Many people are familiar with the disease chickenpox. The virus that causes this disease is very insidious, as it remains in the body for life. Most of the time it is in a latent form and does not bother a person at all. But it happens that the virus wakes up and begins to manifest itself. In this case, the person is diagnosed with herpes zoster. The symptoms and treatment of this disease are worth considering in more detail.
Description of the disease
Herpes zoster also has other names - “herpes zoster” or “herpes zoster” . Its causative agent is the third type of herpes virus (Varicella zoster). As noted earlier, this virus settles in the human body at the time of infection with chickenpox. Thus, herpes zoster is a recurrent herpes virus type 3.
The incubation period of herpes zoster can last for many years. According to medical statistics, most often a recurrence of shingles occurs in people aged 50 to 80 years (up to 60% of cases), but people under the age of 20 are least susceptible to this disease (less than 10% of cases).
Shingles is classified as an infectious disease because it:
- has a viral origin;
- its symptoms are similar to an infectious disease;
- affects the nervous system;
- transmitted by airborne droplets.
It is worth noting that Varicella zoster is a very unstable virus. If you heat it or expose it to ultraviolet light for ten minutes, it will be completely eliminated. However, the virus feels much more comfortable in the cold. Varicella zoster can withstand freezing without dying.
Diagnostic features
Which doctor should I contact if I suspect shingles? The primary diagnosis should be carried out by a dermatovenerologist, but as practice shows, if the disease begins to manifest itself with an increase in temperature or painful sensations, then patients, thinking that they have the flu, turn to a general practitioner.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Triderm for lichen in children
Diagnosis of herpes zoster
Differential diagnosis of heprevirus involves excluding signs of other diseases with similar symptoms. These include:
- eczema;
- bullous form of erysipelas;
- renal colic;
- catarrhal appendicitis;
- embolism or thrombosis of the branches of the pulmonary artery;
- pleurisy of the lungs;
- angina pectoris or, as it is popularly called, “angina pectoris”;
- inflammation of the appendix.
Laboratory diagnosis of herpevirus
To make a clear diagnosis, the patient is prescribed various procedures, among which it is worth highlighting the most effective:
- polymerase chain reaction (laboratory diagnostics that allows you to identify pathogenic microorganisms that cause infectious diseases);
- virus isolation in cell culture;
- immunofluorescence analysis (fluorescent antibody method);
- serological studies (study of antigens or antibodies in the blood);
- microscopic examination.
These laboratory diagnostic tests are required for severe or atypical forms of herpes zoster, as well as for children with a weakened immune system.
Symptoms and sensations
When the virus enters the body for the first time, which most often happens in childhood, a person is accompanied by hyperthermia, weakness, rash and itching. Within a week, the body develops stable immunity. However, when the virus is activated, a person suffers re-infection, but it manifests itself in a different form.
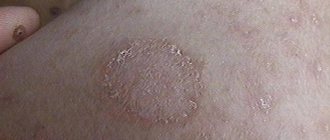
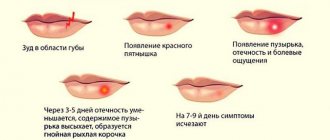
The first thing that begins to worry is itching, which is replaced by sharp pain in a certain area of the body. The temperature may rise, and sometimes slight dizziness occurs. The virus affects nerve areas, so tingling is also added to the symptoms. After two to three days, red spots appear on the body, which gradually begin to fill with a cloudy liquid. Such blisters very quickly turn into small ulcers, after which they become covered with a brown crust. As a rule, the disease goes away within two weeks, and pigmentation remains on the affected areas of the body for some time.
It is extremely important to remember that until the sores crust over, you should not come into contact with many people, as the virus is very contagious and can be passed on to others. To prevent family members from becoming infected, they should start using antiviral drugs in prophylactic doses.
An itchy rash may appear on only one side of the body along the nerve trunks. Most often, shingles affects the costal part and shoulder blade, less often - the neck and hips. A feature of the disease is that the affected areas are very painful, as the functioning of nerve cells is disrupted. Sometimes the pain is comparable to the sensation of a burn or electric shock. With mechanical contact, pain may intensify. The pain persists for some time after the ulcers have healed.
Forms of the disease with atypical herpes↑
Atypical herpes zoster also has several forms. Before prescribing drugs (for example, acyclovir), the diagnosis should be confirmed by specialists, since in the initial stages the symptoms are often similar to other diseases.
- Gangrenous - a severe rash that has the ability to spread across the skin, changing the direction and intensity of spread;
- abortive - blisters do not appear on the skin, but the pain remains;
- bullous - blisters merge into large papules;
- generalized - after a rash on the skin, the virus spreads to neighboring tissues, including mucous membranes;
- hemorrhagic – traces of blood are visible in the blisters;
- ophthalmic – localized around the eyes, can lead to glaucoma, cause paralysis or dysfunction of the facial nerves, and lead to loss of vision;
- ear – accompanied by pain in the ears, in rare cases resulting in hearing loss;
- cystic - the bubbles grow greatly, often gathering in groups;
- meningoencephalic - the virus affects the brain, which in 60% of cases results in the death of the patient.
When the virus relapses, it becomes weaker, but the risk of complications increases.
Causes and diagnosis of pathology
The main reason for the appearance of herpes zoster is the instability of the immune system. According to doctors, relapses can occur due to anything (stress, hypothermia, surgery, etc.), which can have a detrimental effect on the immune system.
The body suppresses the zoster virus throughout its life. But when defense mechanisms fail, it is simply impossible to cope with the virus. Most often, such disruptions in the functioning of the immune system and activation of the zoster virus are observed in the following cases:
- taking medications that suppress the immune system;
- AIDS, HIV;
- stress;
- depressive states;
- overheating or hypothermia;
- surgery and organ transplantation;
- oncological formations;
- radiotherapy and radiotherapy.
If a herpetic rash appears, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. In general, it is not difficult for a specialist to diagnose shingles, but the overall clinical picture can be blurred by general symptoms - intoxication, pain, weakness, fever. Therefore, differential diagnosis is carried out from eczema, chicken pox, erysipelas and herpes.
Depriving forms
To determine the degree of damage and choose a treatment method, several forms of herpes zoster are distinguished, depending on the type of rash and its contents:
- Bullous from the Latin word bulla, meaning bubble. These are single or fused vesicles with serous contents.
- Hemorrhagic - the same blisters, but with a bloody-serous composition, due to the weakness of the vascular wall. Usually accompanied by a serious violation of the general condition, observed in those weakened by a chronic disease.
- Gangrenous - characterized by the purulent contents of vesicles, melting of the surface layers of the skin, the formation of trophic ulcers and rough scarring. It is observed in the elderly and against the background of white and red blood diseases.
- Generalized – observed in patients with tuberculosis, AIDS, tumors and after radiation treatment and chemotherapy.
Treatment of herpes zoster
The most important rule in the treatment of herpes zoster is to immediately begin complex therapy. Measures must be taken immediately after the first symptoms, as delaying treatment can lead to complications.
Herpes zoster is treated by getting rid of the rash and suppressing the virus itself. So, it’s worth considering how to treat herpes zoster.
The first thing you need is antiviral drugs for topical use. Zovirax, Panavir and, of course, Acyclovir cope well with the external manifestations of herpes. A good remedy that inhibits the reproduction of the virus is Hyporamine ointment (5%), which is based on sea buckthorn extract.
Next, you need to choose an antiviral drug, but for oral administration. This may be Acyclovir tablets, Valacyclovir or Valtrex.
In cases where the pain at the site of the rash is unbearable, painkillers from the NSAID group are appropriate. This could be Meloxicam or Nimesil. For itching, an antihistamine - Suprastin or Tavegil - is suitable. And of course, a special place should be given to vitamin therapy. First of all, you should start taking B vitamins, and then those that the attending physician will select, based on the general clinical picture and the condition of the body.
Antibiotics for herpes zoster are rarely prescribed and only in cases where pyoderma develops or a bacterial infection occurs in parallel with herpes zoster. The need to take them is determined by the attending physician, but, as a rule, it is recommended to take drugs such as Tetracycline, Gentamicin or Oxacillin in difficult cases.
Treatment of herpes zoster with ointment
Treatment of herpes zoster using external means alone is ineffective. To achieve a complete cure, it is necessary to neutralize the virus that caused the development of dermatomycosis using antiviral drugs. External treatment is carried out comprehensively in order to achieve maximum therapeutic effect.
Acyclovir (ointment), epervudine, interferon, and alpizarin can be used as external medications. Alpizarin ointment is characterized by antibacterial, immunomodulatory, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. Epervudine and acyclovir are considered effective antiviral external agents aimed at combating the virus.
In addition to the anti-inflammatory and antiviral effect, interferon has an immunomodulatory effect. Since the shingles virus is formed as a result of immune disorders, during treatment special attention should be paid to increasing the body's defenses. Antiseptic drugs that are prescribed for chickenpox - castellani, zelenka - are also excellent for external use. They have drying and antimicrobial properties.
Virus prevention
There is a special vaccine against the zoster virus, Zostavax. It helps the body develop immunity to the virus. It has been proven that the vaccine protects the body by 50%. However, studies have shown that if a person does become infected with the virus, the disease occurs in its mildest form. You can protect your body not only by vaccination , but also by following some important rules:
- Avoid nervous tension.
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
- Monitor your diet and try to consume vitamins such as B, A, D, P, C, E in the right quantities.
- Keep the body in good shape, avoid a sedentary lifestyle.
In general, such universal rules are aimed at increasing the protective functions of the body. Therefore, if you follow them, you can protect yourself not only from the zoster virus, but also from many other diseases.
To summarize, it is worth noting that herpes zoster is a very unpleasant disease that causes a lot of inconvenience. The only thing a person can do to avoid a relapse of the zoster virus is to maintain a normal immune system and adhere to the basics of a healthy lifestyle. But if the virus does become active, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment. It is important to immediately consult your doctor, who will determine the stage of herpes zoster and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Antiviral agents
It is not possible to completely get rid of the virus, so the doctor prescribes drugs that only force it to return to a dormant state.
Acyclovir is considered the most effective remedy in this regard. The tablets are effective for both herpes zoster and herpes simplex.
Adults are prescribed 200 mg two to five times a day, regardless of meals. The duration of the course of treatment is determined by a specialist, but in any case not less than a week.
Valaciclovir also effectively copes with the attack of the virus - it is a derivative of acyclovir and has a stronger effect. Most often prescribed to elderly patients whose immune defenses are very weak. The action of the drug is aimed at suppressing the virus, which slows down its reproduction. Take 3 times a day, 2 tablet units. Therapy is carried out within a week.
Famvir acts similarly to previous drugs - it prevents the multiplication of viral DNA. Adults take 250 mg. 3 times/day. If the pathogen has penetrated the internal organs, the dosage is increased to 500 mg at a time, the frequency is the same.