Author of the article
Arthur Viniaminovich Artemyev
Urologist, gynecologist, practicing specialist
Articles written
64
Contact the author
Gynecological problem - endometrial polyp requires special attention and timely action. Without appropriate treatment, this pathological process can set the stage for the development of more serious gynecological diseases: polyposis, infertility, malignant cell degeneration.
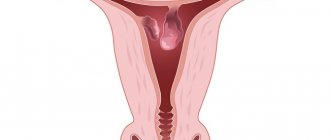
What is an endometrial polyp?
The endometrium is the inner wall of the uterus. A benign neoplasm localized in the uterine cavity is formed from endometrial cells. The problem is hyperplastic in nature and can be represented by a single or multiple growth of pathological tissue. When the quantitative indicator tends to values above 2 polyposis units, it is customary to talk about the disease – polyposis. Single endometrial polyps of the uterus are neoplasms amenable to therapeutic intervention. Multiple or recurrent types of the disease require a more complex approach to treatment.
Causes of endometrial polyposis.
The exact cause of uterine polyps is unknown, but they are sensitive to the hormone estrogen. You may be more likely to develop polyps if any of the following conditions apply to you:
- Age from 40 to 50.
- The period before menopause.
- Obesity, or if your body weight exceeds the norm by more than 30%
- You have currently or in the past taken the anti-estrogen drug Nolvadex (tamoxifen).
High blood pressure and the presence of cervical polyps are also cited as risk factors.
However, research shows that less than 1% of all uterine polyps are associated with cancer.
Fibrous polyps are more often detected in women before menopause. Sometimes placental neoplasms arise as a result of insufficiently clean curettage during abortion, incomplete removal of the placenta during childbirth, frozen pregnancy or miscarriage. In this case, tissue fragments and blood clots gradually transform into polyps.
Diagnosis of endometrial polyposis.
Endometrial polyposis can be detected using ultrasound or hysteroscopy.
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic technique that allows you to examine the uterine cavity using an optical system that opens up wide possibilities for detecting polyps.
It is important to help the body recover quickly, this will help identify asymptomatic infections quickly and avoid long-term inflammatory diseases.
In the next article we will look at the treatment of endometrial polyposis. At the end of this post, I would like to wish you excellent health and a speedy recovery.
Classification by type of structure
Depending on the type of cells that formed the neoplasm, several types of polyps are distinguished:
- Fibrous;
- Glandular;
- Mixed – glandular-fibrous;
- Adenomatous.
The growth can have a round, oval, oblong shape. The neoplasm is attached to the wall of the uterus using a “leg” or is located on a wide longitudinal base.
The glandular polyp is formed from stromal cells with a predominant inclusion of a noticeable amount of glandular uterine tissue. A neoplasm with scant inclusion of a glandular base and consisting of fibrous tissue is called a mixed glandular-fibrous polyp. A fibrous polyp consists only of fibrous cells without additional inclusions. The adenomatous variant of the pathological growth is represented by the formation of atypical glandular tissue. This type of polyp carries risks of malignant transformation.
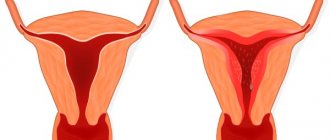
Polyps also have size differences. They can be small, medium and voluminous. Small polyps hardly manifest themselves at all and can go away on their own or grow if the pathology develops unfavorably. Small polyps can be discovered accidentally during a routine examination. Large and medium growths have characteristic symptoms. But many of the signs are similar to those of other gynecological ailments, so a more precise diagnosis is required.
Forms of the disease
Formations in the endometrium can be single, multiple and diffuse. Single polyposis has a favorable prognosis; it is diagnosed in 30% of cases, group polyposis in 20%. Diffuse is characterized by the appearance of a large number of growths. The tendency to malignancy reaches 70%.
According to the histological structure, adenomatous endometrial polyp is:
- Tubular. It is composed of multiple interlacings of glandular processes.
- Villous. Located on a shortened leg. Its structure is similar to cauliflower.
- Mixed (combined). Combines different tissues - glandular and villous.
Adenomatous polyps with a short stalk are more susceptible to malignancy. The malignancy index of endometrial villous growths is the highest (40%). After removal they often reappear. Tubular ones are almost not prone to transformation into cancer.
Table - Formations with and without atypia
| No signs of atypia | With atypia |
| Accompanied by slight changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm of glandular cells. |
The rate of malignant transformation is low.
Has a high potential for transition to a non-invasive cancer tumor (in a separate cell), but the probability of pathology progression does not exceed 5%
It is characterized by a pronounced change in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the epithelium of growths.The mutation rate is high.
The structure of atypical cells of adenomatous endometrial polyp is similar to cancer cells
To determine the nature of the pathology, you need to see a doctor and undergo a thorough examination.
Causes of development and risk factors
The diagnosis of endometrial polyp is most often made in women over 35 years of age. However, young girls and women under 30-35 years of age may also encounter this problem, although much less frequently than the older category. Glandular polyps are most often diagnosed in young women. But in patients who are premenopausal or menopausal, fibrous and adenomatous variations of polyps are often found.
The pathology is considered quite common. In the age group under 35 years, a polyp is diagnosed in 5% of patients. In older women, the disease occurs more often - in 25% of patients.
Polyps in the large intestine
Formations can form along the entire length of the intestine. The colon is the second place in the frequency of cases of adenomatosis and polyps in general. Men and women are affected equally. Age-related risk is noted; the older the generation, the greater the percentage of patients with pathology. The hereditary factor is clearly visible. The number of formations is associated with the risk of malignancy. It is believed that 5 or more growths are a 100% harbinger of cancer.
Symptoms
Manifestations are noticeable at a serious stage of adenomatosis, similar to other intestinal diseases:
- Flatulence;
- Stool disorders in both liquid and solid form;
- Pain in the abdomen, lower back, sides;
- Belching;
- Heartburn;
- Nausea;
- Itching of the anus;
- Discharge of mucus and blood in feces;
- The same phenomenon without the emptying process;
- Anemia, dizziness, weakness.
Treatment
Polypectomy is performed during a colonoscopy. In case of difficult access to the formation, laparoscopic surgery is performed. For severe lesions, resection by open surgery. Be sure to follow a diet. One type of diet in the first month after removal, and some restrictions for life.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Single growths in the uterine cavity do not manifest themselves in any way. The form of pathology that requires immediate therapeutic intervention is distinguished by a number of symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- Unusually heavy and/or prolonged menstrual cycle;
- Painful periods;
- Presence of spotting and spotting outside the active phase of the cycle;
- Bleeding;
- Increased leucorrhoea;
- Painful intercourse;
- Unpleasant sensations and spotting during and after sexual intercourse;
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- Mastopathy of unknown etiology;
The symptomatic picture may be accompanied by additional signs: apathy, lethargy, mood swings, sexual dysfunction, loss of appetite. In the presence of chronic diseases, symptoms of decompensation may appear: hyperglycemia in diabetes mellitus, the appearance of characteristic pain in inflammation of the ovaries, weakness and apathy in thyroiditis.
Polyps in the gallbladder
A very rare pathology is polyps of this small organ. Occurs in less than 1% of cases among people over 45 years of age. A large formation that can block the duct is very dangerous, resulting in the impossibility of releasing bile.
Symptoms
Appear when the duct is blocked:
- Yellow tint to the sclera of the eyes and skin;
- Pain in the organ area;
- Morning sickness;
- Bitter taste;
- Other symptoms of digestive disorders.
Treatment
The drugs Ursosan or Ursofalk are prescribed - these are complex action drugs, including choleretic, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and other properties. If the situation is dangerous, a gallbladderectomy is performed, that is, its complete removal.
Diagnostics
To detect and establish the nature of the endometrial polyp, a number of specific studies are used:
- Inspection;
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- Smear;
- Hysteroscopy.
Based on all or part of the listed diagnostic studies, the patient is given an accurate diagnosis. Treatment is selected depending on the nature, size and nature of the polyps.
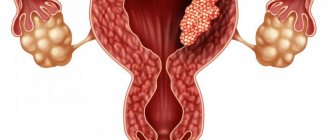
Treatment of endometrial polyp
For serious forms of the disease (medium, large) polyps, surgery is considered the only effective treatment. To prevent the growth and degeneration of polypous tissue, it is necessary to remove the growth. Depending on the shape and size of the polyp, one of three removal methods can be chosen:
- Hysteroscopy;
- Medical curettage;
- Hysterectomy.
- Hysteroscopy is performed under general anesthesia. The operation does not last long (up to 40 minutes). During the intervention, polypous growths are excised without damaging adjacent tissues. This operation is indicated for young women who have been diagnosed with a glandular form of neoplasm.
- Medical curettage is performed under general anesthesia, rarely under local anesthesia. Using a gynecological curette, the upper affected layer of the uterus is removed. This type of operation is performed when there is intensive growth of pathological tissues.
- Removal of the uterus is a radical method of treating endometrial polyps, which is more often recommended for postmenopausal women who are at risk of cancer. Hysterectomy is performed only if an adenomatous polyp is diagnosed, which suggests a high risk of malignant degeneration.
Polyps in the stomach
This organ of the gastrointestinal tract is the most common site of localization of adenomatosis. Such formations can malignize in 2-3 years into carcinoma - a cancerous tumor. The reasons for its appearance are different: hereditary predisposition, poor nutrition, bad habits, gastritis and stomach ulcers. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is considered one of the provocateurs of pathology.
Symptoms
Gastric polyps manifest themselves in large sizes or extensive lesions with signs that are characteristic of any gastrointestinal pathology:
- A feeling of a full stomach that is not associated with food;
- Pain;
- Belching;
- Loss of appetite;
- Nausea and vomiting; rotting food debris may be present;
- Heartburn;
- Increased gas formation;
- Bad breath;
- A special symptom is pigmentation around the lips and on the palms (less often in other places).
Treatment
To get rid of it, a polypectomy is performed using a gastroscope. Polyps in the stomach can be removed during an endoscopic examination. The procedure does not require anesthesia or recovery. However, after it is carried out, in order to reduce relapses, a special diet is prescribed. You will have to forget about unhealthy food and bad habits.
In serious cases, resection of the area affected by polyposis is performed. A minor formation of a calm nature may be left under observation.
Drug therapy consists of taking antibiotics for Helicobacter pylori, anti-inflammatory drugs and relieving the symptoms of the pathology.
Folk remedies
A formed polyp requires surgical removal. However, there are folk remedies that can be used for preventive purposes, as an addition to the main treatment to prevent relapses and maintain the immune system after intervention.
The choice of traditional medicine should be agreed with the attending physician.
Borovaya uterus: infusion
The medicinal plant, boron uterus, guards women’s health and is considered effective for many gynecological diseases.
The infusion is prepared from 5 tablespoons of dry suspension of the plant. The dry component must be poured with good quality vodka (0.5 l) and left in a dark room for 14 days. You need to take the infusion 40 drops before meals 3 times a day. Treatment lasts 90 days.
Herbal decoction based on boron uterus
For preparation you will need: dry suspension of the hogweed uterus, crushed, a mixture of bloodroot and angelica. These components are taken in the amount of 2 tablespoons. Add cumin, nettle and cinnamon one spoon at a time. A homogeneous mix must be formed from these components. Then, you should take one tablespoon of the mixture and place it in a fireproof container and pour 2 cups of boiling water. Next, the product is heated in a steam bath for 25 minutes. After cooking, the cooled broth must be strained. The product should be taken 1/3 cup during the day after meals. Treatment lasts 3 months.