Hip dislocation most often occurs in physically developed young and middle-aged people, and rarely occurs after the age of fifty. It is a prolapse of the femoral head from the acetabulum with rupture of the joint capsule, surrounding ligaments and muscles. The hip joint is the largest joint in the human body and is protected by strong ligaments and muscles, so significant physical impact must be sustained to cause this type of injury. Of all dislocations that occur, this injury accounts for no more than five percent.
In children, hip dislocation, or so-called hip dysplasia, is a congenital pathology that occurs on average in 3% of newborns, in some countries this figure reaches 12%. At its core, dysplasia is a malformation of the hip joint in which the structure of all its elements is disrupted. The risk of developing dysplasia is due to the following factors:
- heredity;
- toxicosis during gestation;
- early pregnancy (before 18 years of age);
- hormonal disorders in the body of a pregnant woman;
- developing large fetus;
- delays in embryo development.
Types of hip dislocations
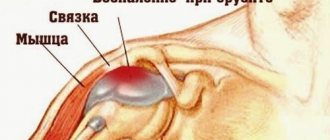
The main types of hip dislocation with characteristic visual signs are anterior and posterior. In the anterior one, the knee joint turns outward, the head of the femur protrudes in the groin area, and recesses form in the gluteal area. The damaged leg looks longer than the healthy one. With the posterior type of injury (occurs five times more often than the anterior one), the clinical picture is the opposite - the head of the bone protrudes in the gluteal region, a recess forms in the groin area, and the leg looks shorter than healthy. Visual symptoms of subtypes of injury are presented in the table:
| Type of damage | Characteristics |
| Posterosuperior (iliac) | The head of the bone is displaced behind the ilium |
| Posteroinferior (ischial) | The head is located at the ischium, joint deformation is minimal |
| Anterosuperior (suprapubular) | The head is located in front of the ilium |
| Anteroinferior (obturator) | The head moves towards the pubic bone, the leg bends |
A central dislocation is a fracture of the bottom of the acetabulum, accompanied by protrusion of the femoral head into the pelvic area. A separate type of injury is the congenital type, which occurs as a defect in the formation of the articular joint during the prenatal period of development.
What it is?
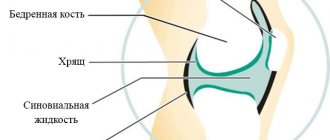
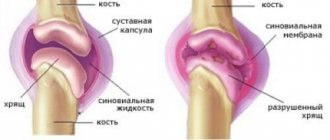
The hip joint consists of the acetabulum and the spherical head of the femur, and the peculiarity of the articulation is that not only the head, but also most of the femoral neck enters the articular cavity. It belongs to the type of ball (bowl-shaped) joints of a limited type, therefore its movements are less extensive than in free ball joints. The stability of the hip joint is maintained by muscles, fibrous capsule and ligaments. Such strength and limited movement ensures rare, but very serious dislocations in this place.
Hip dislocation in adults is an injury in which the femur is forced out of the acetabulum and into the pelvis. The types of dislocations are shown in the table:
| Pathology | What's happening | |
| View | Subspecies | |
| Acquired | Rear location (90%) | The femur lies behind the acetabulum of the pelvis. |
| Front (8%) | The bone is located in front. | |
| Central (very rare) | Fracture of the floor of the acetabulum, the femoral head goes into the pelvic cavity. | |
| Congenital | Underdevelopment of the hip joint during the uterine period. | |
Mechanism of injury
A joint dislocation occurs under the influence of powerful force or speed, so the most common causes of injury are road traffic accidents or falls from great heights. In this case, the traumatic effect is not on the hip joint, but on the bone, which acts as a lever. The articular capsule is damaged, nearby tissues are damaged, and bone components come out of the articular cavity.
Symptoms of hip dislocation
The symptoms of different types of injury (anterior and posterior) vary slightly, although a number of common signs are present. Hip fractures are more common in older adults, and the classic symptoms of a dislocation may indicate a more serious injury. With old damage (when more than three weeks have passed since the injury), lameness when walking, pelvic distortion, and sometimes curvature of the spine are added to the general symptoms. General signs of damage to the hip joint can also appear in the presence of characteristic injuries in the anamnesis.
Symptoms characteristic of any type of hip bone dislocation are sharp, acute pain and the inability to step on the leg painlessly. Additionally, the following symptoms are observed:
- asymmetry of healthy and damaged limbs;
- inability to move the hip without pain;
- joint deformity;
- the appearance of swelling and bruising in the buttock or groin area (depending on the type of dislocation);
- forced non-physiological position of the leg (depending on the type of injury).
Posterior type hip dislocation is characterized by a number of the following symptoms associated with the location of the femoral head after injury:
- the leg is shortened (compared to a healthy one);
- there is retraction in the groin, and swelling in the buttock area;
- the leg is adducted, bent and turned inward.
Central dislocation is characterized by displacement of the head of the bone into the pelvic area, accompanied by fragmentation of the elements of the acetabulum. Symptoms of this type of injury include the following changes:
- leg length decreases;
- the injured limb is abducted and slightly bent;
- The x-ray shows a deformation of the lateral wall of the pelvis.
With the anterior type of injury, due to changes in the position of the femoral head, the following characteristic symptoms are observed:
- the leg is slightly moved outward from the knee, extended with the anterosuperior, bent with the anterior-inferior;
- the injured limb looks longer than the healthy one;
- a swelling forms in the groin area, the gluteal area sinks.
Symptoms
Hip dislocation has a number of characteristic symptoms:
- sharp and sharp pain;
- limited mobility of the injured leg;
- deformation change of the hip joint;
- reduction in leg length on the side of the injured hip;
- forced position of the limb.
Any attempt to move the leg causes very strong pain in the hip joint. Any movements of the injured lower limb are limited and are accompanied by resistance with a springing effect. The patient cannot perform any active swings of the injured leg at all.
The symptoms of this pathology in older people are very serious, since in old age general wear and tear of the entire skeletal system is detected. Most old people are diagnosed with osteoporosis.
Hip dislocation in old age has the following symptoms:
- persistent aching pain;
- inability to lift the heel off the floor;
- hematoma in the groin area;
- asymmetry of inguinal folds;
- the injured leg is shorter than the healthy limb;
- light crunch of bones.
Often a dislocation in older people is accompanied by a hip fracture, since over time the density of bone tissue decreases and its fragility increases. This is very dangerous for old people, since as the body ages, metabolic processes slow down and the ability to regenerate—naturally repair damage—decreases.
Congenital dislocation of the hip in children is called hip dysplasia. Early diagnosis is difficult due to not clearly expressed signs. It is difficult for parents to determine this pathology; only a pediatrician can do this.
If the hip is dislocated, the child's symptoms will be as follows:
- late attempts to walk;
- limping or walking on tiptoes;
- violation of the symmetry of the internal folds of the thigh;
- clubfoot;
- the foot of the affected leg is turned outward;
- Due to the highly pronounced flexibility and elasticity of the joint, the femoral head of the femur constantly comes out with a click from the socket back and forth.
Treatment for a hip dislocation depends on the symptoms, which will vary depending on the location of the injury. If we are talking about an anterior dislocation, then a typical sign of compression of the vessels of the thigh will be. In case of posterior dislocation, damage to the obturator nerve is diagnosed.
One of the main complications with posteroinferior hip dislocation is damage to the sciatic nerve. Often with such an injury occurs:
- separation of the edge of the acetabulum;
- damage to the cartilaginous part of the femoral head.
The most dangerous complications from such an injury can be:
- arterial compression;
- compression by internal hematoma;
- damage to the arteries around the femoral head.
Complications of this kind often cause constant pain, impaired functioning of the limb even after reduction of the dislocation, and sometimes necrosis.
It must be taken into account that this damages the soft tissues surrounding the joint, which also aggravates the patient’s situation. Depending on the symptoms, treatment for hip dislocation will be prescribed.
Congenital bilateral hip dislocation
The pathology is an anomaly of intrauterine development, in which dysplasia of the hip joints develops. Symptoms of the disease in a newborn are the following disorders:
- asymmetry of the buttocks, the presence of extra folds on them;
- the appearance of a crunch when bending the legs;
- x-shaped foot placement;
- involuntary clenching of the hand into a fist due to the development of pathology;
- c-shaped body position;
- curvature of the spine in the lumbar region, increased tone of the back muscles.
Dislocations in the hip area account for no more than 5% of the total number of dislocations. As a rule, damage is formed as a result of a fairly strong application of traumatic force carried out at high speed. For example, this can happen in case of an accident, falls from a significant height, or various collapses.
Posterior hip dislocation is a more common injury. It occurs when the hip suddenly flexes or rotates inward. Then the back of the hip joint capsule is ruptured by the head of the femur emerging from the acetabulum. The position of the dislocated head of the joint determines whether the dislocation will be iliac or sciatic.
Anterior hip dislocation is a less common injury. It is indirect and can occur if a person falls from a height onto his outstretched leg. The head of the femur will move downwards, rupturing the joint capsule. Anterior dislocations are obturator and pubic.
Symptoms of hip dislocation
Symptoms of a hip dislocation should be differentiated depending on the type of injury. In general, the victim complains of quite serious pain in the hip joints.
In addition to deformation and forced positioning of the injured limb, the main symptom of hip dislocation is severe pain. With a posterior hip dislocation, the leg bends and the knee rotates inward. The greater the flexion, the greater the likelihood of sciatic posterior hip dislocation. Accordingly, with an iliac dislocation, the leg is bent less.
Each type of hip dislocation is characterized by the following physical manifestations:
forced placement of a limb;
change in the shape of the hip joint;
strongly or not very much, but, nevertheless, obvious shortening of the leg on the side where the damage occurred.
Even the most insignificant displacements in the area of the presented joint are painful, sharply limited and are accompanied by specific resistance. If we talk about more active movements, then they seem impossible.
In the case of an anterior dislocation, the person’s limb is turned to the outer part, retracted to the side. At the same time, it will also be bent not only in the hip, but also in the knee joint. Anterior and inferior dislocation resolves with more obvious flexion and abduction of the injured area.
Dislocations that occur directly in the hip can be accompanied by and with the separation of a small part of the vertical cavity. In some cases, the cartilage at the top of the femur is broken. With posterior and lower hip injuries, severe contusion of the sciatic nerve is often determined. When the hip is dislocated in the anterior part, compression of the femoral vessels is likely; in the anterior and lower part, there is strong pressure on the obturator nerves, which causes sharp pain.
A hip dislocation that occurred quite a long time ago or is not recent is accompanied by much less obvious clinical symptoms, since pain in the joint area decreases over time. The change in the length and shape of the leg begins to be compensated by the tilt of the pelvis and a sudden increase in lordosis (curvature in the lumbar region) of the spine.
Since hip dislocations are often combined with fractures, an X-ray examination is required to make a diagnosis.
First aid for a hip dislocation is to administer pain medication to the injured person and immediately hospitalize the patient. In this case, you need to try to prevent the patient from moving.
Complications after treatment and prognosis
Every mother should know that the previously common tight swaddling, or swaddling with a “soldier”, is strictly contraindicated for this pathology, since this disrupts blood circulation in the joints, and this is the reason for the disruption of their nutrition.
When driving in a car, use a seat belt; Damage In such cases, with severe development of disorders in the joint, hip replacement may be required - its removal and installation of a prosthesis.
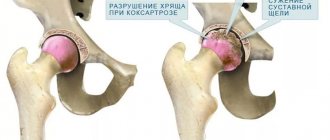
With a posterosuperior hip dislocation, the head of the femur is palpated under the muscles of the buttocks, with a posteroinferior dislocation - next to the ischium.
b – posteroinferior dislocation
medikmy.ru
Causes of hip dislocation
Dislocations in the hip area occur as a result of indirect trauma. In this case, it is the femur that receives the role of a specific lever that affects the entire hip joint.
After implementing the forced influence, the tip of the femur:
tears the capsular cavity of the joint;
destroys or damages ligaments;
comes out of the cavity into the joint area.
The cause of a posterior hip dislocation is usually a car injury. The mechanism of such a detrimental effect is a noticeable rotation or extension of the limb turned towards the inside, adducted and tucked.
Dislocation of the hip in the anterior region most often occurs in the event of a fall from a height onto an abducted limb turned to the outside in a tucked position.
Diagnosis of hip dislocation
To make a diagnosis, the following “achieved” methods are used:
- History of the disease: in old age there is an injury with a fall on the hip joint.
- Complaints exactly.
- A general examination with determination of the clinical picture was detected.
- The final days are radiology diagnostics (x-rays may be of the hip joint). On radiographs, the entire fracture zone is the line of action (on the negative image).
A hip dislocation should not be confused with bruises, subluxations and various fractures of the pelvic and femur bones.
Distinctive symptoms of other injuries:
- A bruise is characterized by pain in the area of the hip joint, however, passive movements and a significant amount of active movements are retained in full.
- Fractures of the acetabulum and femoral neck can resemble and often accompany hip dislocation.
- With subluxation, the signs are much less pronounced. The limb retains a certain amount of active movement.
- A femoral fracture is characterized by obvious deformation and local pain. Passive movements in the joint are preserved.
- When the pelvis is fractured, there is pain when pressing on it, but the limbs retain full mobility.
Types of hip dislocation
The classification of hip dislocations is carried out according to several principles. First of all, it is necessary to highlight the anterior and posterior dislocations of this area.
Dislocations in the anterior part should be divided into anterior and superior (suprapubic), as well as anterior and inferior (obturator). The posterior ones are classified as follows: posterior and superior (iliac), as well as posterior and inferior (sciatic). Considering the presented classification, the treatment process may be different, depending on the nuances of the diagnosis.
A separate category of hip dislocation is a birth defect. Research carried out to date has proven that dysplasia is the basis of congenital dislocation in the hip area. We are talking about a violation of the optimal formation of each part of the joint presented throughout the entire development in the mother’s womb.
These initial dysfunctions become catalysts for further ones: incomplete development of the pelvic bones, movement of the top of the femur, slowing down the process of ossification (ossification) of the described elements of the joint.
Treatment of hip dislocation
The treatment process is quite simple and involves the fastest possible reduction and fairly short fixation. After this, it is imperative to carry out specific therapy (physiological procedures and therapeutic exercises).
A traumatic type of dislocation in the hip area is accompanied by a reflex contraction of the large muscles of the thigh and gluteal regions. For successful and competent reduction, these muscles should be relaxed as much as possible. In this regard, reduction of femoral dislocation is carried out in hospital treatment under general anesthesia using muscle relaxants. This should be considered an indispensable condition.
In the process of reducing recently received anterior and inferior, posteroinferior and posterolateral injuries of the hip, the Dzhanelidze method should be used (as the least traumatic, but quite painful). If we are talking about the reduction of older or fresh anterior and superior dislocations, then the Kocher method will be relevant.
In the case of anterior and superior dislocations in the hip area, the Dzhanelidze method is not used, because the likelihood of breaking the tip of the femur during reduction is too high.
After skeletal traction has been applied, it must be continued for at least three to four weeks. After this, the victim will need to move with crutches for about 10 weeks. We are also talking about prescribing special therapy and therapeutic exercises.
Damage to the cartilage at the end of the femoral bone during its dislocation is almost always accompanied by the development of arthrosis of the hip joint, which becomes a catalyst for changes in its shape. An alternative name for the presented phenomenon is coxarthrosis in the long-term period.
In such situations, especially with the obvious development of disorders in the joint area, there may be a need for hip replacement. To do this, it is first removed and then the prosthesis is fixed.
If we talk about congenital hip dislocations, then two fundamental methods of treating this pathology have been developed: conservative and operative (that is, surgical). If the diagnosis is made not only on time, but also correctly, then exclusively conservative methods of treatment are used.
In such a case, a splint is selected individually for the baby, which makes it possible to hold the limbs in the following positions:
on the bend in the hip and knee joints at an angle of 90 °C;
abductions in the area of the hip joints, which has a positive effect on their subsequent proper development and formation.
Reduction of the end of the femur should be carried out quite slowly, gradually and without causing any injury. Any force in this case is unacceptable, because it easily damages the top of the femur, as well as other tissues of the joint.
Conservative treatment of children with congenital dislocations of any category is the most important method. In addition, the sooner it is possible to achieve alignment of the acetabulum and the end of the femur, the more successful conditions will be created for the subsequent formation of the entire hip joint.
The optimal time to begin treatment is the first days of the baby’s life, that is, precisely the period when secondary changes in the area of the socket and proximal tip of the femur are minimal. At the same time, conservative treatment is more than applicable even with delayed diagnosis in older children. These can also be children who have reached the age of one, that is, precisely when a fully formed dislocation in the hip area is detected.
All activities related to the diagnosis and treatment of children with all types of hip dislocations should be carried out in the first three months of life. Any later dates should be considered late. If we talk about surgical interventions, they are carried out in the case of older dislocations.
Treatment methods
Treatment for hip dislocation involves hip reduction, which is done under general anesthesia. If the injury is fresh, then use the Dzhanelidze method. The patient should lie face down on the table with the limb hanging down. One of the doctors should fix the pelvis with his hands, pressing it to the table. The injured limb is carefully bent at the hip and knee joints and then abducted.
The doctor needs to move the hip forward and perform several rotational movements. When the hip is realigned, clicks will be heard, and passive movements in the joint will also be restored. This procedure is carried out only after a complete examination, since a fracture, and not just dislocation of the acetabulum, is also possible.
In case of a stale injury, the Kocher method is recommended for reduction:
- place the patient on his back;
- fix the pelvis, pressing it to the table surface;
- abduct your leg to the maximum and bend at the hip joint;
- perform axial traction to release the femoral head from behind the posterior edge of the acetabulum;
- using rotation, smoothly move the femoral head opposite the socket;
- Continuing the stretch, quickly straighten the leg, abduct and rotate it to the inside.
As a result, the dislocation is eliminated. After the manipulation, an x-ray should be taken. If the dislocation cannot be eliminated the first time, the procedure must be repeated again. After reducing the dislocation, the joint should be unloaded using skeletal traction. This is necessary to prevent aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. The duration of such treatment is usually at least a month.
Timely assistance will help to quickly restore the damaged joint. In the first days after injury, you need to use pain-relieving gels. Anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed only after the acute pain subsides.
Traumatologists usually prescribe the following drugs:
- Voltaren;
- Bystrumgel;
- Venoruton;
- Fastum-gel.
Thanks to its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, swelling is reduced and the pain threshold is reduced. If a hip is dislocated, treatment and selection of the necessary ointment is performed by a traumatologist. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. Unqualified assistance can only lead to a worsening of the patient’s situation.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are also prescribed during rehabilitation. The patient is given a massage and sent for therapeutic exercises for the hip joint. As for congenital hip dislocation, there are special exercises that are offered to the patient during exercise therapy.
If a patient is diagnosed with a hip dislocation with an acetabular fracture, the patient is examined for the presence of large joint fragments and their displacement. In this case, surgical intervention will be required. The operation must be done as soon as possible, no later than two weeks after the injury.
Indications for mandatory intervention are:
- signs of sciatic nerve damage;
- open fracture;
- displacement of the femoral head to the center;
- non-reducible posterior dislocation of the femur;
- significant detachment of soft tissues.
If a patient is diagnosed with traumatic shock, measures are first taken to stabilize his condition. Hip dislocations and fractures are very dangerous; they require careful examination and monitoring by a traumatologist.
Prevention of hip dislocation
In order to prevent dislocation in the area, it is recommended to carefully monitor safety in everyday life and while playing sports.
So, there is a need for:
training various muscle groups, rational exercise;
using exclusively comfortable clothing and shoes to prevent falls;
using professional protective equipment throughout sports activities. We are talking, at a minimum, about knee pads and thigh braces;
refusing any trips in icy conditions, paying attention to slippery and wet surfaces.
In order to completely restore the hip joint after a dislocation, it will take, if there are no complications, 2 to 3 months. This period can only be extended if there are concomitant fractures. Thus, the doctor may insist that long-term traction of the skeletal type be carried out with further sets of exercises. This is done using a device for continuous inactive movement.
Independent movement using crutches is possible only in the absence of any pain. Until the lameness disappears, it is recommended to resort to additional aids for moving, for example, a cane.
After this, it is recommended to use general strengthening drugs that will affect the structure of bone tissue. It is also important to carry out certain exercises, the list of which should be compiled by a specialist. Their regularity will be the key to recovery. In addition, it is necessary to treat the damaged hip area as carefully as possible, because now it is one of the weakest points of the body.
Remembering all the rules of prevention and treatment, it is more than possible to quickly and permanently get rid of any consequences of hip dislocation while maintaining the optimal rhythm and tone of life.
The hip joint is one of the most powerful and largest bone joints in the body. Due to its anatomical features, it should be noted that it has a large range of motion. This is achieved due to the presence of a spherical shape of the head of the femur, the acetabular notch of the pelvic bone, as well as a large area of the articular surface. The close anatomical connection is caused by the presence of a strong capsule that performs a protective function, as well as powerful ligaments that can withstand heavy loads.
Hip dislocation is a fairly rare type of injury; it occurs in up to 5% of all cases of joint damage. The most common cause of its development is traumatic exposure to high force. The pathology affects males and females equally. With the exception of the congenital condition, it is necessary to note an increase in the frequency of occurrence in adults, this is largely due to the loss of tissue elasticity.
Causes
The main cause of hip dislocation is injury. It should be noted that for pathology to develop, it must be indirect in nature, when congruence is disrupted due to the protrusion of the femur. This anatomical part is a kind of lever that can lead to rupture of ligaments and capsules. This may be a blow to the knee or foot towards the patient's torso. In addition, injury occurs when falling from a great height. An extremely rare case is a fall from one’s own height or lower.
In addition, the pathology may be congenital. In this case, the development of the disease is facilitated by impaired bone development in the fetus or injury during childbirth. Dislocation of the femoral neck often develops as a result of dysplastic changes.
Causes and symptoms
This type of injury can be caused by falling from a height.
Hip dislocation usually occurs due to injuries after an accident, a fall from a height, sports activities, etc. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the femoral area immediately after dislocation;
- inability to move the injured limb;
- unnatural turn of the leg;
- a clicking sound indicating that the head of the femur is sliding into the acetabulum;
- shortening of the injured leg compared to the healthy one;
- numbness and tingling, especially after injury to the sciatic or femoral nerve;
- muscle weakness caused by motor nerve damage or muscle paralysis.
Classification
There are several classifications of hip dislocation, which differ in different criteria. This information is necessary not only for making a diagnosis, but also for choosing further tactics of action.
Depending on the direction of the femur, there are:
- posterosuperior displacement. The femoral head is displaced behind the ilium;
- posteroinferior displacement. The head will be displaced onto the ischium;
- anterosuperior displacement. The head is located at the anterior iliac spine;
- anterior inferior displacement. The direction of the head is marked towards the pubic bone.
Depending on the time of occurrence, dislocations are divided into:
- congenital. Their formation does not always occur in the prenatal period. In some cases, it develops during labor;
- purchased. This type develops as a result of an injury.
Symptoms
Manifestations of hip dislocation are typical; the main symptoms and those most characteristic of a particular type should be highlighted. The main symptoms characteristic of hip dislocation include the development of severe pain. The patient is in a forced position; any touch to the affected area causes tears or screaming.
Displacement of a limb from its physiological position leads to the inability to perform motor activity. The patient cannot stand or even lean slightly on the affected leg. Performing passive movements is difficult, active manipulations are impossible. Upon palpation, powerful muscle tension is determined.
Development of redness in the hip joint area with the addition of edema. The severity of the latter is determined by the extent of the injury, as well as damage to other structures and the duration of the pathological process.
In order to determine the exact type of dislocation and select treatment tactics, it is necessary to clearly identify additional symptoms, which vary depending on the nature of the injury. With a posterior dislocation, the leg will be bent and adducted to the inside. Its length will decrease, while a fold with a slight recess will form in the groin. In the buttock area, on the contrary, you can palpate a bulge that is firm to the touch. This formation is the head of the femur.
Anterior dislocation or subluxation of the hip joint is accompanied by abduction of the leg to the outside. The leg is most often in an extended position, and its length exceeds the healthy one. It is possible to palpate the presence of a bulge in the groin, and the appearance of smoothness on the buttock side.
Congenital dislocation
This condition is one of the most common pathologies of the musculoskeletal system in early childhood, along with clubfoot or torticollis. Its diagnosis is not difficult and is included in screening for identifying diseases in early childhood.
The main symptoms of congenital hip dislocation include the appearance of a characteristic clicking sound, changes in the length of the limbs, the appearance of asymmetry in the area of the inguinal folds, as well as different average physiological position of the legs. The choice of treatment tactics will depend on the severity of the pathology and on the age of the patient. In the initial stages, when no secondary changes occur, a splint with long-term use is required. Reduction of the hip occurs independently without unnecessary trauma to the tissues, in particular the ligamentous apparatus. In order to treat the joint, if secondary changes appear, surgical intervention with reduction and subsequent completion of a full course of rehabilitation is necessary.
Treatment of congenital hip dislocation in children requires careful medical supervision.
Features in newborns
Signs of congenital hip dislocation in children are recognized immediately after birth.
Grade 1 dysplasia can be detected in an infant by an orthopedist.
Pre-dislocation of the hip joint (grade 1 dysplasia) is detected during the first orthopedic examination of the child. The cause is disturbances in the development of the hip structures, causing underdevelopment of the pelvic bones, separation of the articular surfaces, and slow ossification. Unnoticed dislocations in the future will lead to inflammatory diseases of the joint and other serious complications. Typically, infants are diagnosed with unilateral dislocation; in rare cases, bilateral dislocation occurs. Pathology of the hip joint in children with cerebral palsy is a common concomitant disease and the main orthopedic deviation. For children, only conservative treatment is indicated.
Diagnostics
Upon admission of a patient to a medical institution and before taking measures aimed at eliminating the pathological condition, it is necessary to perform basic diagnostic procedures. Initially, the doctor examines the patient in order to assess the extent of the injury, the condition of the surrounding tissues, the amount of physical activity and the presence of concomitant diseases.
As a rule, diagnosing hip dislocation is not difficult, since the signs are characteristic of the pathology. To confirm the condition, you must use additional methods, which include:
- performing x-rays of the pelvic bones and hip joint. A study is being carried out by scanning two projections, they will exclude serious conditions;
- performing computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. During the examination, small-sized damage can be detected. They are necessary in cases that are difficult to diagnose or in the presence of concomitant severe injuries.
Closed hip reduction
If the above-described treatment methods do not bring positive results, using general anesthesia, with a straight body, the legs are raised vertically and carefully spread in different directions. Then the problem joint is fixed using a special plastic frame. After 6 weeks, the patient should be examined. If there are positive results from this procedure, the joint is fixed for another 90 days. If the method does not bring any results, the doctor resorts to surgery.
First aid
Treatment in this case is carried out by any person who accompanies the victim or happens to be near him. Further tactics and possible prognosis will depend on the correctness of these procedures. First aid is provided as soon as possible after the dislocation occurs. This will help not only reduce the severity of pain, but also the degree
- increasing swelling of the surrounding tissues, which will help with reduction. A person needs to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- call an emergency medical team as soon as possible, which will deliver the victim to a medical facility in the most gentle position possible;
- administer a drug that has analgesic properties or ask the patient to ingest it. In this case, drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help;
- immobilize the affected limb. You should not try to correct a dislocation or subluxation of the hip joint on your own, as this can lead to serious complications. The pelvic bones and limbs should be placed on a hard surface, which can be made from available materials. Bandages, belts or tourniquets are used for fixation.
Apply ice or any cold object to the joint area. Reducing blood flow helps reduce the severity of swelling and pain. In order to avoid hypothermia, you should place a napkin or any other fabric between the skin and the object.
Patients are interested in the question of whether they can perform the reduction themselves. Only a specialist with a proven skill can correct the joint correctly.
Possible complications
Subluxation is dangerous because such displacement compresses the nerves and blood vessels, causing problems with innervation and blood circulation, which can lead to serious consequences, deterioration of the condition of the tissues, including their necrosis. If the correct diagnosis was not made in childhood, the disease can manifest itself in an adult and cause pain, flat feet, scoliosis, lameness and even disability.
Joint dysplasia is very rare in adults, but dislocations and subluxations can occur in anyone at any age due to injury or increased stress.
Similar:
- Causes and signs of outward foot subluxation - what you should know about the injury to help a person
- What is the difference between a dislocation and a subluxation of the jaw, differences in symptoms and treatment of injury
- The main treatment options for coccyx subluxation, first aid for the victim and further prognosis
- What to do if a child has a subluxated cervical vertebra: methods of treatment and correction
- Symptoms and treatment of hip dislocation in adults and children
- Signs of knee subluxation, treatment methods and rehabilitation features
- The first symptoms of subluxation of the shoulder joint, causes and possible consequences of the injury
Treatment
Therapy for dislocation is predominantly conservative. If there is no ligament rupture or damage to other elements of the joint, the femoral head is reduced into the acetabulum. This manipulation is carried out if there is a sprain of the ligamentous apparatus. To perform this procedure, a necessary condition is to obtain anesthesia. Without general analgesia, reduction of the dislocation is impossible due to severe tension in the muscle fibers. For this purpose, muscle relaxants are prescribed. The reduction is performed by a traumatologist together with an assistant.
The result of reduction is the appearance of a characteristic click, facilitation of motor activity in the limb and its occupation of a physiological position. The duration is no more than 15 minutes.
After achieving the result, it is necessary to fix the limb by applying a plaster splint. Subsequently, the patient should remain at rest in a supine position. If necessary, the patient is prescribed painkillers during the first days after the injury.
Complicated dislocation of the hip joint poses a big problem for specialists. This is largely due to the increased risk of poor prognosis and difficulty in restoring the joint. A similar picture arises with an additional rupture of the ligamentous apparatus, bone damage, or the absence of effect from an attempt at reduction. Treatment is carried out as planned with the choice of optimal tactics.
The procedure is performed in an operating room under the patient's anesthesia. The operation is performed with an incision for suturing the tissue, open reduction, and subsequent suturing.
Reducing a dislocation requires the application of significant physical force, so the doctor needs the help of an assistant.
Rehabilitation
This stage is one of the most important when treating a dislocated hip joint. At this time, a large number of procedures are performed to prevent complications.
The initial stage of rehabilitation measures is massage. The procedure allows you to reduce pain, swelling, improve blood circulation, and also facilitate movement after removing the splint. The duration and intensity must be increased gradually.
Physical therapy should be performed at the immobilization stage. Its implementation is aimed at preventing the development of contractures, thrombosis, and muscle atrophy. Initially, you need to carry out physical activity on your toes, gradually adding new exercises.
Physiotherapeutic effects are allowed to be used only after all symptoms have subsided. Its action is aimed at improving blood flow and restoring muscle tone. The most effective among them are the methods of dynamic currents, UHF, and magnetic therapy.
The optimal course of action is selected by the attending physician. Before performing it, all contraindications should be excluded. An obligatory point is the implementation of dynamic monitoring of the effectiveness of procedures.
This period can be extended due to the presence of concomitant fractures or associated injuries. For 2 months, the patient must observe a protective regime without additional load on the joint. To reduce it, you need to use crutches or a chair for transportation. Motor activity in the joint is completely excluded; for this purpose, fixing methods are used, such as plaster splints. The patient will have to listen to the doctor’s recommendations on how to live in the future after the injury, whether it is necessary to adjust the diet.
Types of rehabilitation procedures after hip dislocation
Rehabilitation activities include:
- Massage of the lower limb, hip joint area. Useful for normalizing blood circulation in the damaged area, muscle tone, relieving puffiness and swelling.
- Physiotherapy. Proper functioning of the muscular system is extremely important in the healing process. At the beginning, passive movements in the joint are used, then the activity is gradually increased, from light to intense exercises. The patient can engage in more active sports after the cast is removed.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment. Diadynamic currents, ultra-high frequencies, magnetic and thermal methods are more often used.
- Sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated for all patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Mud therapy, hydrotherapy and others have a positive effect.