lazolvan) are used to relieve symptoms, but it is important to understand that their task is to eliminate the signs of the disease, and not the pathology itself.
Treatment
Treatment of allergic asthma includes the same medications as therapy for asthma of other origins. But we must not forget that the course of the disease also depends on the degree of susceptibility to the allergen:
- If a person suffers from allergic reactions, he should, if necessary, take antiallergic drugs, which are available in abundance in the pharmacy chain. Such drugs block special receptors that are affected by histamine. Even if an allergen enters the body, allergy symptoms are not as severe or are not observed at all. If contact with an irritating substance cannot be avoided, then you need to take antiallergic medications in advance.
- There is an original treatment method in which doses of the allergen are introduced into the human body in increasing volumes. Thanks to this treatment, a person’s susceptibility to the irritant is reduced, and attacks of bronchial asthma become less frequent.
- Inhaled administration of certain hormonal drugs and long-acting β2-adrenergic receptor blockers are the most common methods of treatment. Thanks to such drugs, it is possible to control the disease for a long time.
- The patient is injected with specific antibodies that are antagonists of immunoglobulin E. This therapy helps to stop the high sensitivity of the bronchi for a long time and prevent relapses of the disease.
- Cromones - these medications are often prescribed to treat allergic-type asthma in children. Treatment of adult patients with such drugs does not bring the desired result.
- Methylxanthines.
- If the disease is in the acute stage, the patient may be prescribed strong adrenergic receptor blockers. In addition, in such cases, the patient is given adrenaline injections and hormonal drugs are prescribed in tablets.
To relieve an attack of suffocation, special medications are used in the form of inhalations . This form of the drug goes directly to the site of inflammation and has a therapeutic effect instantly. Medicines in the form of an aerosol rarely cause side effects, since they work only locally and do not have a systemic effect on the entire body.
Treatment of patients with allergic bronchial asthma is carried out on an outpatient basis. Only in severe cases can the patient be hospitalized for assistance, most often this occurs during an exacerbation of the disease. Asthmatics are registered with a doctor and are regularly observed by specialists.
Dangerous complications of allergic bronchial asthma include heart and respiratory failure. In severe cases of the disease, the patient may die from suffocation.
Forecast and preventive measures
To prevent the development of the disease you should:
- Avoid contact with professional influencing factors; sometimes it is worth changing jobs.
- Monitor the quality of food. Give preference to a healthy lifestyle.
- Do not start treatment for colds.
- Drug treatment should be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
- It is important to quit smoking.
If a diagnosis already exists, it is necessary to keep the situation under control:
- Follow all doctor's recommendations.
- Don't skip medications.
- Do not be in smoky rooms.
- Avoid emotional stimuli and stress.
With timely detection of the disease and correctly prescribed treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. In cases where the disease gets out of control, the course becomes severe, which leads to respiratory failure and, in the event of attacks, death is possible.
Reasons for development
In asthma of allergic origin, the so-called IgE immunoglobulins are directly involved in the body's specific immune response. The danger is that these antibodies cause an immediate allergic reaction. Therefore, an attack of bronchial asthma usually begins suddenly, literally within a few minutes after the penetration of the allergen. The development of the disease, which is also called atopic bronchial asthma, can be influenced by various factors:
- bad heredity;
- infectious diseases of the respiratory tract;
- smoking;
- harmful working conditions;
- long-term use of medications.
And exacerbation and attack are most often caused by inhaled allergens:
- pollen of flowering plants;
- animal hair;
- fungal spores;
- household dust;
- domestic tick secretions.
Forms of the disease
According to the principle of occurrence, allergic asthma is:
- Household form of asthma. Occurs as a result of the formation of hypersensitivity to dust. Most often it worsens in winter, when there is not enough air humidification. The attack is long lasting and goes away after changing the home environment. Often, household asthma is accompanied by bronchitis, which arises from an allergic reaction of the body.
- Fungal atopic form of asthma. Depending on the formation, the dispute can be either year-round or seasonal. The attack worsens at night, in rainy weather, when fungal spores grow. The body is sensitive to the seasonal formation of fungi, so the patient feels better in winter when snow falls.
- Pollen form of asthma. It worsens when plants bloom. First, the patient develops a runny nose due to allergies, then an attack of suffocation appears. Pollen asthma can occur from eating grains or seeds.
- Infectious-allergic asthma. This form occurs if chronic foci of inflammation develop in the respiratory system.
- Epidermal-atopic form of asthma. Occurs when there is an irritant present in the skin, saliva or fur of animals.
According to the level of progression of the disease, they are divided into:
- Mild intermittent degree. An attack of suffocation occurs rarely, about a couple of times a month. There are no attacks at night.
- Mild persistent degree. The attack occurs 4-6 times a month, night attacks are possible a couple of times a month.
- Average degree. The attack worries me every day, night suffocation occurs at least 4 times a week. The attack interferes with physical activity.
- Severe degree. The attack appears 4-5 times a day, the same number at night.
Allergic asthma: characteristics, causes and treatment
Bronchial asthma is an extremely common disease, affecting approximately 10% of the world's population. This disease is chronic, develops rapidly and has characteristic attacks in which the lumen of the bronchi narrows significantly, which entails attacks of suffocation. Allergic asthma occurs when the allergy is extremely neglected and is also chronic in nature. In this article we will consider in detail the causes of atopic asthma, its characteristics, as well as the treatment of this disease.
Causes of the disease
The reasons why allergic bronchial asthma may occur are as follows:
- Genetic predisposition. Medical scientists have proven that asthma itself cannot be inherited, but a predisposition to development is transmitted. If one of the parents is sick, then the chance of developing a childhood disease will be 45%. If both parents are sick, then in 70% of cases the child experiences immediate hypersensitivity.
- Frequent relapses of diseases of the bronchial tree resulting from infections. As a result of the inflammatory process, a hypersensitive environment develops in the bronchial cavity.
- Long-term tobacco abuse. Even passive smoking increases the risk of developing asthma. Smoking during pregnancy increases the likelihood of developing the disease by 68%.
- Spending a long time in a room with fungus, mites, mold or dust.
- Eating food with preservatives, dyes, GMOs.
- Long-term use of medications that irritate the body's immune function.
- Harmful working conditions.
- Disturbed ecology in the place of residence.
Sometimes the reasons that influenced the occurrence of pathology are complex.
Disease prevention
The following recommendations will help reduce the likelihood of allergic asthma:
- Take antihistamines twice a year.
- Ventilate the room several times a day.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. Try to adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
- Monitor your vitamin D levels and take complex products containing different vitamins and minerals.
- Lead an active lifestyle and play sports.
- Perform breathing exercises daily.
- In spring and summer during the flowering period, additionally use anti-allergy medications and keep the windows closed.
- Wash clothes in boiling water.
- Wear clothes made from hypoallergenic natural materials.
- Install a humidifier in the bedroom.
- Get rid of carpets, feather pillows, toys.
It must be remembered that preventive measures do not guarantee that an asthma attack will not begin if there is a hereditary predisposition. However, with their help, the number of asthma attacks can be reduced. There is no medicine that can prevent asthma.
Why is bronchial asthma dangerous?
Why is bronchial asthma dangerous? First of all, this disease poses a threat to the body with its complications. Severe attacks of suffocation, characteristic of uncontrolled asthma (that is, when prescribed treatment is ineffective), cause significant physical suffering to the patient and have a negative effect on his psyche.
However, in addition to this, uncontrolled asthma can cause many pathologies, which are usually divided into groups depending on which organ or system of the body is most affected.
The greatest danger in uncontrolled asthma is
- acute and chronic respiratory complications
- cardiac complications
- brain
- metabolic
- gastrointestinal
The first two groups of complications (respiratory and cardiac) can pose a direct threat to the patient’s life.
From this point of view, acute respiratory complications such as:
- status asthmaticus (prolonged attack of suffocation)
- acute respiratory failure (a sharp decrease in the amount of oxygen entering the lungs)
- spontaneous pneumothorax (lung rupture)
- emphysema of the lung.
Cardiac complications of asthma such as:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure during an asthma attack
- arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
- sudden cardiac arrest.
Cerebral complications of asthma are also dangerous, among which respiratory encephalopathy plays a leading role. In this case, the activity of the brain is disrupted due to a deterioration in its oxygen supply. This deterioration is associated with impaired gas exchange in the lungs due to bronchial obstruction.