Betahistine is a histamine receptor antagonist. Instructions for use will show you how to properly take 8 mg, 16 mg and 24 mg tablets for the treatment of dizziness, headaches and Meniere's syndrome. What Betagistine helps with, information on prices, analogues and patient reviews will also be presented in the article.
Release form and composition
Betahistine is produced in the form of tablets that are taken orally. Each tablet for dizziness is round in shape and colored whitish-yellow.
Original packages from different manufacturers contain 20 or 30 doses, as well as official instructions, which are approved in Russia.
- Tablets are flat-cylindrical, round, white, marked with the dose of the active substance (8 mg).
- The tablets are oblong, biconvex with rounded edges, with markings applied to the surface indicating the dose of the active substance - 16 and 24 mg, respectively.
The main active ingredient is betahistine dihydrochloride.
Betagistin-Teva tablets 24 mg No. 60 in Nur-Sultan (Astana)
Instructions for medical use of the drug
Betagistin-Teva
Trade name Betagistin-Teva
International nonproprietary name Betahistine
Dosage form Tablets, 16 mg and 24 mg
Composition One tablet contains the active substance - betahistine hydrochloride 16 mg or 24 mg, excipients: povidone K90, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, crospovidone, stearic acid
Description Cylindrical tablets of white or almost white color, with a chamfer on both sides, with the imprint “B 16” on one side and a score on the other (for a dosage of 16 mg). Tablets are round, biconvex, white or whitish in color, with a score on one side (for a dosage of 24 mg).
Pharmacotherapeutic group Other drugs for the treatment of diseases of the nervous system. Remedies for dizziness. Betahistine. ATX code N07CA01
Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics After oral administration, betahistine hydrochloride is absorbed quickly and completely. Plasma protein binding is low (less than 5%). Betagistine hydrochloride is rapidly metabolized in the liver to the inactive main metabolite, 2-pyridylacetic acid and dimethylbetagistine. The half-life is 3.5 hours. Excretion of betahistine hydrochloride is 90% through the kidneys in the form of the main metabolite. Pharmacodynamics Betahistine hydrochloride is a synthetic analogue of histamine. Acts on histamine H1 and H3 receptors of the inner ear and vestibular nuclei of the central nervous system. Improves microcirculation and permeability of capillaries of the inner ear, increases blood flow in the basilar arteries, normalizes endolymph pressure in the labyrinth and cochlea.
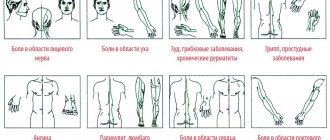
Indications for use For the treatment of Meniere's disease or Meniere's syndrome, vestibular dizziness of various origins (dizziness with nausea and vomiting, ringing in the ears, hearing loss)
Method of administration and dosage The recommended starting dose is 24 mg per day (or 16 mg 2 times a day) orally during or after meals. The daily dose can be increased to 48 mg. During the course of treatment, the dose is adjusted depending on the therapeutic effect. The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the attending physician individually. A stable therapeutic effect occurs after two weeks of treatment. The best results are observed after several months of treatment.
Side effects Rarely - headache, drowsiness - increased intracranial pressure - feeling of heat - palpitations, tightness in the heart - gastrointestinal disorders: nausea, vomiting, heartburn, pain in the epigastric region, flatulence (these symptoms will be less pronounced if you take the drug during meals or reduce dosage) - exacerbation of a history of bronchial asthma, rash, urticaria, itching, anaphylactic reactions
Contraindications - hypersensitivity to betahistine hydrochloride and/or to any of the components of the drug - pheochromocytoma - pregnancy and lactation - childhood and adolescence under 18 years of age - galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption Precautions: - gastric ulcer - bronchial asthma - in patients with urticaria, rash or allergic rhinitis - severe hypotension
Drug interactions The metabolism of betahistine is inhibited by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory drugs, including subtype B (eg, selegiline). Since betahistine hydrochloride is a histamine analogue, simultaneous use of H1 antagonists may cause a mutual weakening of the effect of the active agents.
Special instructions Caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug in patients with peptic ulcers (including a history), as dyspepsia may develop. Symptoms of hives, rashes, and allergic rhinitis may worsen when taking betahistine. Features of the influence on the ability to drive a vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms Due to the side effect of drowsiness, a decrease in the ability to drive a car and control machines is possible.
Overdose Symptoms: dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, ataxia, facial flushing, dizziness, increased heart rate, bronchial spasm and edema, and convulsions may also occur after taking very high doses. Treatment: symptomatic (gastric lavage, use of activated carbon). There is no specific antidote.
Release form and packaging 10 tablets in a blister pack made of PVC film and aluminum foil. 3 or 6 contour packages together with instructions for medical use in the state and Russian languages are placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions Store at a temperature not exceeding 25ºС. Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life: 3 years Do not use after expiration date.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies By prescription
, Germany
Packer "Merkle GmbH", Germany
Why is Betahistine prescribed?
Tablets are prescribed for problems with the vestibular apparatus, that is, vestibular vertigo. Moreover, it is prescribed both for treatment and for preventive purposes.
This drug is used for Meniere's syndrome or disease, hearing loss, dizziness, tinnitus, headache, vomiting, nausea.
After taking the tablets, the maximum concentration in the blood is observed three hours later. The drug is excreted by the kidneys within 24 hours; the half-life is four hours.
pharmachologic effect
A drug that improves microcirculation.
The active component of the drug is structurally similar to histamine, which is a regulator of many physiological processes.
The mechanism of its effect on the human body is as follows:
- Blocking H2 receptors located in the central nervous system. Increased production of neurotransmitters that affect other types of sensory nerve endings.
- Stimulation of H1-, blocking of H3-histamine receptors. The former are located in the neuroreceptor cells of the inner ear and promote local vasodilation, while the latter are responsible for the release of serotonin and other neurotransmitters that reduce the activity of the endings of the vestibular nerves.
- Normalization of the transmission of nervous excitation in the vestibular analyzer - a section of the inner ear in which there is a complex of neurons responsible for the balance of the human body in static conditions and during movement.
- Dilatation of microblood vessels, relaxation of their sphincters.
- Improving blood microcirculation in the cochlea and labyrinth (inner ear), increasing blood flow to its vascular stria.
- Normalization of the pressure of the endolymph filling the cavity of the vestibular apparatus, elimination of endolymphatic hydrops characteristic of Meniere's disease.
At the same time, unlike natural histamine, betahistine does not create side effects in the form of impaired permeability of the walls of blood capillaries, lowering blood pressure, increasing the tone of the smooth muscles of the bronchi and gastrointestinal tract, and the production of digestive juice.
Betaserc, patient reviews of which indicate positive dynamics for dizziness of various natures, has the following therapeutic effect:
- reducing the number of episodes of dizziness and the severity of their manifestation;
- stopping tinnitus;
- normalization of coordination of movements and balance;
- reduction of hearing impairment.
Mechanism of action of Betaserc
Thus, the pharmacological properties of the drug are characterized by a double effect: relieving dizziness and improving blood supply to the inner ear. This influence is carried out selectively.
In addition, the drug increases blood flow in the vertebrobasilar and carotid areas of the brain, which helps improve cognitive abilities in patients with chronic vascular insufficiency.
Suppression of the activity of the vestibular nuclei has been confirmed by experiments conducted on animal models. They showed a marked increase in serotonin levels in the medulla oblongata, which has a vestibulodepressive effect.
Medical instructions for use
Betahistine must be taken strictly according to the instructions.
Dosage for adults
Anti-dizziness tablets must be taken with food or after meals at a dosage of 8 or 16 mg three times a day during the initial stage of treatment with this drug.
Maintenance doses of the drug usually range from 24 to 48 mg per day at the discretion of the attending physician. The daily dose should not exceed 48 mg. The dosage can be adjusted taking into account the individual health characteristics of patients. Sometimes improvement may only be seen after several weeks of treatment.
Treatment of patients with liver, kidney and heart failure
For patients with liver failure, treatment with Betahistine should be prescribed after a thorough study. Treatment of patients with renal and heart failure is also prescribed.
Treatment of elderly patients
In old age, Betahistine should be used with caution, since in this population group there is a high probability of negative reactions from the body to the active and auxiliary substances included in the medicine.
Instructions for use for children and adolescents
Betahistine tablets are not recommended for use in children and adolescents under the age of 18 due to the lack of data on the safety and effectiveness of the drug.
Interaction
Antihistamines and MAO inhibitor drugs (for example, selegiline) reduce the effect of Betagistine.
The metabolism of the drug may be inhibited by MAO blockers.
Betahistine is an analogue of histamine, so it is possible that the former may influence the effectiveness of histamine H1 receptor blockers.
Antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs and Betaserc mutually reduce the therapeutic effect when taken simultaneously. Metabolism may also deteriorate when using MAO blockers (monoamine oxidase), which include drugs such as Phenelzine, Selegeline and other antidepressants.
Interaction with antihistamines is due to the antagonistic process of action on H1 receptors.
Period of pregnancy or breastfeeding;
Individual hypersensitivity, intolerance or allergic reactions to any components of the drug.
The drug should be used with caution if a person has bronchial asthma or a history of gastric or duodenal ulcers. These diseases are not absolute contraindications, but if they are present, the person’s condition should be carefully monitored by a doctor during the entire period of using Betaserc.
Contraindications
Betaserc, patient reviews of which indicate the effectiveness of the course regimen, is prescribed for the following diseases:
- Meniere's disease, in which there is an increase in the amount of endolymph and its pressure in the labyrinth of the ear, endolymphatic hydrops occurs in the form of attacks of gradually increasing deafness, a feeling of fullness and tinnitus, dizziness, nausea and other autonomic disorders. Deterioration of balance may continue for several days after an acute attack. This disease is both hereditary and acquired.
- Other pathologies accompanied by dizziness, deterioration of hearing acuity, disorders of the vestibular system:
- dropsy of the labyrinth or its inflammation;
- stroke;
- inflammation of the vestibular nerve;
- labyrinthine disorders after neurosurgical intervention;
- brain tumors.
- Vertebro-basilar syndrome, in which blood flow in the basilar artery of the brain deteriorates.
- Acute attacks of dizziness (vertigo).
- Cervical osteochondrosis, in which the normal movement of blood in the arteries of the brain is disrupted due to mismatched signals from the cervical proprioceptors.
- Encephalopathy resulting from traumatic brain injury.
- Atherosclerosis of the arterial vessels of the central nervous system, in which blood flow is disrupted due to narrowing of the lumen of the arteries by cholesterol deposits, up to their complete blockage.
- Dyscirculatory encephalopathy resulting from hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, as well as against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
The drug can be used not only to treat, but also to prevent vertigo. Unlike other drugs for similar purposes, it does not have a sedative effect and does not depress the central nervous system, which helps to activate compensatory processes during rehabilitation and recovery.
Studies have shown that its use in complex drug therapy in elderly patients with chronic cerebral circulatory disorders can reduce the manifestations of vestibular and vegetative-vascular disorders.
Betaserc is well tolerated by patients of all age groups. According to reviews, the advantages of the drug include its effectiveness, ease of administration and selection of the required dosage.
A few contraindications for this medication include the following:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (in the acute phase);
- bronchial ac src=»https://healthperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/vinilin-balzam-shostakovskogo-3.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»600″ height=»321″[/ img]
- hormonally active tumor of chromaffin cells of adrenal or extra-adrenal localization (pheochromocytoma);
It also cannot be used in case of individual intolerance to the components and in the first trimester of pregnancy. In medical practice, there is no data on the safety of the drug during lactation and on the possibility of its penetration into breast milk. Therefore, the drug is usually not prescribed to nursing mothers.
The decision on the possibility of its use in these cases is made only after analyzing the therapeutic effect and possible complications for the child.
Instructions for use indicate a wide range of uses of the drug Betahistine:
- Meniere's syndrome or disease;
- diseases accompanied by sudden dizziness, vomiting, nausea, tinnitus, hearing loss (similar to Meniere's disease);
- insufficient blood circulation in the brain after an ischemic stroke;
- to increase the level of memory and mental activity in elderly patients;
- age-related balance disorders;
- motion sickness in transport;
- prevention of cerebral vascular lesions.
As well as treatment of dizziness caused by disorders of the vestibular apparatus of various etiologies:
- infectious diseases;
- post-traumatic encephalopathy;
- severe cerebrovascular accidents;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels (as one of the components of complex therapy);
- lesions of the neck organs;
- disorders caused by taking medications;
- hemorrhages in the cerebellum;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- vestibular neuritis;
- benign positional vertigo after neurosurgical and ophthalmological interventions;
- labyrinthitis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- psychogenics.
It is not recommended to take the drug if:
- lactose deficiency;
- lactose intolerance, poor absorption syndrome of glucose-galactose;
- hypersensitivity to betahistine and/or to individual components of the drug.
Prescribe with caution for the following diseases:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum;
- bronchial asthma;
- pheochromocytoma (adrenal tumor).
Patients must be examined regularly during treatment.
Due to the lack of studies, the drug is not prescribed to children (under 18 years of age).
The drug is not prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding, since there is no data on the effect on fetal development.
It is also unknown whether the drug is excreted in breast milk.
Betahistine does not have a negative effect on the functioning of the kidneys and liver. There is no need to adjust the dose in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency.
For patients over 60 years of age, less intensive therapy is recommended than for people in the middle age group (due to the fact that the compensatory function of the body increases in old age).
Indications for use of Betaserc:
- Meniere's disease;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency, atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries, post-traumatic encephalopathy (as a component of complex therapy);
- syndromes characterized by tinnitus, increasing hearing loss, dizziness, including hydrops of the inner ear, labyrinthine and vestibular disorders, labyrinthitis, vestibular neuritis, benign positional vertigo.
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- pheochromocytoma;
- not recommended for use in persons under 18 years of age.
It is recommended to use the drug with caution (under medical supervision) for persons with peptic ulcer disease or bronchial asthma.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
There is no proven data on the safety of the drug for pregnant women, since no special studies have been conducted in women. The potential threat to the formation and development of the child has not yet been determined. For this reason, Betahistine is prohibited for use in women. In particularly difficult cases, it may be prescribed in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters.
Breastfeeding women should also not be treated with Betagisitn, since it is unknown whether the active substance passes into milk or not. The question of prescribing medication should be decided after analyzing the benefits of breastfeeding for the child and the possible threat to his health.
What is it prescribed for?
Self-medication can lead to irreparable consequences.
"Betagistin" is available only with a doctor's prescription, the dosage is determined for each case individually. Unauthorized changes to prescriptions can have detrimental health consequences. The drug is prescribed for Meniere's syndrome, headache attacks due to pathologies of the inner ear, and for diseases of the vestibular system with frequent dizziness. Reduces the risk of developing deafness or hearing loss. "Betagistin" can expand the basilar artery, which leads to normalization of memory and improvement of cognitive abilities.
Analogs
- Asniton;
- Betaver;
- Betahistine hydrochloride;
- Betahistine dihydrochloride;
- Betaserc;
- Betacentrin;
- Vasoserc;
- Vestibo;
- Westicap;
- Denoise;
- Microzer;
- Tagista.
When choosing analogues, you must remember that the instructions for use of Betahistine, price and reviews do not apply to drugs of similar effect. Replacing the drug is permissible only after the recommendation of a doctor.
Side effects
The instructions for use of the drug Betahistine indicate the following manifestations:
- from the gastrointestinal tract: heaviness in the stomach, nausea, heartburn, indigestion;
- skin reactions (rare): rash, urticaria, Quincke's edema;
- cardiovascular system: tachycardia, increased intracranial pressure;
- CNS: drowsiness, headache;
- immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, for example, anaphylaxis;
- other manifestations: feeling of heat.
Statistically, the drug is tolerated quite well by patients.
Overdose
Symptoms: vomiting, cramps, nausea, dry mouth, abdominal pain.
Signs characteristic of too high histamine levels may also occur: facial flushing, decreased blood pressure, edema, tachycardia.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote. Symptomatic treatment and general measures to remove toxins are carried out (taking activated carbon, gastric lavage).
The drug is generally well tolerated by patients, but in rare cases the following side effects may occur:
- Gastrointestinal tract:
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of heaviness or pain in the stomach;
- flatulence;
- dyspeptic disorders.
- Immune system disorders in the form of allergic manifestations:
- rash (hives may occur);
- itchy skin;
- Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
The drug does not affect blood pressure, does not cause inhibition of psychomotor reactions, or decreased concentration and attention. Therefore, it is safe for the treatment of patients whose activities involve operating high-risk technical devices and mechanisms, including cars.
special instructions
If the patient has a history of duodenal or gastric ulcer, as well as bronchial asthma, pheochromocytoma, taking Betagistine tablets must be carried out under the constant supervision of specialists.
This medicine is not recommended for use in children under 18 years of age. This is due to the fact that there is no reliable data on the positive effects of using the drug at this age.
Betahistine should not be prescribed to pregnant women or breastfeeding women. If there is an urgent need for a woman to take it during lactation, breastfeeding must be stopped. You can resume feeding after complete discontinuation of the drug.
Betagistine tablets are not able to influence the patient’s reaction and memory, and also do not have a hypnotic effect. For this reason, they are not contraindicated for drivers and persons engaged in potentially hazardous activities that require quick reaction.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Taking the tablets orally is accompanied by rapid absorption of the active component in the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in the blood serum accumulates after 3 hours. Metabolic products, which are inactive compounds, are excreted mainly through the kidneys in the urine during the day (85% of the initial dose). The half-life is about 3-4 hours.
Eating food reduces the rate of absorption, but the total absorption is almost the same as in the case of administration on an empty stomach. The main metabolite is 2-pyridylacetic acid, which has no biological activity. The rate of its elimination remains constant when taking the drug in a dosage of up to 48 mg.
Pharmacodynamics
An artificial analogue of histamine. The effect of betahistine has not been fully studied. There are only a number of hypotheses confirmed by clinical data:
- active substance – partial stimulator of H1-histamine receptors and blocker of H3-histamine receptors of the vestibular centers of the nervous system; improves histamine metabolism and its release due to the above properties;
- betahistine increases blood circulation in the inner ear, relaxing vascular sphincters in this area, and also enhances microcirculation in the brain;
- betahistine stimulates the restoration of vestibular function after vestibular neurectomy in animals and humans;
- dose-dependently reduces the generation of impulses in neurons of the vestibular nuclei.
The therapeutic effect of betahistine was demonstrated in patients with Meniere's syndrome and vestibular vertigo, which was expressed by a decrease in the severity and frequency of dizziness attacks.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, the active substance is actively absorbed from the intestine and is almost completely transformed to form a derivative of 2-pyridylacetic acid. The content of betahistine in the blood is low.
Concomitant food intake may slow down the absorption of betahistine. Reaction with blood proteins does not reach the 5% barrier. The maximum concentration of 2-pyridylacetic acid in the blood occurs 1 hour after consumption. The half-life is approximately 3 and a half hours.
The metabolite is actively evacuated in the urine. Excretion of betahistine itself through the kidneys or intestines is negligible.
Indications for use
Indications for use approved by manufacturers are the following diseases:
- prevention and treatment of dizziness of various etiologies, including VSD;
- vertebrobasidal insufficiency;
- post-traumatic encephalopathy;
- atherosclerotic brain lesions;
- vestibular neuritis;
- labyrinthitis;
- dizziness caused by ophthalmic or neurosurgical operations;
- a feeling of discomfort in the hearing organs. Betahistine is often prescribed for tinnitus in various vestibular and neurological pathologies;
- Meniere's disease.