Sinus arrhythmia is a disease accompanied by disturbances in the rhythm of heart contractions. The difference between heart contractions exceeds 10%, the pulse remains normal. Physiological arrhythmia occurs due to deep breathing, eating, stressful situations, and physical activity. Treatment is selected depending on the type of disorder, accompanying symptoms, and the age of the patient. The disease is not classified as dangerous. In some cases, arrhythmia is prone to self-limitation, especially in young and adolescent patients.
What it is
Sinus nodes are anatomical areas that contain myocyte cells that generate electrical impulses and heart contractions. In the right ventricle there is the sinoatrial node of Kiss-Flerc, which responds to the initial rhythm of the heart: it sends signals to the atrioventricular nodes. In case of sinus arrhythmia, the sinus node itself remains the leading rhythm. Normal cardiac activity is rhythmic and uninterrupted. Any disturbances in the beat, rhythm, or functioning of the chambers are referred to by the general term arrhythmia.
Depending on how quickly the electrical impulse travels through the muscle tissue, sinus rhythms can be:
- normal: up to 90 beats per minute
- accelerated: over 105 beats
- slow: less than 55 beats
Arrhythmias are diagnosed in 12-16% of patients in cardiology departments. People of older age groups, as well as patients who abuse alcoholic beverages and narcotic substances, are at risk. In childhood, manifestations of arrhythmia are observed, but such a disorder is a natural reaction to the rapid growth of the body and is not a pathological condition.
Definition of this condition
At the time of the disease, the process of contraction of the heart muscle changes; basically, this condition is considered a symptom, and not a full-fledged clinical case. Those. this disease is a symptom of another disease. And this disease is not always associated with the heart. In ordinary life, even in a healthy state, there is no absolutely even heartbeat, because the speed differs in calm and during excitement. The pulse quickens, and this is normal, because a change in the frequency of beats per minute is very necessary for the body to adapt to external stress. But if differences in heart rate occur for no reason or are more than 10%, then you can already talk about the disease and contact your family doctor.
This disease occurs when the process of electrical stimulation of the muscular system of the heart (myocardium) is exposed to certain adverse factors. These factors can change the rate at which impulses are transmitted into it, and automatic contractions begin to speed up or slow down. Typically, a person's beat rate is eighty per minute. Sometimes varies depending on external and internal influences. A change in beat speed helps classify a specific arrhythmia into one of its four types.
Classification
They are classified depending on the heart rate into physiological, tachyarrhythmia, bradyarrhythmia, and extrasystole.
Physiological (respiratory)
Respiratory arrhythmia is not a deviation. Most often observed in children and adolescents. Accompanied by an acceleration of the heart rate on inhalation and a slowdown on exhalation. In an adult patient, it can occur against the background of diseases of the brain and nervous system or a severe infection.
Tachyarrhythmia
With tachyarrhythmia, the heart does not fill completely with blood, the heartbeat exceeds 85-95 beats/min, and a lack of air is felt. Sometimes the pulse does not become slower, even if the person is calm or sleeping. Some patients may not notice the symptoms described. There is a disturbance in blood flow and a negative effect on internal organs.
People with dysfunction of the thyroid gland and autonomic nervous system are at risk. Sinus tachyarrhythmia is the safest. Complications occur in rare cases, in the absence of quality treatment and exposure to negative factors.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a cardiologist online
Bradyarrhythmia
With bradyarrhythmia, the production of regular and irregular electrical impulses, as well as the ventricular rhythm, slows down. The heart rate decreases to 55 beats per minute or less. It is observed with diets, prolonged fasting, increased intracranial pressure, and thyroid dysfunction. If the heart rate drops to 45-40 beats per minute, the patient may lose consciousness. In severe cases, death is possible.
Extrasystole
Extrasystole is one of the variants of cardiac arrhythmia, in which an extraordinary contraction of the entire heart or extrasystoles is observed. A strong shock is felt, the heart skips a beat, anxiety arises, and there is not enough air. Cardiac output decreases, cerebral and coronary blood flow decreases. As a result, angina pectoris, fainting, paresis, atrial fibrillation, and sudden cardiac death may occur.
Idiopathic extrasystole occasionally occurs even in a healthy person. With organic extrasystoles, myocardial damage is observed: infarction, cardiosclerosis, myocarditis, malformations, coronary heart disease.
Consequences and forecasts
It is very difficult to give any remote forecasts regarding heart diseases in general and arrhythmias in particular. It is known that with sinus arrhythmia in children and adolescents, most often the symptom goes away on its own after the period of growing up, and the child, as a rule, completely stops complaining about the heart. If over time the child does not improve, and the symptoms progress more and more, then you should immediately visit a doctor and select therapy.
For older people, the development of the situation is entirely determined by their underlying disease, the one that led to the development of arrhythmia as a symptom. If it is successfully treated, then the arrhythmia is highly likely to go away, while if the treatment does not produce results or the patient refuses treatment altogether, then the prognosis may be the most unfavorable.
What are the most serious consequences:
- Serious risk of fainting or cardiac arrest. It is dangerous because cardiac arrest can lead to death without immediate assistance.
- Stroke. Sudden and serious changes in the load on blood vessels can lead to their damage or even rupture. This is especially dangerous for the blood vessels of the brain. A hemorrhagic stroke (with bleeding in the brain) can kill or disable a person.
- Heart attack. One of the most common causes of death in our time. Requires hospitalization in a hospital and a rehabilitation course.
- Heart failure. This will in the future affect the level of exercise that a person can afford, and will also be a factor in the development of other heart problems.
- Cerebrovascular accident. Helps reduce concentration, attention, increase dizziness, and brain hypoxia. It seriously reduces a person’s quality of life.
- Thromboembolism. Blood circulation disorders always contribute to the development of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels. A blocked vessel seriously harms the nutritional process of the organ to which it goes, and therefore this problem can lead to the worst consequences for the patient.
Stages
There are 3 main stages of development:
- Symptoms are absent or very rare and resolve on their own. Elderly people, teenagers, and athletes may experience breathing problems, which requires consultation with a doctor;
- the patient complains of weakness, shortness of breath, fatigue. Arrhythmia occurs against the background of other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- stage 2 symptoms worsen. Lack of timely treatment is fraught with complications.
A mild course most often does not manifest itself, is a feature of the body, and often occurs in old age.
The mechanism of development of sinus arrhythmia
The sinus node is a group of cells in the wall of the heart that produce an electrical impulse.
It is in the sinus node that a normal heartbeat impulse begins to form. It flows along fibers of the heart wall called the conduction system. This system diverges into many fibers, and the smallest of them end in each fiber of the heart wall. This mechanism ensures rhythmic and harmonious functioning of the heart (contractions occur at equal intervals, maintaining the optimal frequency within 60-90 per minute). It is the conduction system that ensures the correct sequence of contractions of the heart chambers. Failures in this system provoke the development of heart diseases, against the background of which heart rhythm disturbances develop.
According to the severity, this pathology is of two types - moderate and severe.
Moderate sinus arrhythmia is characterized by mild symptoms or occurs without obvious signs, and is more often recorded in childhood and adolescence.
Severe sinus arrhythmia is more common in older people, is characterized by obvious clinical manifestations, and is combined with various diseases.
Causes
The development of the disorder is influenced by external and internal factors. External factors include:
- prolonged exposure to hot or extremely cold climates
- poisoning with alcoholic beverages, drugs, toxic substances, nicotine
- long-term use of certain groups of medications: cardiac glycosides, diuretics, antiarrhythmic drugs
Of no small importance is a person’s hereditary predisposition to heart rhythm disturbances. Treatment is selected depending on the underlying cause of the disease. Risk factors include excess weight, rickets, postnatal encephalopathy, rheumatism, cardiovascular disorders, children under 8-10 years of age. In older people, arrhythmia almost always occurs against the background of another cardiac pathology, taking certain groups of medications, drinking coffee, fatty foods, or smoking.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
Cardinal (cardiac) causes that can provoke sinus arrhythmia include:
- heart defects (congenital, acquired) – conditions in which the structure of the wall, valve, or heart vessels is damaged
- coronary heart disease - a pathology accompanied by insufficient blood supply and oxygen starvation, pain in the heart
- Myocardial infarction is a disease in which a certain area of the heart muscle dies as a result of oxygen starvation
- cardiomyopathy – a disease accompanied by structural changes in the heart muscle
- heart failure - with such a disorder, the heart cannot fully perform one of its main functions - pumping blood
Sinus arrhythmia can also occur due to myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle.
Diseases of other organs
The normal rhythm of the heart can be disrupted by:
- endocrine diseases: diabetes mellitus, adrenal gland dysfunction, thyroid gland
- hormonal disorders: thyrotoxicosis
- pheochromocytomas - a disease of the adrenal glands that leads to increased adrenaline and norepinephrine
Arrhythmia can occur due to hypoxia (insufficient oxygen supply) caused by bronchitis and bronchial asthma.
Pathological conditions
Pathological conditions that can provoke arrhythmia:
- electrolyte disorders, in which the balance of salts in the body is shifted
- fever
- severe anemia
- prolonged exposure to severe infection
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
The nervous system takes part in the regulation of cardiac activity. Consequently, neuroses, vegetative-vascular dystonia, neuritis can provoke sinus arrhythmia. When exposed to the vagus nerve, bradycardia develops.
Features of the course of pathology in pregnant women
It is impossible not to notice that those changes in the body of women that occur during pregnancy can provoke not only toxicosis or general weakness. Often, hormonal imbalances in the body of pregnant women can also be complemented by various disorders in the functioning of the heart.
Changes in the body during pregnancy
It is sinus arrhythmias that are considered the most common companions of pregnant women in the first or third trimesters of pregnancy.
In most cases, moderate heart rhythm disturbances during pregnancy do not pose a real threat (neither to the fetus nor to the expectant mother) - the problem can disappear on its own after a certain period of time or resolve itself after childbirth.
But, in some cases, heart rhythm disturbances during pregnancy may indicate the development of a serious cardiovascular pathology in a woman.
That is why doctors insist that at the first manifestations of arrhythmia, a pregnant woman should seek medical advice!
The main feature of the course of sinus arrhythmia in pregnant women can be considered the direct dependence of the problem on the mood and attitude of the woman herself to what is happening.
If a woman carrying a baby is nervous and worried a lot, the arrhythmia only intensifies, but if the pregnant woman knows how to get along with herself, heart rhythm disturbances appear less pronounced.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear depending on the stage of the pathological process. The patient complains that the heart beats unevenly and freezes from time to time; it may periodically stop for a few seconds, after which it begins to beat faster.
A characteristic symptom is accompanied by:
- lack of air
- pain in the left side of the sternum, which can radiate to the upper extremities
- shortness of breath
- dizzy
- weakness
The limbs become cold, a pulsation is felt in the temples, and the patient cannot take a deep breath.
Features in children
Sinus arrhythmia is often observed in children in a physiological (respiratory) form. This condition is accompanied by a sinking heart, a feeling that its beating is suspended, and then resumes with a vengeance.
It can cause a failure of the system that takes part in the formation and conduction of impulses, as well as:
- features of intrauterine development that led to defects and diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- prolonged dehydration;
- impact of neoplasms;
- severe intoxication of the body (vaccinations, use of medications);
- development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
The risk group includes children 4-8 months old, preschoolers from 3.5 to 4.5 years old, schoolchildren over 7 years old. A young child cannot accurately formulate which symptom is bothering him. It is important for parents to closely monitor the baby's health.
Consultation with a pediatrician requires the development of the following manifestations:
- cyanosis of certain parts of the body: nail plates, nasolabial folds, feet. The skin is pale;
- increased sweating;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- increased anxiety or lethargy, apathy;
- decreased appetite, up to complete refusal of breast milk or any other food;
- prolonged sleep disturbances: the child often wakes up and cries for a long time;
- development of shortness of breath with minimal physical activity: crawling, lifting, walking.
The gold standard for diagnosing cardiovascular disorders is an electrocardiogram. In order to get the most accurate results, it is important to ensure that the procedure is carried out correctly. If the child is excited and scared, or is in an uncomfortable position, the results may be distorted. The little patient should be in the most comfortable conditions possible and should not experience emotional pressure or stress. Additionally, an echocardiogram and blood test are prescribed.
Treatment begins with organizing a daily routine. The baby must sleep enough hours and eat a healthy and balanced diet. It is necessary to ensure that the child does not overeat before bedtime; plant foods should predominate in the diet. Massage of the collar area and long walks in the fresh air are recommended. Do not ignore routine examinations with doctors.
The prognosis in most cases is favorable: the arrhythmia goes away on its own, without the use of additional therapy. In severe cases, there is a possibility of complications in the form of heart failure, asystole, and fibrillation.
Treatment and rehabilitation
It should be remembered: heart disease does not allow self-medication. Under no circumstances try to relieve any symptoms on your own; consult a doctor. Strict monitoring by a specialist and correct prescriptions will help to quickly eliminate or reduce health consequences.
As a rule, doctors recommend the following to their patients:
- Healthy lifestyle and regime. If the patient is prone to bad habits: smoking, alcohol, overeating, then the doctor strongly recommends adjusting the diet and giving up substances that are harmful to health. And this should become a way of life, not a temporary panacea.
- Drug therapy. In addition to, in fact, antiarrhythmic drugs, these are also sedatives (to reduce the body's response to stress), and in some cases tranquilizers. The latter is rarely prescribed and only for concomitant diseases of the nervous system.
- Physiotherapy. It very much depends on the methods. The most commonly used treatments are reflexology, water therapy (therapeutic baths), laser therapy, and exposure to magnets.
- Installation of a pacemaker (the method is most often used for bradycardia). If the heart rhythm does not correct or there is a serious deterioration in the condition, the doctor may recommend a pacemaker. This is a method that is required in severe stages of the disease.
- Surgical intervention. Also a last resort technique when other methods have not shown effectiveness.
- Traditional medicine. Please note that not all such techniques have proven their clinical significance. And when treating with folk remedies, do not forget about the supervision of a specialist.
However, in the case of a particular patient, the doctor must carry out all the necessary diagnostic procedures, collect a complete medical history and prescribe therapy only based on the needs of each specific person who applies. Each patient has different circumstances of the disease, which can affect the heart and its rhythm.
Of course, each patient should return to a healthy rhythm of life as quickly as possible in order to reduce the load on the heart and cardiac muscle. This will not only simplify and speed up treatment, but sometimes also completely get rid of some symptoms of the disease.
Features in teenagers
In adolescents it can be observed as a result of hormonal changes. There may be sudden heart failure, lack of air, weakness, and dizziness. Such a disease can also be triggered by heart disease, innervation disorders, exposure to medications, and toxic substances. There are complaints of loss of strength, heart failure, dizziness, pain in the chest area. The heartbeat often increases and the state of health worsens after physical activity.
Adolescents over 12 years of age are recommended to periodically visit a cardiologist and have an electrocardiogram done. It is also necessary to check hormonal levels and conduct electrophysiological studies. During the stress test, ECG results are recorded against the background of physical activity. In orthostatic tests, pressure, pulse and other indicators are determined when the patient moves from a lying position to a sitting or standing position.
If respiratory arrhythmia is detected, no specific treatment is required. In other cases, the treatment strategy is selected depending on the diagnostic results obtained and the presence of associated symptoms.
For prevention, it is recommended for adolescents:
- eliminate stress
- eat right: introduce fiber into your diet, which is rich in vegetables, fruits, salad leaves, and berries. Avoid fried, heavy foods, canned food, minimize animal fats
- observe the work and rest schedule
- watch your weight
- refrain from spending long periods of time at the computer
- take medications only after consulting a doctor
- refrain from bad habits: drinking alcohol, smoking, caffeine-based drinks
It is necessary to promptly treat any dysfunction of internal organs and contact specialists at the first signs of the disease. If drug treatment is necessary, the doctor may recommend taking antiarrhythmic drugs, painkillers and sedatives, and vitamin complexes.
Treatment options
Treatment methods for sinus arrhythmia are determined by the severity of the disease and its causes. Thus, in case of serious irreversible pathological changes, sick sinus syndrome, surgical implantation of an artificial pacemaker (pacemaker) is necessary.
In case of pathologies, implantation of a pacemaker is necessary
Conservative drug therapy includes taking antiarrhythmic drugs that act on electrical processes in the heart and correct autonomic regulation: membrane-stabilizing sodium channel blockers (lidocaine, quinidine); beta blockers; drugs that slow down repolarization (amiodarone, ibutilide); calcium channel blockers.
Since atherosclerosis can cause arrhythmia, learn about the pros and cons of using fibrates, as well as the features of using phytosterol preparations for vascular atherosclerosis.
Long-term use of antiarrhythmic drugs negatively affects the prognosis of the disease, so they are prescribed only for severe sinus arrhythmia. Symptomatic therapy for neurogenic arrhythmia uses:
- tranquilizers,
- antidepressants,
- sedatives,
- psychotherapy.
Phytotherapeutic sedatives are used from the arsenal of traditional medicine. The patient is required to avoid taking coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods; you need to give up nicotine.
Elimination of causes
After identifying the cause of pathological sinus arrhythmia, treatment focuses on treating the underlying disease that caused the arrhythmia:
- neurogenic;
- coronarogenic;
- toxic-inflammatory;
- metabolic and dyshormonal.
Etiotropic therapy of neurosis, thyrotoxicosis, heart failure, rheumatic carditis, anemia, pulmonary pathologies; chronic foci of infection and other diseases leading to arrhythmias can return normal heart rhythm even without the use of antiarrhythmic drugs.
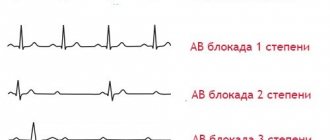
Diagnostics
If arrhythmia is suspected, a comprehensive diagnosis is required:
- conducting electrocardiography;
- examination of laboratory parameters: TSH, T3, T4 (thyroid gland), biochemical blood test. Allows you to identify the root cause of the development of sinus arrhythmia associated with hormonal changes or other diseases;
- episodic and Holter monitoring. For 24 hours, the patient wears a portable device that measures fluctuations in heart rhythms. The results obtained are recorded in a separate notebook, where they also note what the patient did during the day: at what time he ate food, slept, did exercises, felt a deterioration in his condition, woke up at night, etc.;
- load tests;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the heart to identify the cause of bradycardia;
- orthostatic tests;
- electrophysiological studies;
During a general examination, the pulse is checked, the heart is listened to and tapped. Conduct an oral survey of the patient regarding any interruptions in cardiac activity, “fading,” weakness, and shortness of breath. They examine what diseases the patient has in the medical history and clarify the likelihood of a hereditary predisposition to cardiovascular disorders. They ask about living conditions, as well as working and rest conditions, psycho-emotional state, and the presence of bad habits.
Conclusions and case studies
In conclusion, it is important to note that the state of sinus arrhythmia is not always considered pathological! There are situations when such heart rhythm disorders are included in the concept of a physiological norm. However, this is not a reason to ignore the problem.
Note! Practicing cardiologists never tire of repeating that if you detect the slightest discomfort in the heart area, it is easier and more correct to immediately consult a doctor and find out the causes of the ailment.
It is quite possible that in the early stages the problem can be dealt with as quickly as possible, without resorting to serious medication or other treatment.
Patient Valentina, 45 years old, consulted a cardiologist with complaints of feelings of periodic interruptions in heart pulsation, increased heart rate, general weakness, and severe fatigue in the evenings. After a full diagnosis, a diagnosis was made - moderate sinus tachycardia. General strengthening, immunostimulating, and preventive treatment is recommended.
Author of the article:
Elena Demidova
about the author
Did you like the article?
Let us know about it -
rate
First aid
In case of a sudden attack, it is necessary to correctly provide first aid to the patient:
- immediately call an ambulance;
- Before the car arrives, ventilate the room and ensure a sufficient amount of fresh air;
- calm the victim, use herbal sedatives (leonwort tincture);
- if the person is conscious, ask him to take a deep breath through his mouth, hold his breath and strain. Stay in this position for 4-8 seconds, slowly exhale through your mouth, curling your lips into a tube. Repeat the described exercise 4-5 times. This method activates the parasympathetic nervous system, slows down the heart rate, and eliminates heart failure;
- massage the sinocarotid zone - the space under the lower jaw separating the external and internal branches of the common carotid artery. The massage is done with the thumb of the river for several minutes;
- to normalize the pulse, ask the patient to sit down, close his eyes and start counting heartbeats out loud;
- in case of disturbances of consciousness, tilt your head forward, make sure that nothing is squeezing your neck;
- if necessary, perform artificial respiration.
You can gently press on the eyeballs for 30-60 seconds. Repeat after a few minutes. This method helps normalize heart rate and heart rhythm. It will have a positive effect if the attack is provoked by a stressful situation, overwork or other condition not related to impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostic methods
Of course, a person himself can detect abnormalities in his heart rhythm. But sometimes, under the influence of psychological factors, these sensations can be subjective. That is, a person feels sick, although in fact his heart rhythm is within normal limits.
In order not to be in constant fear for your health, you need to undergo a full examination. What methods are there? The simplest is an ECG. Severe sinus arrhythmia is easily identified.
The cost of the study is minimal, and in municipal institutions it costs nothing at all. Done quickly at the time of application. A cardiologist will be able to decipher the result. After decoding, a diagnosis is made.
An ECG is carried out like this: sensors on suction cups are attached to the arms, legs, and chest, thanks to which the heart rhythm is read. If a routine ECG shows an abnormality, the patient may be given an exercise test to make a more accurate diagnosis. A special device reads the rhythm during physical activity. In addition, 24-hour monitoring of heart rate is often recommended. Then a monitor is attached to the person, which measures heartbeats at home around the clock. The patient must record his feelings in a special journal.
These research methods are more informative, because during normal research a failure may not be noticed. It also very often makes sense to do an ultrasound of the heart, during which the reasons that contributed to the development of severe sinus arrhythmia will be identified. Treatment will be discussed below.
Treatment
Cardiology patients are recommended to review their usual lifestyle. Therapy is based on dietary correction: replacing animal fats with vegetable fats, limiting salt when diagnosing heart failure. Significant stress should not be allowed: both physical and emotional. Diet therapy prevents the development of atherosclerosis and other serious complications.
If the arrhythmia is provoked by psycho-emotional overstrain or stress, specific therapy is not required. The patient should relax, calm down, and the heart rhythm will quickly return to normal.
Drug therapy
The selection of medications depends on the underlying condition causing interruptions in cardiac activity:
- for hormonal disorders (for example, severe thyroid dysfunction), drugs that normalize the level of thyroid hormones are used
- symptomatically, you can use herbal remedies with a sedative effect: motherwort, hawthorn, valerian
- To eliminate arrhythmia, medications with antiarrhythmic effects are used: Verapamil, Propanorm, Ritmonorm
- for anemia, use iron-based preparations intended for internal administration or intravenous infusion
- poisoning, fever, intoxication are eliminated with the help of sorbents, correctors of water-salt metabolism disorders
If the selected medications are ineffective, you must consult a doctor again and reconsider the treatment regimen.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy involves exposure to heat and an electromagnetic field. The patient is prescribed a course of reflexology and a consultation with a psychotherapist.
Surgical methods
Surgical methods are indicated when conservative treatment is ineffective:
- for severe defects, cardioplasty is indicated
- prolonged bradycardia requires the use of pacemakers
- To restore coronary circulation, coronary bypass surgery is indicated
- if the functioning of the thyroid gland is impaired, removal of its nodes may be recommended
Surgical treatment is a last resort. If the doctor insists on using radical therapy, it makes sense to consult with other specialists and draw a conclusion based on several authoritative opinions.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Heart rhythm disturbances can be prevented by following a healthy lifestyle.
After accurately determining the diagnosis, the cardiologist must tell the patient how to treat sinus arrhythmia of the heart. The pathology does not require treatment if sinus arrhythmia appears due to the action of any external factors or if the sinus rhythm on the ECG is irregular, but moderate and does not deviate too much from normal. Medicines are not required when the illness is normal and does not affect blood pressure, there is no fainting or changes in skin color.
Severe sinus arrhythmia in adults requires mandatory drug therapy. First of all, a patient with sinus arrhythmia must change his lifestyle: give up bad habits, give the body light physical activity, but make sure that the condition is normal, walk more in the fresh air. The treatment uses drugs from the group of beta-blockers, sedatives and metabolic drugs. The following tablets are prescribed:
- "Trimetazidine";
- "Omacor";
- "Aymalin";
- "Panangin";
- "Caviton";
- "Persen."
If the patient has sinus bradycardia, a pacemaker may be installed. To maintain the body, doctors advise taking complexes of multivitamins and microelements. In the case where the cause is early ventricular repolarization syndrome, energy-tropic drugs are prescribed: “Kudesan”, “Carnitine”.
Prevention
For prevention, it is necessary to observe a work and rest schedule and refrain from psycho-emotional stress. Moderate physical activity, breathing practices, and long walks in the fresh air at least 3-4 times a week are useful. It is worth reviewing your diet and enriching it with foods rich in omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, leafy vegetables, berries, and fiber. It is recommended to refrain from fried foods, smoked foods, canned food, alcoholic beverages, and smoking.
Medicines can only be taken as prescribed and under the supervision of a physician. At the first manifestations of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Concomitant pathologies of the body should also be treated efficiently and in a timely manner.
Sinus arrhythmia is a condition that requires careful attention to your own health. Timely consultation with a cardiologist, correction of diet and lifestyle can reduce the likelihood of complications, prolong life and improve its quality. Patients with severe forms must be under constant medical supervision and undergo a course of treatment in an inpatient setting.
What does sinus arrhythmia mean?
If sinus rhythm is disrupted, sinus arrhythmia occurs. It differs from other arrhythmias in that the sinoatrial node remains the driver, the correct sequence of contractions and relaxations is maintained, but their rhythm (intervals between contractions) is disrupted.
Sinus arrhythmia is not always a pathology. Often this condition occurs under stress - physical or emotional, and goes away immediately after the external factor ceases.